RNA and transcription units
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
genetics - RNA and transcription units
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
mRNA
directs the synthesis of proteins
proteins
source of mRNA determines the identity of newly made ____
leader, coding, and trailer
the 3 sequences that make of the structure of mRNA
leader sequence
sequence that makes up mRNA that is important for initiating protein synthesis
coding sequence
sequence that makes up mRNA that has the longest area and holds the nucleotides that encode the amino acid sequence
trailer sequence
sequence that makes up mRNA that is after the end of synthesis and regulates the lifespan of the mRNA
heteronuclear RNA
hnRNA
hnRNA
the precursor to mRNA
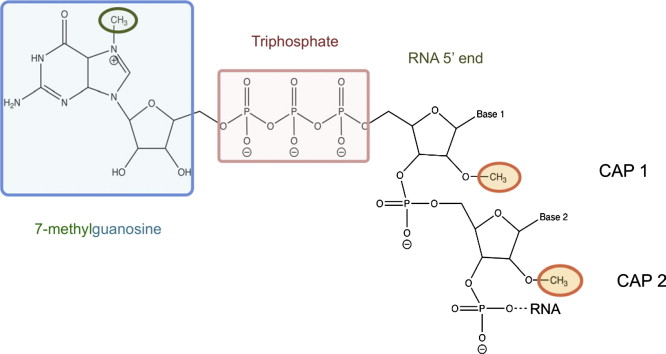
capping
process of adding specialized guanosine residue to the 5’ end of RNA, this aids in the initiation of protein synthesis
protects 5’ end from exonuclease
how does capping aid in the initiation of protein synthesis?
7-methyl-guanosine
specialized guanosine residue added to the 5’ end of RNA
exonuclease
enzyme that chews the ends of the DNA strand
enzyme that chews the middle of the DNA strand
tailing
process of adding a string of As (25-200) to the 3’ end of RNA: the Poly-A tail, defines the lifespan of the mRNA
splicing
process of cutting out portions of RNA and piecing together the remaining portions to be exported into the cytoplasm
larger
pre-mRNA inside the nucleus is ____ than mRNA in cytoplasm
introns
removed during splicing; non-coding sequence
exons
pieced together during splicing; the coding sequence
promoter, transcribed region, terminator
What are the 3 parts of the DNA sequence needed for synthesis?
promoter
one of the transcription units, has a 5’ sequence, is the site where RNA pol is loaded onto DNA, the site of transcription initiation, has regulatory elements
transcribed region
one of the transcription units where RNA pol uses ssDNA as template, the site of elongation
terminator
one of the transcription units, has 3’ sequence, is the site where RNA pol is dislodged from DNA, and the site of ending transcription
capping of mRNA
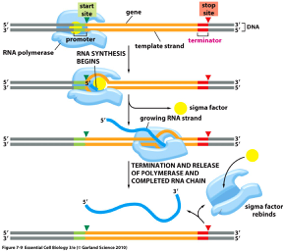
what doe sthis image show?
binds promotor to recruit RNA pol
what is the purpose of the sigma factor in this diagram?
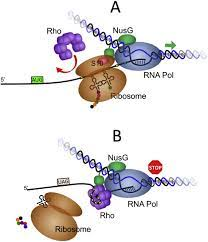
cause RNA pol to release RNA strand
what is the function of rho in this image?
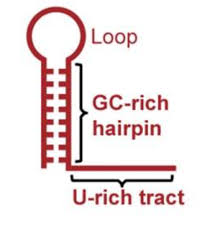
terminate transcription by removing RNA pol
what is the function of the hairpin structure?
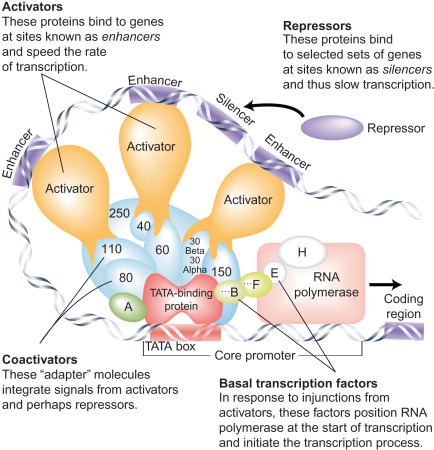
transcription factors
what is this image showing?
multiple copies of rRNA genes being transcribed
what is this image showing?
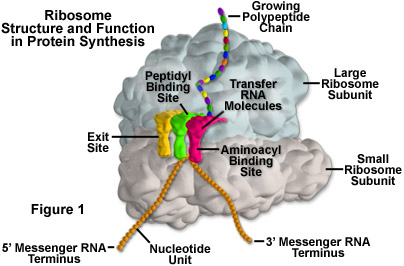
ribosome
what is this image showing?
-35s, Is, -10s, Is
what is the order of the 4 different sequences in a bacterial promotor?
prinbow box
what is the other name for the -10 sequence in a bacterial promotor? this functions as one of the binding sites for RNA polymerase to initiate transcription
-35s and -10s
what are the 2 binding sites for RNA polymerase in bacteria?
16-19
The first intervening sequence (Is) in bacteria is how many base pairs long?
6-9
the second intervening sequence (Is) in bacteria is how many base pairs long?
RNA start site
what comes after the second intervening sequence in a bacterial promotor?
length
what about the intervening sequence must stay the same for regular transcription to occur?
sigma factor
binds promotor and recruits RNA polymerase
released from promotor
what happens to the sigma factor after RNA polymerase begins transcription?
helicase
what type of enzyme is rho?
mRNA
rho binds ____, moves 5’ → 3’
rho dependent termination
type of termination where something catches up to polymerase, finds RNA:DNA hybrid, and disrupts it?
rho independent termination
type of termination that uses inverted repeats in sequence of terminator to dislodge RNA pol
AT-rich region
what usually follows inverted repeats?
hairpin structure
what structure is created by inverted repeats in the nucleotide pattern?
3
eukaryotic promotors have ____ different classes
enhancers
regions of DNA distant from promotor that regulate level of expression ot promotor
distance and position
enhancers are ____ and ____ independent
basal factors, activators, coactivators, repressors
what are the 4 types of regulatory proteins in eukaryotes?
basal factors
one of the 4 regulatory proteins in eukaryotes; similar to transcription factors, proteins that bind promotor and recruit RNA pol
activators
one of the 4 regulatory proteins in eukaryotes; bind enhancers and stabilize transcription factors
coactivators
one of the 4 regulatory proteins in eukaryotes; assist the activators, not DNA binding proteins
repressors
one of the 4 regulatory proteins in eukaryotes; bind silencers and prevent activators from binding