Other Laboratory Tests
1/189
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
most important part in predicting fertility of domestic animals
semen quality evaluation
effective harvesting of the semen involves
obtaining the maximum number of sperms of highest possible quality in each ejaculate
ultimate objective of semen collection
make maximum use of superior sires
semen collection is a complex procedure involving
coordinated efforts between the animal handler and the collector
age when semen can be collected in bull
12 months
age when semen can be collected in boar
6-8 months
age when semen can be collected in ram
6-9 months
age when semn can be collected in stallion
20-24 months
age when semen can be collected in dog
8-12 months
why is bull preparation essential?
decrease microbial load
increase semen volume, sperm concentration
decrease reaction time
bull preparation involves
clipping of preputial hairs
preputial washing with warm, normal saline
cleaning and washing the bull
ordinary washing soap and mild brush
paper towel or damp towel
preputial hairs must be clipped leaving a tuft of 2cm all around
a tuft of 2cm all around
preputial washing with warm normal saline may be used to
decrease microbial load
clean and wash the bull, especially the ______________, _______ before the semen collection
hind quarter
1 hour before
during bull preparation, special attention must be given on
lower abdomen area and prepuce
paper towel or damp towel may be used to
remove excess water
a teaser/dummy is a
female animal in estrus
teaser/dummy preparation
cleaned the same way as the bull
during teaser/dummy preparation, special attention should be given to
the back and perineum area
washing area should not be more than _____ away from _________________
20m away
collection area/serving area
washing area should be made of
rough concrete
the floor of the washing area should be
slanting with drainage facility of water, dung, etc.
washing area should have an
adequate facility of water with reasonable pressure
collection area should be away from
noisy places
collection area should not be more than _____ away from ____________________
3om away
semen evaluation laboratory
the ground of the collection area must not beor unstable, as it may pose safety hazards during the semen collection process.
slippery/muddy
collection area should be fenced with _______________ to avoid ____________
strong metallic bars to avoid escape of bull
this is needed in the collection area for the restraint of the teaser
one slanting metal stanchion fitted with wooden arms
there should be sufficient space in the collection area for
free movement of bulls and the semen collector
methods of semen collection
pan collection method
vaginal spoon method
sponge method
breeder’s bag method
sperm collector method
artificial vagina (AV) method
massage method
electro ejaculation
fistula method
dummy female

what is this called?
artificial vagina
most commonly used and best method of semen collection
artificial vagina (AV) method

used for semen collection from lame bulls and in dogs
massage method
used for semen collection from lame bulls
electro ejaculation
massage method
fastest and most sanitary method of semen collection
artificial vagina (AV) method


why is artificial vagina (AV) method done?
semen is collected in natural status
semen is collected in hygienic condition
frequency of semen collection
2-3x a week
more frequent semen collection results in
poor semen quality

advantages of artificial vagina method
Practically the whole ejaculate is collected in uncontaminated and natural stage.
It is free from the extraneous secretions.
Sterile conditions of the apparatus ensure disease control.
The viability of the sperm is better.
No female is needed if dummy is a success.

disadvantages of artificial vagina method
Occasionally it is difficult to get the males to serve the artificial vagina.
The apparatus involved is slightly costly and requires technical hands.
why is semen evaluation essential?
to investigate infertility problems
for breeding soundness evaluation of bulls
for semen extension and processing
methods of semen evaluation
macroscopic/physical
microscopic
biochemical
macroscopic evaluation of semen
color
volume
consistency
pH
color of semen
creamy to milky white color
pH of semen
6.6 to 6.9
microscopic evaluation of semen
mass motility
individual motility
sperm concentration
live sperm count
abnormal sperm count
biochemical evaluation of semen
fructolysis index
methylene blue reduction test
resazurin reduction test
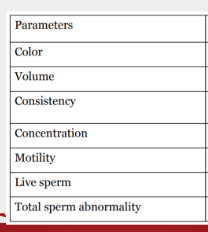
normal values of semen in cows
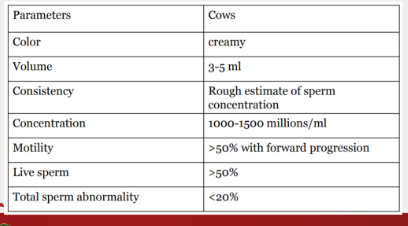
normal sperm morphology
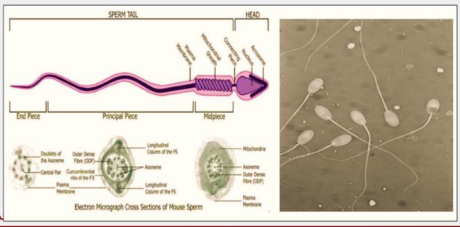
why do we need to check for sperm abnormalities?
only morphologically normal sperm participate in fertilization process which is prerequisite to fertilization
sperm abnormality is detected by
Nigrosin staining technique

edit
classification of sperm abnormalities
primary
secondary
abnormality caused by aberration during spermatogenesis
primary
abnormality caused by aberrations at the subsequent developmental stages
secondary
i.e. after spermatogenesis is complete and sperm has left the seminiferous tubules
secondary sperm abnormalities could be due to
dysfunction of epididymis, seminal vesicles, and genital diseases
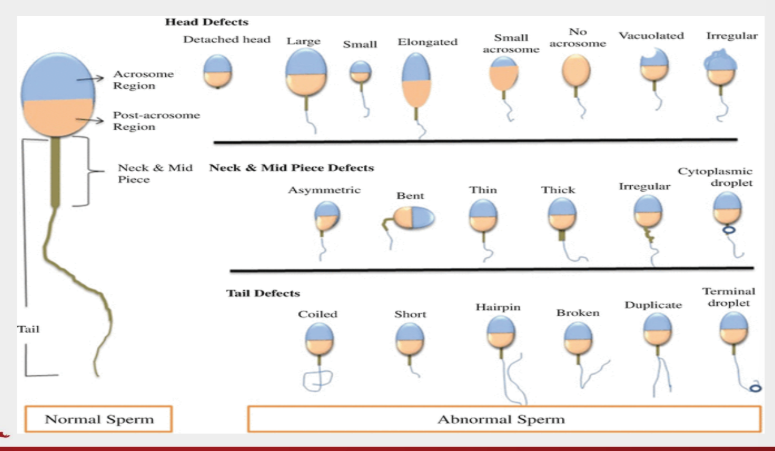
primary sperm abnormalities include abnormalities in the
head
middle piece
tail
sperm head abnormalities
mega
micro
pyriform
elongated
double and abnormal
detached
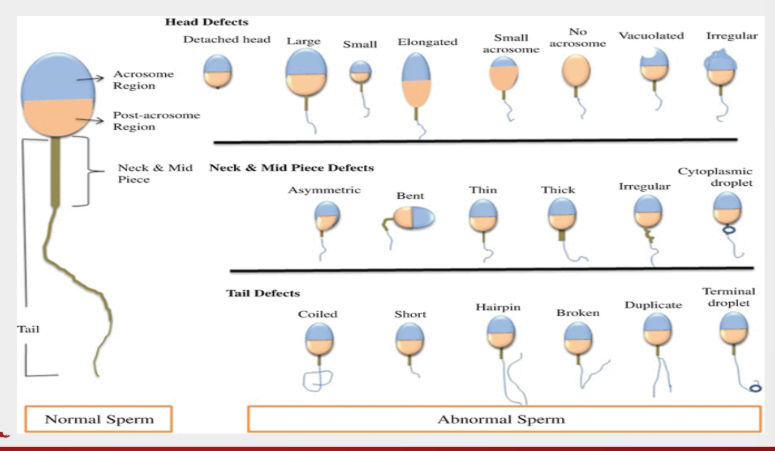
sperm middle piece abnormalities
abaxial attachment
thick short
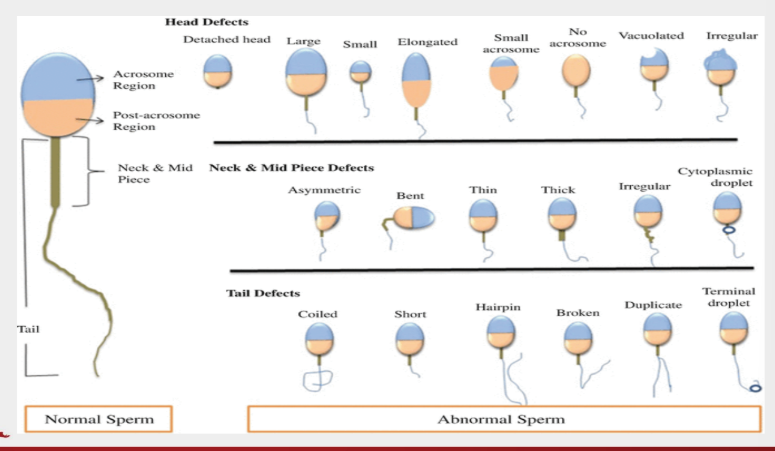
sperm tail abnormalities
double
stumpy
ring form
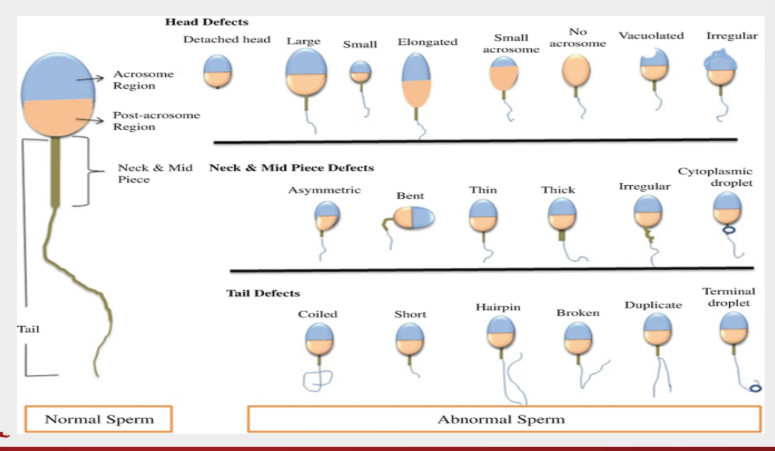
secondary sperm abnormalities include
normal detached heads
loose heads
coiled midpiece
presence of cytoplasmic droplets
chemical medium used for preservation, extension and protection of sperm cells against various shocks during processing, storage and transportation used for artificial insemination
extender or diluent
advantages of a good extender
provide energy for metabolic activities within sperm cell
maintain osmotic pressure and pH of the medium
keeps a check on the contamination of the medium to protect semen from microbial growth
basic components of a semen extender
egg yolk
buffer
antibiotics
egg yolk function on semen extender
membrane stabilizer, cryoprotectant
buffer function on semen extender
provides buffering capacity to semen
antibiotics function on semen extender
to check microbial growth
extenders used for chilled semen
egg yolk-citrate extender
tris-yolk extender
egg yolk-citrate extender is used in
cow bull and buffalo bull
tris-yolk extender is used in
buffalo bull
antibiotics added to the extender
penicillin - 1000 IU/ml
streptomycin - 1000 μg/ml
composition of citrate buffer
Sodium citrate dihydrate :2.9 g
Penicillin G sodium :1 lac Unit
Dihydrostreptomycin sulphate :100 mg
DDW :100 ml
composition of tris buffer
Tris buffer :3.028 g
Citric acid monohydrate :1.675 g
Fructose (Anhydrous) :1.250 g
Penicillin G sodium :1 lac Unit
Dihydrostreptomycin sulphate :100 mg
DDW :100 ml
semen preservation
Refrigeration method at 4-6°C
Ultra low temperature at bovine sperm frozen at -80°C , in dry ice or liquid nitrogen
Semen at room temp at 18-25 °C
advantages of frozen semen
selective mating
early progeny testing
maximum utilization of sires
long storage
reduced transportation cost
disease control
reduced feeding and management cost of bulls
progeny even after death of the bull
no wastage of semen
no need for sterilization of AI gun
no fear of breakage of AI gun
disadvantages of frozen semen
• Semen from about 10 to 20 percent of bulls will not withstand freezing. These
are often bulls of low fertility.
The ampouling, freezing and storage equipment are very costly.
In the freezing process about 40 percent spermatozoa are killed. Hence, increased number of spermatozoa per insemination are required.
If proper bull health is not maintained, frozen semen has great potential for the
spread of viral and bacterial diseases.
bulls with _______________ have semen that will not withstand freezing
how many percent of bulls?
low fertility bulls, around 10-20% of bulls
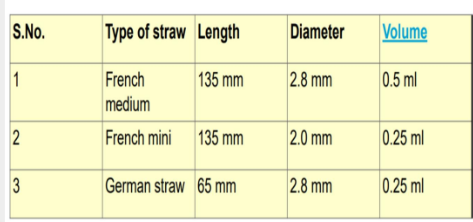
Packing Methods for Freezing
straw method
medium straws
mini straws
French straws
glass ampoules
German straws - mini tubes-landshut method
this was introduced by a scientist of Denmark in 1940 for packing of liquid semen
straw method
Adler in 1960 froze semen packed in straws using
liquid nitrogen vapor
Cassou in 1965 modified Adler’s technique and was then called as
medium straws
Cassou in 1968 brought further improvement in semen packing by __________________ which is then called as
reducing diameter for better freezing
mini straws
Van Denmark and Kinney (1954) packing method
glass ampoules
Simmet (1972) packing method; also known as; capacity?
German straws
mini tubes-Landshut method
65mmx2.8mm - 0.25ml capacity
dimensions of French and German straws
the French straws have two ends -
factory seal end
laboratory seal end
the seal end that was formed while manufacturing the semen straw at the factory
factory seal end
the seal end that is open when purchased and is formed at the semen processing laboratory
laboratory seal end
the laboratory seal has to be created in the semen processing laboratory after __________________________ before _____________
filling the straw with diluted semen
freezing
factory seal has two cotton plugs with ____________________
PVA powder in between them
laboratory seal formed with ____________________ or ___________________ after ____________________
PVA powder
sealing machine
filling of semen
best temp & time in thawing frozen semen
warm water, 35-40 degrees Celsius temp, 30 seconds
once semen is stored at lower temperature, there should
never be a change in the temperature of stored semen
semen should also be transferred to other places ______________________ at which it is stored
at the same temp
the vial containing chilled semen should be wrapped in? reason?
wrapped in paper before it is placed in thermos with ice to avoid cold shock to sperms coming directly in contract with the ice in the thermos
frozen semen should always be transported in this container
liquid nitrogen containers
usual sample submissions from small animal clinics
blood samples for CBC and blood chemistry
urine for urinalysis and culture (if suspected with bacterial infection)
smears for cytology examination
tissues for bacterial culture and isolation
usual sample submissions from farms, especially in outbreak investigations
blood samples for serology
diarrheic feces for scour work-ups include parasitology work-ups, microbiology work-ups, and virology work-ups
diarrhea is also known as
scour
a laboratory test or kit designed to identify the cause of diarrhea (scour) in animals, particularly calves and adult animals, by testing for various pathogens and parasites in fecal samples
scour package