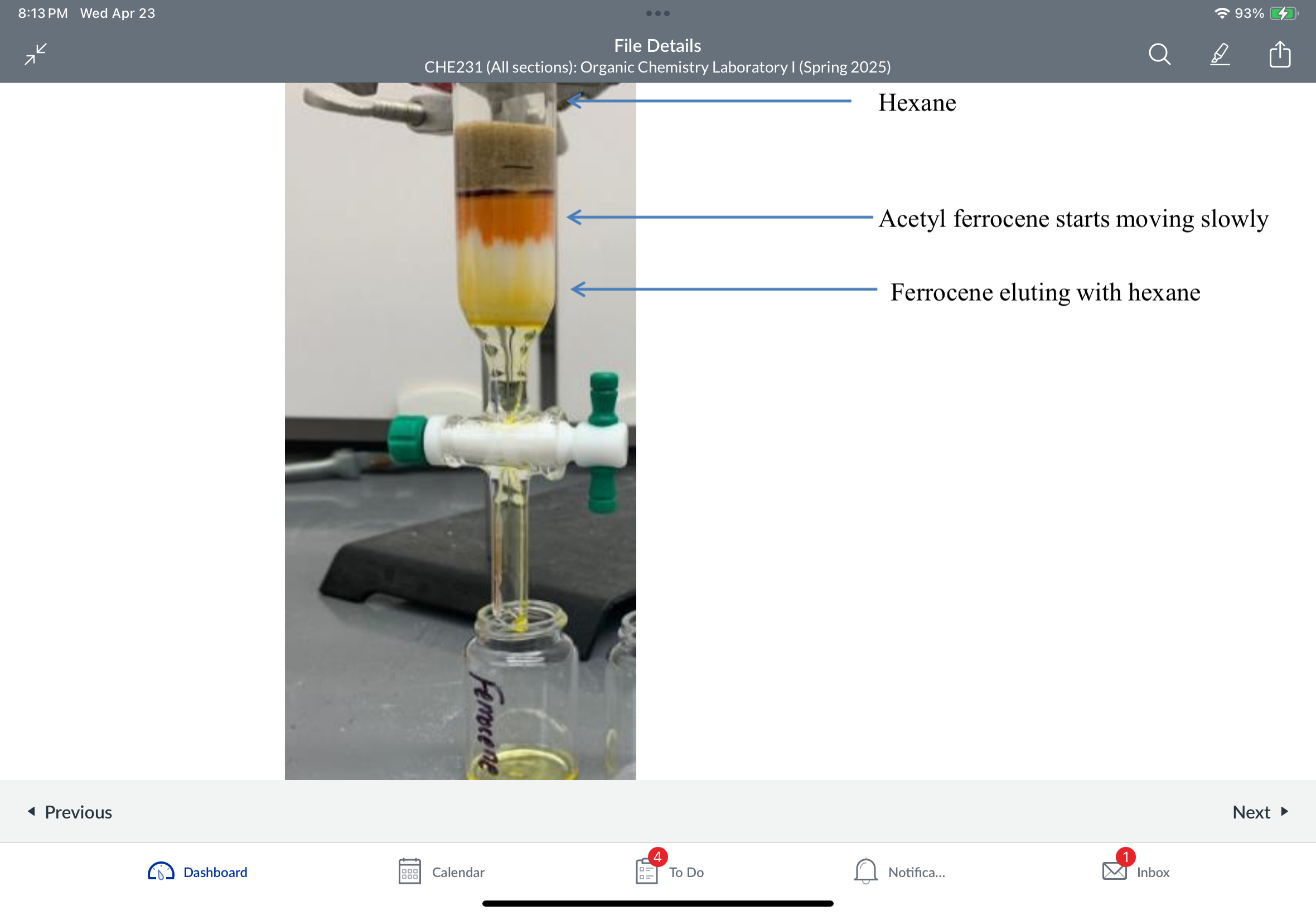
Column Chromatography
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What compound can undergo an aromatic organometallic compound which can undergo electrophilic substitution (Friedel-Crafts acylation) reaction like benzene?
Ferrocene can undergo electrophilic substitution reaction like benzene
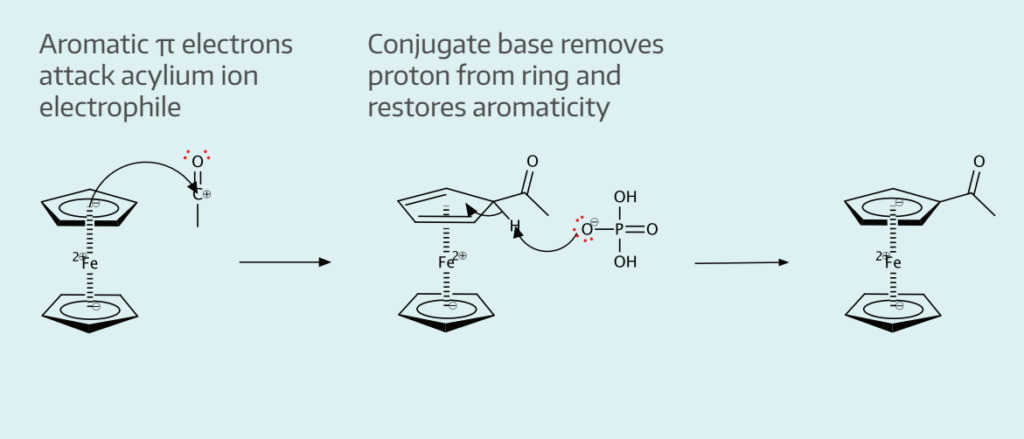
What compound is obtained by the friedal-crafts acylation of ferrocene?
Acetylferrocene is obtained by friedel-crafts acylation of ferrocene
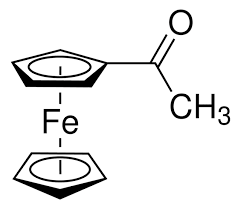
Ferrocene is a yellow colored __________ with the formula Fe(C5H5)2
Organometallic compound: Chemical compounds containing at least one bond between a metal atom and a carbon atom from an organic molecule
What color is acetylferrocene?
Acetylferrocene is orange
Is aluminum chloride a lewis acid or lewis base catalyst?
Acetyl Chloride is a lewis acid
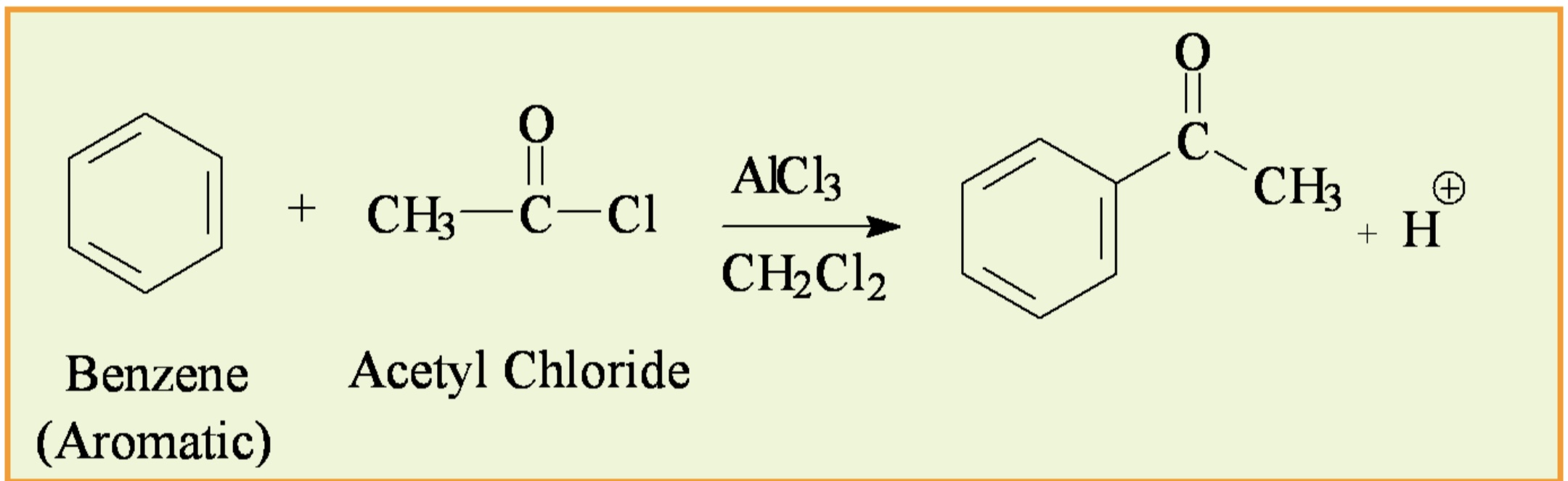
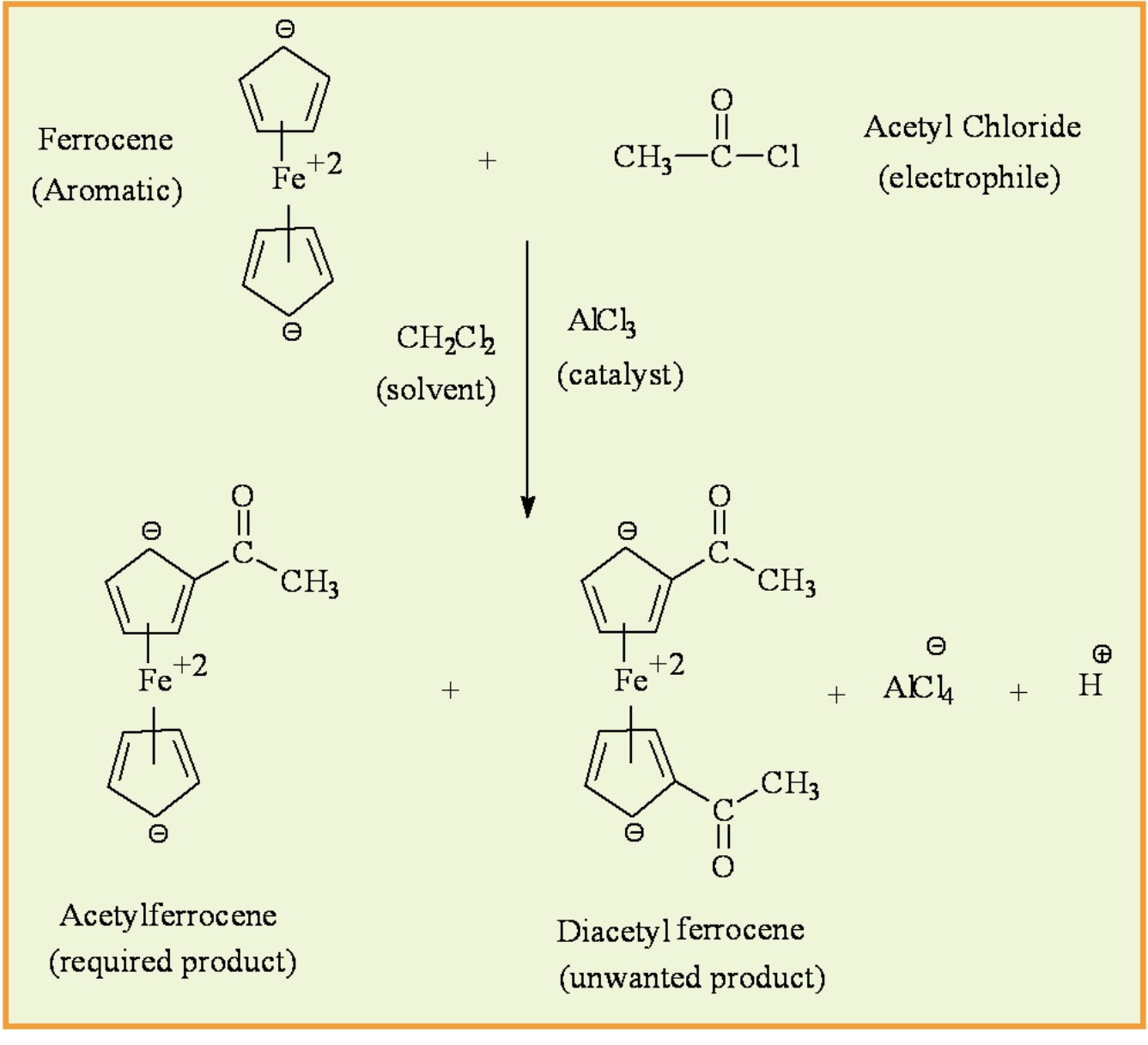
In this reaction, what is the aromatic compound, electrophile, lewis acid catalyst, and solvent?
Aromatic compound: Ferrocene
Electrophile: Acetyl chloride (CH3COCl)
Lewis acid catalyst: Aluminum chloride (AlCl3)
Solvent: Methylene Chloride (CH2Cl2)
What is column chromatography?
This is a LIQUID-SOLID chromatography method used to seperate and purify individual chemical compounds from mixtures of compounds
How does seperation occur in column chromatography?
Seperation occurs by distributing components of a mixture between two phases: the mobile phase (liquid organic solvents of different polarities) and stationary phase (solid: silica or alumina)
What is the stationary phase for the column chromatography v.s. TLC?
Column Chromatography: solid-alumina (polar)
TLC: solid-silica gel
What products are in the mobile phase in TLC?
Liquid organic solvent such as chloroform, hexane
What products are the mobile phase in column chromatography?
Hexane to elute non-polar ferrocene component
Methylene chloride to elute polar acetylferrocene component
More polar solvents move further up on the TLC. Name compound from most polar to least
Most Polar: Methanol, Acetone, Chlororform, ether, toluene, hexane :Least Polar
Which compound elutes first then next? Why?
Ferrocene being LESS POLAR elutes first- travels down faster along the column when non-polar hexane used as a mobile phase
Acetyl ferrocene being MORE POLAR elutes 2nd: travels down next when a more polar solvent methylene chloride (dichloromethane) is used as a mobile phase
How do you determine if the seperation is successful?
Perform a TLC and seperation is based on the parting of the mixture between stationary and a mobile phase
How do you achieve seperation in a column chromatography?
Change the pilarity of the mobile phase