AP Statistics: Key Concepts and Definitions for Exam 1
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Individuals
are the objects described by a set of data. Individuals may be people, but they may also be animals or things.
Variables
is any characteristic of an individual. A variable can take different values for different individuals.
Data
The actual measurements recorded for individuals.
Census
a sample survey that attempts to include the entire population in the 'sample.'
Subjects
(or participants) are the people in the study.
Treatment
any specific experimental condition applied to the subjects.
Control group
Allows for the researcher to control the effects of lurking variable.
Randomized comparative experiment
compared two (or more) treatments.
Lurking (or confounding variable)
has an effect on the relationship among the variables in a study but is NOT one of the explanatory variables studied.
Confounding variables
Two variables are confounding when their effects on a response variable cannot be distinguished from each other.
Placebo
a dummy treatment (no active pharmacological ingredients).
Placebo effect
someone responds favorably to a placebo because of their expectations.
Single blind
participants doesn't know which conditions they are in but researcher does.
Double blind
neither the participants nor the researcher knows which condition.
Population
the entire group of individuals about which we want information
Sample
part of the population from which we actually collect information and is used to draw conclusions about the whole
Sample Survey
chooses a sample from a specific population and uses the sample to get information about the entire population
Convenience samples
sampling methods that are common but do not produce trustworthy data - these methods are usually biased
Voluntary response samples
sampling methods that are common but do not produce trustworthy data - these methods are usually biased
Parameter
is a number that describes the population; a parameter is a fixed number, but in practice, we don't know its value
Statistic
a number that describes the sample; the value of a statistic is known when we have taken a sample, but it can change from sample to sample
P-hat
the sample proportion (statistic) of those who have the trait/opinion of interest
P
the population proportion (parameter) who have the trait/opinion of interest
Variability
how spread out the values of the statistic are when we take many samples
Bias
consistent, repeated deviation of the statistic from the parameter in the same direction when we take many samples
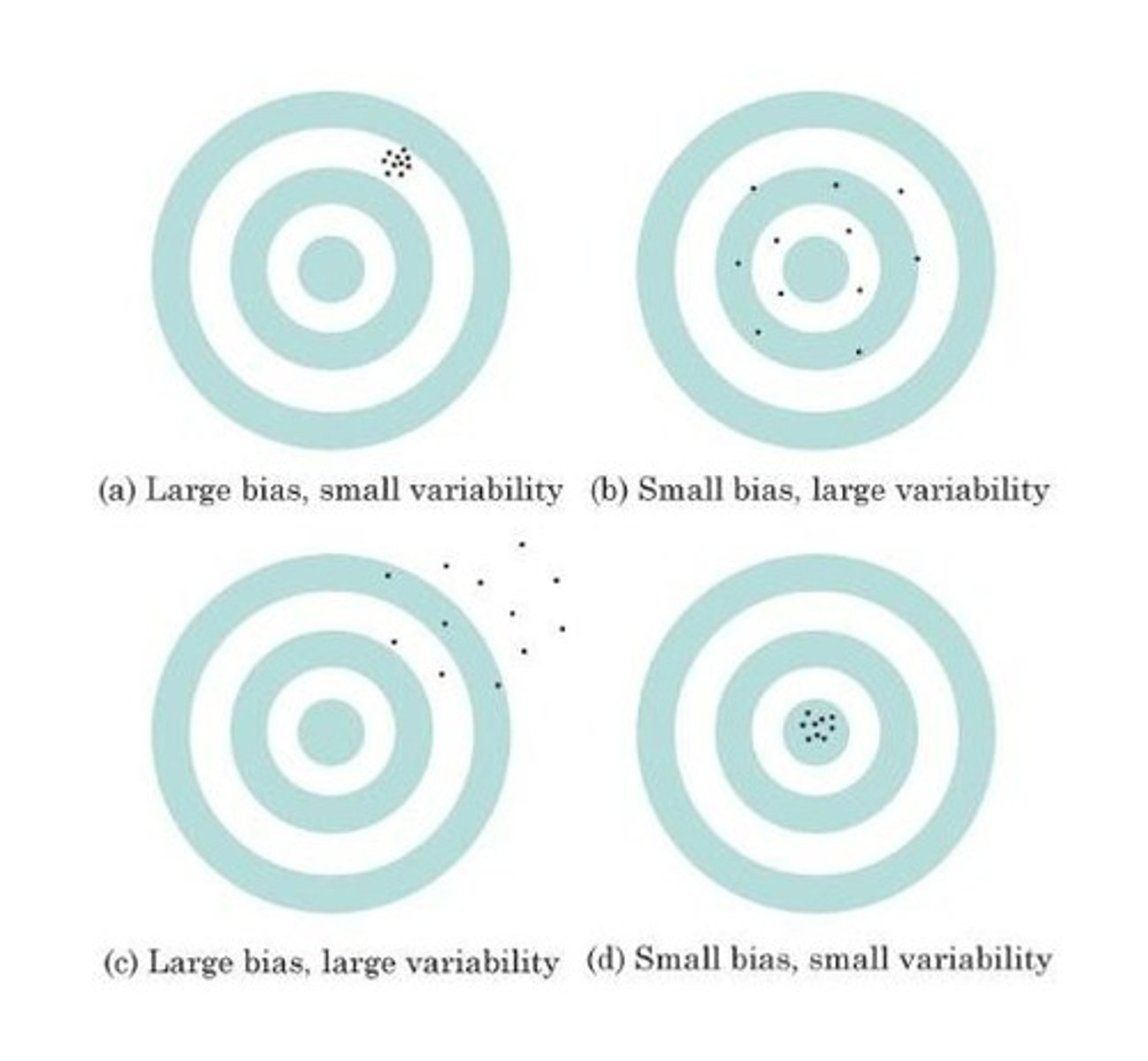
Sampling Variability
statistics will not be the same from sample to sample (because all samples are going to be a little different from each other)
Random error
repeated measurements on the same individuals give different results (despite true value being the same)
Random Sampling
To reduce bias, use random sampling.
Sample Size
To reduce variability, use a larger sample size.
Margin of Error (MOE)
a value that quantifies the uncertainty in our estimate.
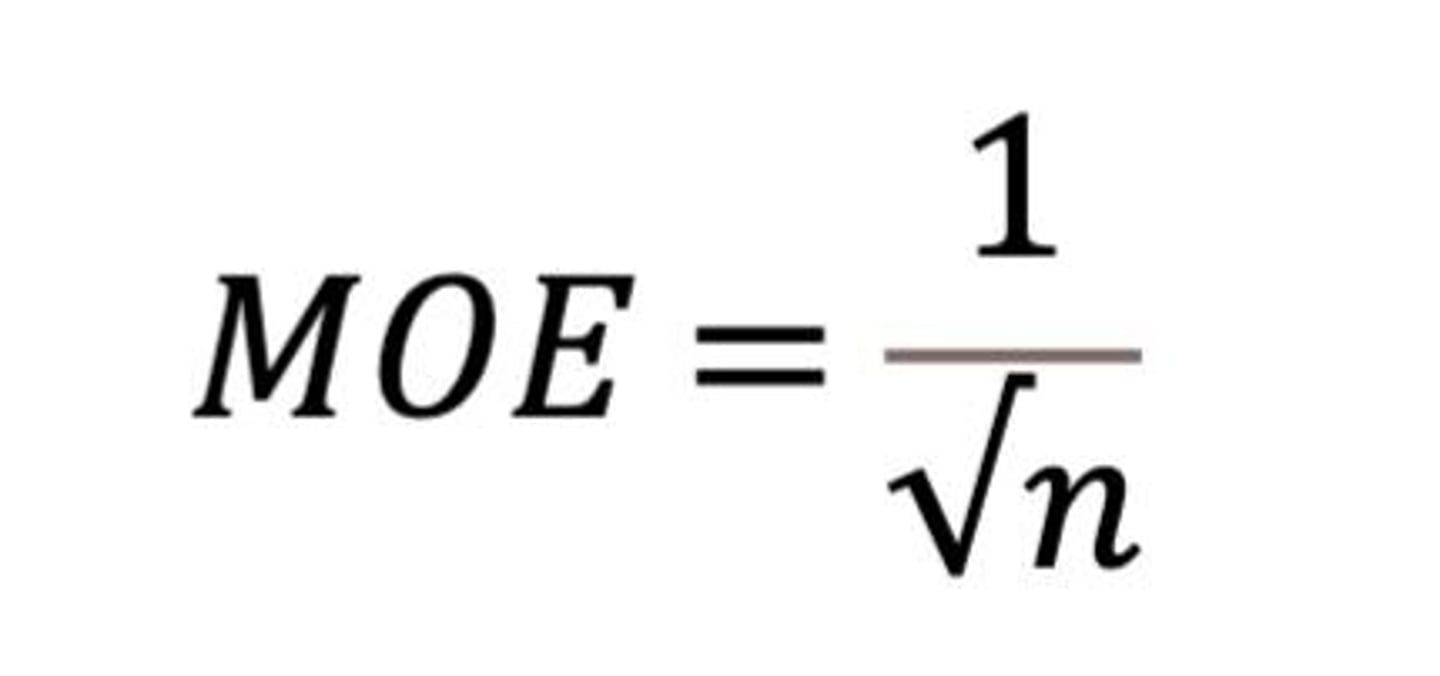
confidence statement
interprets a confidence interval and has two parts: a margin of error & a level of confidence.
Level of Confidence
states what percentage of all possible sample results in a confidence interval which contains the true parameter.
Confidence Interval Formula
Confidence interval formula.
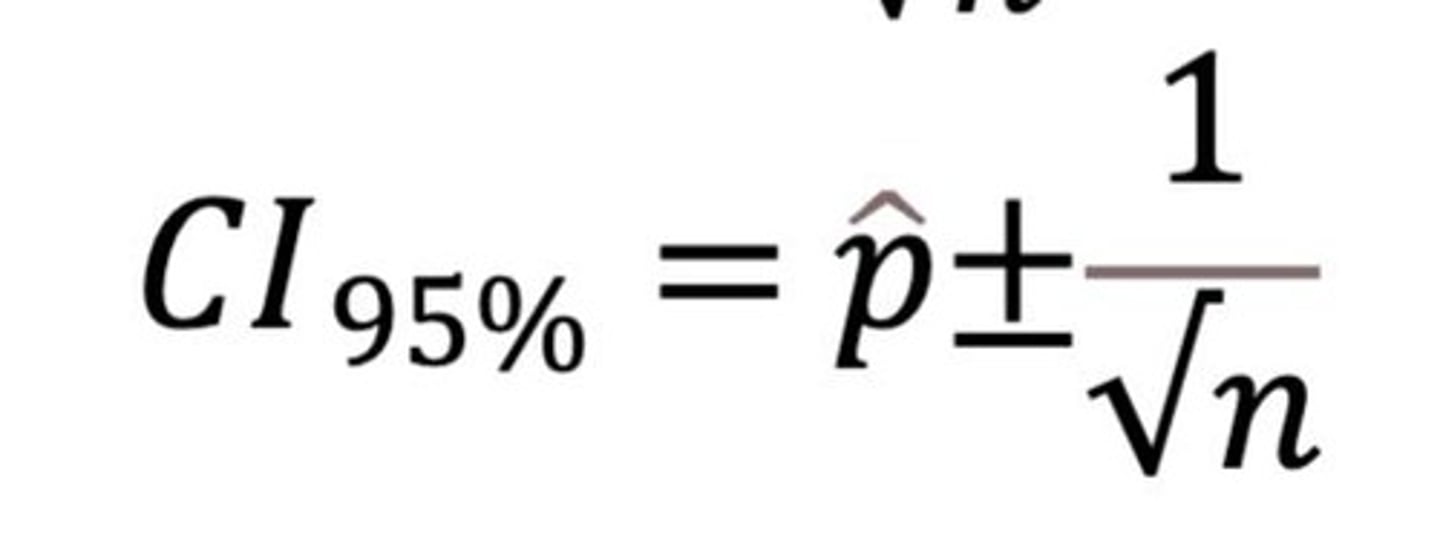
Internal Validity
Internal Validity: a change in the explanatory variable causes changes in the response variable.
External Validity
External Validity: do our conclusions generalize to the wider population.
Predictive Validity
if it can be used to predict things that are related to the property measured.
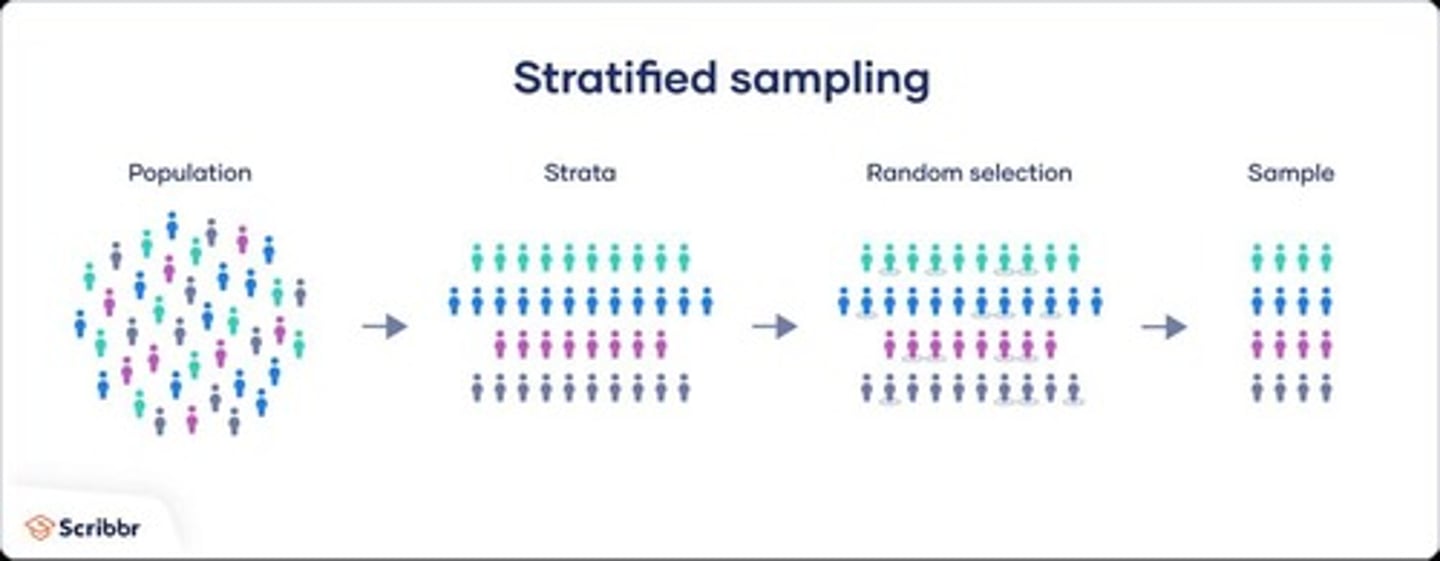
Stratified Random Sample
Step 1: Divide the sampling frame into distinct groups of individuals, called strata. Step 2: Take a separate simple random sample in each stratum and combine these to make up the complete sample.
Matched Pairs Design
design compares just two treatments.
Block Design
the random assignment of subjects to treatments is carried out separately within each block.
Block
a group of experimental subjects that are known before the experiments to be similar in some way that is expected to affect the response to the treatments.
Variance
Use to determine if the random error is small.
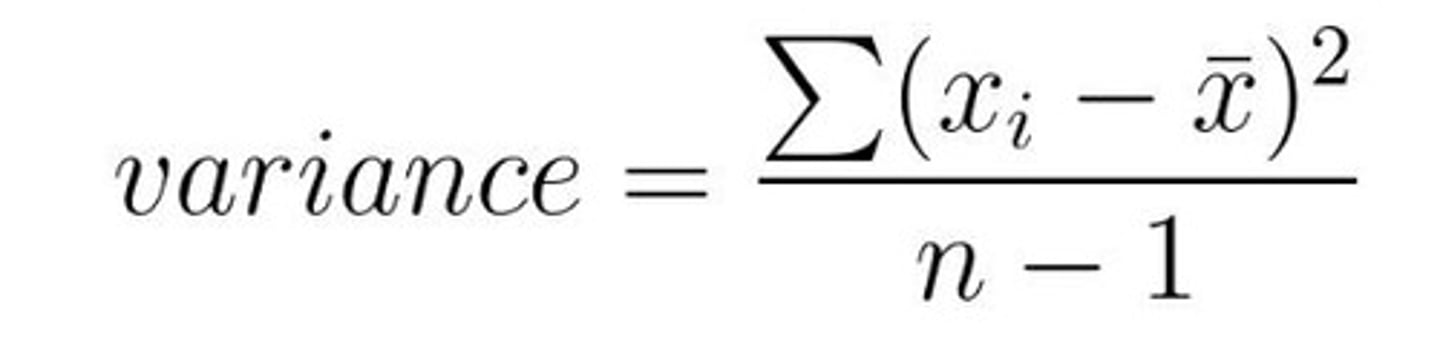
Variance Formula
Σ = sum of, Xi = an individual data point, X̅ = average, n = your sample size.
Measures
A property of a person/thing when a number is assigned to represent it.
Instrument
used to take a measurement.
Units
used to record the measurements.
Example of Measurement
To measure a student's readiness for college, you ask them to take the SAT.
Variable
example: Student's score (in points).
Rate
a fraction, proportion, or percentage at which something occurs.
Count
number of occurrences.