Cell Structure and Function
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
light microscopes
used to study stained or living cells
electron microscopes
used to study detailed structures of a cell that cannot be easily seen or observed by light microscopy
prokaryotic cell
smaller than eukaryotic & simpler
ex: bacteria & archea
inside of the cell is filled with cytoplasm
genetic material in a prokaryote = one continuous, circular DNA molecule that is found free in the cell in the nucleoid
cell wall composed of peptidoglycans that surrounds plasma membrane (lipid layer)
small ribosomes
some bacteria may also have flagella (used for mobility)
no membrane-bound organelles
eukaryotic cell
ex: fungi, protists, plants, and animals
have many organelles
plasma membrane
outer envelope of the cell
made up of mostly phospholipids and proteins.
regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell (semipermeable)
many proteins are associated with the cell membrane
some loosely associated with the lipid bilayer (peripheral proteins) - located on the inner/outer surface of the membrane
others firmly bound to plasma membrane (integral proteins) - amphiatic
some extend all the way through the membrane (transmembrane proteins)
fluid-mosaic model: arrangement of phospholipids & proteins
adhesion proteins
receptor proteins
transport proteins
channel proteins
cell surface markers
carbohydrate side chains found only on the outer surface
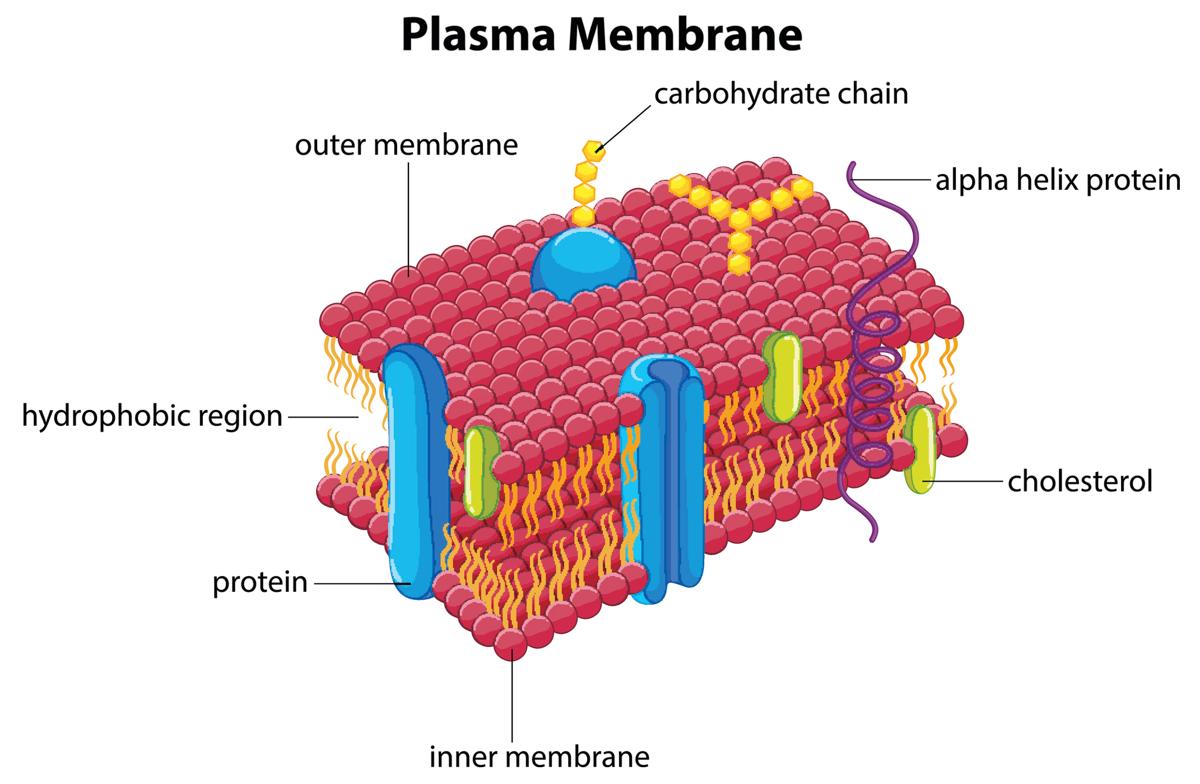
adhesion proteins
form junctions between adjacent cells
receptor proteins
serve as docking sites for arrivals at the cell (ex: hormones)
transport proteins
form pumps that use ATP for active transport of solutes across membrane
channel proteins
form channels that selectively allow passage of certain ions/molecules
cell surface markers
exposed on extracellular surface and play a role in cell recognition and adhesion (ex: glycoproteins)
carbohydrate side chains
found only on the outer surface of the plasma membrane
nucleus
largest organelle in the cell
directs what goes on in the cell
responsible for the cell’s ability to reproduce (DNA - organized into chromosomes)
nucleolus: where rRNA is made & ribosomes are assembled
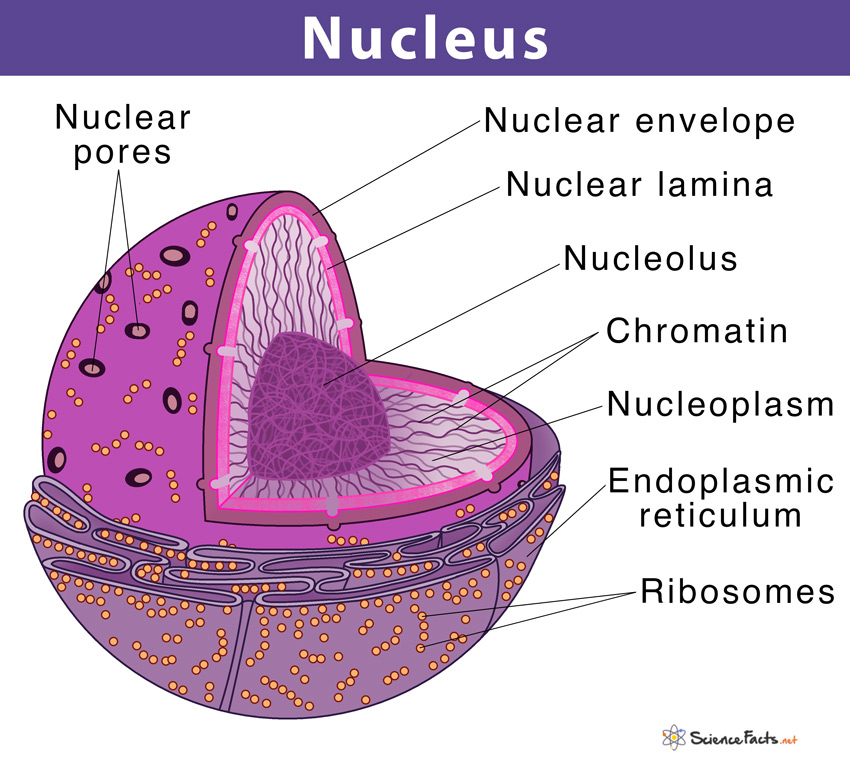
ribosomes
sites of protein synthesis
manufacture all the proteins required by the cell or secreted by the cell
round structures composed of two subunits, the large subunit and the small subunit
composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins
can be either free floating in the cell or attached to ER
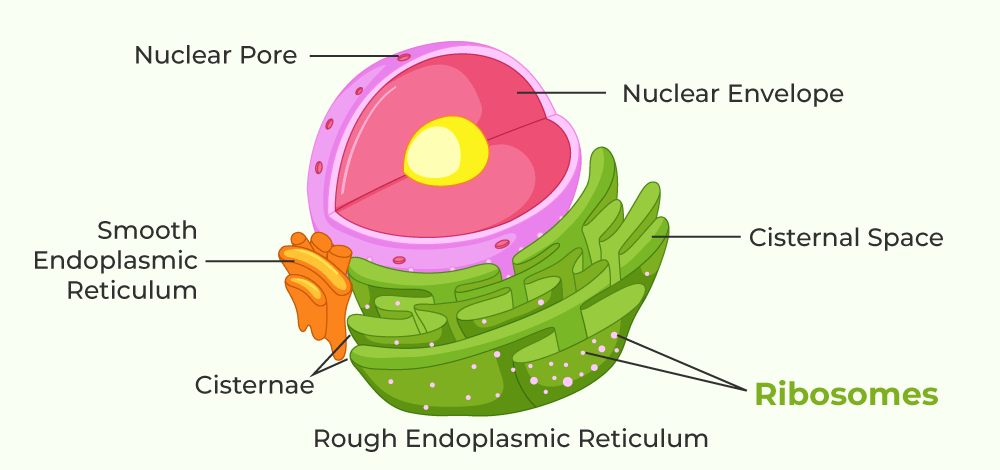
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
continuous channel that extends into many regions of the cytoplasm
provides mechanical support and transportation
rough ER compartmentalizes the cell
smooth ER = lacks ribosomes
makes lipids, hormones, and steroids and breaks down toxic chemicals
Golgi Complex
after the ribosomes on rough ER have synthesized proteins, Golgi complex modifies, processes, and sorts the products
packaging and distribution centers for materials destined to be sent out of the cell
package the final products in little sacs called vesicles, which carry products to the plasma membrane
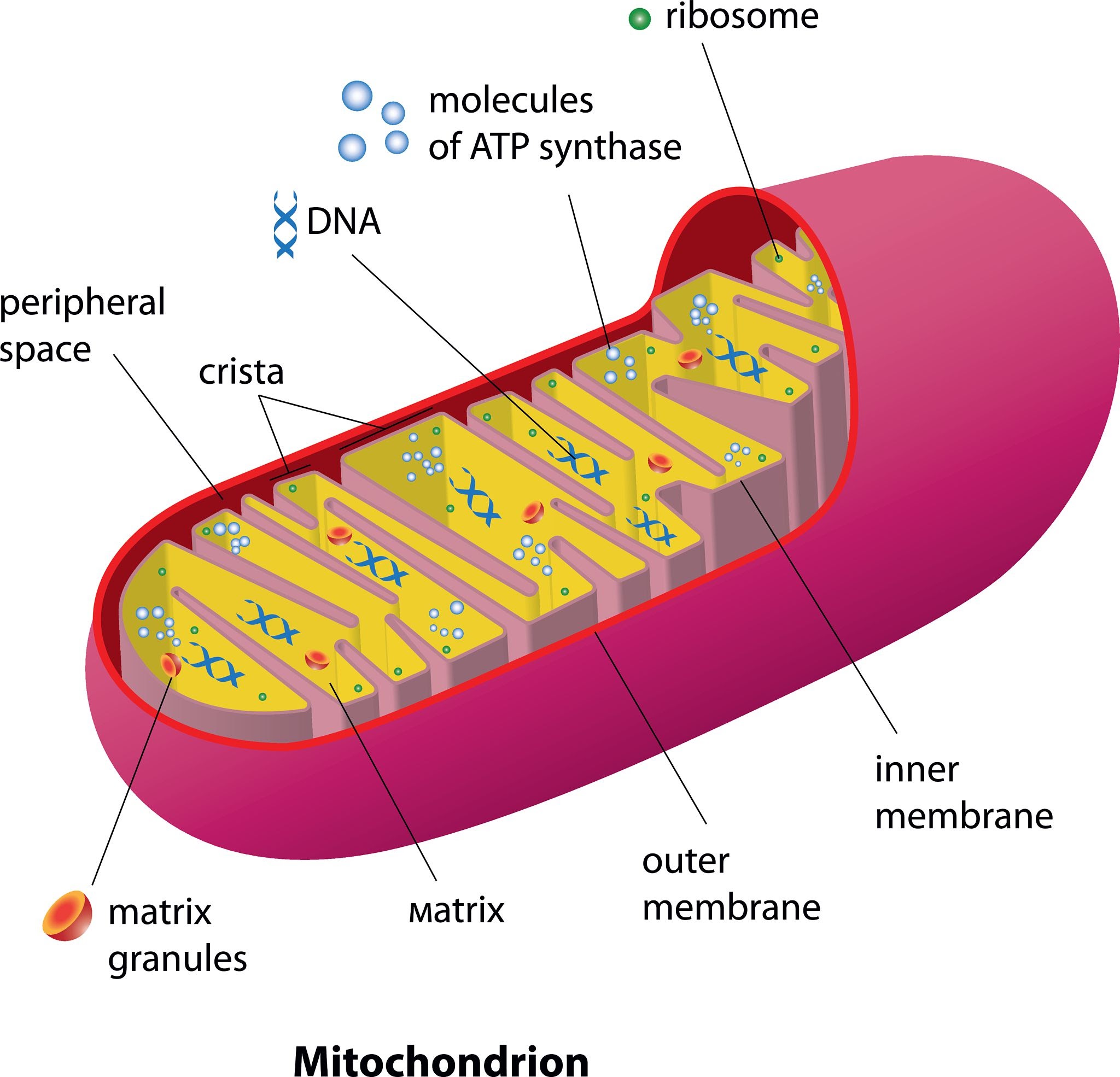
Mitochondria
power stations responsible for converting energy from organic molecules into useful energy for the cell
most common energy molecule in the cell is ATP
inner portion:
forms folds known as cristae
separates from innermost area (the matrix) from the inter-membrane space
outer portion:
separates the inter-membrane space from the cytoplasm
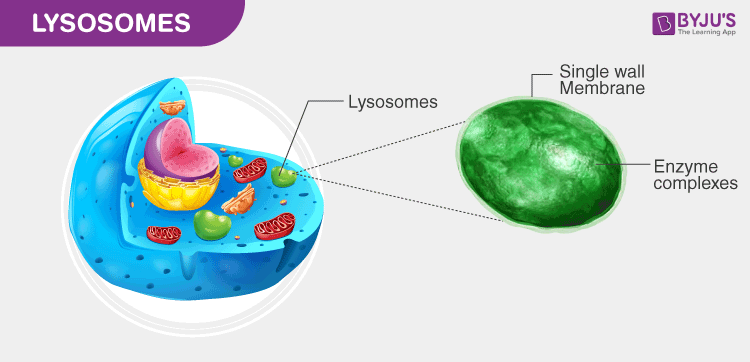
Lysosomes
sacs that carry digestive enzymes
used to break down old, worn-out organelles, debris, or large ingested particles
essential during apoptosis (programmed cell death)
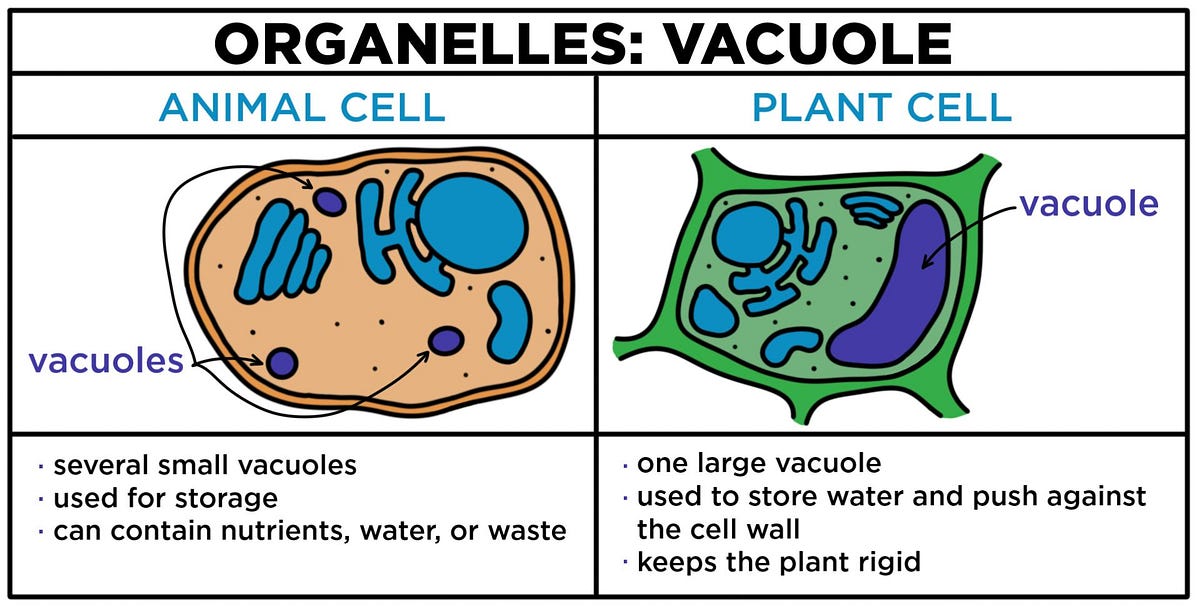
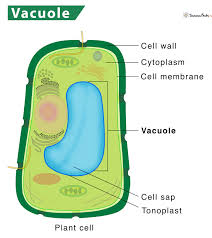
Vacuoles
fluid-filled sacs that store water, food, wastes, salts, or pigments
multiple functions in plant cells (larger as well)
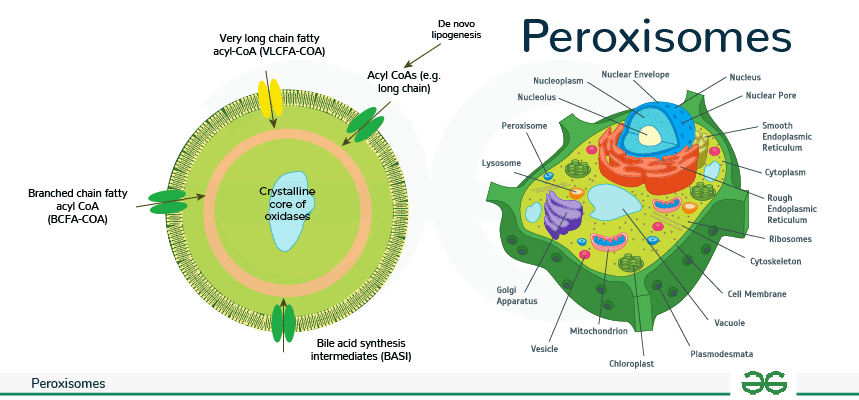
Peroxisomes
detoxify various substances, producing hydrogen peroxide as a byproduct
enzymes that break down hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water
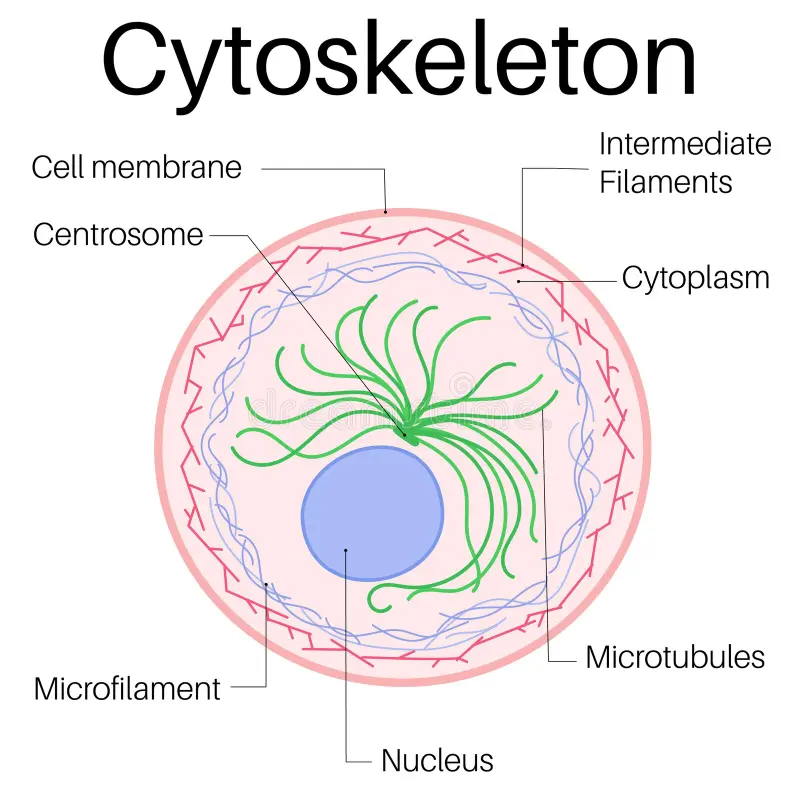
Cytoskeleton
determines the shape of this network of protein fibers
most important = microtubules & microfilaments
microtubules: participate in cellular division & movement
microfilaments: movement (actin monomers that can grow & shrink)
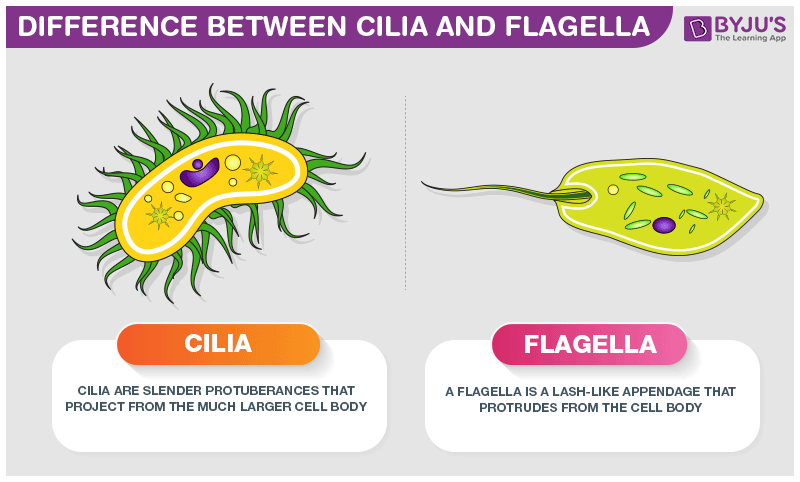
Cilia & Flagella
locomotive properties in single-celled organisms
beating motion of cilia and flagella structure allows it to move
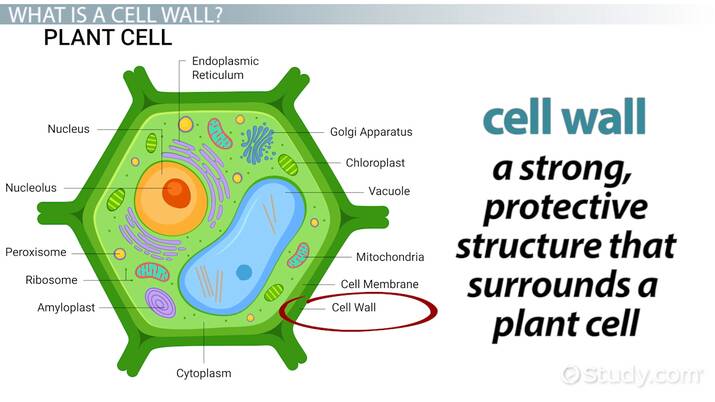
Cell Wall (plant cells)
made up of cellulose
rigid layer for support of cells outside of plasma membrane
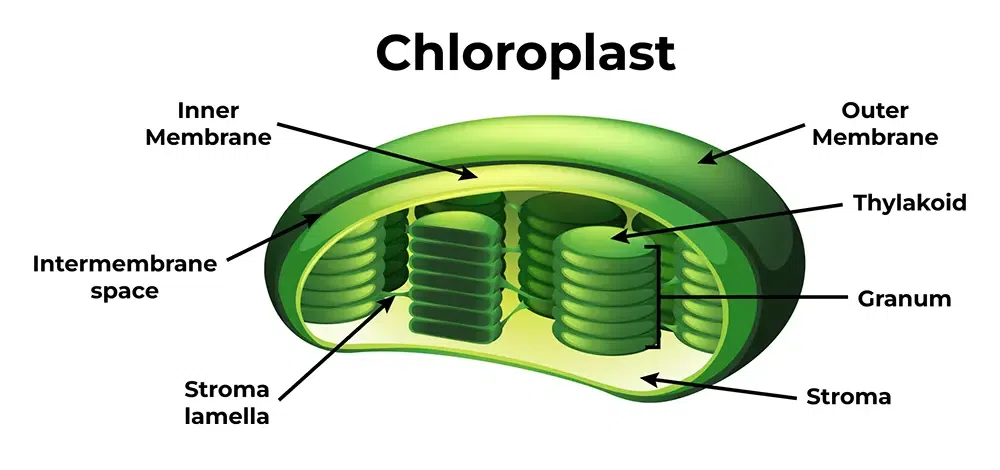
Chloroplasts
contain chlorophyll
gives plants green color
Central Vacuole (plant cells)
large vacuole
structural support
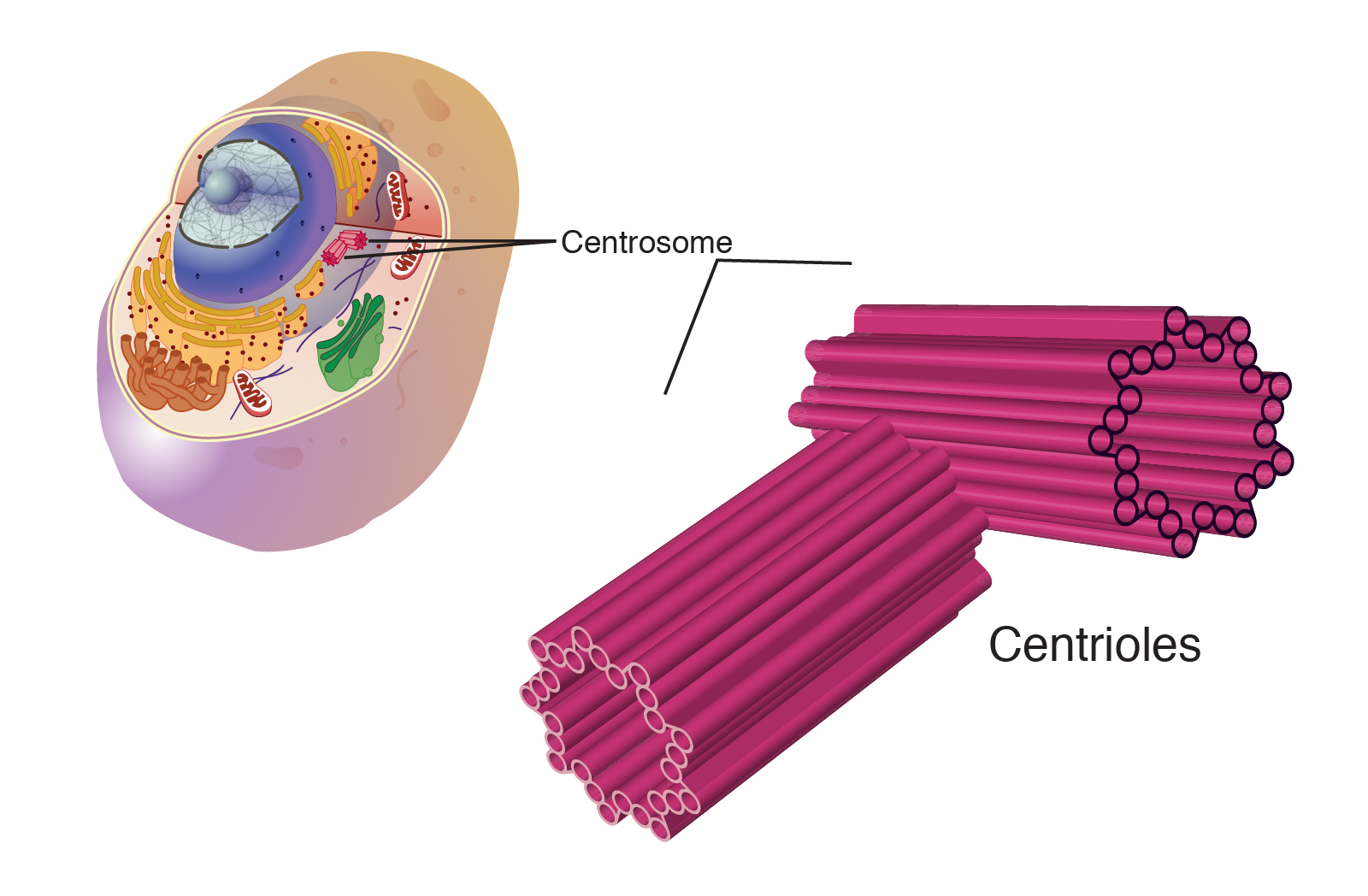
Centrioles (animal cells)
located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope
organize microtubules that serve as the cell's skeletal system
help determine the locations of the nucleus and other organelles within the cell
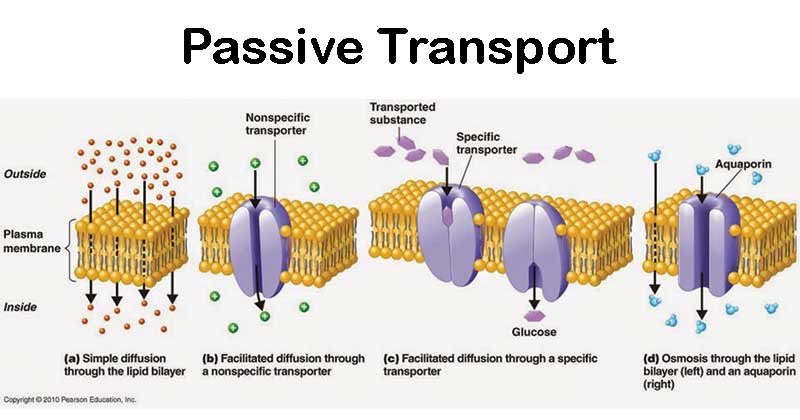
Ability of molecules to move across the cell membrane depends on
the semipermeability of the plasma membrane
the size and charge of particles that want to get through
Aquaporins
water-specific channels
Passive Transport (Simple & Facilitated Diffusion)
diffusion:
high concentration to low concentration - moves along concentration gradient
simple diffusion:
hydrophobic molecules
just drifts through because it’s small & non-polar
facilitated diffusion:
hydrophilic molecules usually
require the help of a channel-type protein
diffusion always = passive transport (no outside energy)
Osmosis
still passive transport BUT the membrane is not permeable for solutes
PLANTS: cell wall protects against osmotic changes if it loses water — can expand & squeeze tightly against the cell wall if it takes in water
cell membrane can shrink away from the wall [plasmolysis]
![<ul><li><p>still passive transport BUT the membrane is not permeable for solutes</p></li><li><p>PLANTS: cell wall protects against osmotic changes if it loses water — can expand & squeeze tightly against the cell wall if it takes in water</p><ul><li><p>cell membrane can shrink away from the wall [plasmolysis]</p></li></ul></li></ul>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d1289da6-6169-4afc-98aa-e3991344ef19.png)
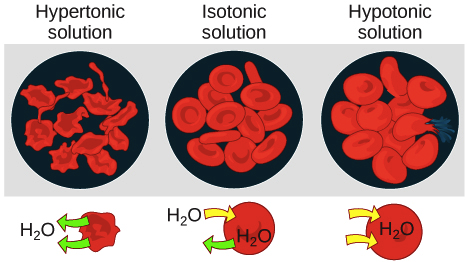
Isotonic solution (osmosis)
solute concentration is the same inside and outside
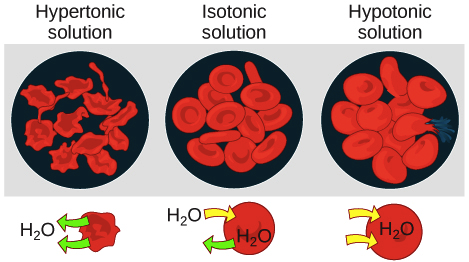
Hypertonic solution (osmosis)
more total dissolved solutes than the cell
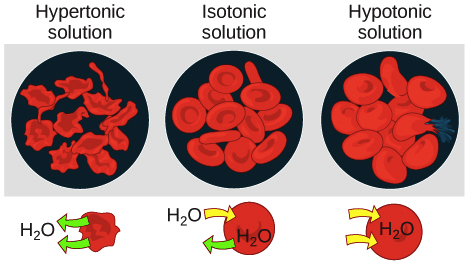
Hypotonic solution (osmosis)
less total dissolved solutes than the cell
Water potential (Ψ)
measure of potential energy in water
describes the eagerness of water to flow from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential
affected by: pressure potential (Ψp) and solute potential (Ψs)
adding a solute lowers the water potential of a solution — water to be less likely to leave this solution & more likely to flow into it
more solute molecules present, the more negative the solute potential is
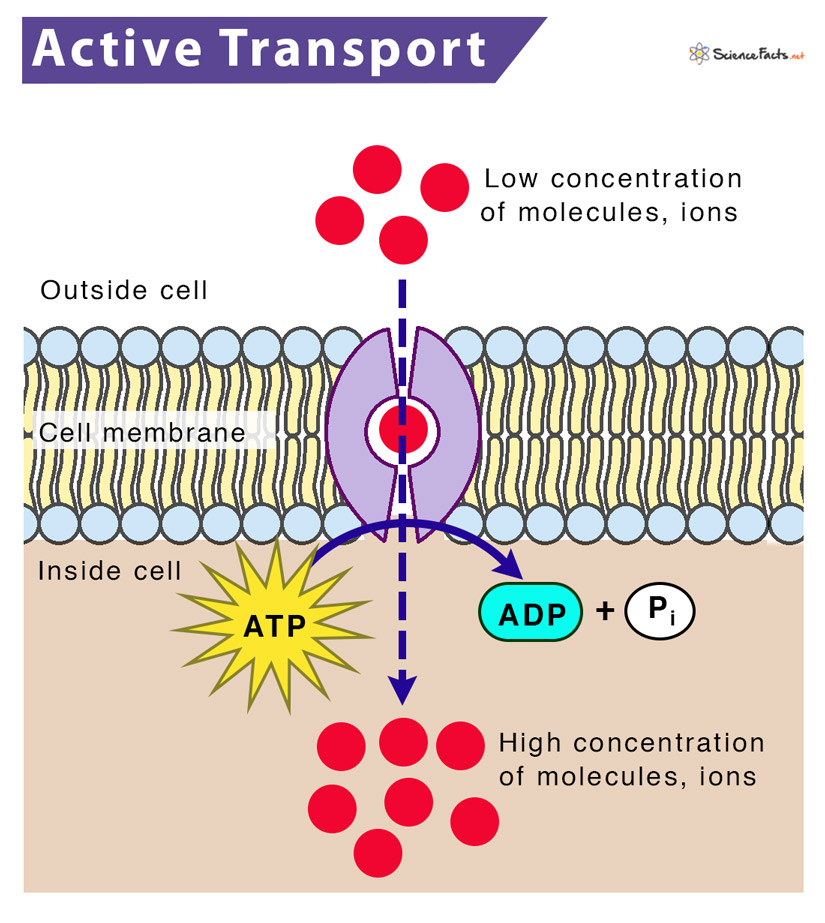
Active Transport
movement against the natural flow
some proteins in the plasma membrane are powered by ATP
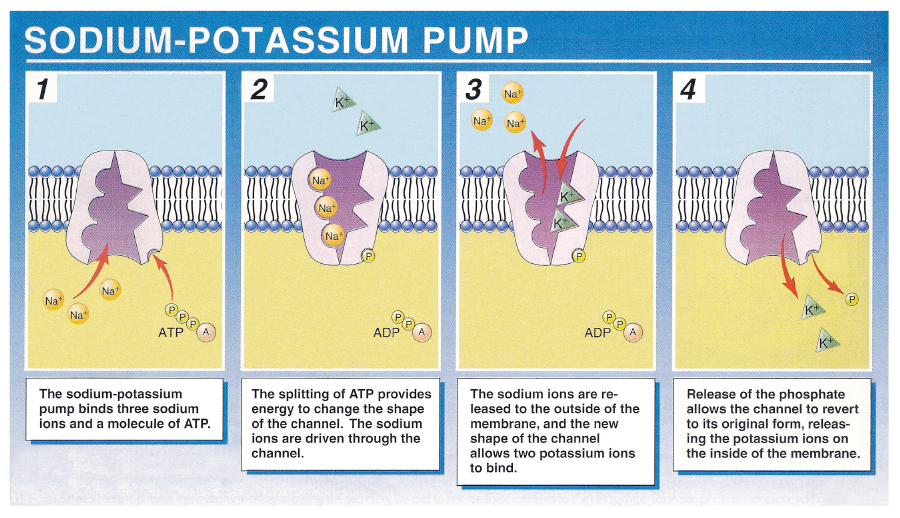
ex: sodium-potassium pump
Sodium-potassium pump
ushers out three sodium ions (Na+) and brings in two potassium ions (K+) across the cell membrane
pump depends on ATP to get ions across that would otherwise remain in regions of higher concentration
Primary Active Transport
occurs when ATP is directly utilized to transport something
Secondary Active Transport
occurs when something is actively transported using the energy captured from the movement of another substance flowing down its concentration gradient
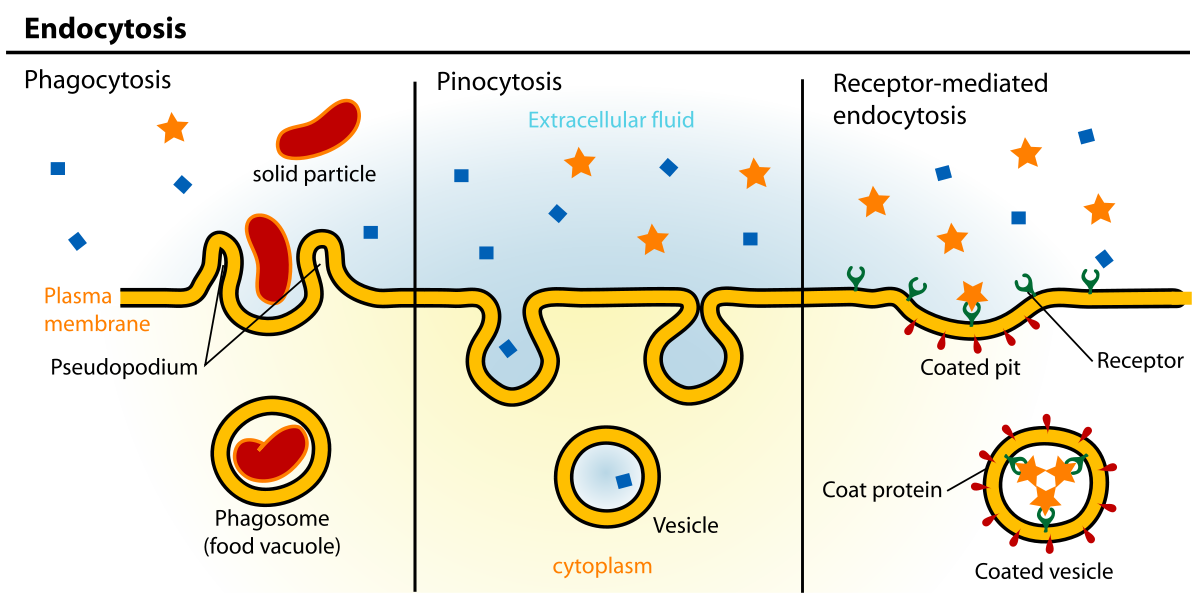
Endocytosis
when the particles that want to enter a cell are just too large, the cell uses a portion of the cell membrane to engulf the substance
forms a pocket, pinches in, and eventually forms either a vacuole or a vesicle
Pinocytosis: the cell ingests liquids
Phagocytosis: the cell takes in solids
Receptor-mediated endocytosis: involves cell surface receptors that work in tandem with endocytic pits that are lined with a protein called clathrin
when a particle, or ligand, binds to one of these receptors, the ligand is brought into the cell by the invagination, or “folding in” of the cell membrane
vesicle then forms around the incoming ligand and carries it into the cell’s interior
Bulk flow
one-way movement of fluids brought about by pressure.
Ex: movement of blood through a blood vessel
Dialysis
diffusion of solutes across a selectively permeable membrane
Exocytosis
cell ejects waste products or specific secretion products
fusion of a vesicle with the plasma membrane, which then expels the contents into the extracellular space
reverse endocytosis