Cranial Nerves (Specific Functions)
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What is the function of the Olfactory Nerve (CN I)?
Special sensory (smell = olfaction)
Where does the Olfactory Nerve (CN I) originate?
Olfactory epithelium inside the superior nasal cavity
What is the foramen associated with the Olfactory Nerve (CN I)?
Olfactory foramina on the cribriform plate
Where does the Olfactory Nerve (CN I) transmit signals after the olfactory bulb?
To the rest of the brain
CN II: The Optic Nerve
Function: special sensory (vision)
Origin: retina
Foramen: optic canal
Destination: diencephalon, then to occipital lobe
What is the function of CN III (Oculomotor Nerve) for extra-ocular eye muscles
Somatic Motor function
Parasympathetic
How many extra-ocular eye muscles does CN III control?
4 muscles that move the eye and 1 eyelid muscle
What are the names of the muscles controlled by CN III?
Superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, inferior oblique, and Levator palpebrae superioris
What is the visceral motor function of CN III?
Pupil constriction and lens convexity
Where does CN III originate?
Mesencephalon (midbrain)
Through which foramen does CN III pass?
Superior orbital fissure
What is the destination of CN III?
Extra-ocular eye muscles (all except two)
What is the function of CN IV: The Trochlear Nerve?
Controls one extra-ocular eye muscle
What type of function does CN IV: The Trochlear Nerve have?
Somatic Motor function
Which muscle does CN IV: The Trochlear Nerve control?
Superior oblique muscle
Where does CN IV: The Trochlear Nerve originate?
Mesencephalon
Through which foramen does CN IV: The Trochlear Nerve pass?
Superior orbital fissure
What is the destination of CN IV: The Trochlear Nerve?
Superior oblique muscle
What is the function of the Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)?
Mixed (sensory and somatic motor) function
What are the three parts of the Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)?
Ophthalmic (V1), Maxillary (V2), Mandibular (V3)
What sensations does the Ophthalmic part (V1) of the Trigeminal Nerve provide?
Sensations from the forehead, upper eyelid, and nose
What sensations does the Maxillary part (V2) of the Trigeminal Nerve provide?
Sensations from the lower eyelid, upper lip, and cheek
What sensations does the Mandibular part (V3) of the Trigeminal Nerve provide?
Sensations from the lower jaw and controls mastication
What is the origin of the sensory parts of the Trigeminal Nerve?
Skin of the face
Where does the somatic motor part of the Trigeminal Nerve (V3) originate?
Pons
What is the foramen for the Ophthalmic Nerve (V1)?
Superior orbital fissure
What is the foramen for the Maxillary Nerve (V2)?
Foramen rotundum
What is the foramen for the Mandibular Nerve (V3)?
Foramen ovale
Where do the Ophthalmic, Maxillary, and sensory part of the Mandibular nerves terminate?
Pons
What is the destination of the motor part of the Mandibular Nerve?
Jaw muscles
Cutaneous territories of the Trigeminal nerve
Trigeminal nerve
V1 Ophthalmic
V2 Maxillary
V3 Mandibular
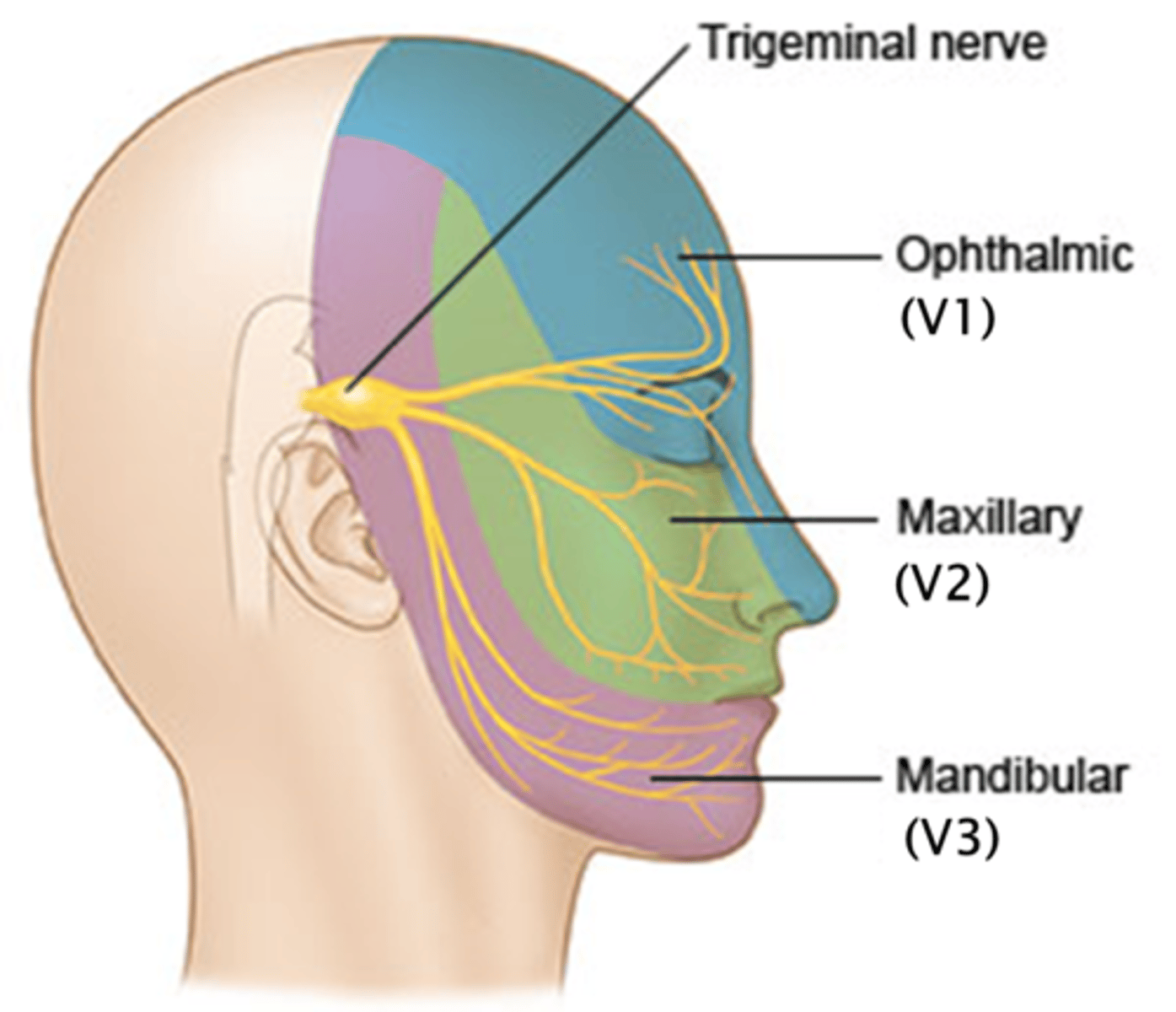
What is the function of the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerve provides facial sensation and jaw muscle function.
Does the trigeminal nerve provide facial muscle function?
No, the trigeminal nerve does not provide facial muscle function.
What is the function of CN VI (Abducens)?
Controls one extra-ocular eye muscle
What type of function does CN VI have?
Somatic Motor function
What is the specific movement controlled by CN VI (Abducens)?
Eye abduction
Which muscle does CN VI innervate?
Lateral Rectus muscle
Where does CN VI originate?
Pons
Through which foramen does CN VI pass?
Superior orbital fissure
What is the destination of CN VI?
Lateral rectus eye muscle
What is the function of CN VII: The Facial Nerve?
Mixed (sensory and motor)
What special sensory function does CN VII have?
Taste
What somatic motor function does CN VII control (Facial Nerve)?
Muscles of facial expression
What is the visceral motor function of CN VII?
Parasympathetic for eye, nose, and mouth secretion
Where do the taste buds that CN VII innervates originate?
Anterior 2/3 of the tongue
Where does CN VII originate in the brain?
Pons and Medulla
Through which foramen does CN VII enter the cranial cavity?
Internal acoustic meatus
What is the destination of the special sensory function of CN VII?
Medulla
What is the destination of the motor function of CN VII?
Muscles of the face
What glands does the visceral motor function of CN VII target?
Lacrimal (tear) glands and small salivary glands
CN VIII: The Vestibulocochlear Nerve Function
Sensory: equilibrium (vestibular portion) Hearing (cochlear portion)
CN VIII: The Vestibulocochlear Nerve
Origin
Foramen
and Destination
Origin: receptors of the vestibule and
cochlea of ear
Foramen: internal acoustic meatus
Destination: Pons
What is the function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) related to general sensory?
General sensory for the posterior 1/3 of the tongue.
What is the function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) related to special sensory?
Taste from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue.
What is the function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) related to visceral sensory?
Monitors blood pressure in the internal carotid artery.
What is the somatic motor function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX)?
Innervates the stylopharyngeus muscle for swallowing.
What is the visceral motor function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX)?
Parasympathetic innervation for saliva production.
Where does the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) originate for general and special sensory functions?
From the posterior 1/3 of the tongue.
Where does the visceral sensory function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) originate?
From the carotid sinus at the base of the internal carotid artery.
Where does the motor function of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) originate?
From the pons and medulla.
Through which foramen does the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) exit the skull?
Jugular foramen.
Where does the sensory information from the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) go?
To the medulla.
Where does the visceral motor of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) target?
The parotid salivary gland.
Where does the somatic motor of the Glossopharyngeal Nerve (CN IX) target?
Stylopharyngeus muscle for swallowing
What is the function of the Vagus Nerve (CN X)?
It has many functions, including visceral sensory, visceral motor, and somatic motor.
What type of sensory information does the Vagus Nerve provide?
Normal visceral sensation from organs, such as fullness and satiety, but not pain.
What type of motor innervation does the Vagus Nerve provide to the organs?
Parasympathetic innervation.
What somatic motor functions are associated with the Vagus Nerve?
Conscious swallowing and vocalization.
Where does the sensory information for the Vagus Nerve originate?
From the organs.
Where does the motor information for the Vagus Nerve originate?
In the medulla.
Through which foramen does the Vagus Nerve exit the skull?
Jugular foramen.
Where does the sensory information from the Vagus Nerve go?
To the medulla.
What are the destinations of the visceral motor fibers of the Vagus Nerve?
Respiratory, cardiovascular, and digestive organs.
What muscles are innervated by the somatic motor fibers of the Vagus Nerve?
Muscles of the palate, pharynx, and larynx.
What is the function of CN XI (Spinal Accessory Nerve)?
Somatic Motor: Neck movement, swallowing
Where does CN XI originate?
Spinal cord and medulla
Through which foramen does CN XI enter the skull?
Foramen magnum
Through which foramen does CN XI exit the skull?
Jugular foramen
What is the destination of the external branch of CN XI?
Sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
What is the destination of the internal branch of CN XI?
Muscles of the palate, pharynx, and larynx
What is the function of CN XII: The Hypoglossal Nerve
Motor: tongue movement
What is the origin of CN XII: The Hypoglossal Nerve
Medulla
Through which foramen does CN XII exit?
Hypoglossal canal
What is the destination of CN XII: The Hypoglossal Nerve?
Tongue muscles