Intro to & Light Dependent Photosynthesis
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
why is photosynthesis important?
autotrophs: photosynthetic organisms that make their own food
heterotrophs: eat other organisms, autotrophs, wouldn’t have source a food or energy
what is photosynthesis?
CO2 + H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + O2
conversion of light energy
carbon dioxide and water converted into high energy compound: glucose
occurs more in the palisade mesophyll but also the spongy mesophyll, in chloroplasts
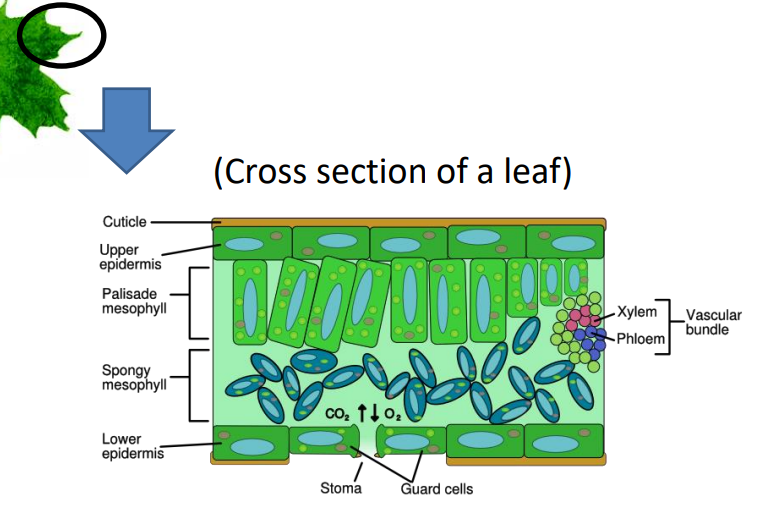
guard cells and stomata
The stoma opens during the day and closes at night (usually)
Sunlight activates a proton pump in the guard cells causing H+ to exit the cells
the influx of K+ ions draws water into the guard cell making them turgid
The swelling of the guard cells opens the stoma
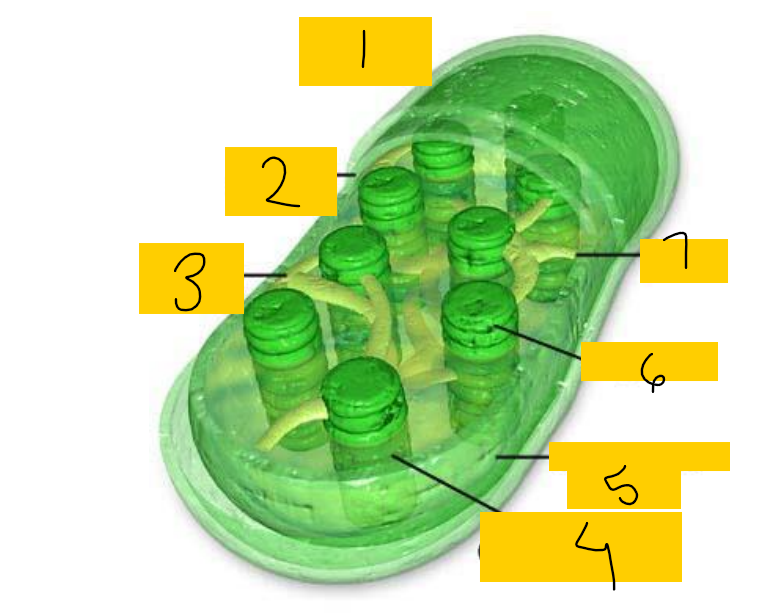
label
outer membrane
inner membrane
stroma lamellae
grana/granum: stack of thylakoids, stacking increases surface area
intermembrane space
thylakoid
stroma: like matrix, jelly like substance
photosystem ETLAR
primary electron accepter
transmembrane proteins
light harvesting unit in photosynthesis
contains antenna complex
contain chlorophyll a that acts as a reaction centre
PSII comes before PSI
noncyclic electron flow
electrons dont cycle back to PSI in chloroplast
electrons move through PSII then PSI then to NADP+
predominant → primary way of flow
Z patterns
most efficient for plant
cyclic electron flow
uses PSI only, electrons cycle back to it
No NADPH or Oxygen produced
only ATP produced
limited energy
two stages that photosynthesis can occur in
light dependent reactions: thylakoid
light independent reactions: calvin cycle, dark reactions
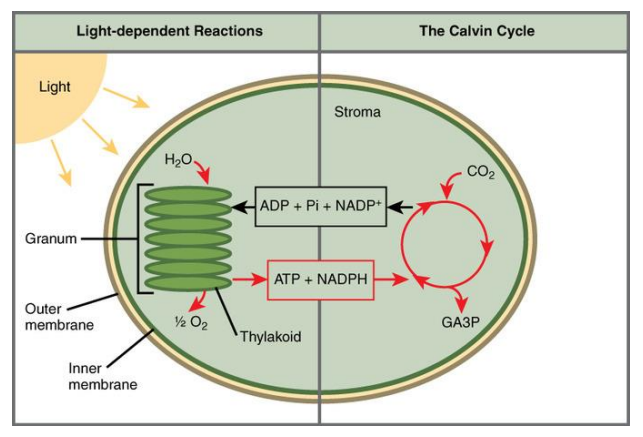
stage one of photosynthesis: beginning of photosynthesis (summary)
Converts solar energy into chemical energy
photons of light hit thylakoid
Light is absorbed by chlorophyll
drives the transfer of electrons to NADP+
1 ATP is produced through photophosphorylation
photon
fundamental particle of light
different pigments of a photosystem
in order highest to lowes
carotenoids: pinkish redish
chlorophyll b: yellow
chlorophyll a: green
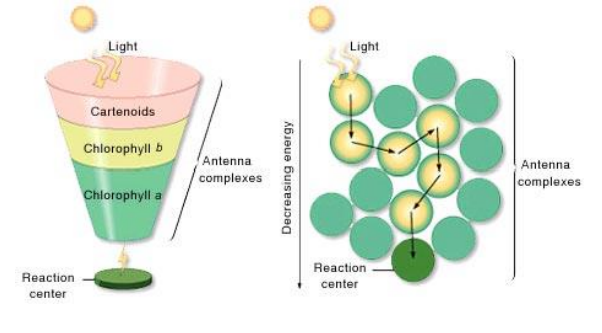
label
light
carotenoids
chlorophyll b
chlorophyll a
reaction center
antenna complexes
light
reaction center
antenna complexes
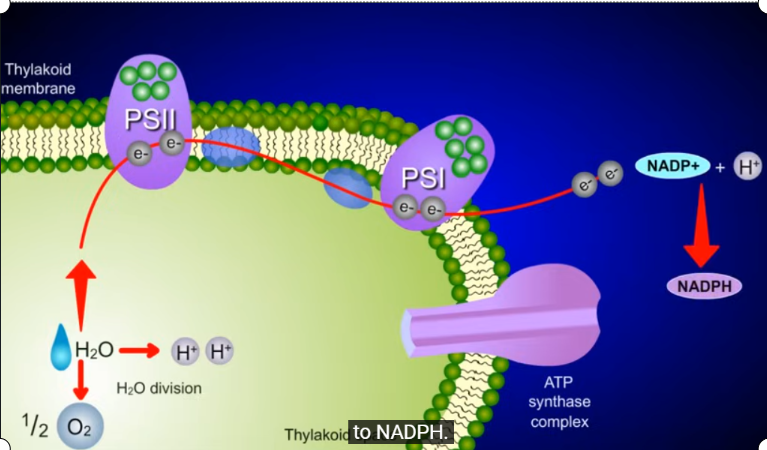
stage one, reaction details of electrons
noncyclic
light dependent
Z pattern
light hits PS II first, photons received
electrons become energized and move to electron accepter molecule in etc
water is split to replace those electrons: oxygen, two hydrogen and 2 electrons
first electrons move to PSI
creates high proton concentration in stroma
protein pumps protons from stroma to thylakoid space
protons move through atp synthase (diffusion) and release energy
energy used to produced atp from adp + phosphate
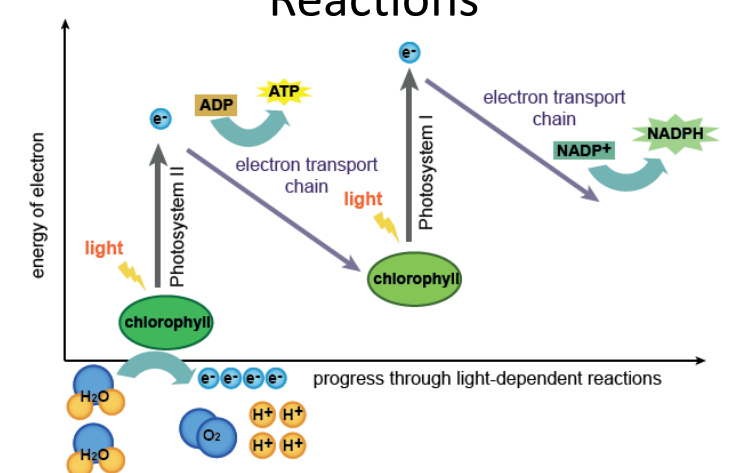
how is NADPH produced?
electrons from PS I gain energy from light
electrons become energized and escape PS I
energized electrons and proton reduce NADP+ to NADPH
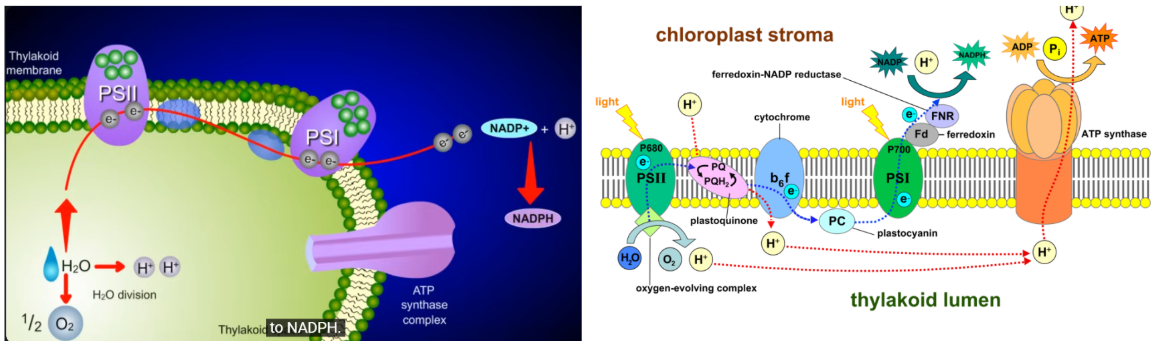
what molecule is in reaction centre of PSII?
P680 that gains energy from light and loses an electron to become P680+
what energy is absorbed at PSI reaction centre?
P700