4 - Normal Model and Measurement Error
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for reviewing lecture notes on the Normal Model and Measurement Error.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Normal Curve
A statistical model that approximates many natural phenomena and can model data resulting from a large number of independent variables.
Probability Density Function (PDF)
A special function which describes the chance associated with a continuous variable X, for all its possible values x, characterized by population mean μ and population SD σ.
Notation for Normal Distribution
If a variable X is Normally distributed with mean μ and standard deviation σ, it is expressed as X ∼ N(μ, σ^2), where σ^2 is the variance.
Standard Normal Curve
A normal curve with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1, denoted as Z ∼ N(0, 1).
General Normal Curve
A normal curve with any mean and any standard deviation, denoted as X ∼ N(μ, σ^2).
Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF)
F(x) = P(X < x) is the area under the Normal curve from −∞ up to a point x, representing the chance of those particular values of X occurring.
68%-95%-99.7% Rule
Approximately 68% of the data falls within 1 standard deviation of the mean, 95% within 2 standard deviations, and 99.7% within 3 standard deviations.
Standard Units (Z-score)
For any point x on X ∼ N(μ, σ^2), the z-score is z = (x−μ) / σ, indicating how many standard deviations the point is above or below the mean
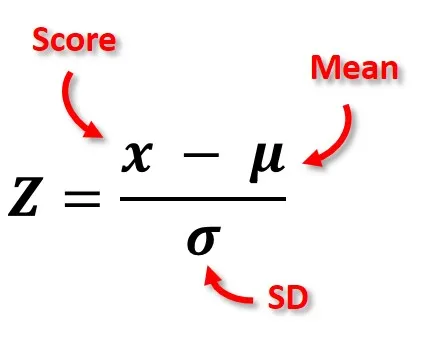
.
Measurement Error
The difference between an individual measurement and the exact value, composed of chance error and bias: Individual measurement = exact value + chance error + bias.
Chance Error
Random, unpredictable variations in measurements, best estimated by replicating the measurement under the same conditions and calculating the standard deviation (SD).
Bias (Systematic Error)
A constant amount added to or subtracted from each measurement, which can be deliberate or accidental, and cannot be estimated by replicating measurements.
Calibration
Comparing the measurement of an instrument to a working standard with a known measurement to reduce measurement errors when selling by weight.