Unit 4 Chemistry Quiz #1
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
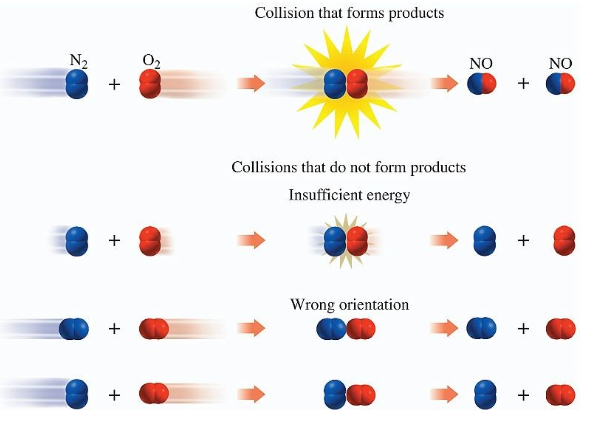
collision theory
chemical reactions can only occur if reactants collide…
-with proper orientation
-enough kinetic energy to break reactant bonds to form product bonds
dissolving
when solute particles become surrounded by solvent molecules
dilute solution
has a small amount of solute dissolved in the solvent
concentrated solution
has a large amount of solute dissolved in the solvent
dissolving ionic compounds
ion-dipole interaction
ionic compounds will only split apart and dissolve if…
-the intermolecular force is stronger than the intramolecular force
dissolving molecular compounds
polar compunds will only separate and dissolve if…
-the attraction between the polar compound + water is stronger than the attraction of the solid polar compound molecules
What are the factors that affect the role of dissolving?
1) Temperature: temperature gives the solvent particles higher kinetic energy thus collide with solute particles more.
2) Agitation (shaking/stirring): spreads out solute particles, more undissolved solute particles come into contact with solvent
3) Particle size (surface area): increased surface area allows more of solute to expose to the solvent
NOTE: smaller particles have greater total surface area
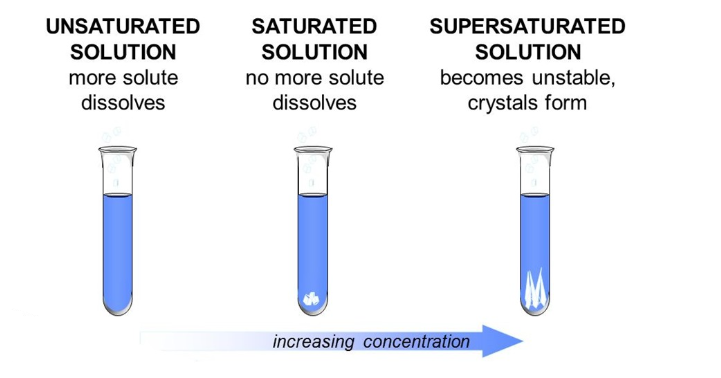
solubility
the maximum amount of the substance that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature
what are the factors that affect solubility?
1) Temperature: increasing solvent temperature increases the amount of energy to pull solute ions or molecules apart
2) Type of solute: different solutes have different solubility in the same substance
3) Nature of the solvent: the solubility of a substance is affected by the type of solvent (like dissolves like)
solubility of ionic compounds are affected by…
-ion size: larger ions are more soluble (weaker attraction)
-ion charge: weaker charges are more soluble
solubility of molecular compunds is affected by…
-molecular size:
small molecules = stronger solubility
large molecules = weaker solubility
solubility in water…
water can dissolve ionic or polar compunds but not non-polar compunds
ionic compounds > polar compounds > non-polar compunds
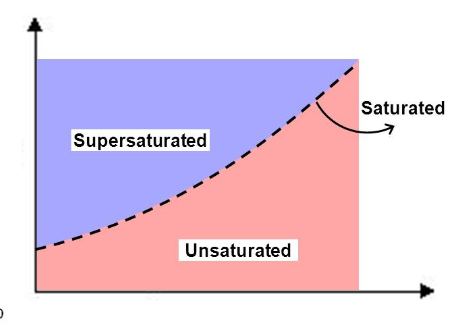
solubility curves
graph showing what mass of solute will dissolve in 100 g of water (solubility) over a range of temperatures