Deuterostomes PART ONE
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
when did prokaryotes first appear?
in the archean eon, around 3500 mya
when did eukaryotes first appear?
in the proterozoic eon, around 2100,1004 mya
when did multicellular soft-bodied animals first appear?
in the proterzoic eon, around 600 mya
what was the archean eon like?
very litttle oxygen
what was the early proterozoic period like?
start of the ‘oxygen crisis’ - cyanobacteria started producing oxygen and the atmosphere starts oxidising
what was the mid-proterozic eon like?
the ‘boring billion’
what was the late-proterozoic period like?
introduction of the first animals, oxygen fills the atmosphere as the ocean had absorbed as much as it could
what was the phaneozic eon like?
introduction of land plants as well as larger, more diverse and disparate animals
what was introduced in the jurassic period?
modern sharks, rays, first birds, lizards
what was introduced in the triassic period?
reptile radiation, first mammals and teleost fish
what was introduced in the permian period
amniote radiation, mammal-like reptiles
what was introduced in the carboniferous period?
fish diversification, first bony fish, first amniotes
what was introduced in the devonian period?
‘age of the fishes’, multiple radiations, first tetrapods
what was introduced in the silurian period?
jawless fish radiation, first sharks
what was introduced in the ordovician period?
jawless fish, land plans
what was introduced in the cambrian period?
complex invertebrates
what percentage of described species are invertebrates?
96%
what does protostome mean?
‘first mouth’
what does deuterostome mean?
‘second mouth’
key development of protostomes?
spiral and determinate cleavage, blastopore becomes the mouth, schizocoelous coelom formation (mesoderm split)
key development of deuterostomes
radial and indeterminate cleavage, blastopore becomes the anus, enterocoelous coelom formation (gut outpocketing)
cleavge pattern types
holoblastic, meroblastic, equal, unequal
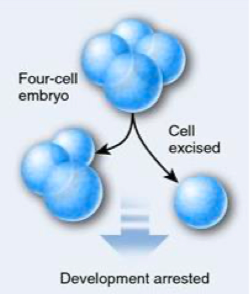
type of cleavage?
determinate cleavage, where developmental fate is established early
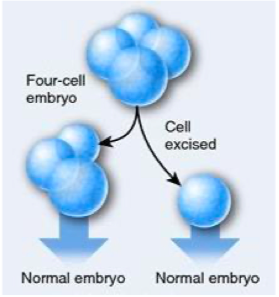
type of cleavage?
indeterminate cleavagewhere early embryonic cells retain capacity to develop into complete embryo (if isolated)
what does the cleavage produce?
blastula
types of blastula?
coeloblastula (hollow), stereoblastula (solid), discoblastula (cell cap above yolk), periblastula (cell layer enclose yolk)
three germ layers of triploblastic animals?
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
what generates the three germ layers of triploblastic animals?
gastrulation
what is gastrulation?
early embryonic process where a blastula reorganises into a three-layered structure (gastrula) with distinct tissue layers
when did deuterostomes first appear?
beyween the ediacaran to cryogenian period, around 660-570 mya
major lineages of deuterostomes?
chordata and xenambulacraria
whats found in the chordata lineage?
tunicates, cephalochordates, vertebrates
whats found in the xenambulacraria lineage?
hemichordates (‘half-chordates’), echinoderms, (xenacoelomorphs?)
what are xenacoelomorpha a phlyum of?
small marine worms
two major lineages of phylum hemichordates?
enteropneusts (around 110sps), pterobranchs (around 25sps)
what are enteropneusts?
solitary, elongate, vermiform animals whose body divides into 3 regions
body regions of enteropneusts?
proboscis, collar, trunk
enterophneusts core physiological processes
open circ, dorsal nerve, gill slits, complete digest sys
enteropneusts feeding technique?
burrowers, filter or suspension feeders
what are pterobranchs?
colonial, tube dwellers with a share tripartite body plan, gill slits and stomochord (shared: enteropneusts)
pterobranchs feeding tehcnique?
feeding arms with tentacles
pterobranch reproduction stratergies?
distinct male/female, but can also reproduce asexually (budding)
hemichordates ecological roles?
nutrient cycling, bioturbation, habitat structuring
benefits of hemichordates helping with bioturbation?
burrows (of burrowing sps) improve oxygenation, nutrient exchange, microbial activity
benefits of hemichordates helping with habitat structuring?
tubes provide habitat, attachment points, shelter for other species
what are planctosphaera?
occasionally found larvae with unknown adult form that could potentially be a distinct hemichordate lineage
what are the major lineages of echinoderms (over 7000 sps)?
asteroidea, ophiuroidea, holothuroidea, echinoidea, crinoidea
what organisms are found in asteroidea?
sea stars, star fish
what organisms are found in ophiuroidea?
brittle stars
what organisms are found in holothuroidea?
sea cucumbers
what organisms are found in echinoidea?
sea urchins, sand dollars
what organisms are found in crinoidea?
sea lillies, feather stars
symmetry found in echinoderms?
radial sym in adults and bilat sym in larvae, gen pentamerous (split into five)
echinoderm skeleton strcuture
calcareous endoskeleton with ossicles (plates) and tubercles (spines)
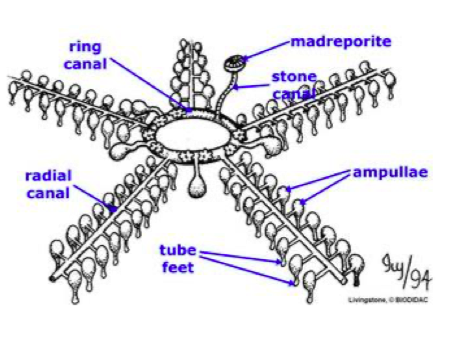
what system is this?
the echinoderms water vascular system?
what is the function of the madreporite?
filters water into the water vascular system
what is the function of the stone canal?
connect the madreporite with the water vascular system
what is the function of the ring canal?
circular water tube that surround the esophagus
what is the function of the radial canal?
ciliated canal in the arm
what is the function of the ampullae?
prevents water from flowing back to the radial canal
what is the function of the tube feet
used for movement