Nervous Systems
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
The simplest animals
with nervous systems,
the cnidarians…
…have neurons
arranged in nerve nets.
In relatively simple
cephalized animals,
such as flatworms…
…a central nervous
system (CNS) is
eviden.
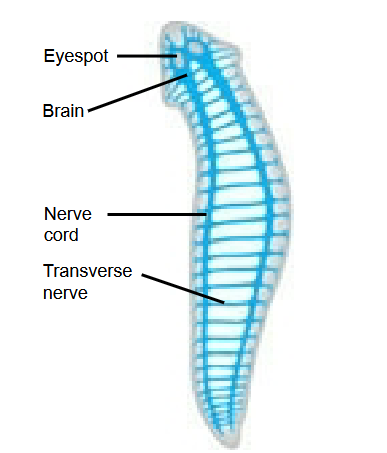
In vertebrates
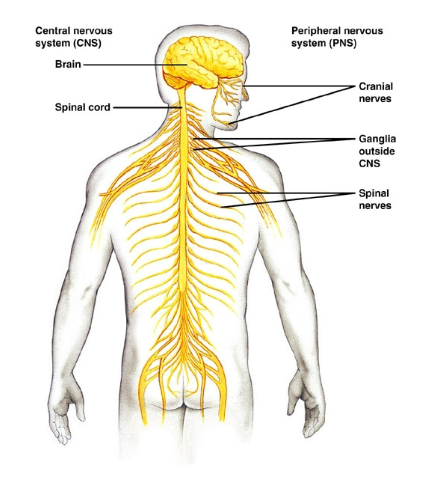
The central nervous system
consists of a brain
and dorsal spinal
cord
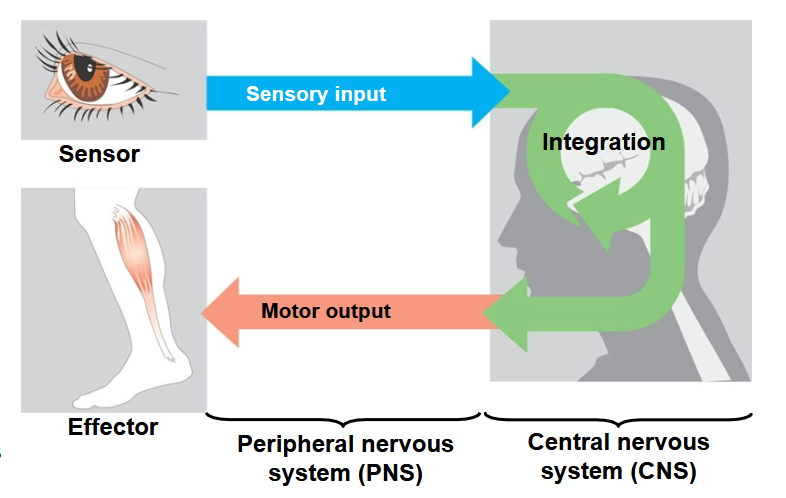
CNS
Central Nervous System
PNS
Peripheral Nervous System
Nervous systems process information in three
stages…
Sensory input, integration, and motor output
Glia are…
…supporting cells; essential for the structural integrity of the
nervous system and for the normal functioning of
neurons.
Astrocytes
Metabolic support, helps feed other cells.
Microglia
CNS; Phagocytic cells (engulfs
microbes)
Oligodendrocyte
CNS; formation of myelin sheath
Astrocytes
Provide structural support for neurons and regulate the extracellular concentrations of ions and neurotransmitters.
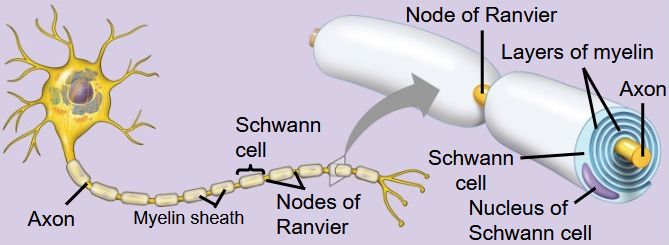
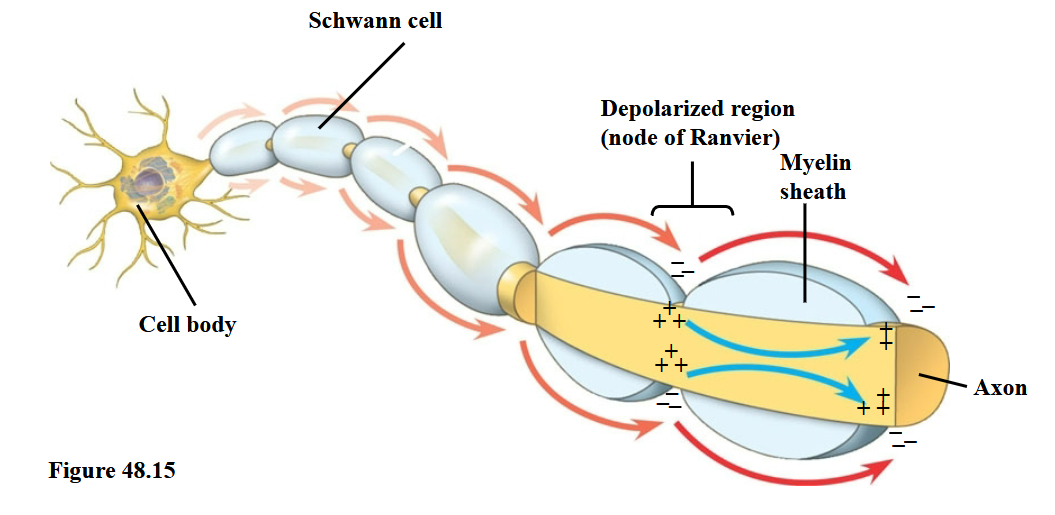
Oligodendrocytes (in the CNS) and Schwann cells
(in the PNS)
Are glia that form the myelin sheaths around the axons
of many vertebrate neurons
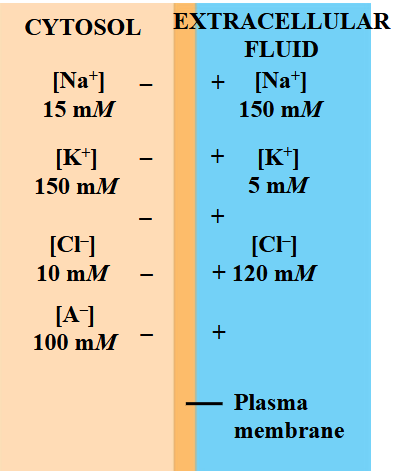
The inside of a cell is…
…negative relative to the outside. (-70 mV)
In all neurons, the resting potential…
…depends on the ionic gradients that exist across the
plasma membrane.
A neuron that is not transmitting signals…
…contains many open K+ channels and fewer open Na+
channels in its plasma membrane
The diffusion of K+ and Na+ through channels…
…leads to a separation of charges across the membrane,
producing the resting potential
Hyperpolarization
An increase in the magnitude of the membrane potential.
Depolarization
A reduction in the magnitude of the membrane potential.
Hyperpolarization and depolarization are both called graded potentials because…
...the magnitude of the change in membrane potential varies with the strength of the stimulus
In most neurons, depolarizations are graded…
only up to a certain membrane voltage,
called the threshold
A stimulus strong enough to produce depolarization that reaches the threshold…
…triggers a different type of response, called an action potential
An action potential is…
…a brief all-or-none depolarization of a neuron’s plasma membrane; the type of signal that carries information along axons.
When a stimulus
depolarizes the membrane…
…Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell. While K+ channels open, and K+ flows out of the cell.
A refractory period follows the…
…action potential; during which a second action potential cannot be initiated.
An action potential can travel long distances by…
…regenerating itself along the axon.
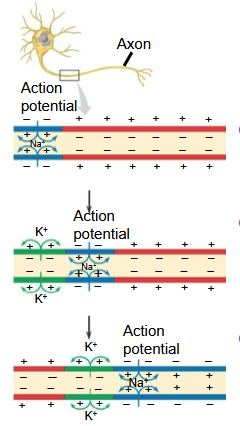
At the site where the action potential is generated,
usually the axon hillock…
…an electrical current depolarizes the neighboring region of the axon membrane.
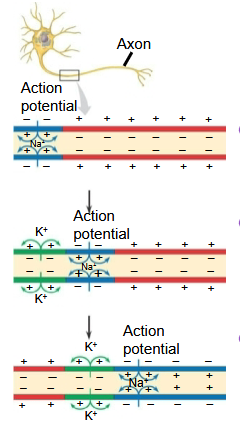
Action potentials in myelinated axons jump between the…
…the nodes of Ranvier in a process called saltatory conduction.
The speed of an action potential…
…increases with the diameter of an axon.
What is the speed of an action potential in invertebrates?
Several centimeters per second to 100 m per
second.
In vertebrates, many axons are myelinated, which causes?
The speed of an action potential to increase.
How do local anesthetics work?
They block the opening of voltage- gate Na+.
Absolute Refractory Period
• Time period during which a second action potential cannot be
initiated.
• Period of sodium channel activation and inactivation
• For large diameter axons = 0.4 miliseconds (1/2,500 seconds)
• For small diameter axons = 4 miliseconds (1/250 seconds)
Relative Refractory Period
Second action potential can be initiated by suprathreshold
stimulus (larger than threshold).
How can the nervous system distinguish stimulus intensities?
Frequency of impulses and the number of sensory neurons activated.
It is established that mature neurons are…
not able to undergo cell division, but new neurons have been observed in the brain of mice. Therefore, the new brain neurons must have come from stem cells.
Electrical Synapse
Electrical current flows directly from one cell to another via a
gap junction.
In a chemical synapse…
..a presynaptic neuron teleases chemical neurotransmitters, which are stored i n the synaptic terminal (the vast majority of synapses)
Indirect synaptic transmission
A neurotransmitter binds to a receptor that is not part of an
ion channel.
Acetylcholine
One of the most common neurotransmitters in both vertebrates and invertebrates; can be inhibitory or excitatory.
Biogenic amines
Include epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin; are active in the CNS and PNS.
Mammals have how many cranial nerves?
12 pairs.
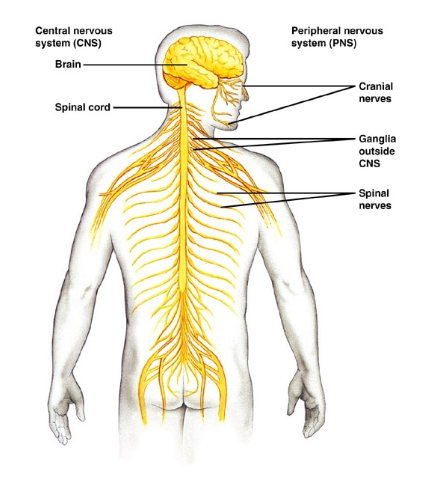
Mammals have how many spinal nerves?
31 paires.
The somatic nervous system…
…carries signals to skeletal muscles.
The autonomic nervous system…
…regulates the internal environment, in an involuntary manner; is divided into the sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric divisions.
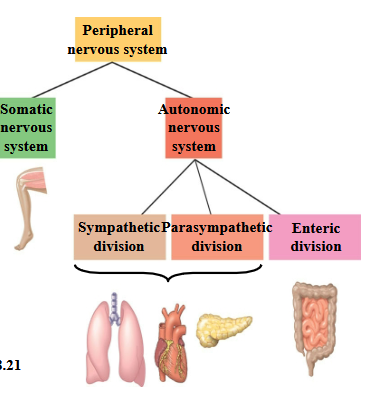
The sympathetic division
Correlates with the “fight-or-flight” response.
The parasympathetic division
Promotes a return to self-maintenance functions.
The enteric division
Controls the activity of the digestive tract, pancreas, and
gallbladder
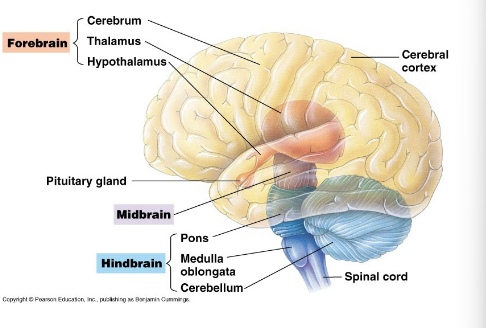
Medulla oblongata and
Ponds
Part of the hindbrain. Conduct information from
spinal cord to forebrain. Control breathing, heart rate,
digestion.
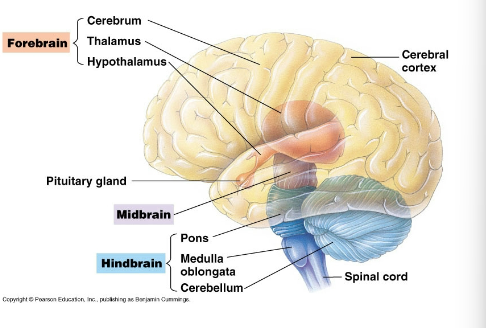
Cerebellum
Part of the hindbrain. Coordinates body movement.
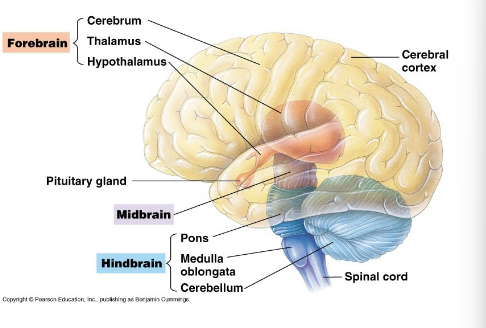
Midbrain
Relays sensory information (e.g. sound) to the cerebrum
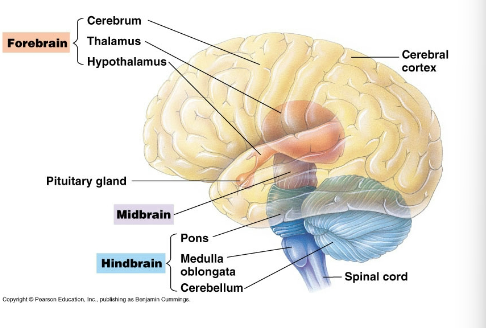
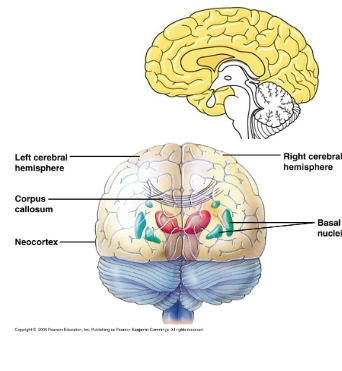
Cerebrum (left and right)
Higher mental activity (thinking, etc.)
Neocortex
Outer most part (less than 5 mm thick has 80 %of
total brain mass)
Cerebral cortex
Outer covering gray matter
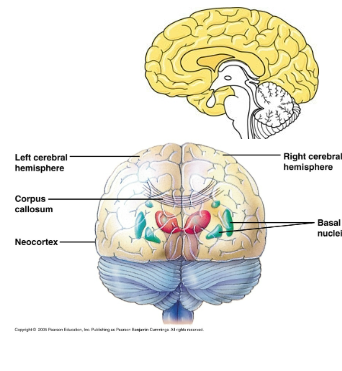
Basal nuclei
Internal white matter
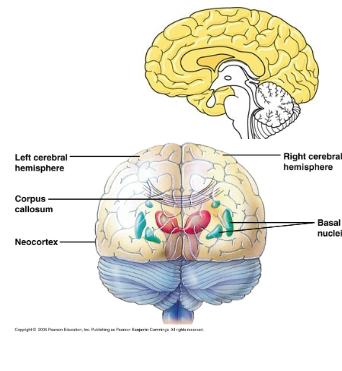
Corpus callosum
Thick band of nerve fibers connecting the hemispheres.
Neurons communicate by…
short-distance chemical signals and long-distance electrical signals
What are ganglia?
clusters of nerve cell bodies
A neuron that transmits an impulse to the central nervous system after the neuron is stimulated by the environment is called a(n)…
sensory neuron
Which of the following is specifically a part or a function of the central nervous system?
integration
The part of a neuron that carries nerve impulses toward the cell body is called a(n)…
dendrite
Cells that provide metabolic and structural support to the neurons are called?
glia
If your fingers touch a hot stove and you suddenly pull back, you have experienced a reflex. What is the correct order of the information processing in this reflex?
sensory input, integration, motor output
Which of the following statements is correct?
A neuron only has a single axon.
In descriptions of synapse organization, which type of cell is the transmitting neuron and which type of neuron, muscle, or gland cell receives the signal?
presynaptic ... postsynaptic
Which of the following statements is correct?
None of the listed responses is correct.
Which of the following statements about the resting potential is true?
Inside the cell, the concentration of potassium is much higher than the concentration of sodium.
The sodium-potassium pump…
expels sodium from the cell
Which of the following statements is true?
Ion channels are selectively permeable, permitting only certain ions to pass
Blocking potassium ion channels in a mammalian cell membrane would…
decrease the magnitude of the membrane potential
What is an increase in the magnitude of the membrane potential called?
hyperpolarization
A drug that causes potassium to leak out of a neuron, increasing the positive charge on the outside, would…
inhibit transmission of nerve signals by the neuron
Threshold is of great significance in the physiology of neurons. What happens if threshold is NOT reached?
positive-feedback depolarization will not occur
Schwann cells make up the…
myelin sheath in axons of the PNS (peripheral nervous system)
An action potential is…
a traveling wave of depolarization in the neuron membrane
The period in which an axon membrane CANNOT generate an action potential is called
the refractory period
Saltatory conduction means that the membrane potential changes…
only at the nodes of Ranvier
Action potentials are generated along a neuron because…
depolarization of the membrane at one point causes an increase of permeability to sodium at the next point
How are neurons structurally adapted to chemically transmit impulses to neighboring neurons?
Axon terminals contain neurotransmitter within synaptic vesicles.
Which of the following statements about the transmission across a typical chemical synapse is true?
The binding of neurotransmitter molecules to receptors on the postsynaptic cell membrane results in changes to the behavior of the postsynaptic cell.
Acetylcholinesterase is the enzyme that degrades acetylcholine. What effect on nerve transmission would occur following the administration of a chemical that inhibited acetylcholinesterase?
Continuous excitatory postsynaptic potentials would occur in the postsynaptic neuron.
In humans, making more serotonin available to brain cells typically…
produces an effect on mood
Which of the following is a natural pain reliever?
endorphins
Which of the following correctly pairs up a type of synapse and its characteristic?
electrical synapse ... gap junctions
Which of the following neurotransmitters typically has inhibitory effects?
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Which of the following is a mechanism by which neurotransmitters can be rapidly cleared from the synaptic cleft?
All of the listed responses are correct.
The interplay of multiple excitatory and inhibitory inputs most affects what part of a neuron?
axon hillock