Microbio Lab 8-13 Final Review
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Which of the following is not an outcome of complement cascade activation?
fever
Fever-inducing agents released by certain microbes are called ___________.
pyrogens
These are the results of bacterial samples inoculated on bile esculin agar (BEA). Why is tube 3 considered a negative result?
there must be at least 50% black-colored media to be considered positive
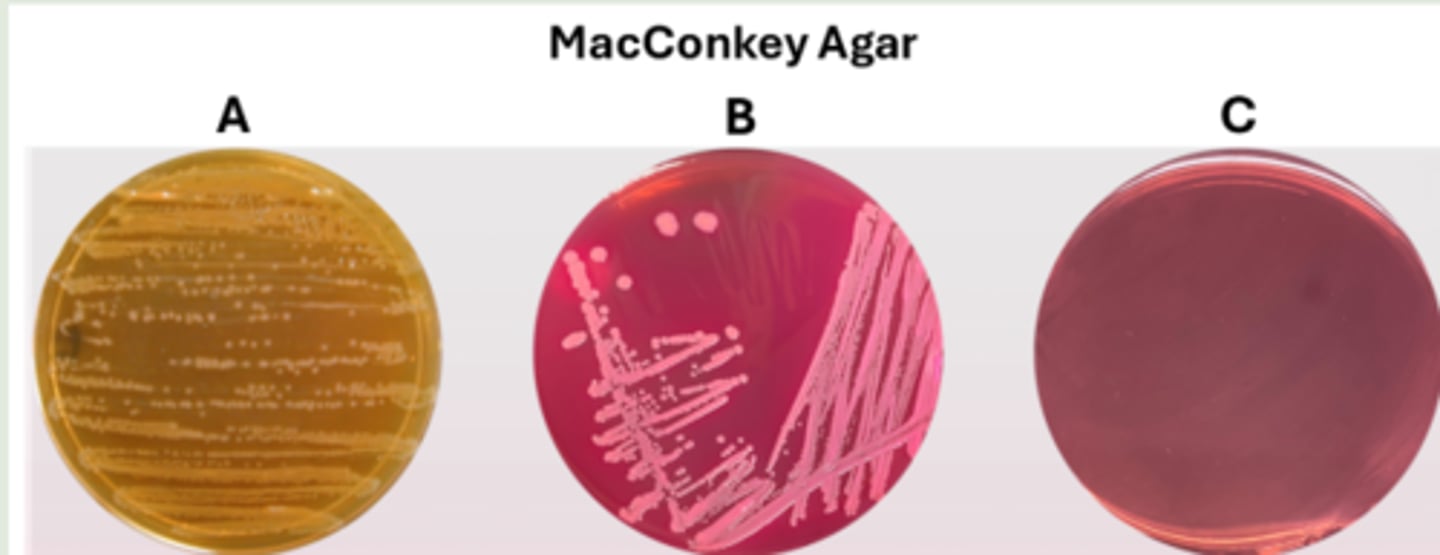
These are the results of three bacterial species inoculated on MacConkey agar. What do the results of sample A indicate?
the bacteria are Gram-negative and cannot ferment lactose

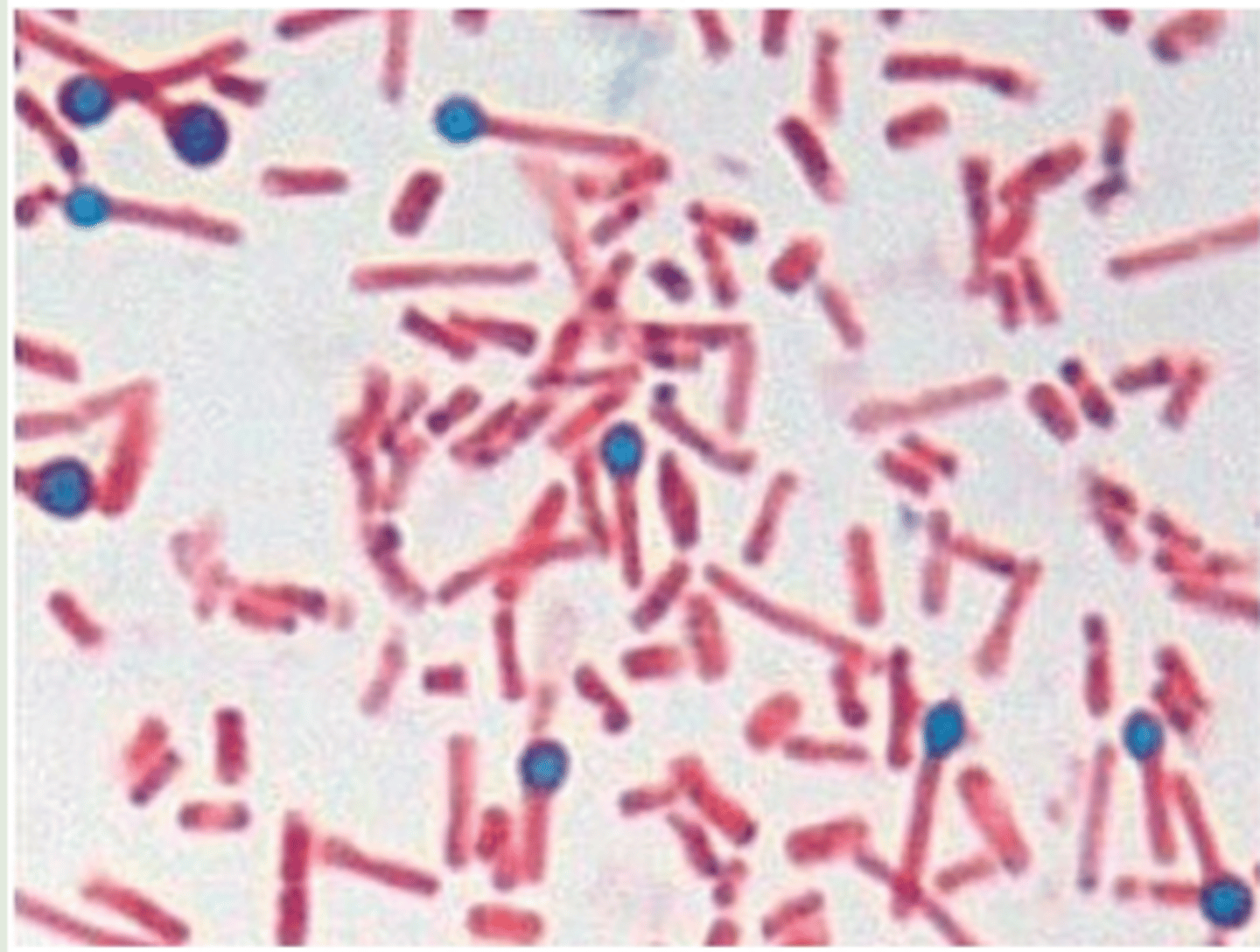
This image depicts an endospore staining result of an organism that causes spastic paralysis due to the production of a powerful exotoxin. This organism is commonly found in soil, but rusty objects can be contaminated with its endospores. If a puncture wound occurs with the rusty object, it introduces the organism and can cause infection. Name this organism.
Clostridium tetani
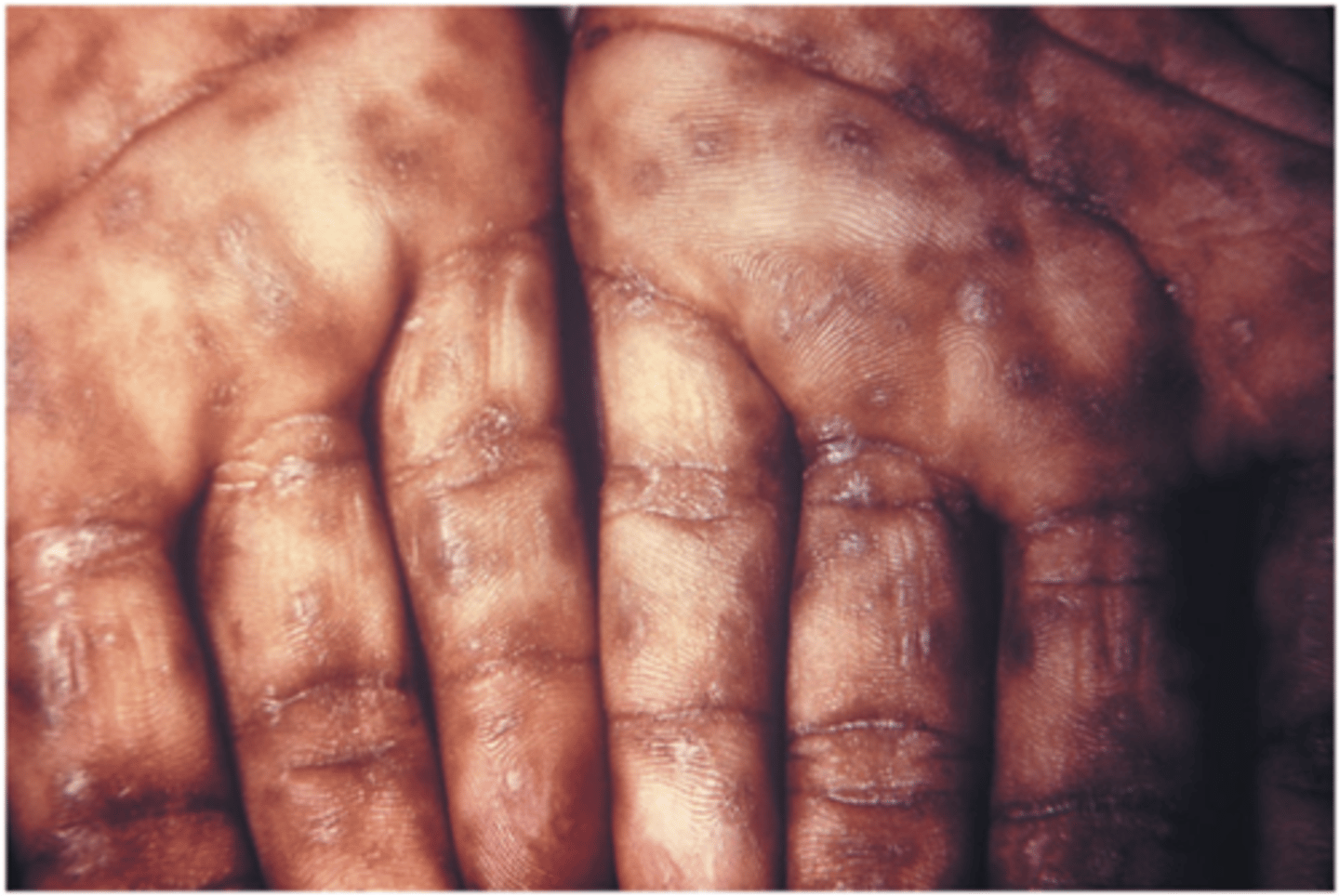
Tears, saliva, mucus, and breast milk contain the enzyme _____________ that destroys certain bacteria.
lysozyme
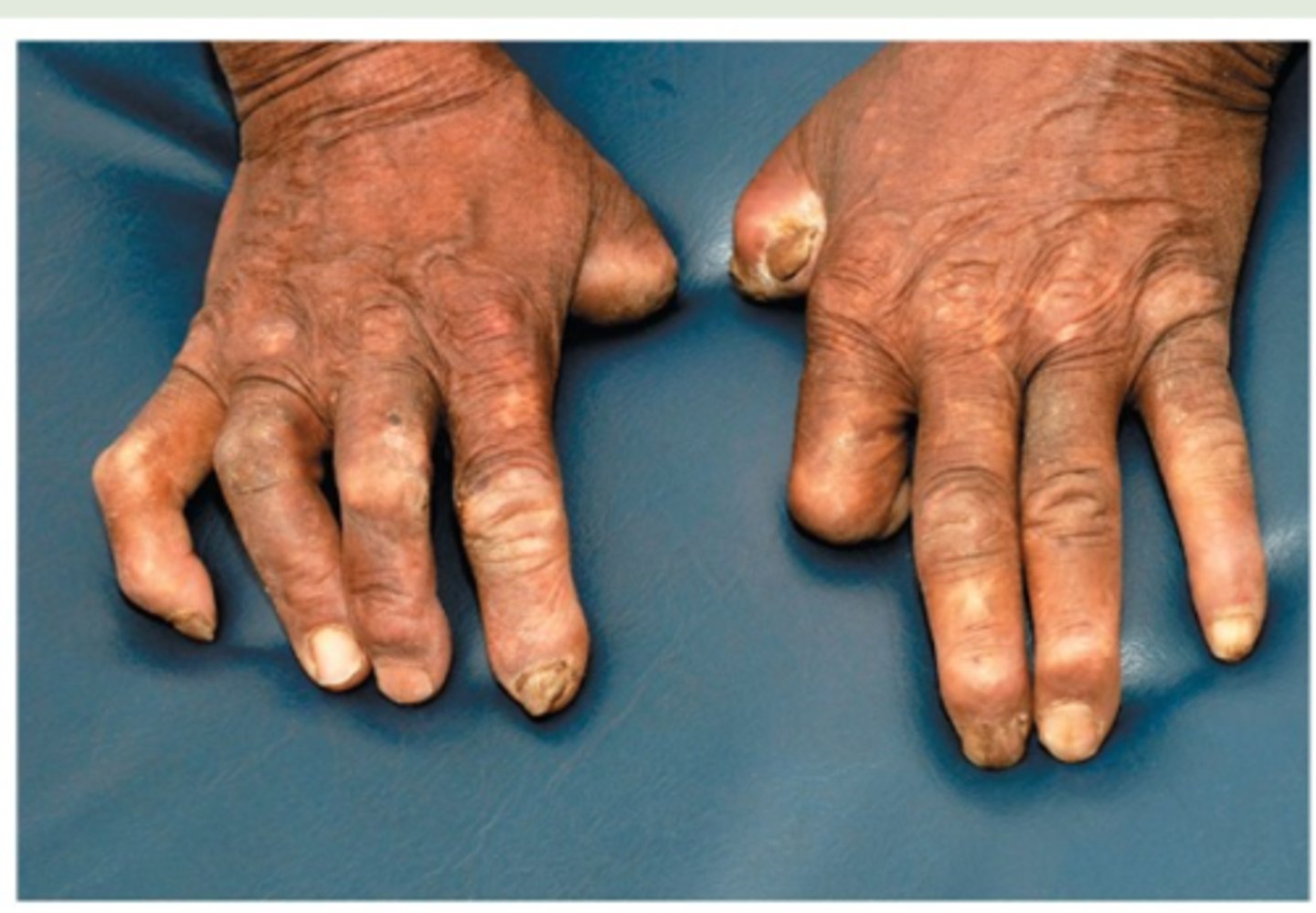
This patient has a disease caused by an acid-fast positive bacterium that grows best between 30-35oC. What bacteria causes this disease and what form of the disease is it?
Mycobacterium leprae; lepromatous form
A child presents with a fever, headache, and a stiff neck. The pediatrician suspects pneumococcal meningitis. What is the etiological agent of this form of meningitis?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
The most common STI in the world that causes genital warts and cervical cancer is caused by ______________.
HPV
Which stage of syphilis usually involves a disseminated rash, which may appear on the skin or on mucous membranes in the mouth, vagina, or anus?
secondary syphilis
Your State Health Department received information from local hospitals about several patients complaining of bloody diarrhea. It was determined that the pathogen is enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) contracted by ingesting contaminated produce. You have been tasked to perform PCR on vegetable samples that are suspected to be contaminated with EHEC. You obtain the following results. Lane one and two are positive and negative controls, respectively and lane 3 contains a known positive sample collected from soil. Analyze the results.
the controls worked, and samples 3 and 5 were positive

A variety of RNA viruses can cause infections of the digestive system. What genome-based diagnostic tool is routinely used to detect RNA viruses in the blood of a patient?
RT-PCR
Which bacteria is the most common cause of Gram-positive uncomplicated UTIs?
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
What is the most dangerous form of neonatal herpes?
disseminated infection
Which bacterium is the etiological agent of PID and ophthalmia neonatorum?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
T cell and B cell receptors only recognize one type of ____________.
epitope
True or False? A sandwich ELISA is more sensitive than a direct ELISA.
True
Which of the following is not considered a part of innate immunity?
cytotoxic T-cells
True or False? Phenol red carbohydrate broth contains a base medium and one specific carbohydrate. Because of this, this medium can be used to test for fermentation of different carbohydrates by adding a specific carbohydrate to the base medium.
True
What is the vector that spreads West Nile Virus and La Cross Virus to humans?
mosquitos
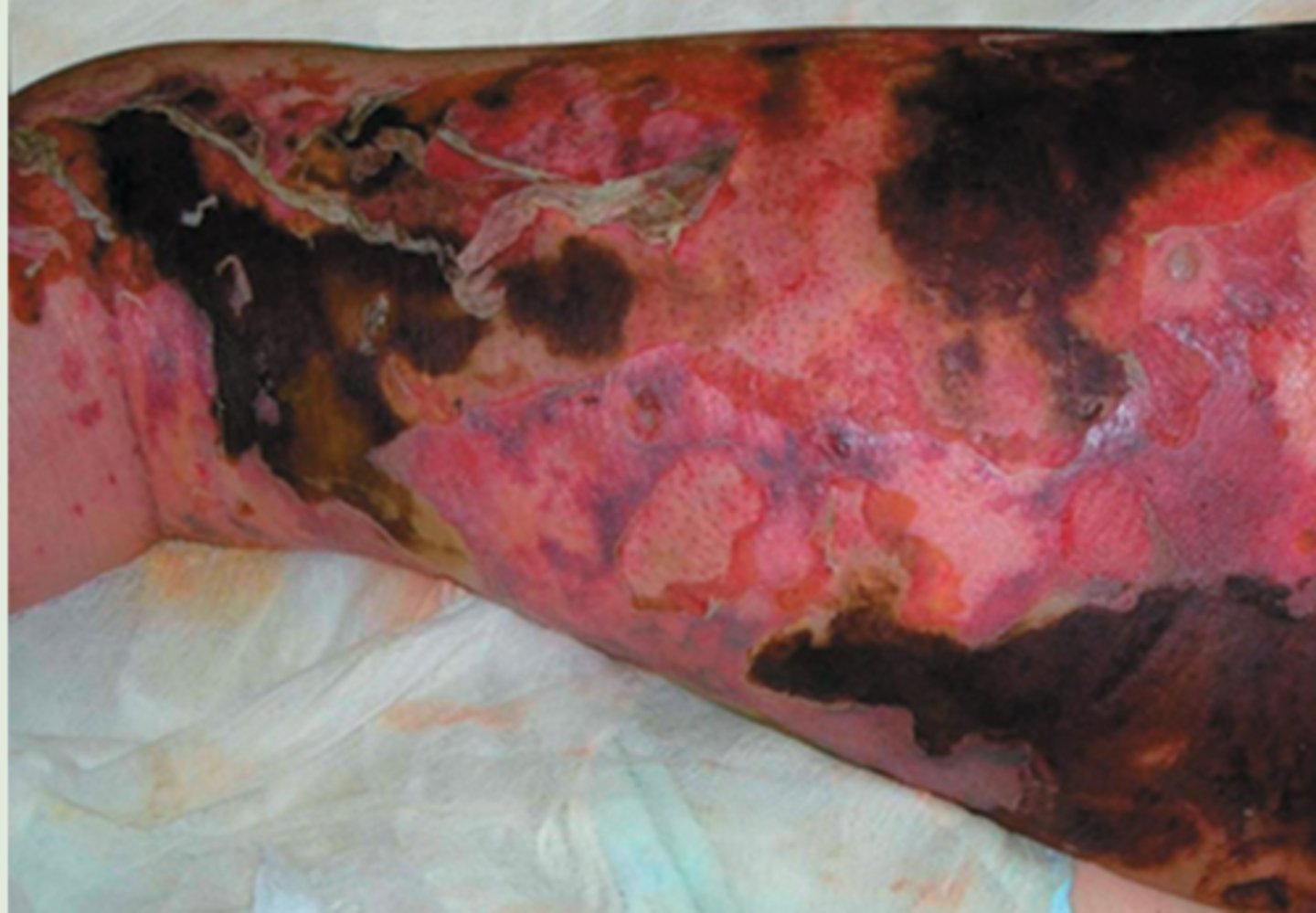
What is the name of the infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes that is depicted in the image?
necrotizing fasciitis
According to the US Environmental Protection Agency, Cryptosporidium has been detected in 65 to 97% of US surface waters (lakes, streams, etc.). What infective stage of the protozoan must be ingested to cause Cryptosporidiosis?
Oocysts
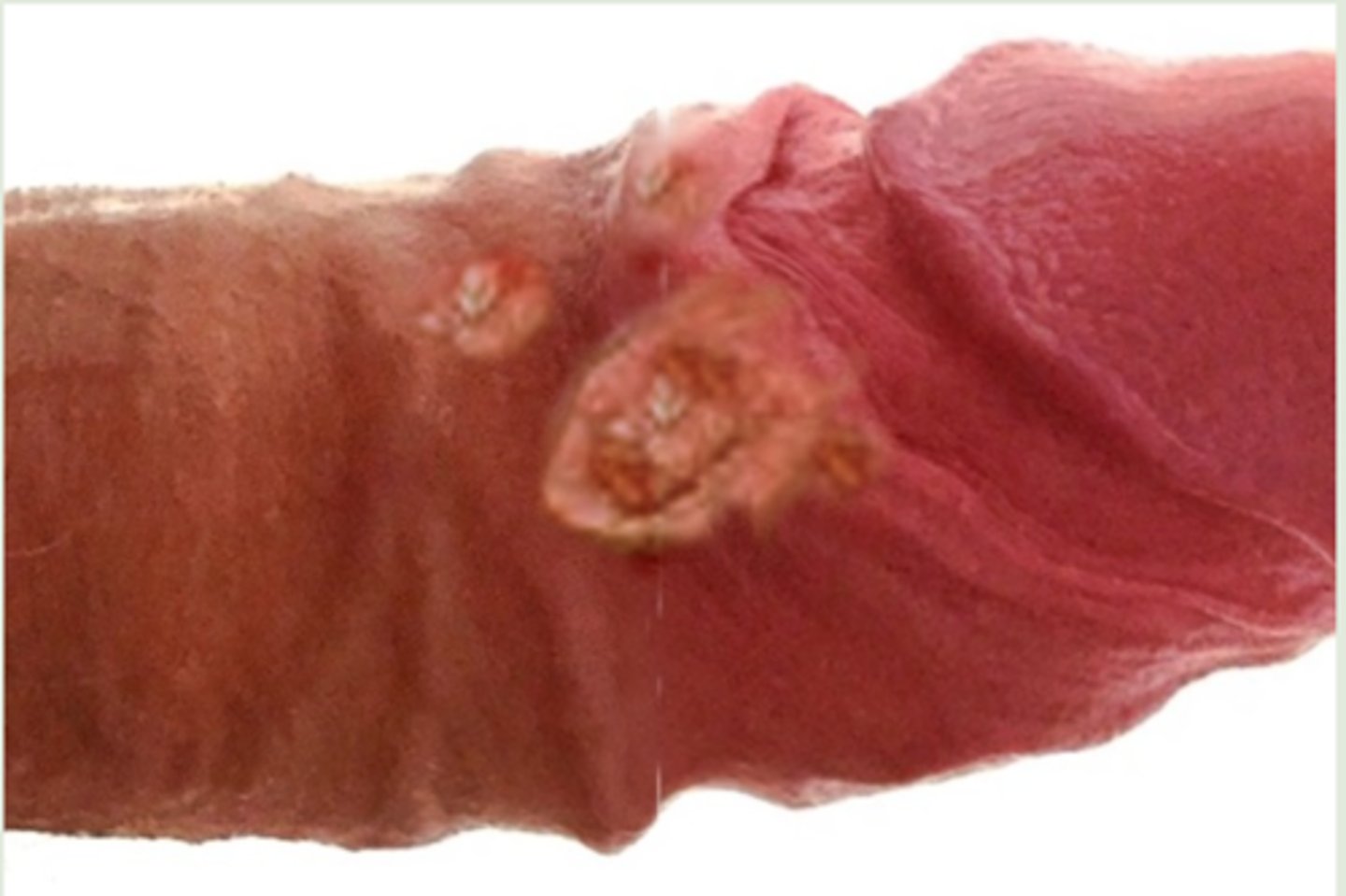
What infection exhibits ulcers that are referred to as "dewdrops on rose petals", describing the look of the clear pustule above a reddened base?
genital herpes
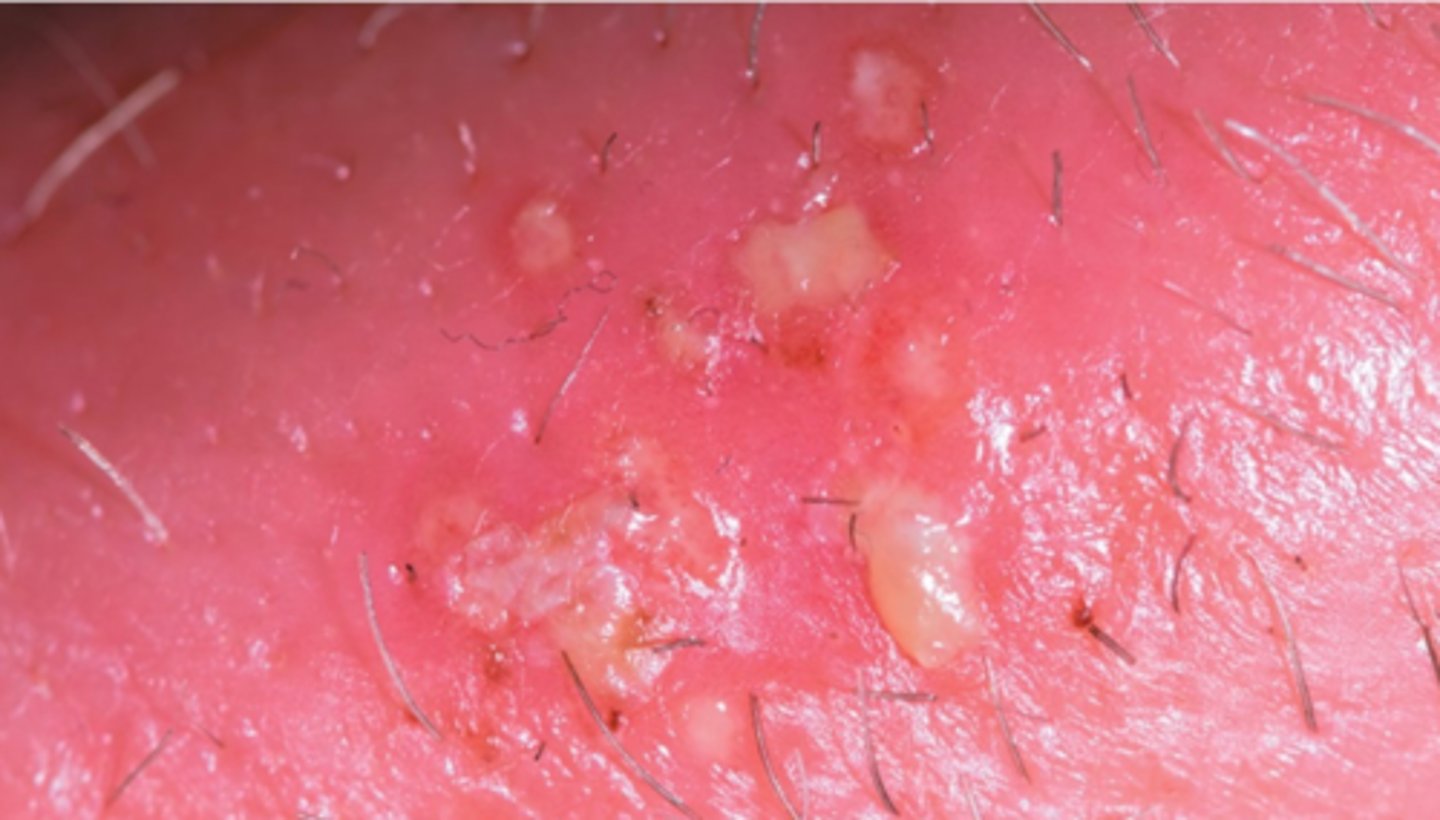
The body's response to an antigen which is beyond what is considered normal is called a/an _________ response.
hypersensitivity
Hepatitis A, B, and C are the primary pathogens that cause infectious hepatitis. Which type(s) of hepatitis is(are) spread by sexual contact or inoculation with contaminated blood?
HBV and HCV
These are the results of an HIV indirect ELISA. The samples and controls are tested in duplicate. Row A is the positive control and row B is the negative control. Interpret the results.
the samples in row C and row F are negative for the presence of anti-HIV antibodies
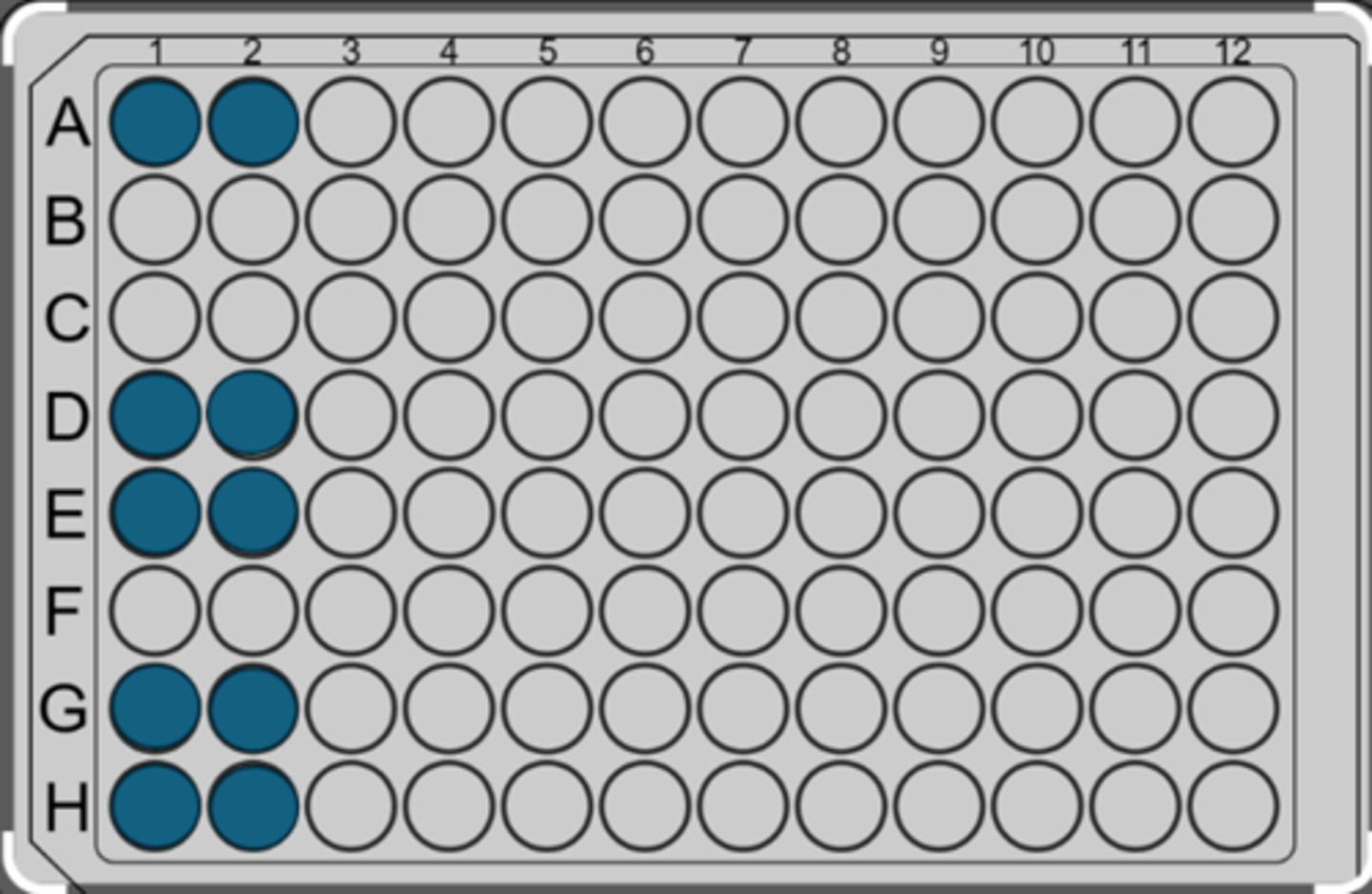
What is the name of the infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus that is depicted in the image?
scalded skin syndrome
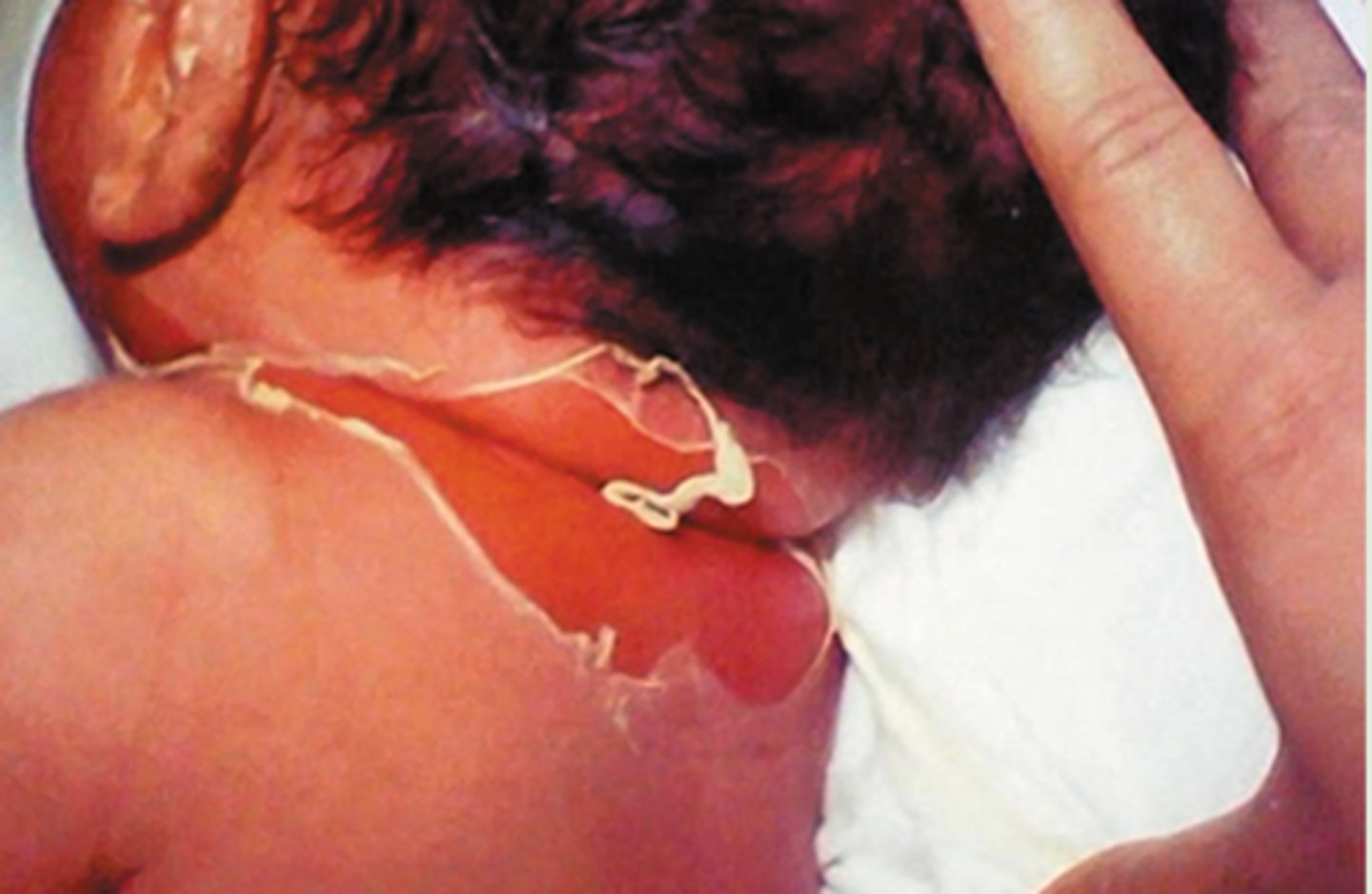
When does hemolytic disease of the newborn occur?
when a previously sensitized Rh- woman is pregnant with her second and subsequent Rh+ fetus
What disease does this vesicular/pustular rash depict?
smallpox
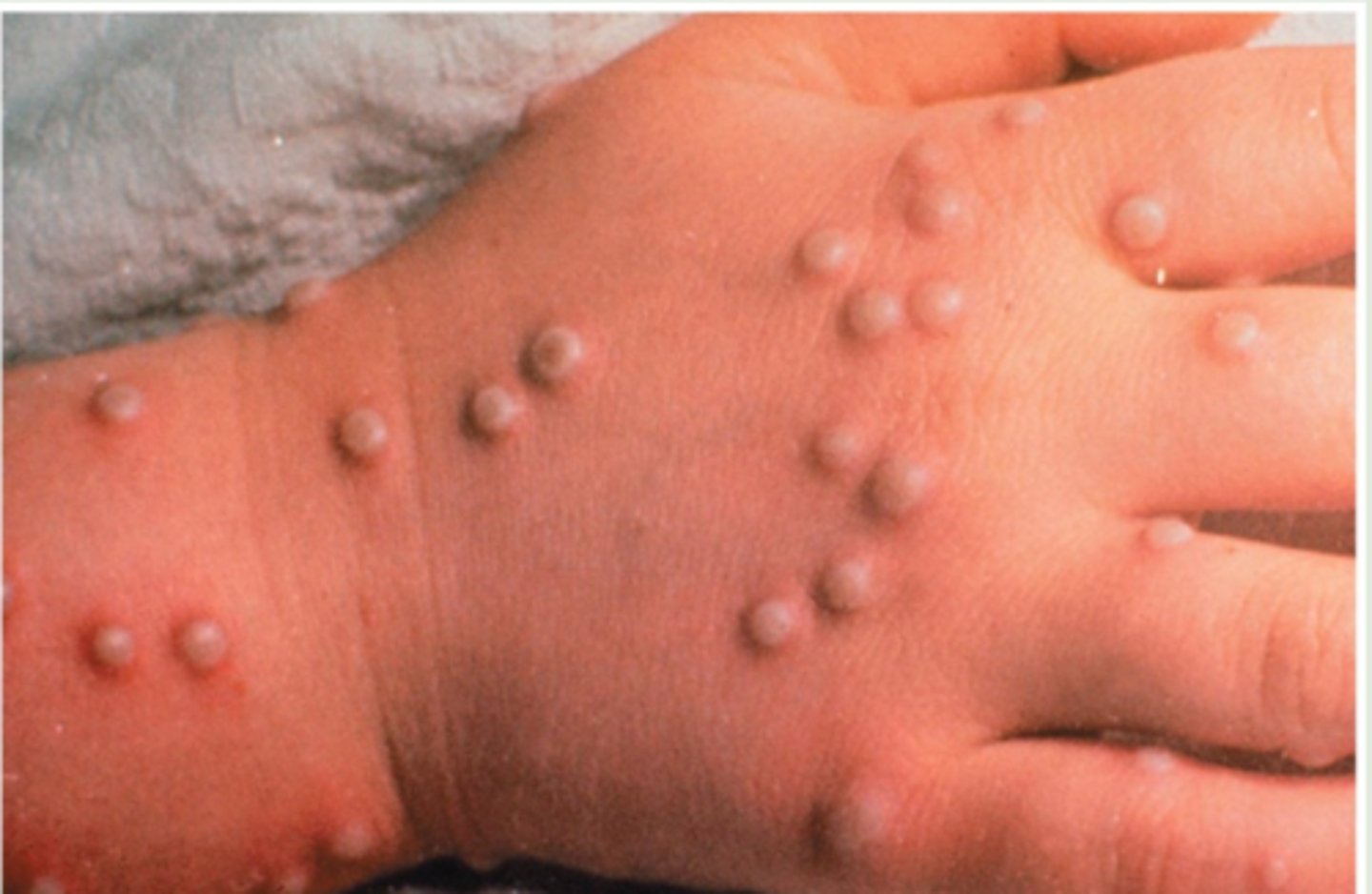
Swollen ________ indicate that a foreign antigen is present, and leukocytes are rapidly multiplying to mount an immune response.
lymph nodes
Name the etiological agent that is the main cause of foodborne illness in the USA and is associated with a rare, but dangerous autoimmune disease called Guillain-Barre'.
Campylobacter jejuni
What is the disadvantage of a direct ELISA?
the antigen in the sample must be in high enough concentration to be detected
A patient has traveler's diarrhea due to an intestinal pathogen. What antibiotic type and antibiotic dose would ensure that the patient recovers with minimal damage to the normal microbiota?
narrow spectrum/low dose
What is the main salivary gland that is inflamed when a patient has the mumps?
parotid
T cells can be classified by certain glycoproteins on their surface called clusters of differentiation (CD). T helper cells are classified as __________, and T cytotoxic are classified as __________.
CD4/ CD8
A powerful toxin called tetanospasmin causes the symptoms of what nervous system infection?
lock jaw
Rubeola is also known as ___________ and the etiological agent is ____________.
measles/ measles virus
You perform a Methyl red Vogues-Proskauer (MRVP) test. What do the methyl red results in Tube 1 indicate?
the bacteria cannot ferment glucose to produce a mix of strong acids
The T helper cell subclass that stimulates B cells to proliferate and differentiate is called ________.
TH2
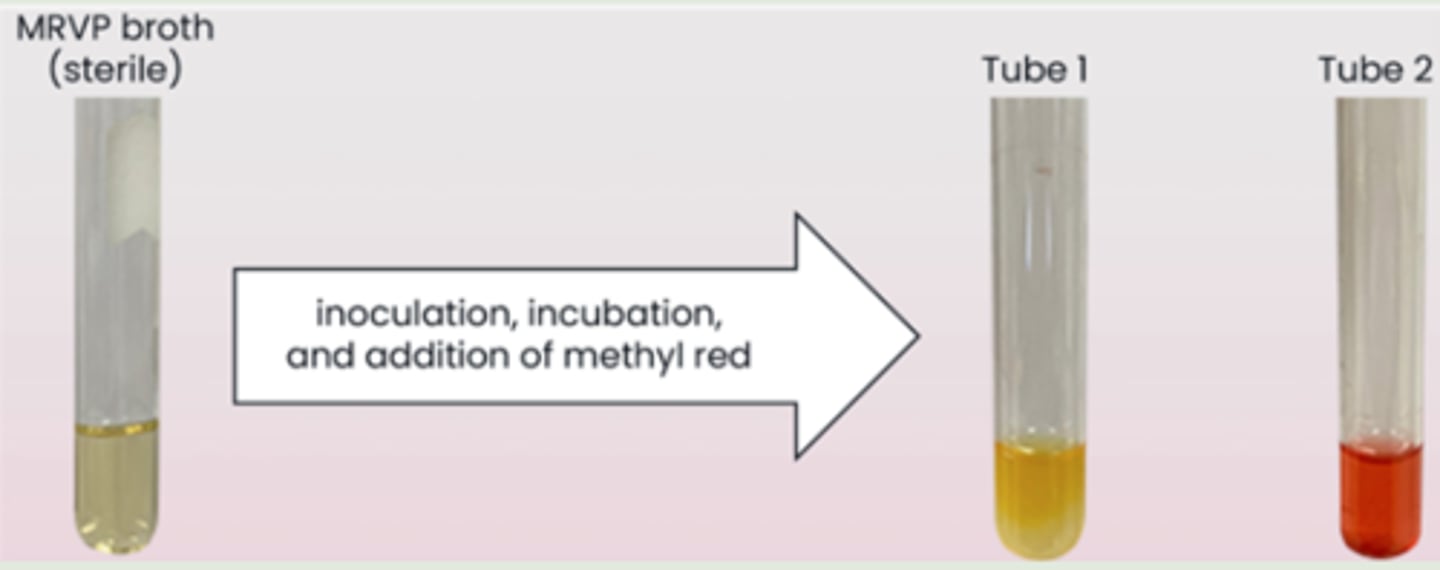
These are the results of a patient sample inoculated in methyl red Vogues-Proskauer broth. After an overnight incubation, methyl red was added to the tubes. What can you conclude from the patient's results
the bacteria ferment glucose to produce a mix of strong acids

These are the results of three bacterial specimens inoculated on mannitol salt agar (MSA). Which plate(s) has/have bacteria that are halotolerant?
plate A and plate B
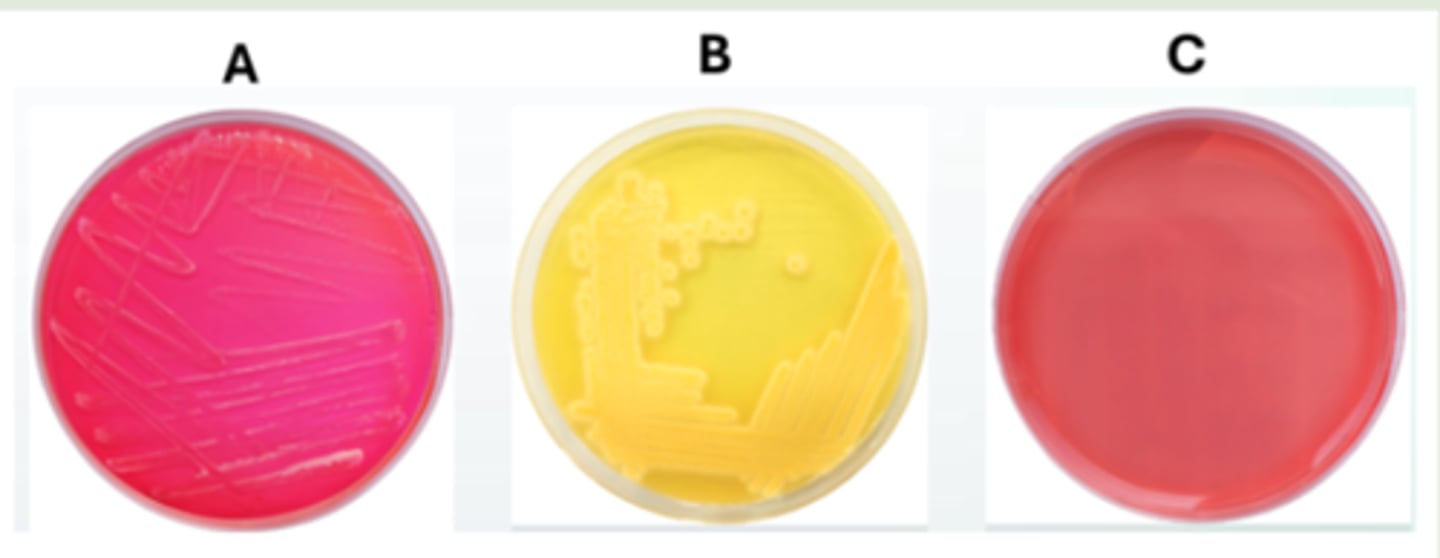
These are the catalase test results of your patient's sample. Can you trust these test results? If so, what is your patient's test result?
the results can be trusted; the patient's sample is negative for catalase

Phenylethyl alcohol (PEA) agar inhibits growth of Gram-negative bacteria, but allows growth of Gram-positive bacteria. If you streaked a mixed culture containing Klebsiella aerogenes and Staphylococcus aureus on PEA agar, which of the bacterial species would grow?
staphylococcus aureus only
It is unclear why hypersensitivities develop, but genetics and environmental factors may play a role. Another proposed factor suggests that individuals living in developed countries may have weaker immune systems due to accessibility of clean food, and water, antibiotics, and minimized exposure to diseases. This is known as the __________ hypothesis.
hygiene
Which biovar of Chlamydia trachomatis causes primary stage, painless ulcers?
lymphogranuloma venereum
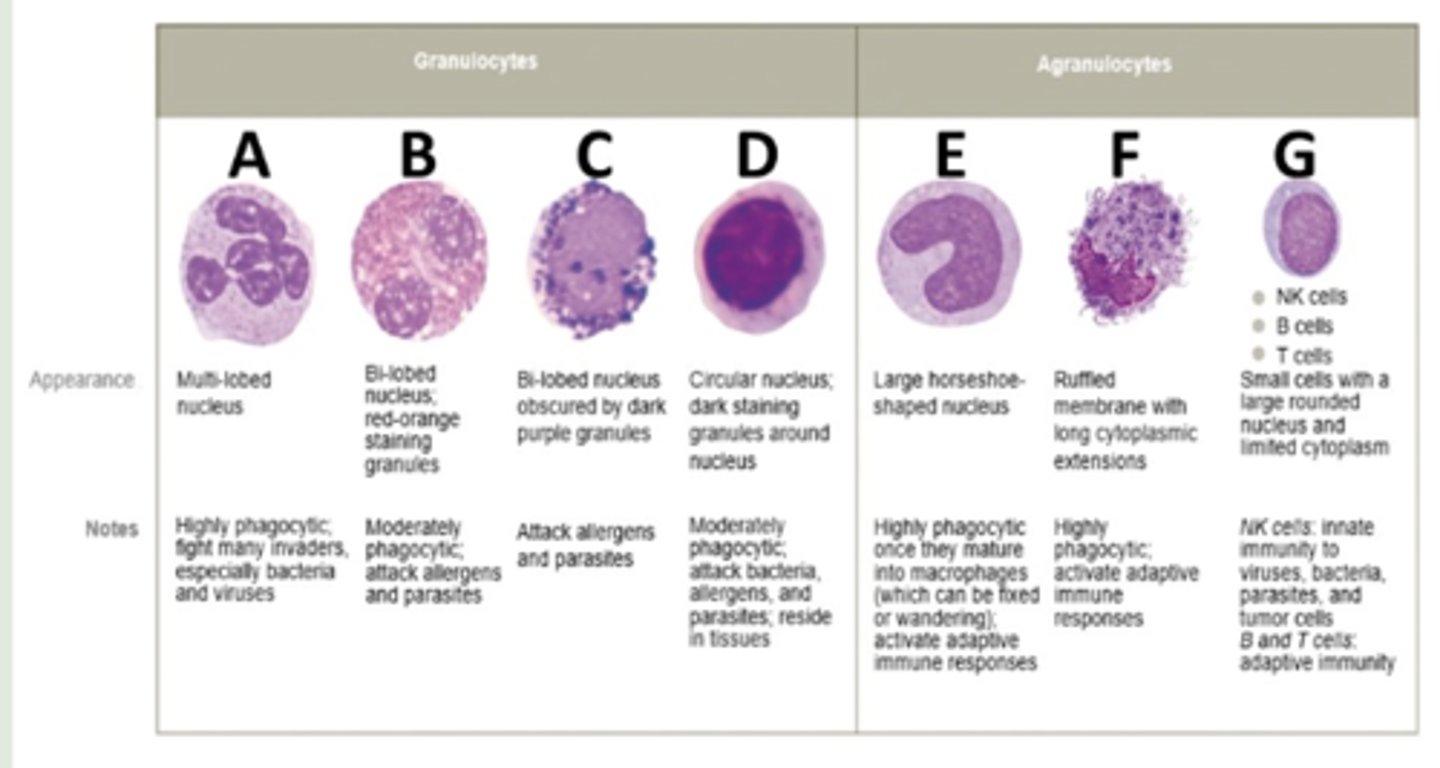
Identify the granulocyte labeled D.
mast cell
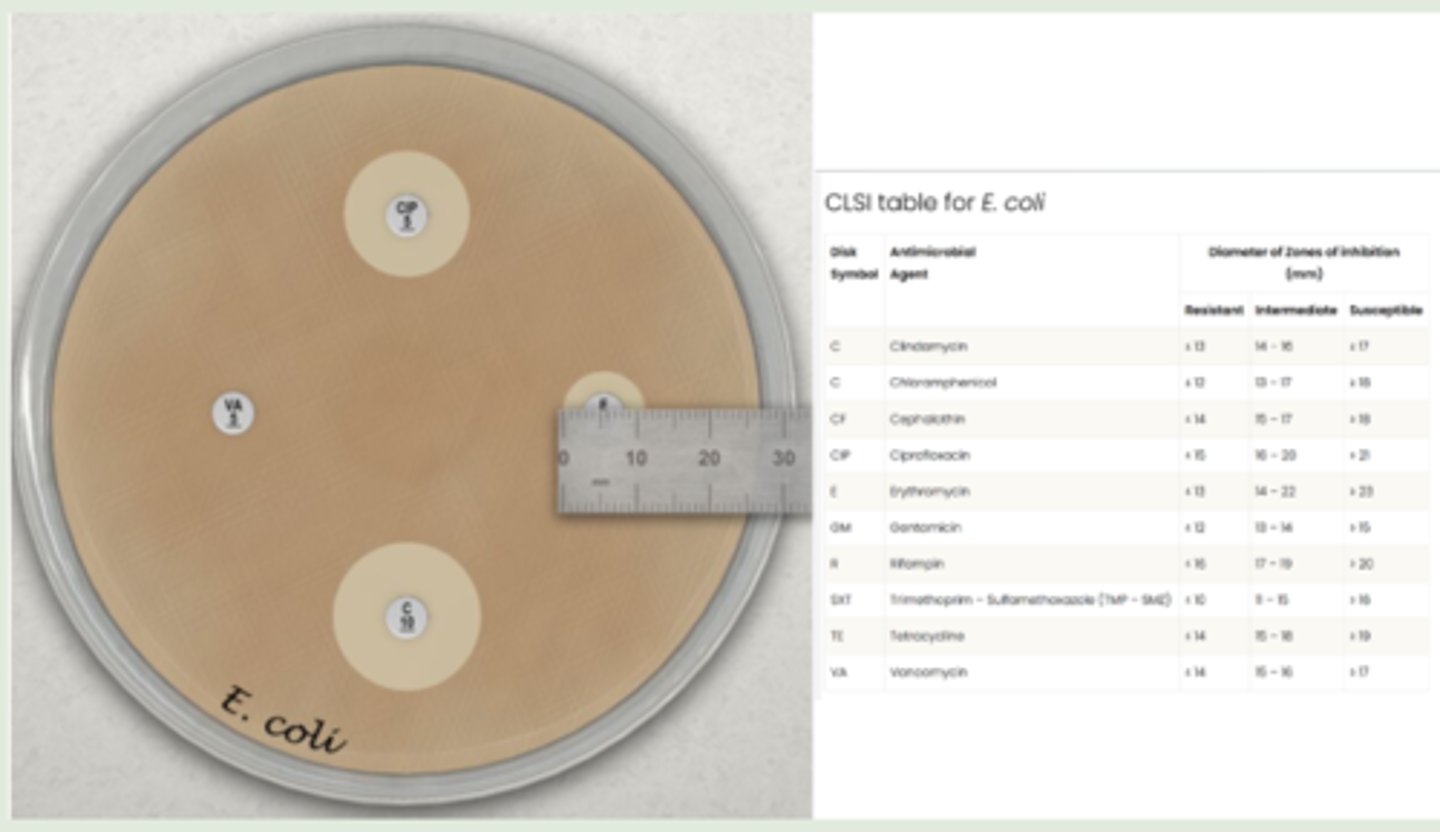
These are the results of an Escherichia coli antimicrobial susceptibility test. Using the CLSI table, analyze the effect of erythromycin (E) on E. coli.
resistant
Enterobius vermicularis causes ___________ infections while Necator americanus causes __________ infections.
pinworm/hookworm
The etiological agent of genital herpes is _______________.
HSV-2
Prions are misfolded proteins that cause transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Which of the following diseases isn't caused by prions?
rabies