Light and Optics Grade 8
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
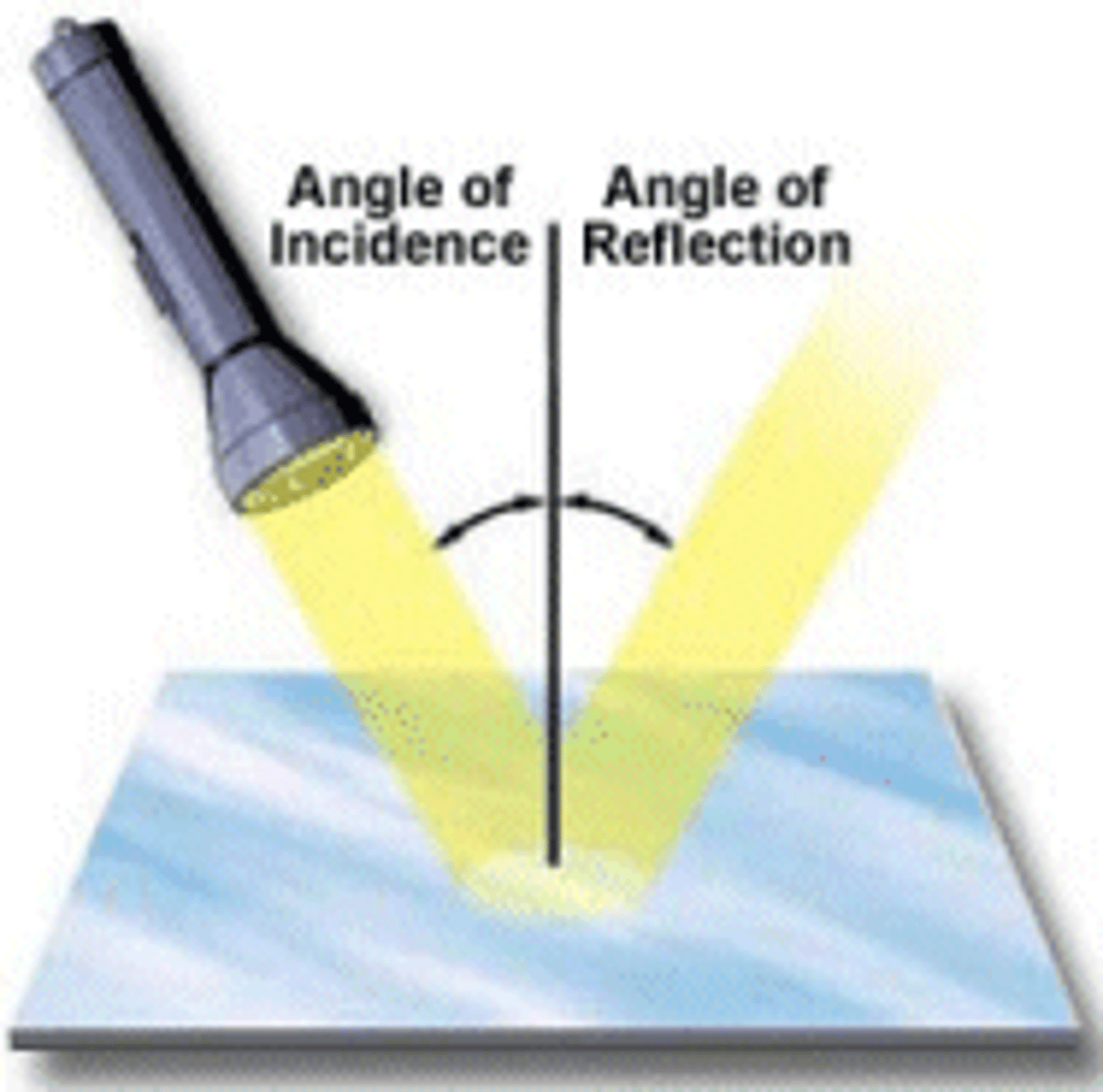
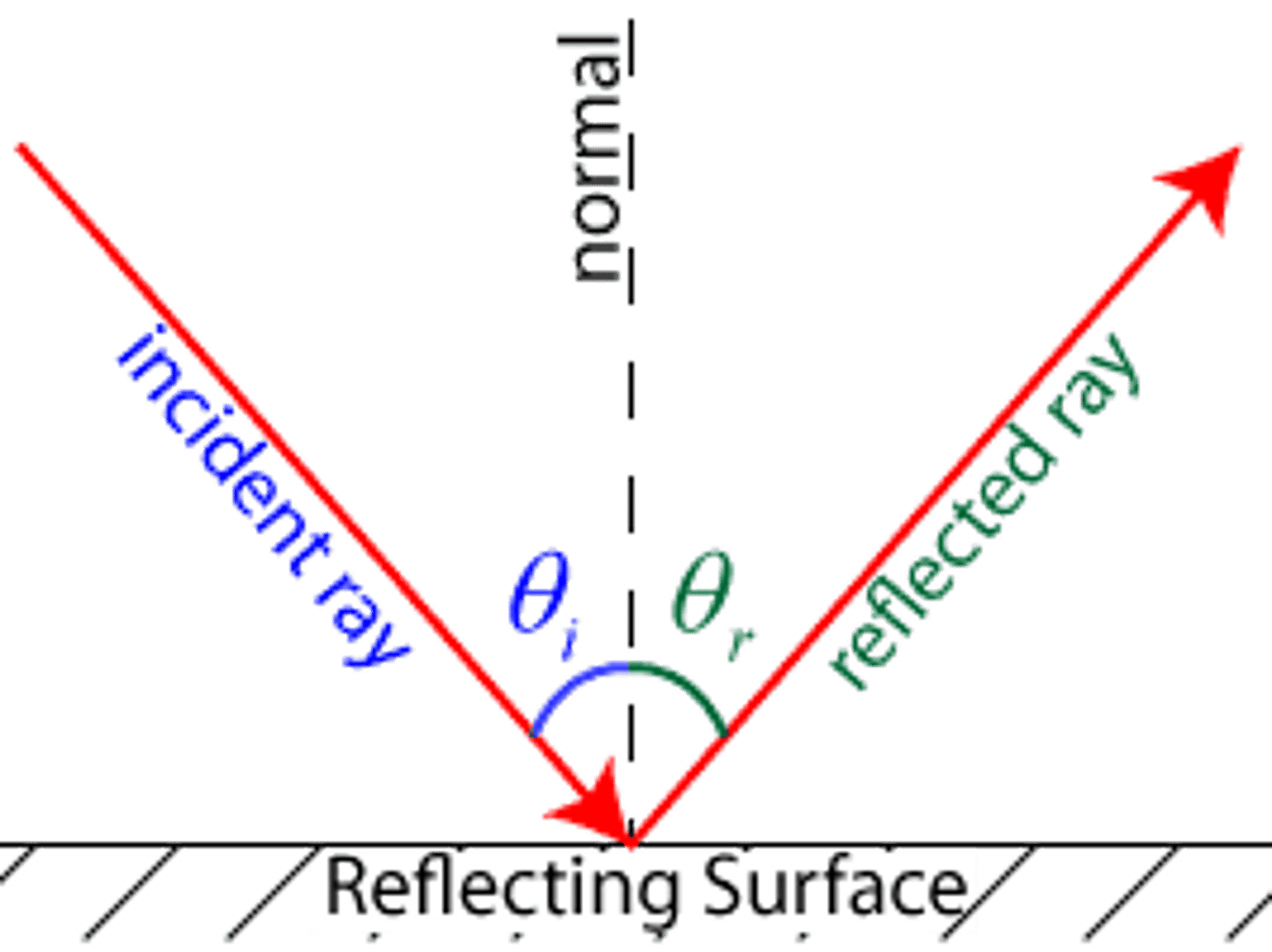
angle of incidence
the angle between the incident ray and the normal
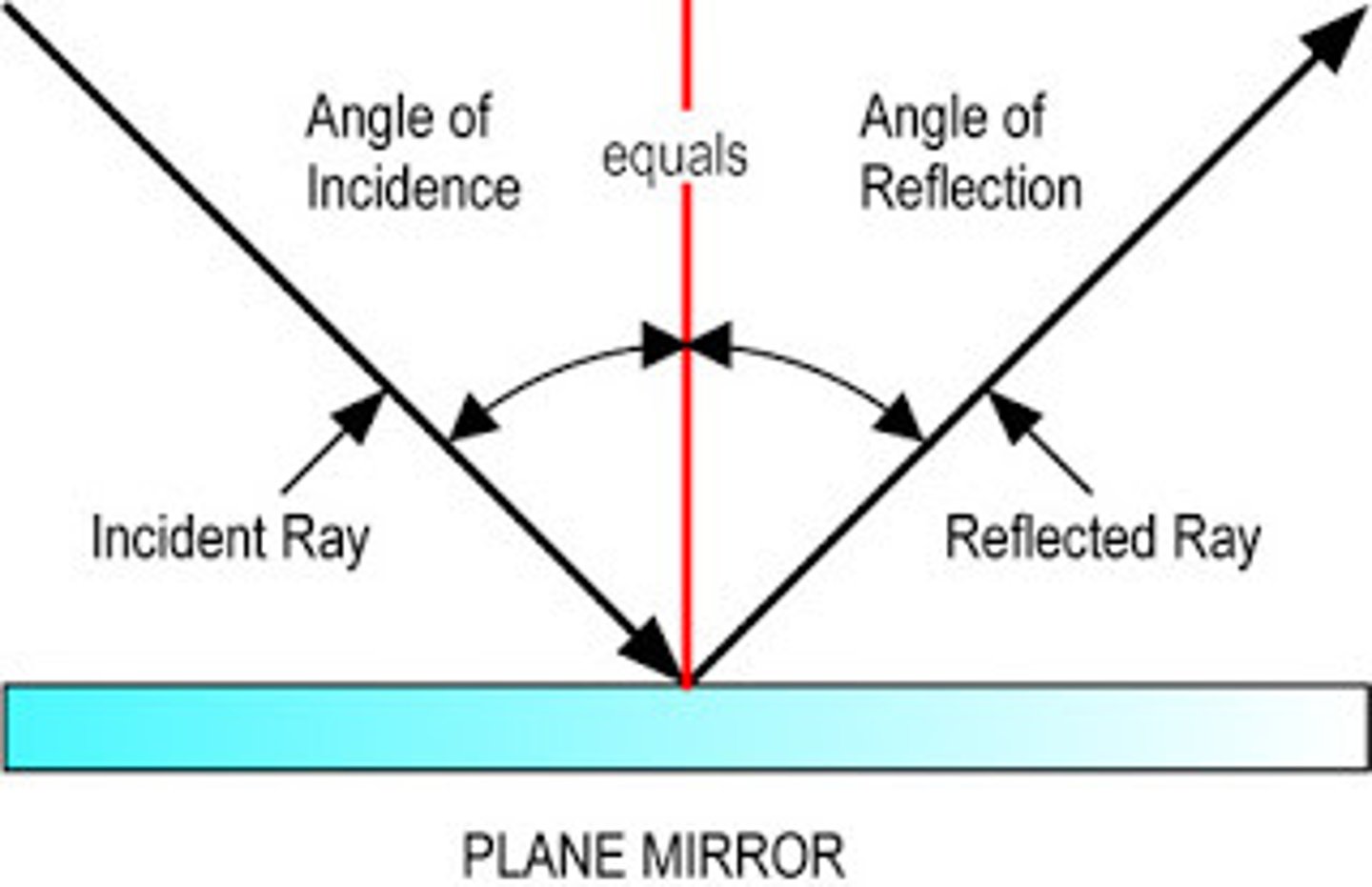
angle of reflection
The angle between the reflected ray and the normal
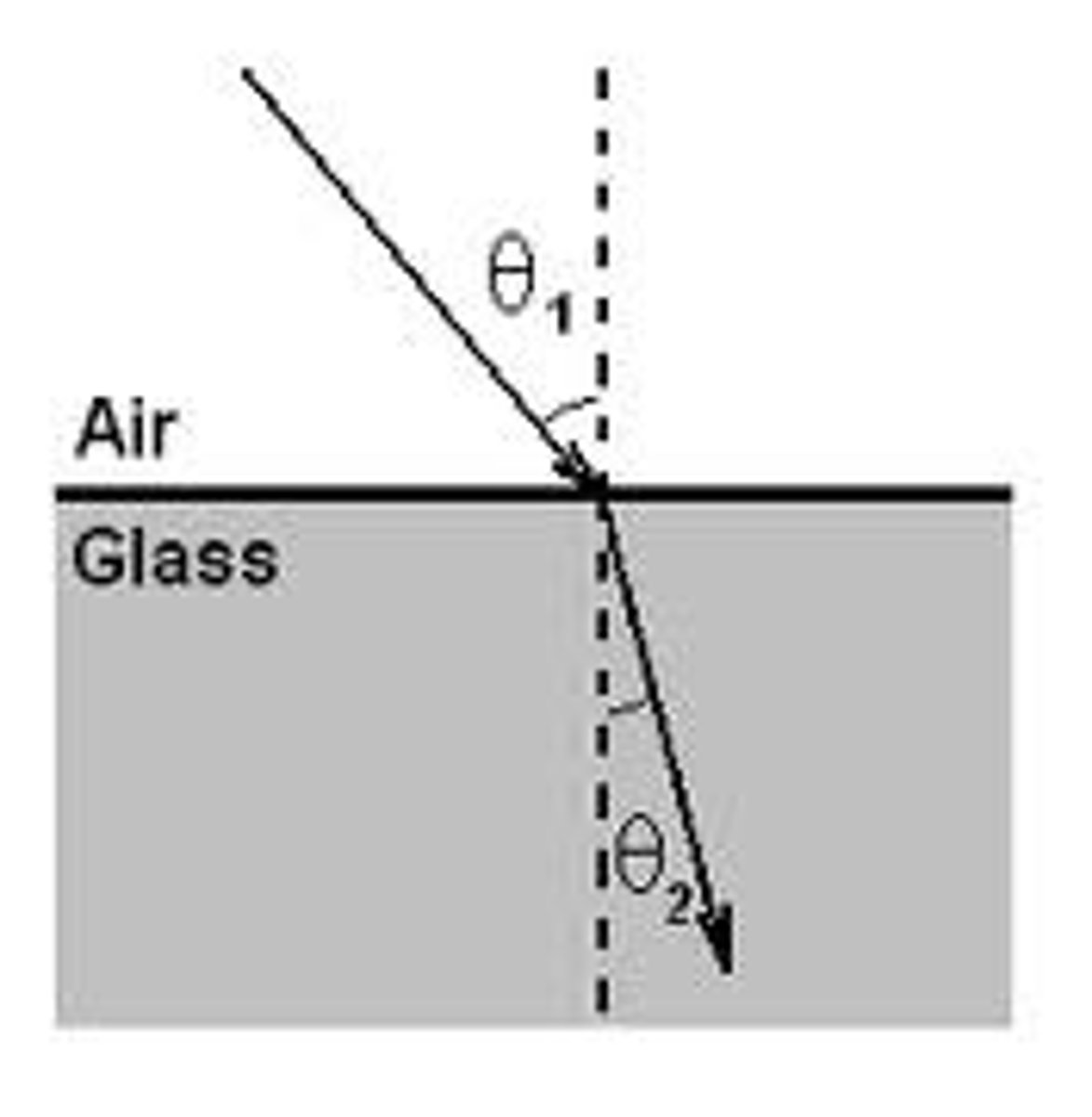
angle of refraction
the angle between the normal and the refracted ray
artificial light source
a human made light source

bioluminescence
the emission of light produced by chemical reactions inside the bodies of living creatures
concave
curving inward and forms larger virtual images
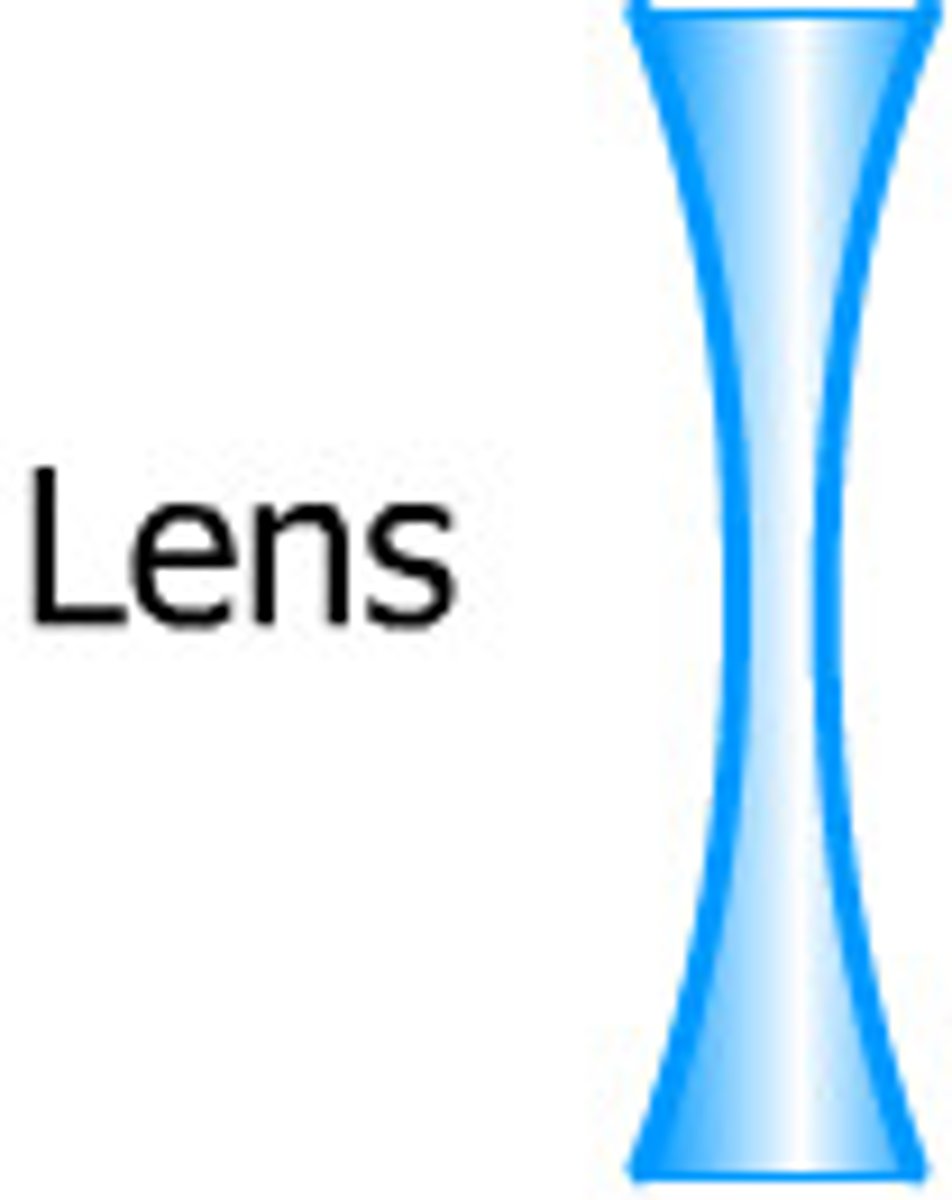
convex
curving outward and forms smaller virtual images

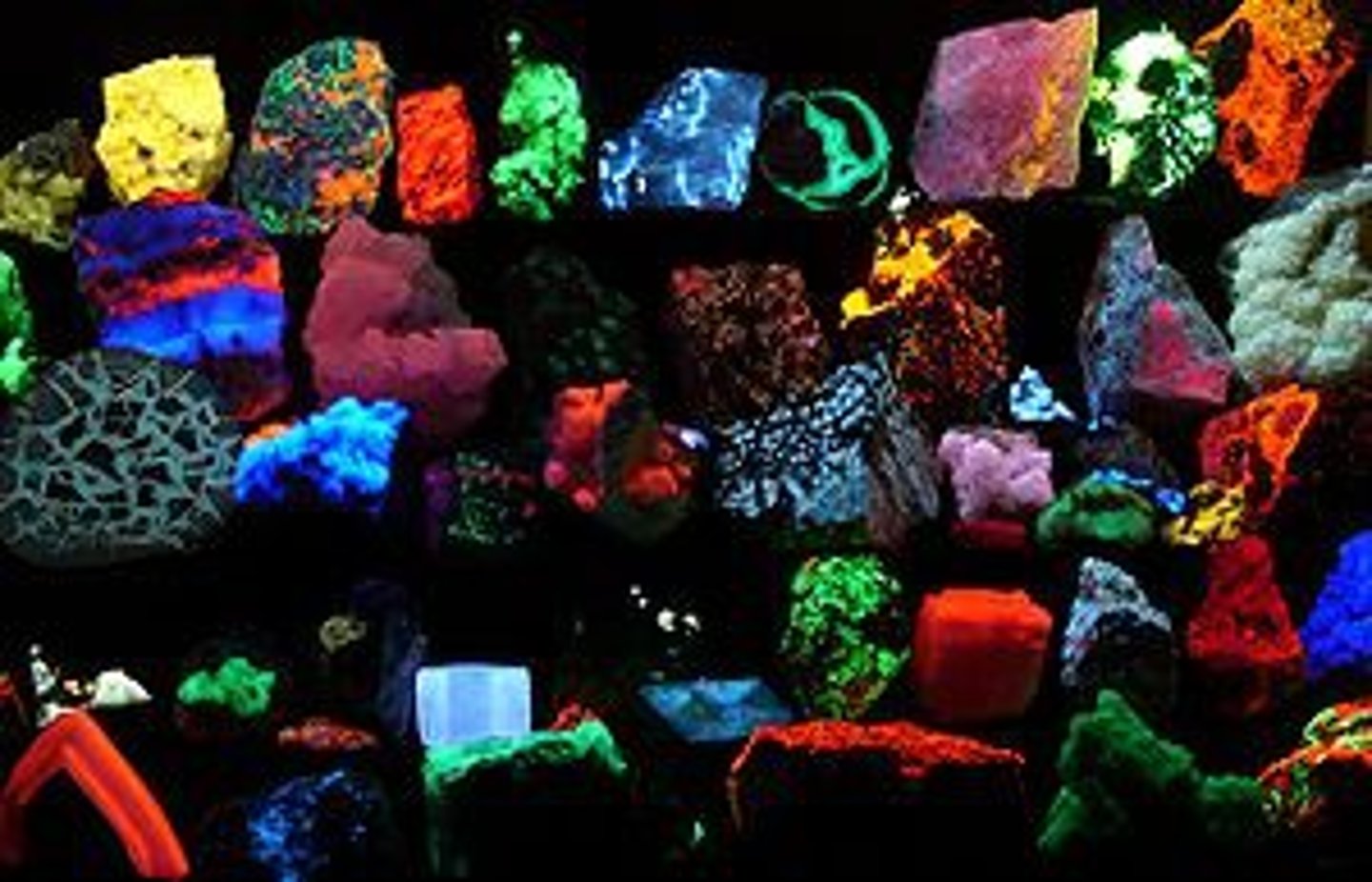
fluorescence
The process in which high energy, invisible ultraviolet light is absorbed by the particles of an object, which then emits some of this energy as visible light, causing the object to glow.

image
the likeness of an object
incandescent source
an object that can be heated to such a high temperature that it emits visible light

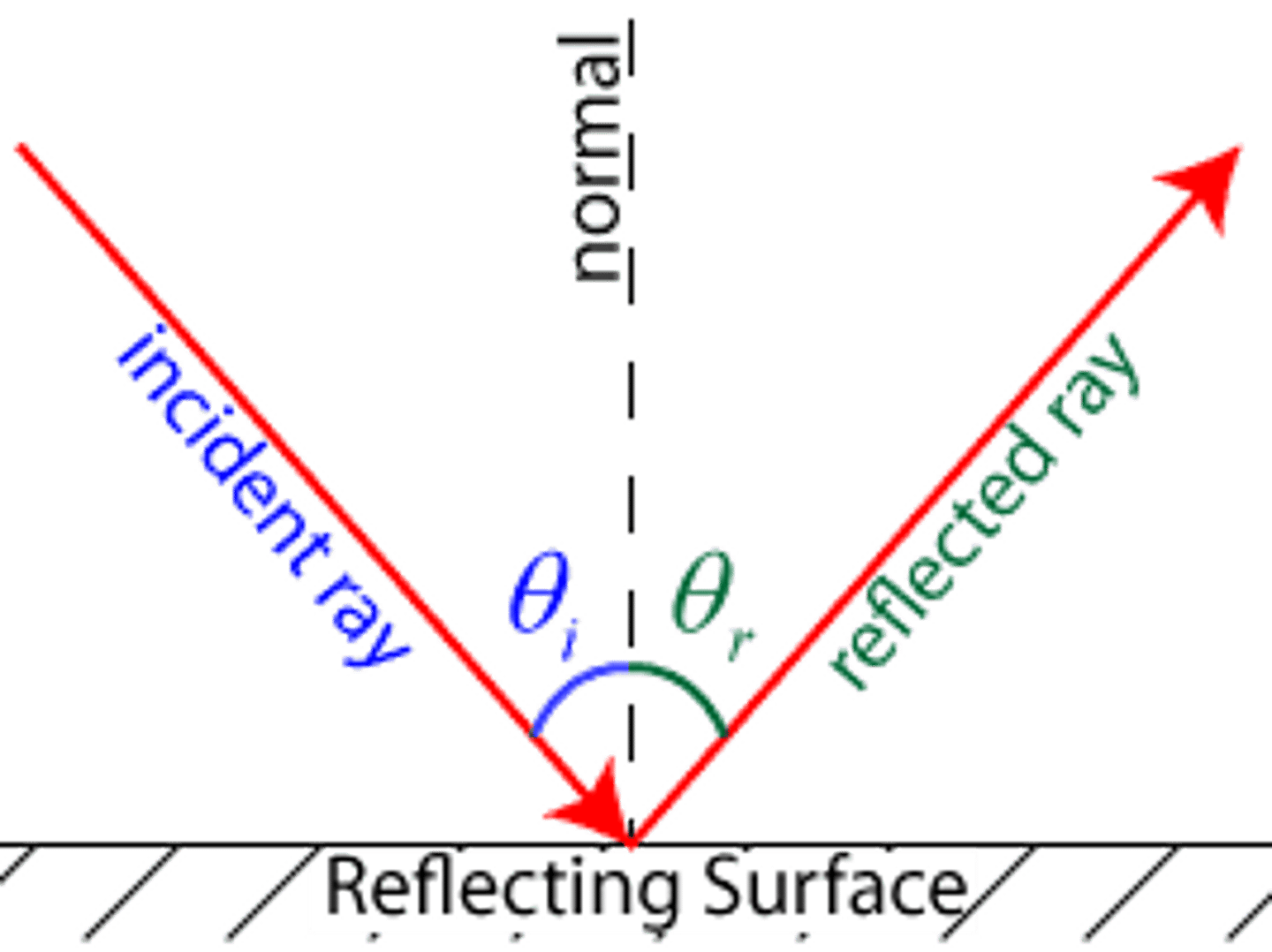
incident ray
the light that strikes a reflecting or refracting
light
a visible form of energy, that either radiates outward from a source in all directions, reflects off different objects into our eyes, can travel through empty space

the first basic principle of light
when light reaches a surface, it can be absorbed and transformed into other forms of energy, amount of energy absorbed dependent on light intensity
phosphorescent
light energy is absorbed by particles, stored and is later emitted as visible light
chemiluminescent
light energy released by chemical reactions

LED'S
light emitting diode. They require less energy, lose minimal energy
the ray model of light
the path a beam of light travels can be represented by straight lines called rays. Light travels in a straight line until it strikes a surface.
how will a transparent material act if light strikes?
light will move through undeflected
how will a translucent material act if light strikes?
light will deflect after moving through
how will a opaque material act if light strikes?
light will be absorbed by the object
reflection
process in which light strikes a surface and bounces back
law of reflection
the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
virtual image
the image you see in a mirror
refraction
process in which the speed of light changes when it travels from one medium to another
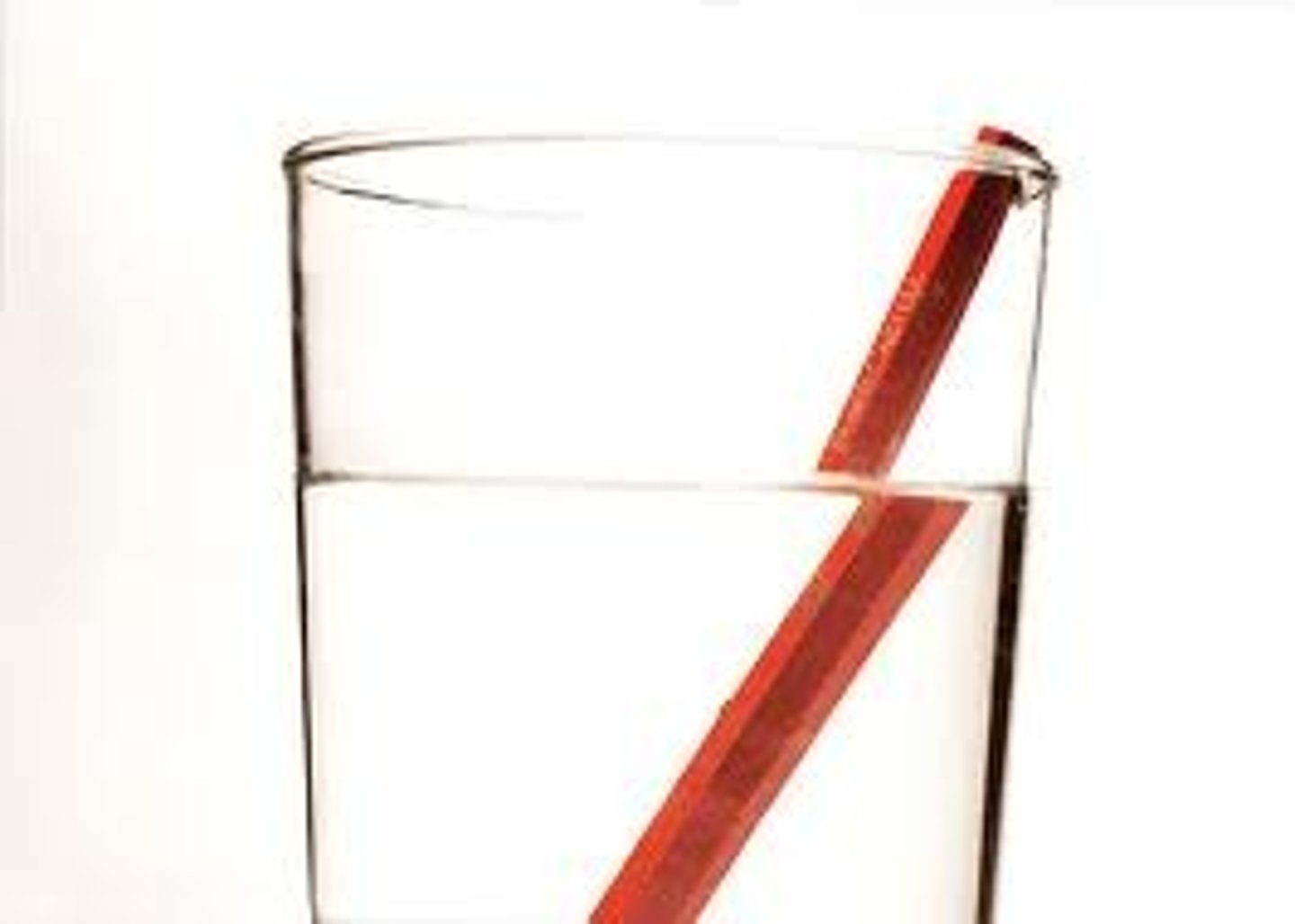

what happens to light when it enters a a less dense medium?
light speeds up. ex: water to air
what happens to light when it enters a denser medium?
light slows down. ex: air to water
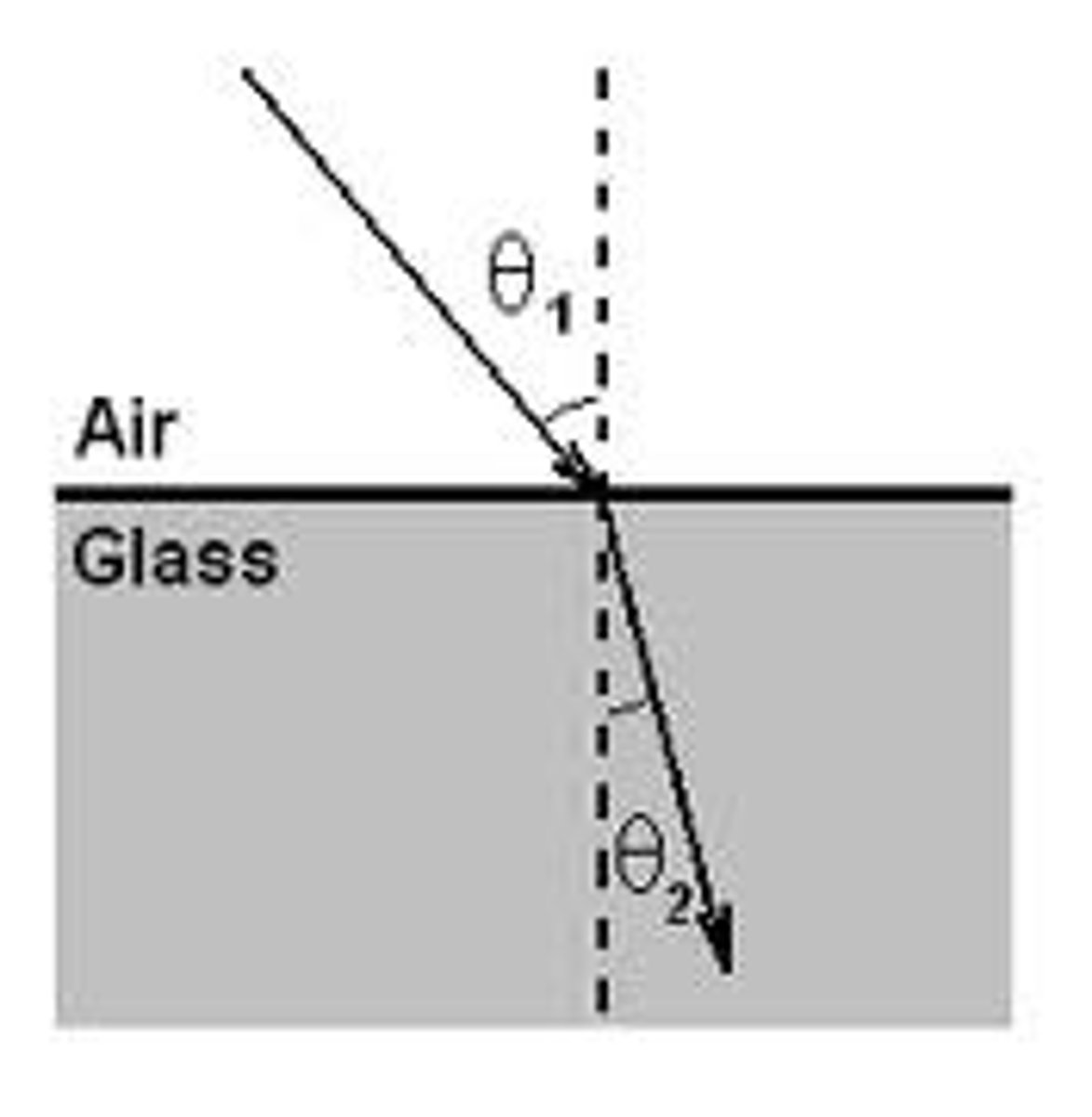
law of refraction
when light travels from one medium into a denser one, it will bend towards the normal line. less dense one, it will bend away from the normal line

what happens when light hits a surface? absorption
occurs mostly on rough, dark, opaque surfaces
what happens when light hits a surface? reflection
light bounces off surface and changes direction. occurs mostly on shiny, smooth surfaces
what happens when light hits a surface? refraction
light travels through the surface, often in a different direction. occurs when light strikes a different transparent medium
pupil
the opening through which light enters the eye
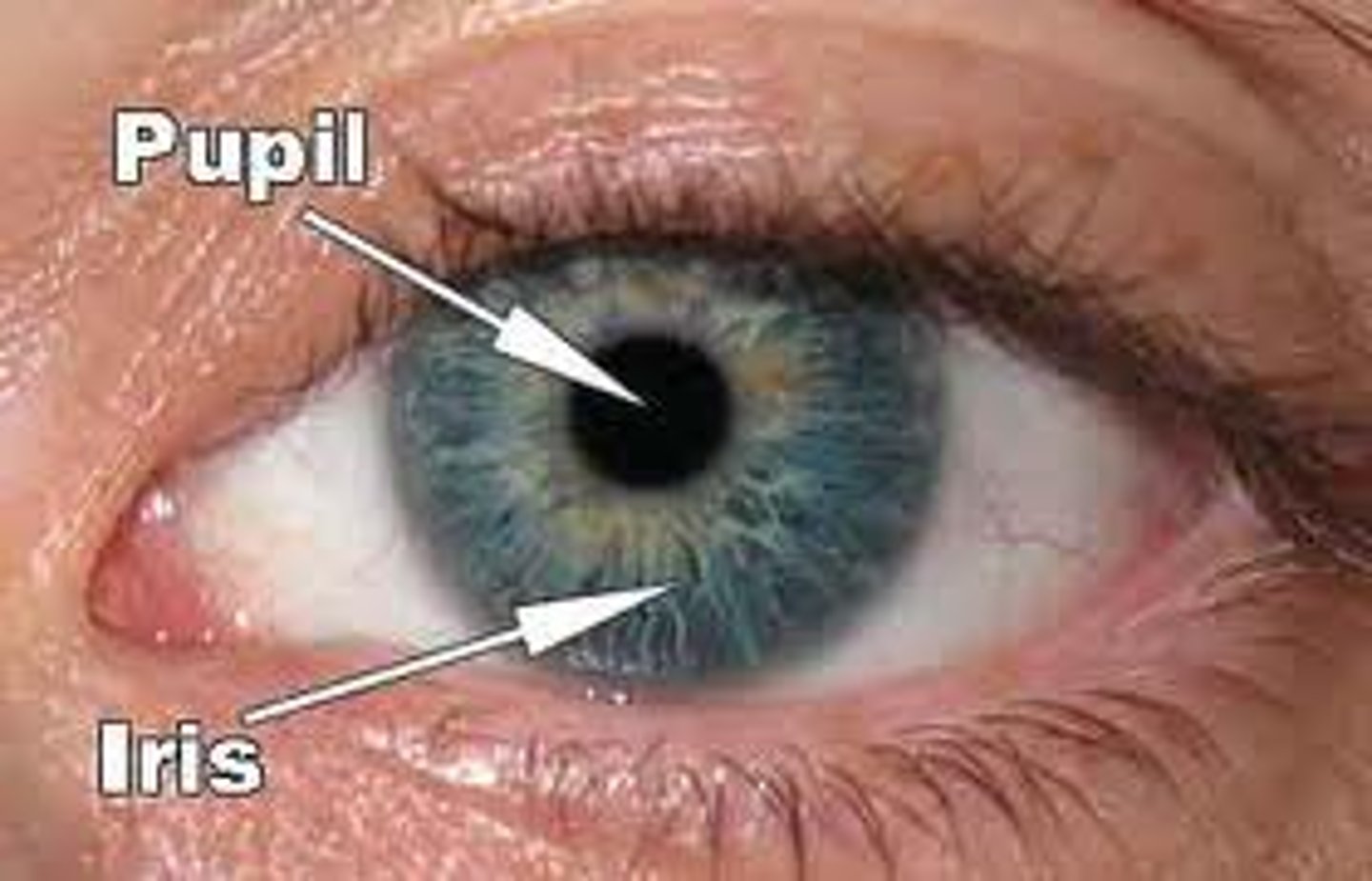
iris
coloured ring surrounding the pupil. expands or contracts the pupil depending on the brightness of the light
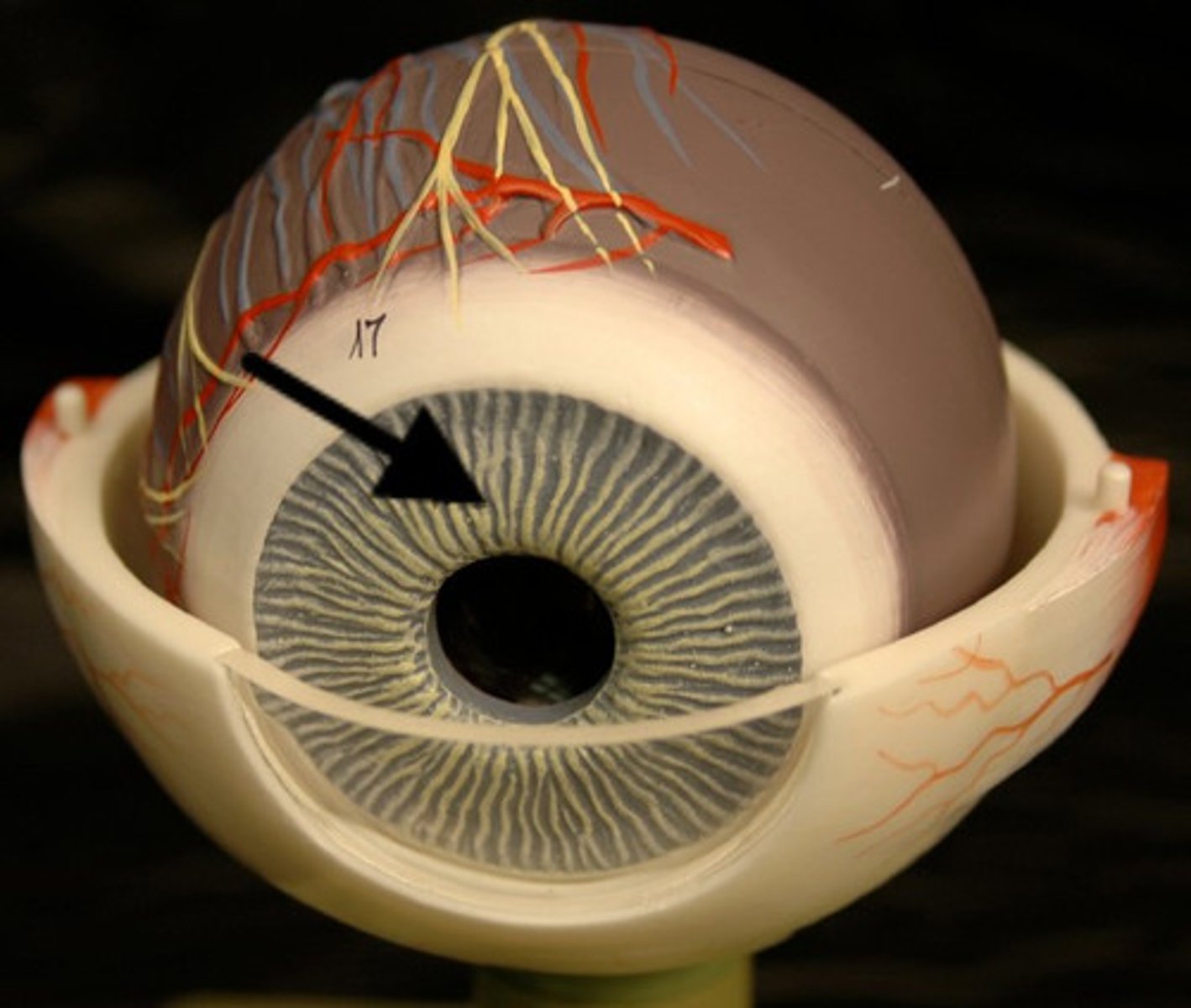
cornea
transparent surface that covers the pupil and iris. refracts light to a small degree
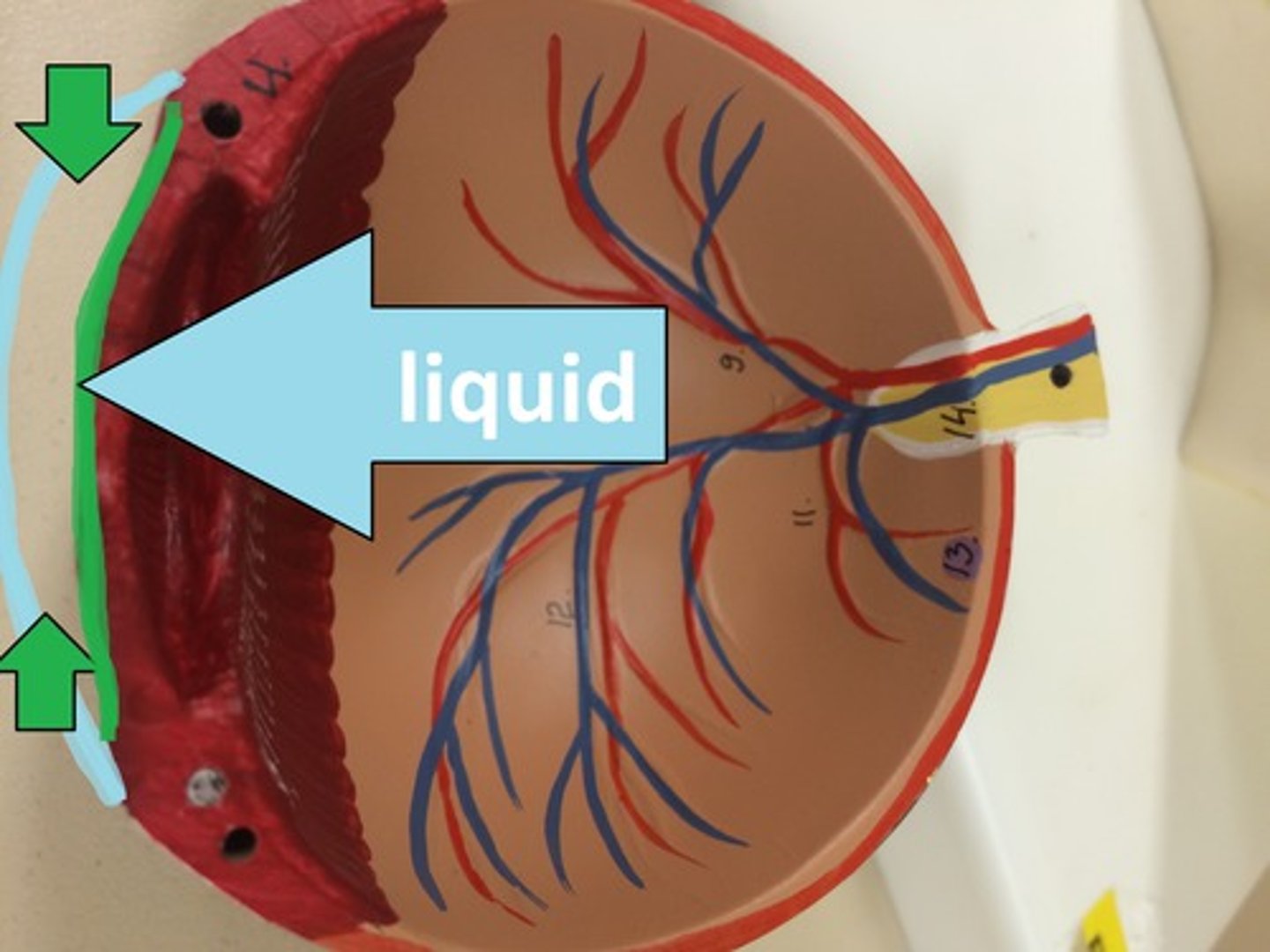
aqueous humour
fluid between the iris and cornea. keeps the eyeball rigid and refracts light
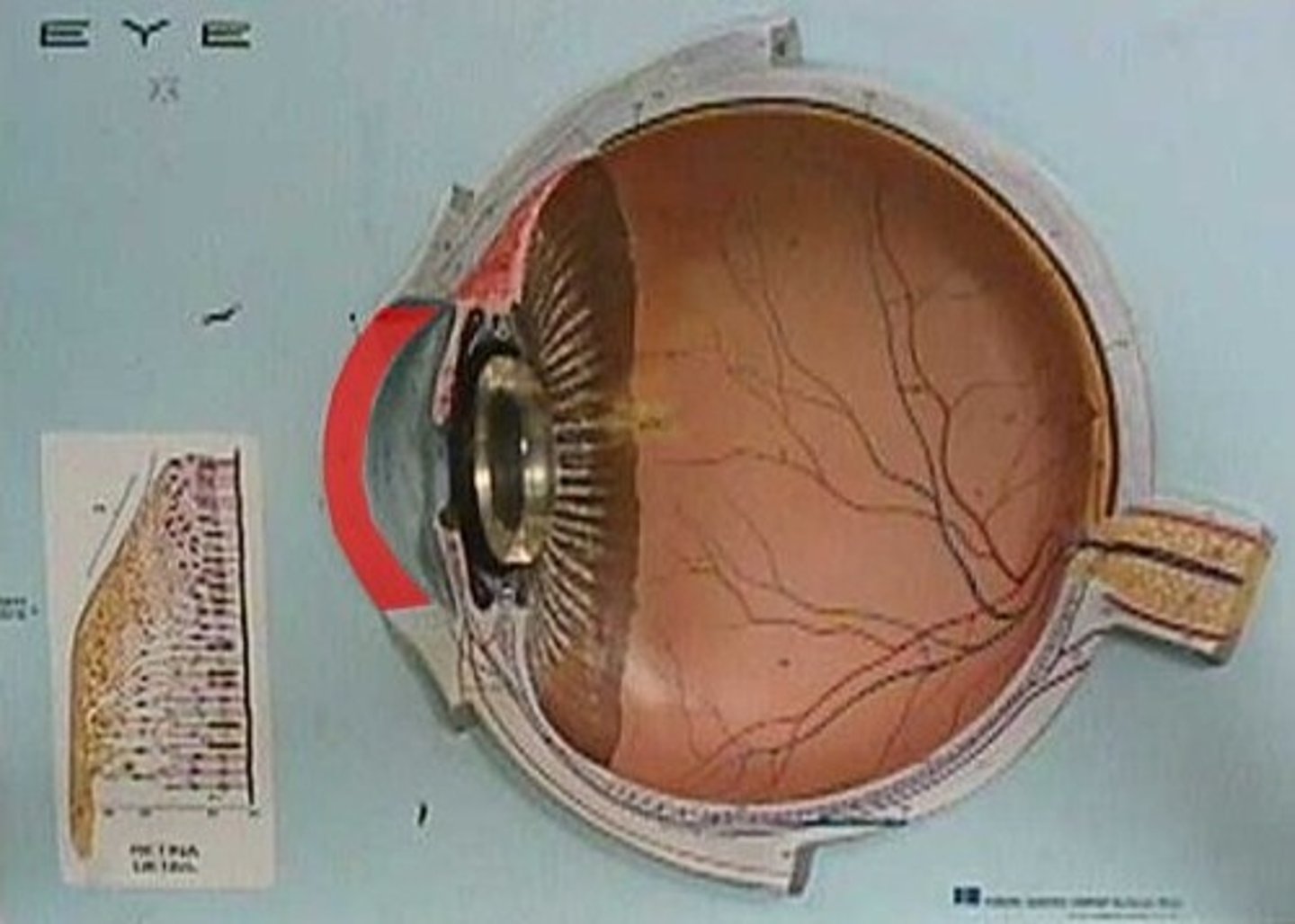
retina
layer of the eye that contains photoreceptors which detect light
lens
focuses the image on the retina
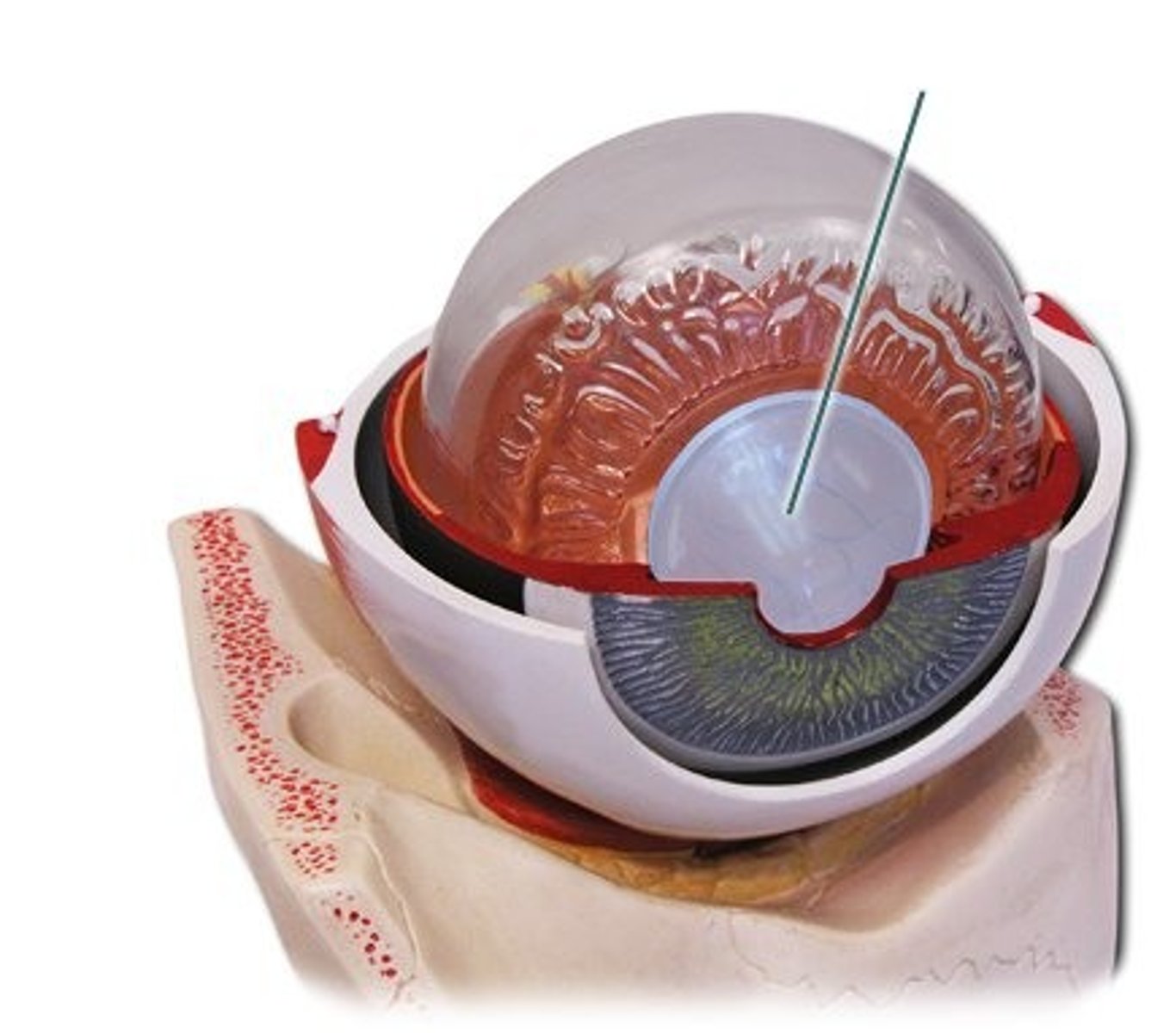
vitreous humour
fluid in the centre of the eye that helps keep its shape
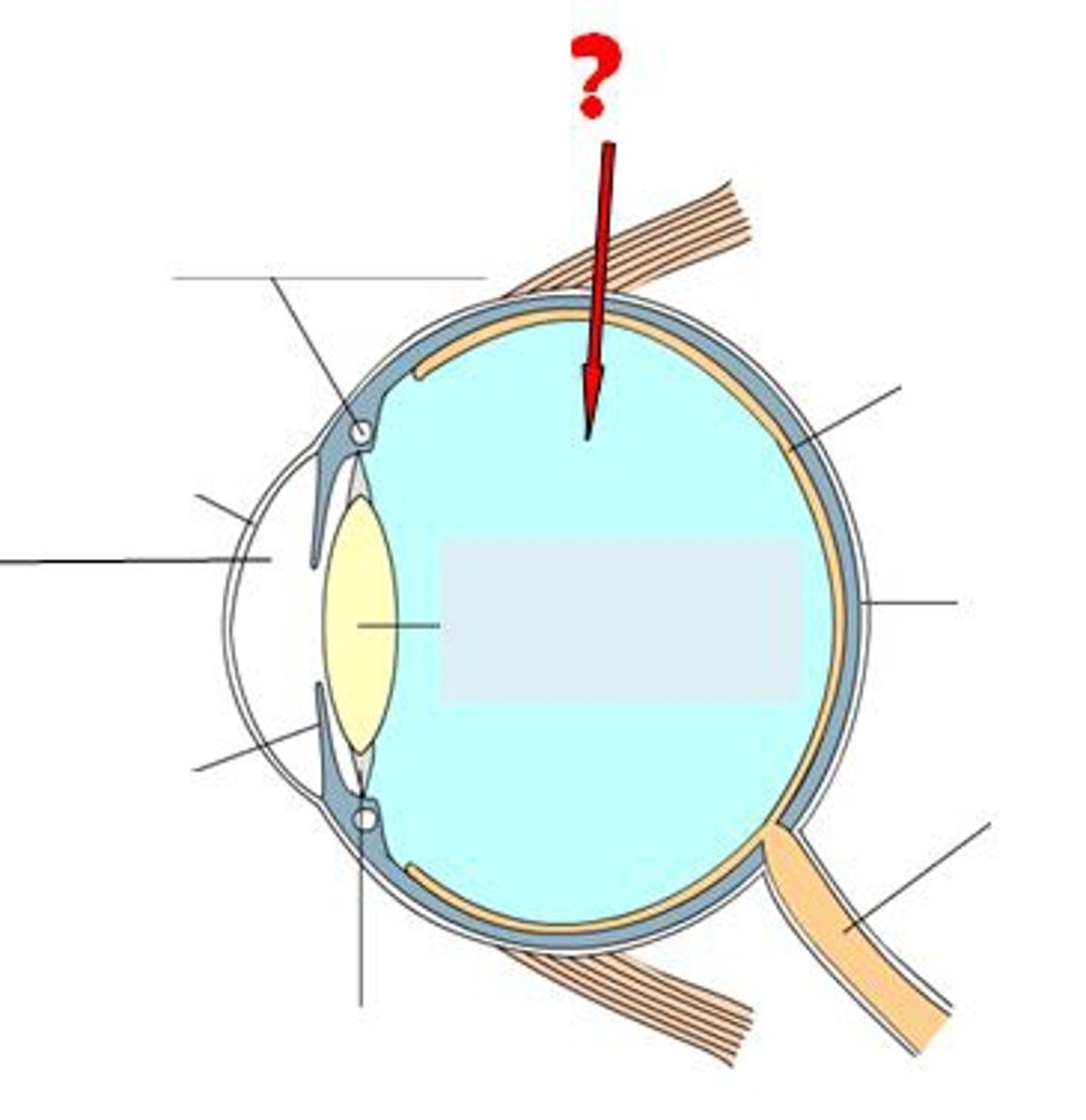
ciliary muscle
adjusts the thickness of the lens to focus on near or far objects
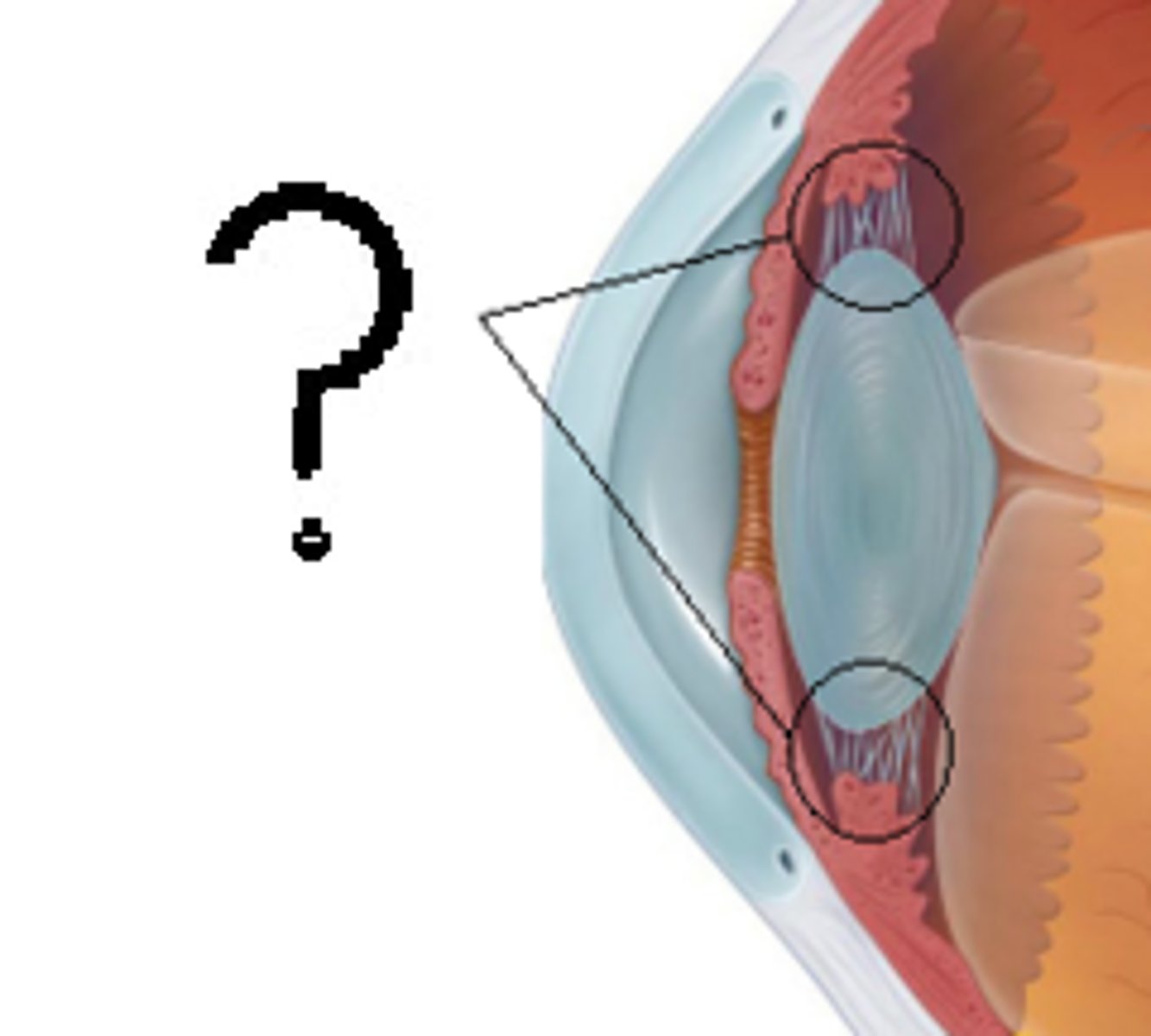
optic nerve
transmits signals from light receptors in the retina to the brain
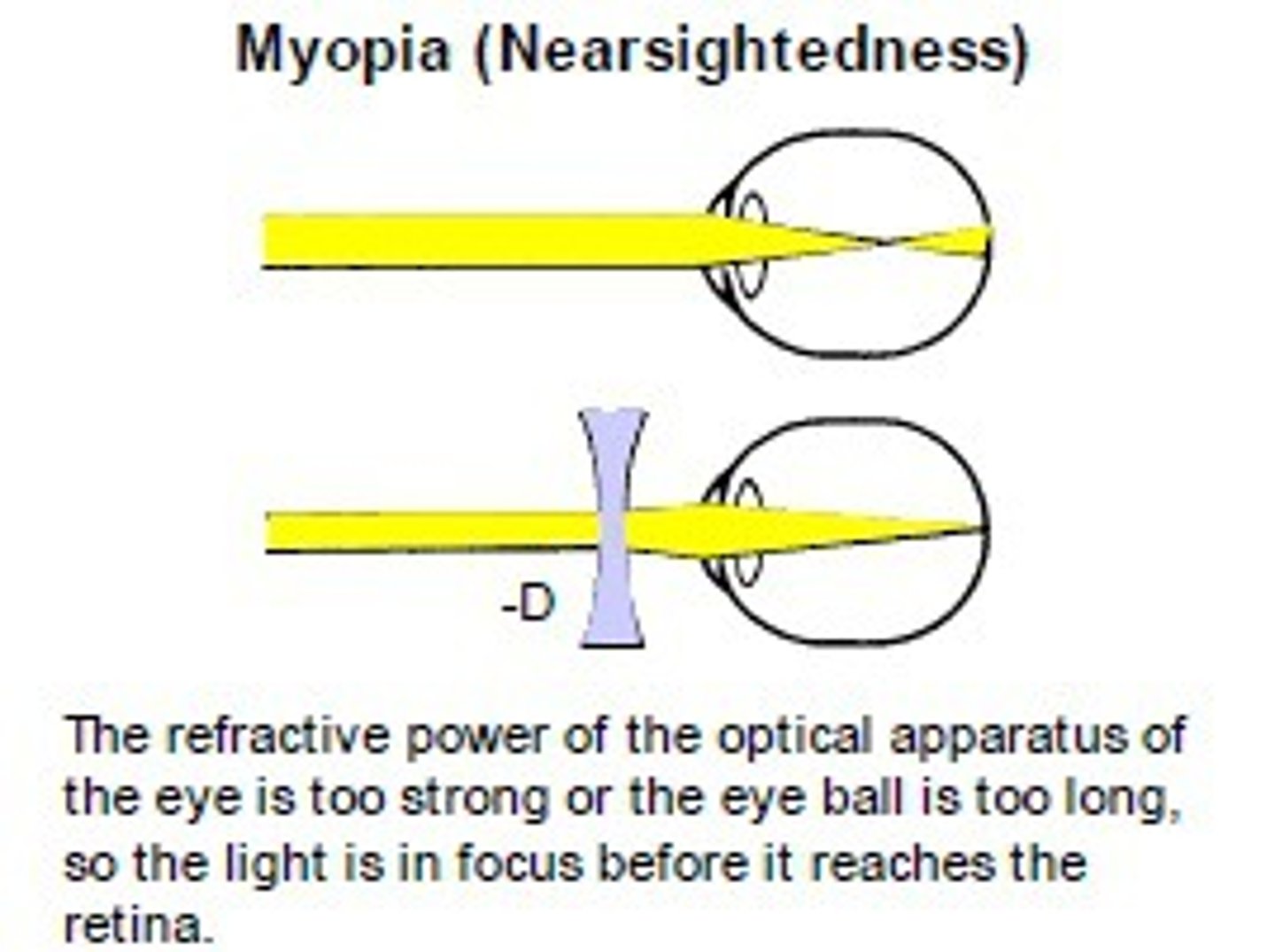
near sightedness
difficulty in seeing distant objects, occurs when an eye is too long, image forms in front of the retina, corrected using a concave lens
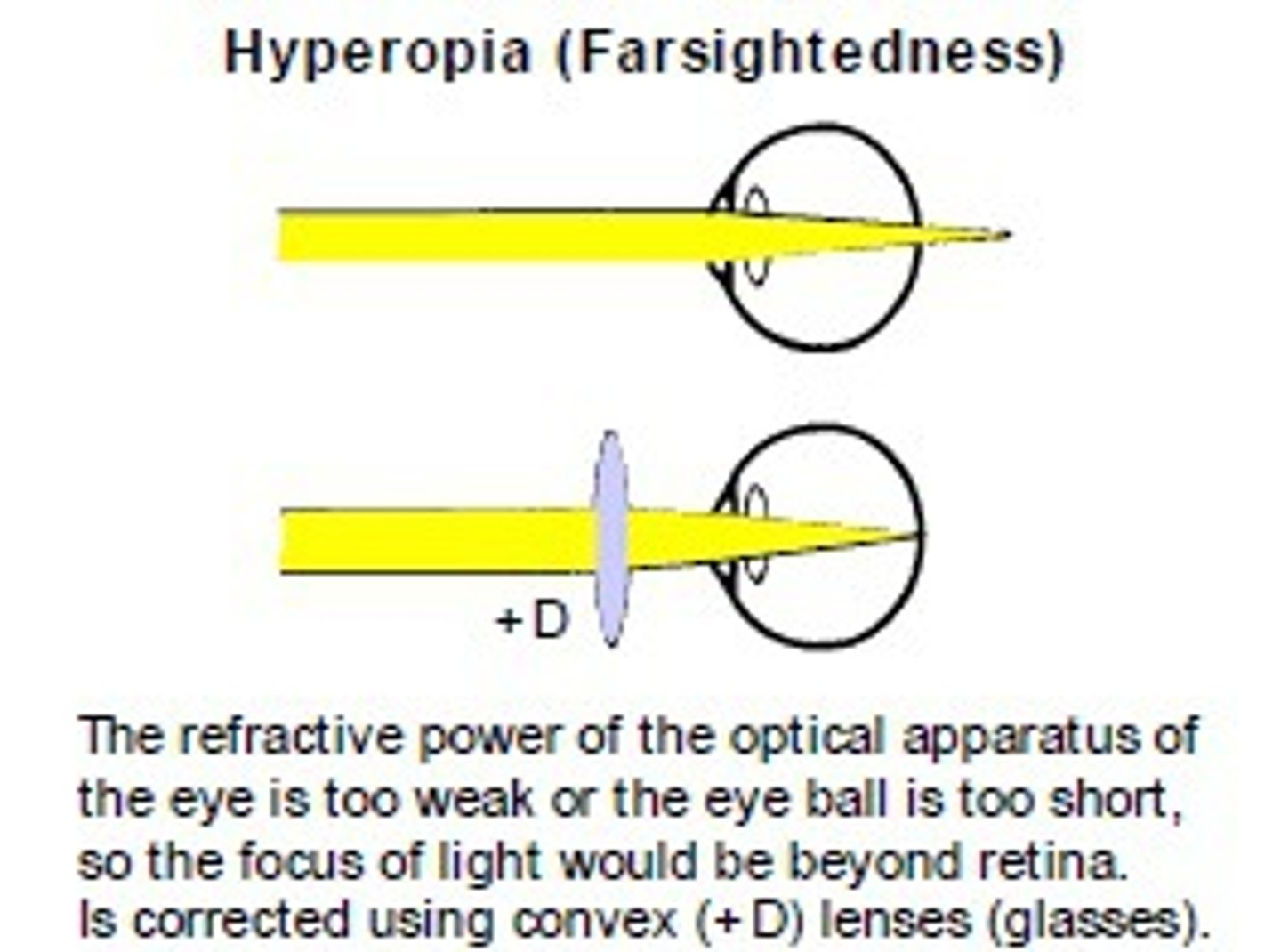
far sightedness
difficulty in seeing close objects, occurs when an eye is too short, image forms in behind of the retina, corrected using a convex lens
luminous
giving off light
natural light source
the non human made source of light such as the sun

non luminous
Does not produce its own light

normal
a reference line drawn perpendicular to a reflecting surface at the point where an incident ray strikes the surface
opaque
not allowing any light to pass through
plane
a flat or level surface
radiant energy
energy transferred or emitted as waves or rays in all directions

radiates
to send out energy in the form of waves or rays
radiation
the transfer of radiant energy, such as light
reflected ray
the light that is cast back from a reflecting surface
translucent
allowing some light to pass through
transparent
allowing light to pass through

iris reflex
when the pupil dilates or contracts to allow more or less light into the eye
refracting telescope
a telescope that uses convex lenses to gather and focus light
reflecting telescope
a telescope that uses a curved mirror to collect and focus light
shutter
a device that opens and closes in front of the lens of a camera
additive primary colors
red, green, blue
amplitude
height of a wave
colour blindness
it's when your cones and rods aren't able to function properly. It forms the inability to process the colours red and green
complementary colors
colors located directly opposite one another on the color wheel
cones
the cones detect fine detail and give rise to color sensations.
rods
retinal receptors that detect black, white, and grey
secondary colors
orange, green, violet
wave model of light
a model of light behaviour that represents light travelling as a wave
wavelength
horizontal distance between the crests or between the troughs of two adjacent waves
x-rays
electromagnetic waves with wavelengths shorter than ultraviolet rays, but longer than gamma rays