1. Phase 1 Therapy
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
what kind of therapy is phase I therapy?
disease control therapy
what kind of therapy is phase II therapy?
corrective surgical therapy
what kind of therapy is phase III therapy?
corrective final restorative therapy
what kind of therapy is phase IV therapy?
professional dental hygiene therapy PDHT (maintenance)
what does phase I therapy consists of?
Patient plaque removal education & scaling and root planing.
Extraction of non-treatable teeth and caries control.
Occlusal therapy (Occlusal adjustment or an occlusal guard)
A complete re-examination following Phase I therapy
In order to perform therapy a _________ is ESSENTIAL along with a comprehensive treatment plan.
COMPLETE examination (radiographs, perio chart, photos, diagnostic casts)
what should be done before charting?
observe brushing and flossing techniques
what can we learn from orthodontics?
charging fees based on phases of treatment (length of time it’s going to take + how much it’s going to take)
t/f: Take a comprehensive medical, dental, and social history because knowing your patient is essential for your success!
true
Always observe your patient’ dental hygiene techniques before/after (which one?) your intraoral examination
before
how long should observing pt’s dental hygiene techniques take?
less than a minute
when should u offer advice to a pt regarding their dental hygiene technique?
AFTER completing the exam which will enable them to practice before their phase I therapy
what are periodontal diagnoses?
periodontal health
gingivitis
periodontitis
peri-implant health
peri-implant mucositis
peri-implantitis
what are periodontal classifications?
periodontal health
pristine
clinical
periodontitis
stages I-IV
grades A/B/C
following an exam, what should the initial treatment plan sequence for your pt be?
emergency therapy (pain, infection)
medical consult
dental consults
disease control therapy
perio re-evaluation
restorative therapy when plaque is controlled
step 4 of the intitial treatment plan sequence for your pt is disease control therapy (beginning of phase I therapy). this consists of…?
plaque control instruction review
scaling and root planing
what are the etiological risk factors of periodontal disease?
toxins from bacterial plaque (primary)
calculus (contains toxins from bacterial plaque)
systemic diseases/conditions
local dental factors
trauma
how are systemic diseases/conditions etiological risk factors?
lowers immune system
how are local dental factors etiological risk factors?
cause plaque retention or the inability to remove dental plaque (malposed teeth, anatomical issues, open contacts, grooves, enamel projections, open contacts, defective restorations, etc.)
how is trauma an etiological risk factor?
– Physical (Scrubbing brushing techniques, other).
–Occlusal (Parafunction: Clenching, Bruxism).
Phase I therapy often includes more than plaque/calculus removal such as…?
1. Plaque Control Instruction, Scaling, Root Planing, Stain and biofilm removal.
2. Caries Control (Provisional restorations).
3. Exodontia as needed (May include ridge preservation depending on the agreed plan.)
4. Occlusal adjustment as needed.
5. Re-evaluation 6-8 (or more) weeks following initiation of therapy.
t/f: it is important to observe and instruct your patient’ dental hygiene techniques P.R.N. at the outset of your Phase I mechanical therapy! Since you taught plaque removal techniques at your examination, this is a review to see what the patient retained from your previous instructions. For all of us, when we are doing our plaque removal techniques, we cannot see the plaque that we are removing, and thus we cannot self-correct our techniques
true
beside SRP, what chemical therapies might also be indicated?
antiseptics, antibiotics
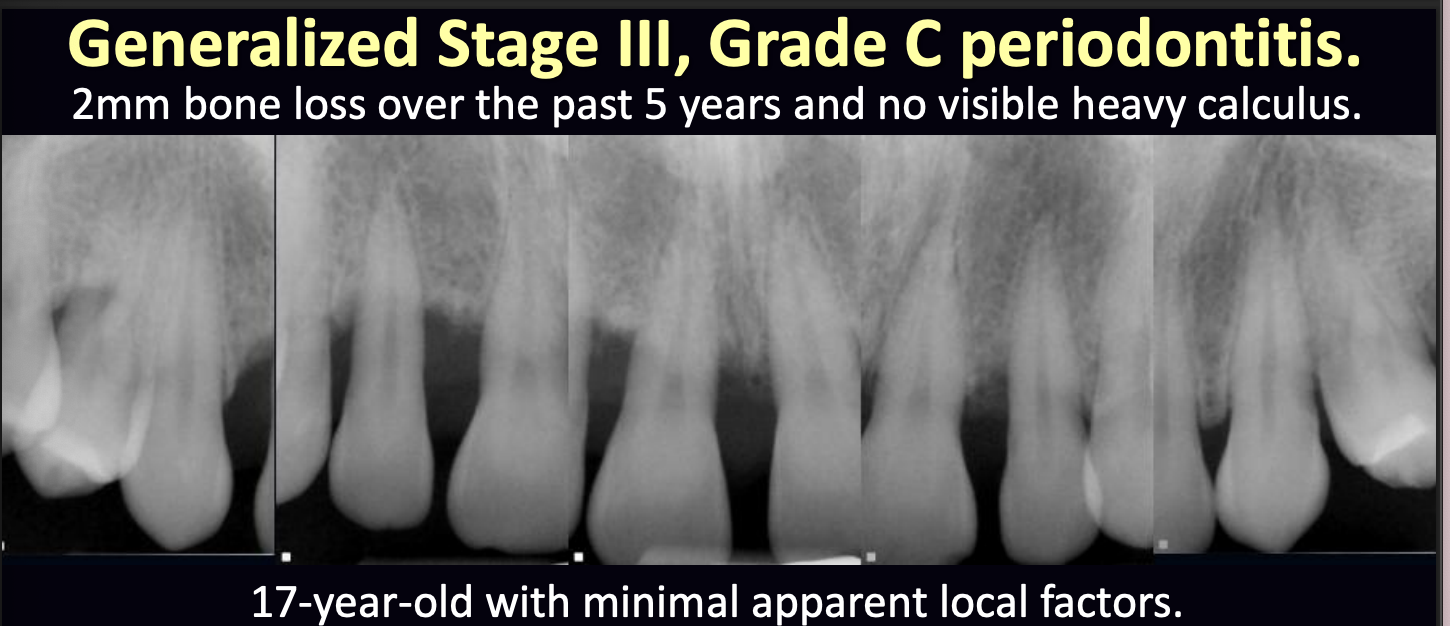
what therapy might be indicated in this case?
systemic antibiotics (chemical therapy) is indicated along with instruction in evidence-based dental plaque removal techniques and thorough scaling and root planing
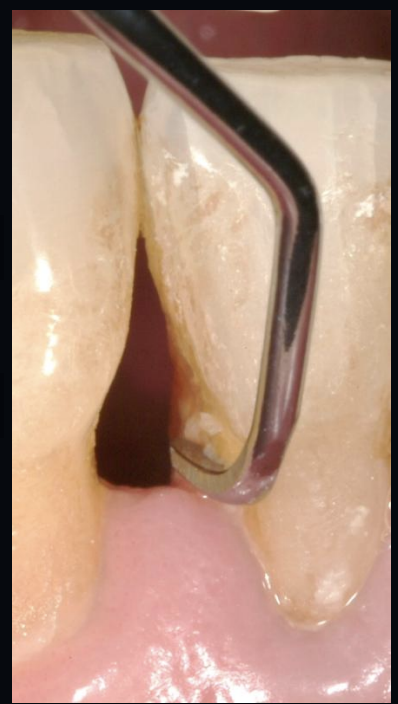
what is the instrumentation of the crown and root surfaces of the teeth to remove plaque, calculus and stains with scalers and curettes?
scaling
what is a treatment procedure designed to remove cementum or surface dentin that is rough, impregnated with calculus, or contaminated with microorganisms and bacterial toxins (waste products)?
root planing
where is root planing done?
ONLY subgingivally with curettes
what is the objective of SRP?
remove calculus, plaque, and stain from tooth surfaces
in what situations can it be difficult to complete SRP in a single visit?
pockets of > or = 5 mm
moderate to heavy calculus deposits
rough root surfaces
when is root planing done?
during active or maintenance therapy for patients with present or past periodontitis
root planing is for the removal of ________ plaque, calculus, and cementum to assure smooth subgingival root surfaces regardless of the probing depths.
subgingival
the goal of root planing is to acheive a very smooth root surface removing the coronal cementum, _____ microns thick, about the thickness of a hair and apical cementum is _____ microns thick.
16-60
150-200
when there is subgingival calculus, _____- have vacated, and now there is a rough root surface now exposed to oral bacteria
Sharpey’s fibers
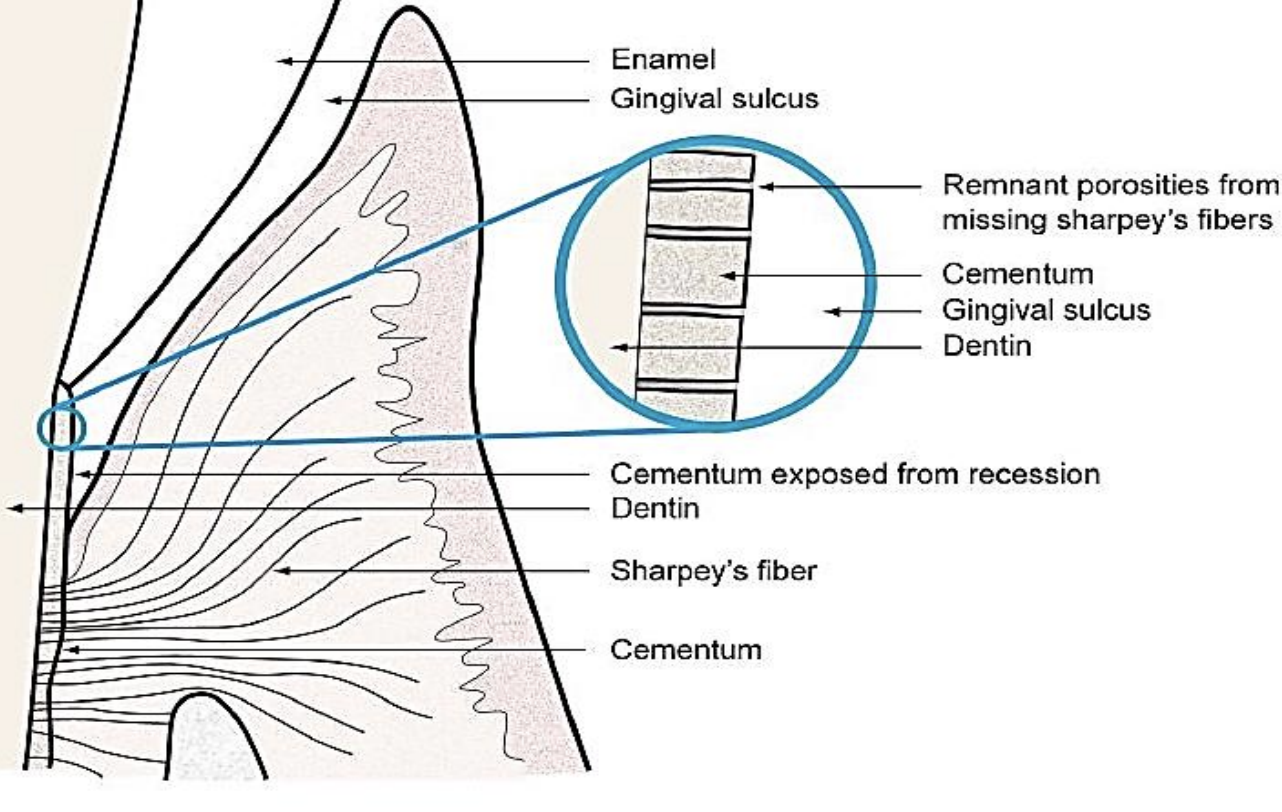
t/f: scalers are used subgingivally
false. scalers are NOT used subgingivally

_____ are used for SRP and may be used supra and subgingivally.
curettes

what are the 5 basic instruments used in SRP?

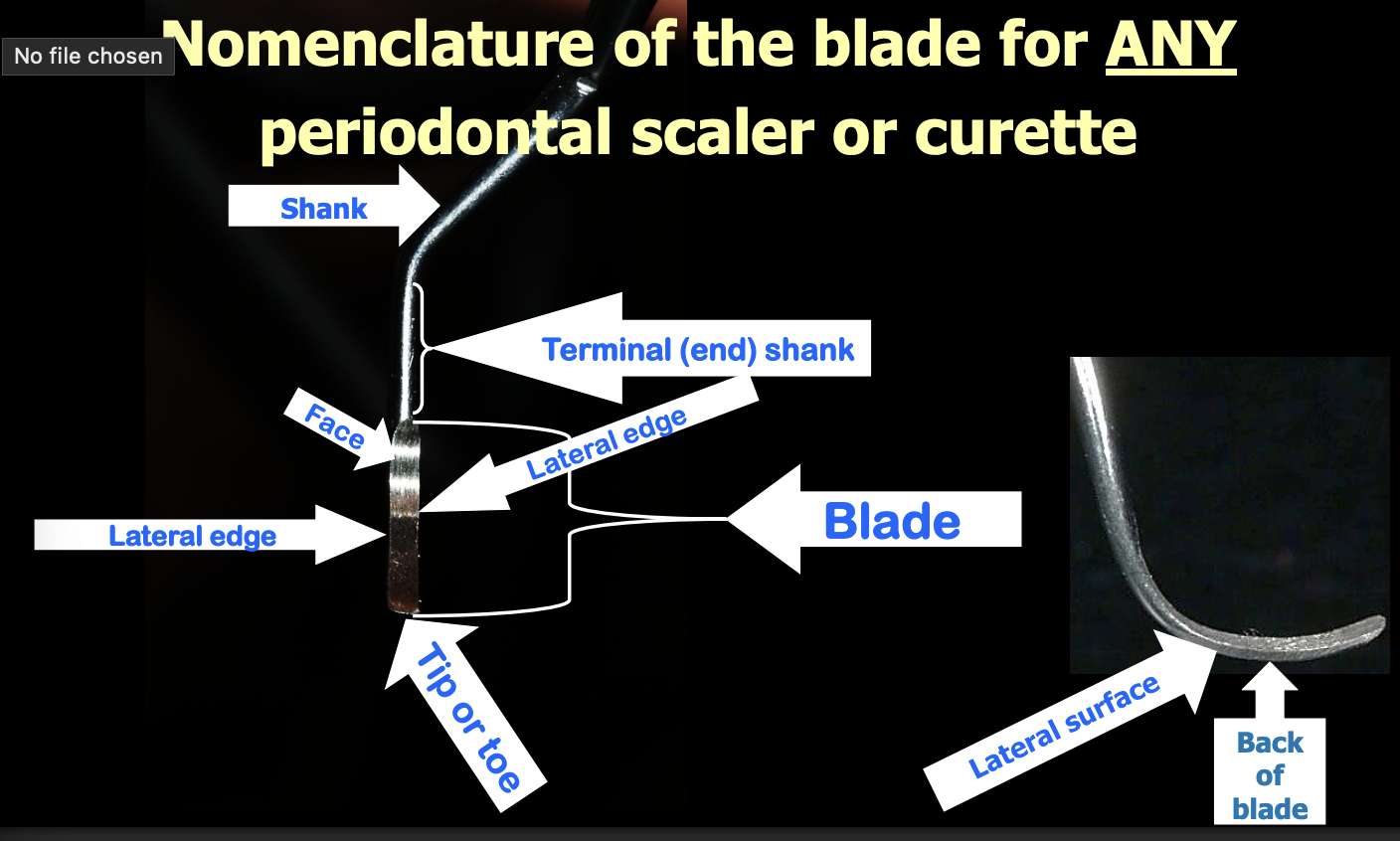
hand scalers are used _____gingivally.
supra
what are hand scalers good for?
heavy calculus deposits
particularly useful for just under contact areas because blade is triangular in cross-section and tapers to a sharp point
what shape is H 6/7 hand scaler ?
curved sickle
what shape is 34/35 hand scaler ?
straight sickle
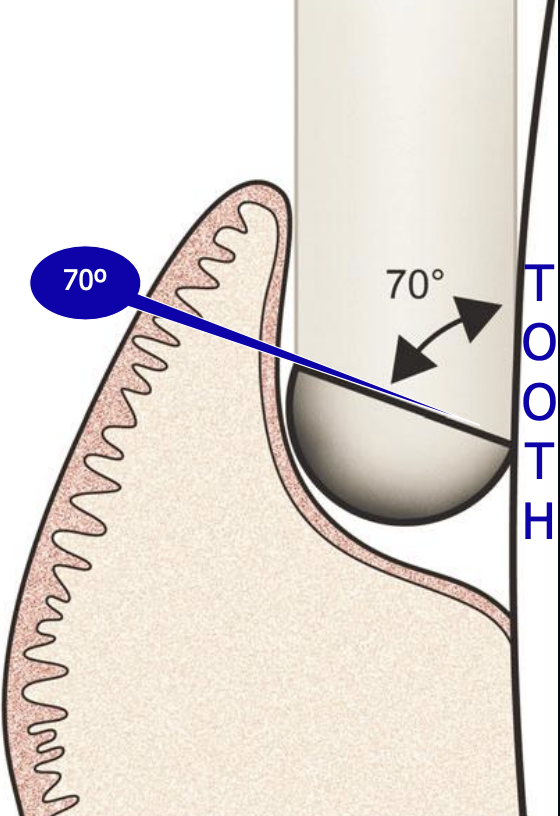
what is the correct angle of the face of the blade to the tooth for efficient SRP?
70 degrees

universal curette

gracey curette
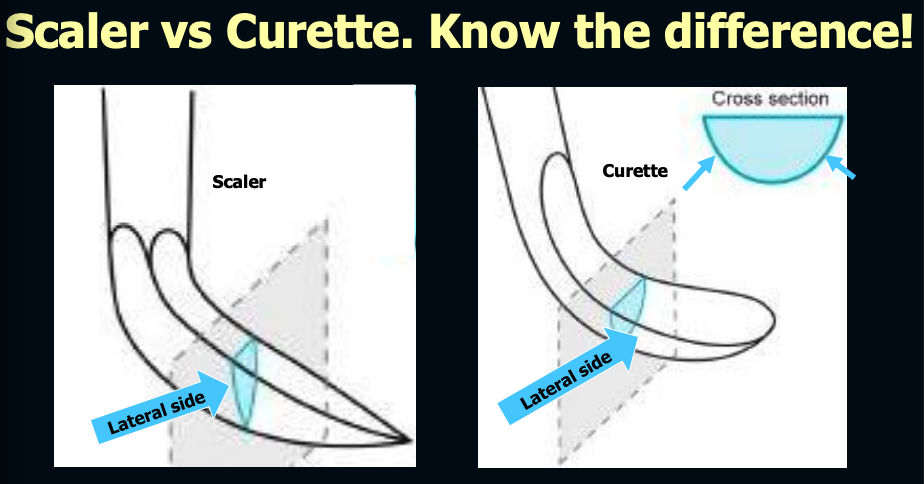
what is the difference between a scaler and curette (in regards to shape)? IMPORTANT
scaler = comes to point at tip
curette = rounded at the toe and back
what is the other name for universal curettes?
the younger-good 7/8
what are the 3 cutting surfaces on universal curettes?
2 lateral edges + toe
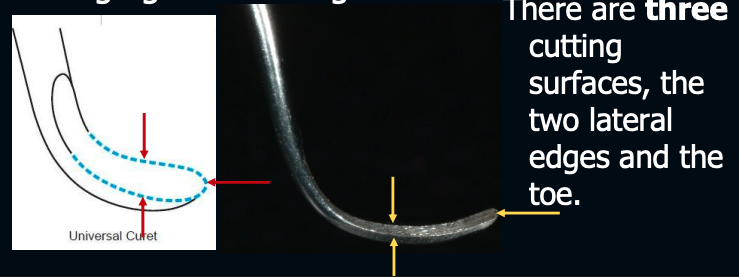
universal curettes are useful for,,,>
adapting to most tooth surfaces
gingival curettage
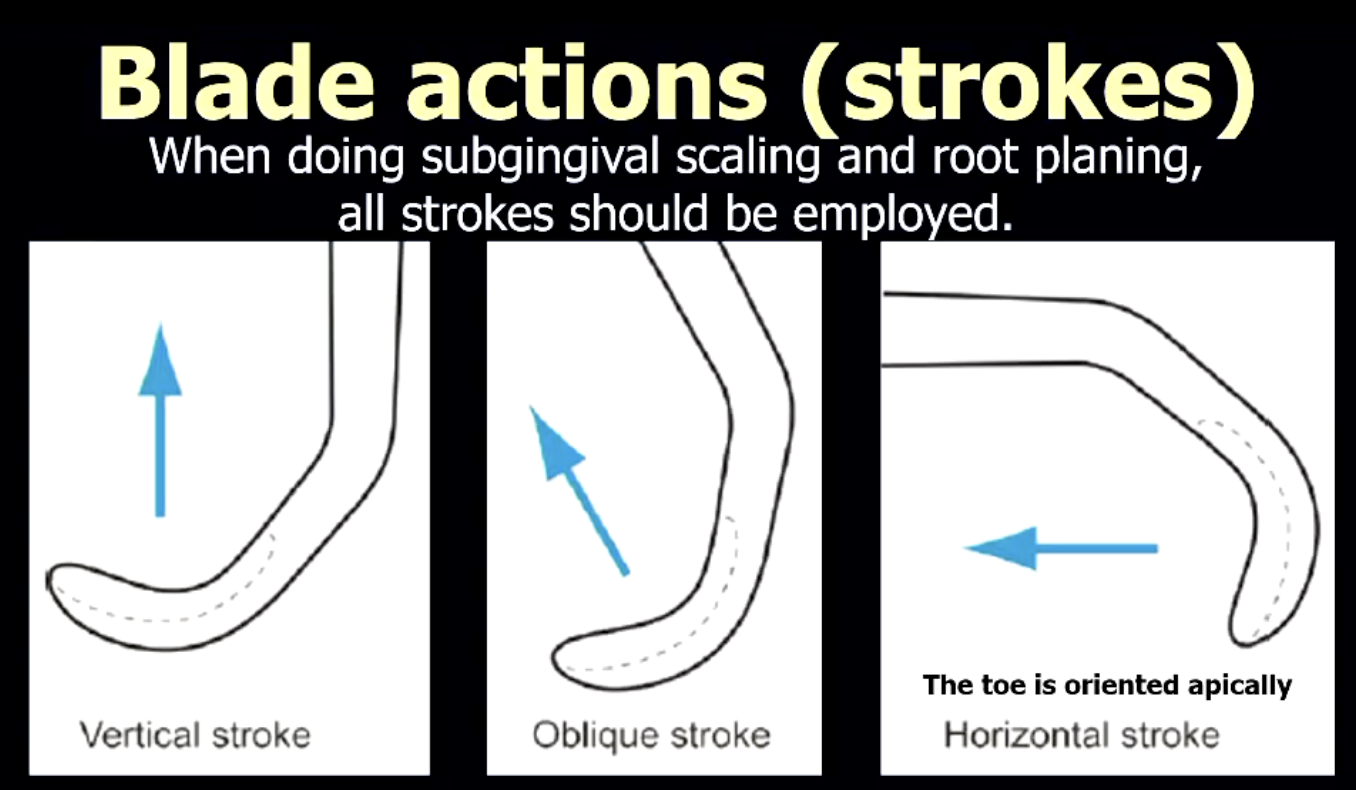
what are the 3 blade actions (strokes) of universal curettes?
vertical
oblique'
horizontal
When doing subgingival scaling and root planing, all strokes should be employed.
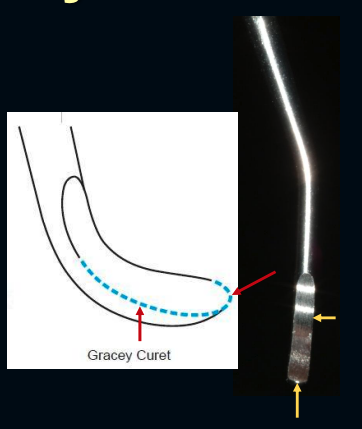
how many cutting edges are there on a gracey curette?
1 lateral edge + toe
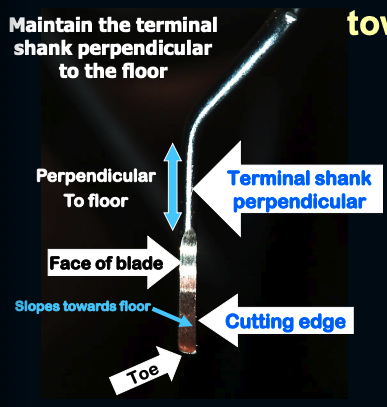
how do you determine the cutting edge of any Gracey Curette?
hold the instrument vertically with the toe pointing towards you
When the terminal shank of any Gracey curette is held perpendicular to the floor, then the cutting-edge slopes towards the floor.
When the TERMINAL SHANK of any Gracey curette is maintained parallel to the tooth surface that is being scaled or root planed using any stroke (vertical, oblique, horizontal), then the blade will always be 70° to the tooth. What is the significance of this?
This means that any Gracey may be used to scale or root plane any surface of any tooth as long as the terminal shank can be maintained parallel to the tooth surface being treated
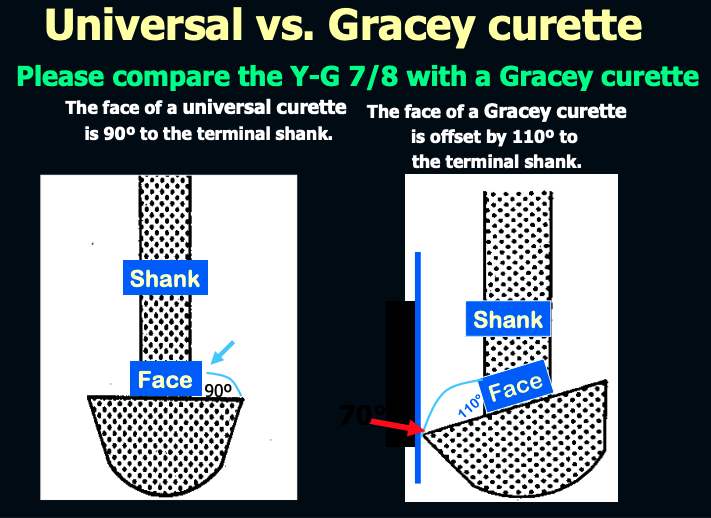
The face of a universal curette is __ degrees to the terminal shank
90º
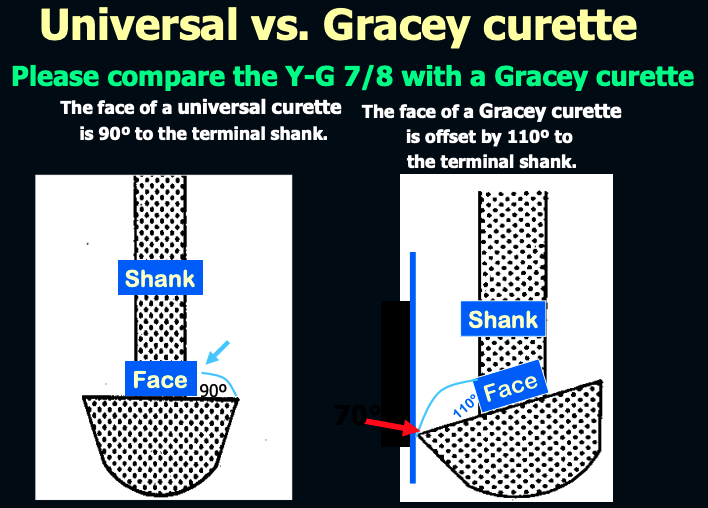
The face of a Gracey curette is offset by ___ degrees to the terminal shank.
110º
it is important to use 2X2 gauze with hand scaling or root planing. what is the procedure?
Dampen it and roll it tight like a cotton roll.
Place it in the vestibule facial and lingual of the mandible and facial of the maxilla.
Wipe your instrument blade.
Blot blood from gingival margin.
Provides a dry and comfortable non-skid finger rest.
Helps to keep tongue away from work area.
Retracts lip and cheek.
Provides access and more visibility.
t/f: Hand instrumentation sharpening is vastly important! It must be done prior to using an instrument and when the instrument becomes dull during use.
true
why is it important to sharpen hand instrument BEFORE every procedure?
➢ Much more precise in cutting.
➢ Less pressure against the tooth.
➢ Good control of the instrument with optimum tactile sensitivity (IMPORTANT)
➢ Less chance of the instrument slipping.
➢ Less operator fatigue and frustration.
what are some power instrumentations tools?
ultrasonics
air polishing
implant maintenance (hand vs power vs air polishing)
NOT FOR ROOT PLANING
is there a signficant difference between using hand or ultraosonic scaling regarding calculus/plaque removal?
no
ultrasonics vs hand instruments:
which is better for accessing furcations and grooves?
ultrasonics
standard ultrasonic and microultrasonic inserts were able to reach and debride the apical plaque border in pockets ranging from __ to __ mm
4-7 mm
what are advantages of ultrasonics?
improved access
ease of use
antimicrobial
does not cut soft tissue or remove tooth structure
what are advantages of ultrasonics: improved access?
thin tips, large variety
more effective in anatomically difficult to access areas
concavities, root proximity
deep narrow pockets, at CEJ
what are advantages of ultrasonics: ease of use?
less technically demanding (but more concentration)
work coronal-apically
effective w light pressure
reduced physical fatigue
no sharpening necessary
what are advantages of ultrasonics: antimicrobial?
lavage: flushes pocket/endotoxins
cavitation: disrupts bacterial cell wall
acoustic microstreaming/turbulence
can add antimicrobials to lavage
what are advantages of ultrasonics: does not cut soft tissue or remove tooth structure?
little or no root surface removal
less soft tissue damage
no root planing or gingival curettage
what are disadvantages of ultrasonics?
aerosols: bacteria and viruses
loss of tactile sensitivity
pt comfort (sensitivity, water, noise)
cannot root plane
changing tips is time consuming (compared to changing hand instruments)
when using ultrasonics, what aerosol management methods are important to use?
pre-procedural mouth rinse
HVE
PPE (face shield, mask)
retraction
air filtration
t/f: the combination of ultrasonics and hand instrumentation is more effective than either technique alone
true
t/f: ultrasonics and hand instruments have a similar effect on resolution of inflammation
true
endotoxins are _____ adherents
surface
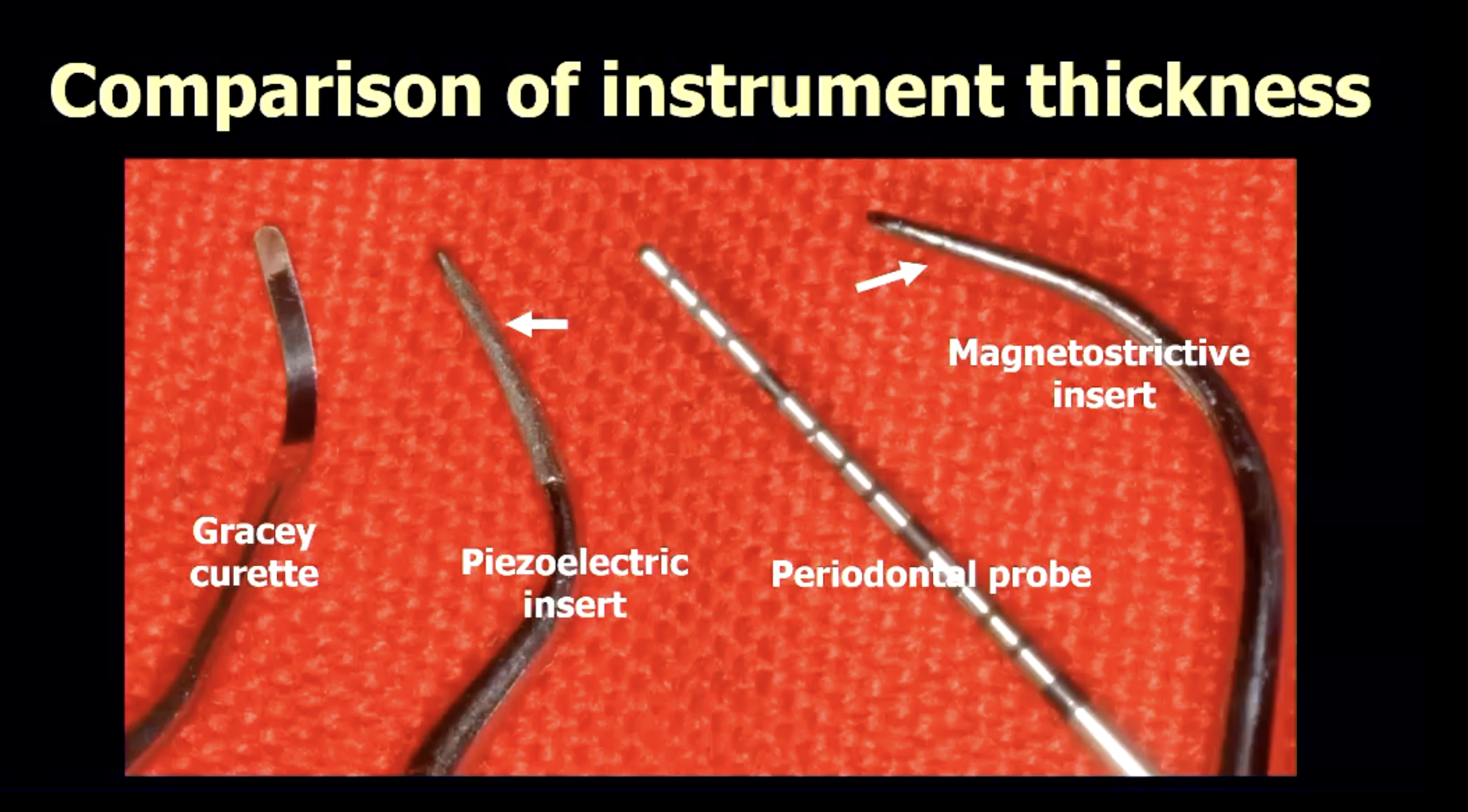
what are types of ultrasonic scalers?
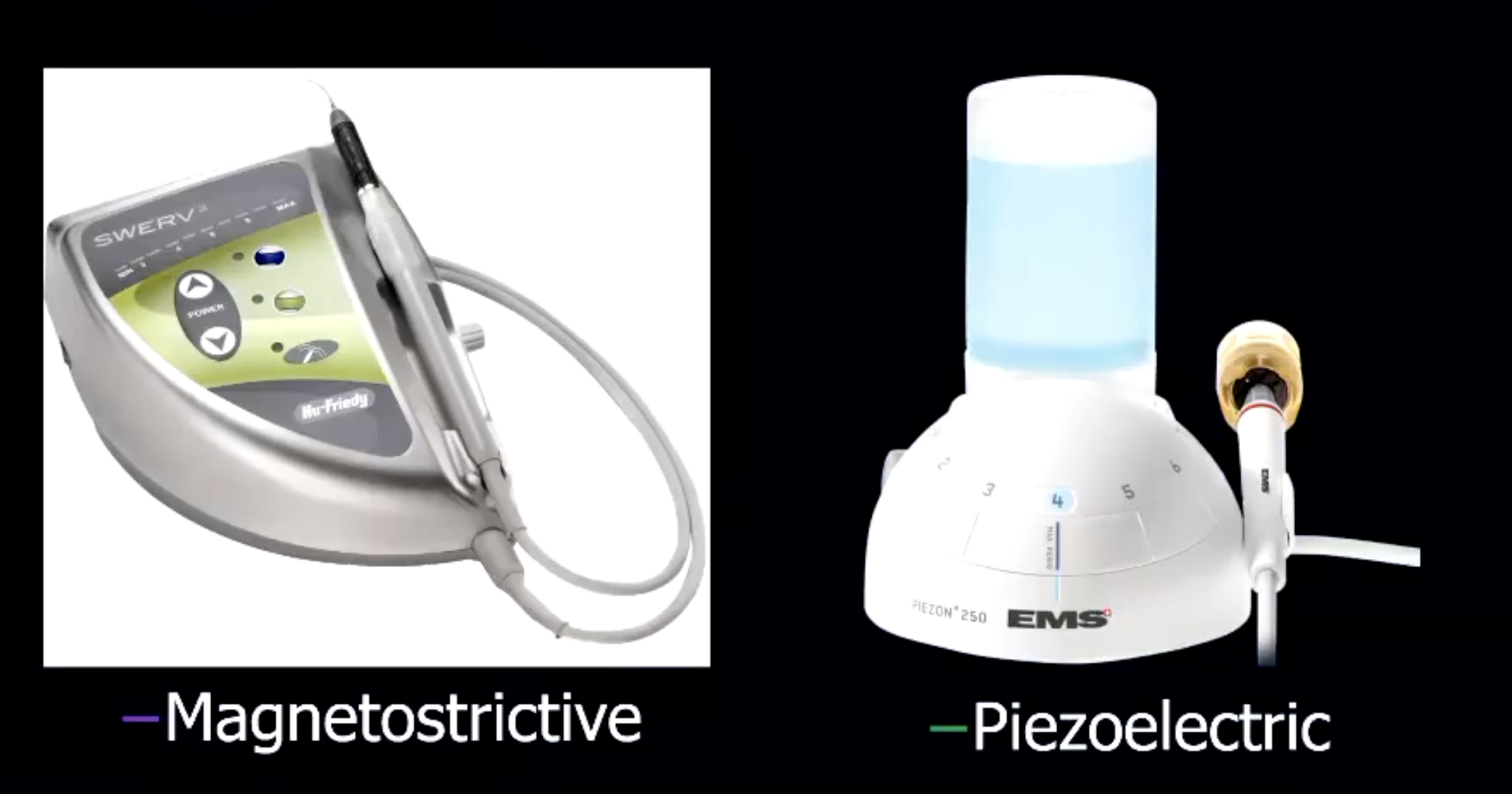
what is the difference between magnetostrictive vs piezoelectric ultrasonic scalers? (in terms of motion of tip)
magnetostrictive → oscillating tip
piezoelectric → linear motion tip (use side of tip NOT front/back)
what is the correct adaptation technique when using power instrumentation?
adapt the tip similar to periodontal probewh
what 8-step protocol should be followed for PDHT?