Production of ethanol, biodiesel, triglycerides and saponification
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is biofuel?
Refers to any fuel drived from biomass, including plant or algae material and animal waste (living things)
Considered renewable energy source (feedstock material replenished readily)
What are the advantages of biofuels?
Renewable
Reduce greenhouse gasp emission compared to fossil fuels
Diversifying energy sources reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
What are the disadvantages of biofuels?
Biofuels have economic and environmental costs associated with their refining and expanding biofuel production
May compete with land needed for food crops.
What is an enzyme?
A biomolecule that acts as a catalyst to speed up specific chemical reactions within living organisms
What does an enzyme facilitate?
Essential processes in cells, including digestion, energy transformation and macromolecule synthesis. Without enzymes, many of these reactions would occur too slowly to sustain life.
What is a catalyst?
A substance that increases reaction rate by providing an alternate reaction pathway with lower activation energy, allowing for a greater proportion of reactant particles to have energy greater than the activation energy for that reaction.
How do enzymes work?
1.Enzymes have an active site, a specific region where they bind to their substrate (the molecule they act upon). The active site’s shape complements the substrate’s shape, like a lock and key.
2.Once the substrate binds to the active site, the enzyme undergoes a conformational change, which strains the substrate’s bonds. This lowers the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
3.Enzymes provide an optimal environment, by donating or accepting protons, forming temporary covalent bonds, or creating an ideal pH or ionic environment.
4.The substrate is converted into products. Enzymes release the products and return to their original conformation, ready to catalyse more reactions.
What are the ways that enzymes folded structure is altered, resulting in enzyme denaturing?
1.Temperature: High temperatures disrupt the intermolecular forces that maintain an enzyme’s shape. The enzyme loses its functional 3D structure, rendering its active site ineffective.
1.pH Extremes: Exposure to extreme pH can also denature enzymes. The altered pH affects the charges on amino acids, disrupting the enzyme’s folding pattern.
What is the acid-catalysted reaction of ethene of water?
Occurs by the mixture of steam and ethene and passing it over a bed of silica particles that are coated with phosphoric acid.
What is the reaction equation for acid-catalyzed reaction of ethene and water?
CH2CH2(g) + H2O(g) —> ←- CH3CH2OH(g) H = -45 kJ
What type of reaction is acid-catalyzed reaction for ethene and water
Exothermic reatcion: Heat is released
Decreasing the temperature shifts it to the right (towards products)
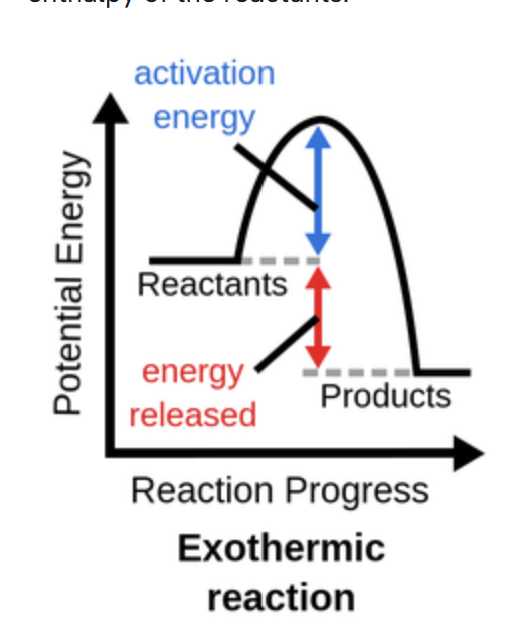
What are the reaction conditions for acid-catalyzed reaction of ethene and water?
Pressure of 6-7 MP. High pressure favors the formation of products as the number of moles is fewer in the products
A moderate temperature is used. Although a high temperature will have a higher reaction rate, because this is an exothermic reaction, higher temperatures will lead to lower yield of ethanol. Therefore temperature cannot be too high (around 300 degrees)
Ethene to water ratio is 1:06 is used to ensure water is the limiting reagent. This prevents dilution and washing away of the phosphoric acid from the catalyst bed.
Using collision theory, explain why increased pressure is needed for the acid-catalyzed reaction of ethene and water
Pressure can be increased by decreasing volume
This results in the same quantity of particles being exposed to a smaller volume
They’re therefore closer to one another and to the walls of the reaction vessel
This increases the frequency of collisions
This increases the number of successful collisions
As a result the rate of reaction and therefore the production of ethanol increases.
Explain the increase in pressure affect on the acid-catalyzed reaction of ethene and water BASED ON LE CHATELIERS PRINCIPLE
According to Le Chatelier’s principle, the equilibrium will shift in the direction to decrease the pressure. To decrease the pressure, the equilibrium will favor the side with fewer moles, which is the right side, so it will favour the formation of ethanol, increasing its concentration
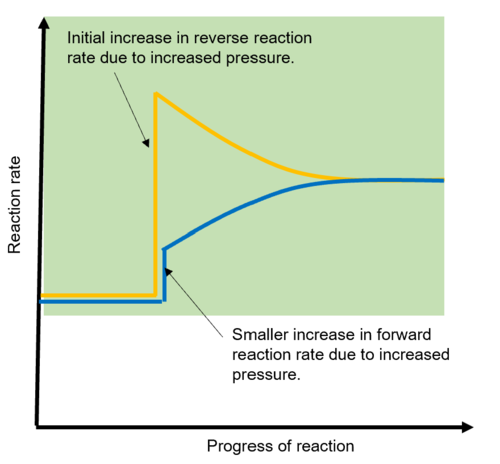
Using collision theory, explain the effect on increasing temperature in acid-catalyzed reaction of ethene and water
As a substance temperature increases the particles have more average kinetic energy
They move at a faster speed/ greater velocity
This increases the frequency of collisions
This increases the number of successful collisions
This leads to a greater portion of the particles having energy greater than the activation energy
As a result, reaction rate increases
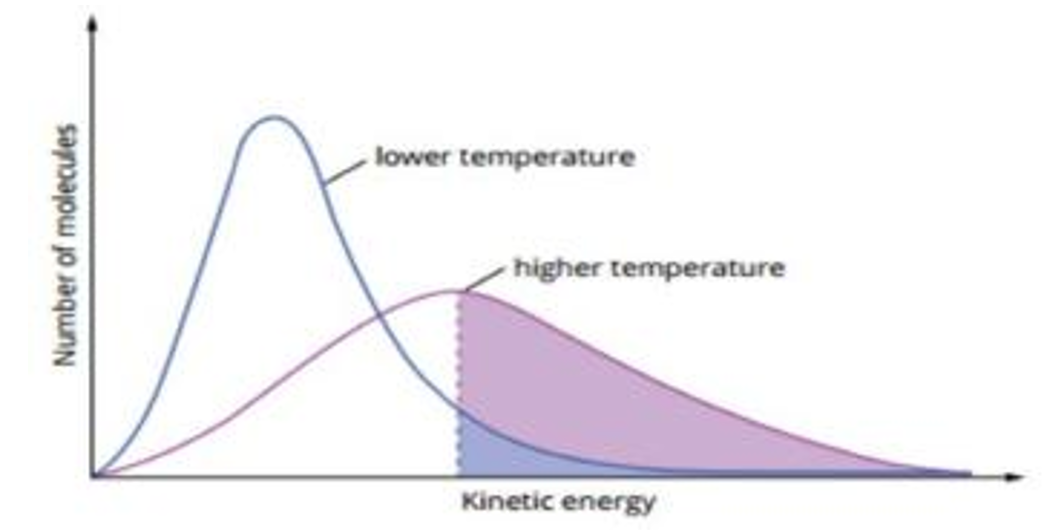
Why is not too high temperatures needed in the acid-catalyzed reaction for ethene and water?
According to Le Chatliers principle, when temperature increases, the system favour the endothermic reaction to decrease the temperature, which is the left side. The reverse reaction will increase, favouring the formation of reactants but decreasing the concentration of ethanol used up in the reaction.
In contrast, when temperature decreases the system will move in the direction to increase this temperature and so it will favor the exothermic reaction. Therefore, decreasing the temperature will cause the equilibirum to shift to the right to increase ethanol concentration
What is the fermentation of biomass to produce ethanol?
Hydrolysis (chemical process which breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids by the addition of water) reaction of sucrose sugars using an enzyme called invertase to produce simple sugars like glucose and fructose.
Fermentation (anaerobic process where simple sugars produce ethanol for use as fuel) step occurs when these simple sugars are converted into ethanol molecules using an enzyme called zymase (yeast)
What is hydrolysis equation in the fermentation of biomass and draw it
C12H22O11(aq) + H2O(l) —→ (invertase) 2C6H12O6(aq)
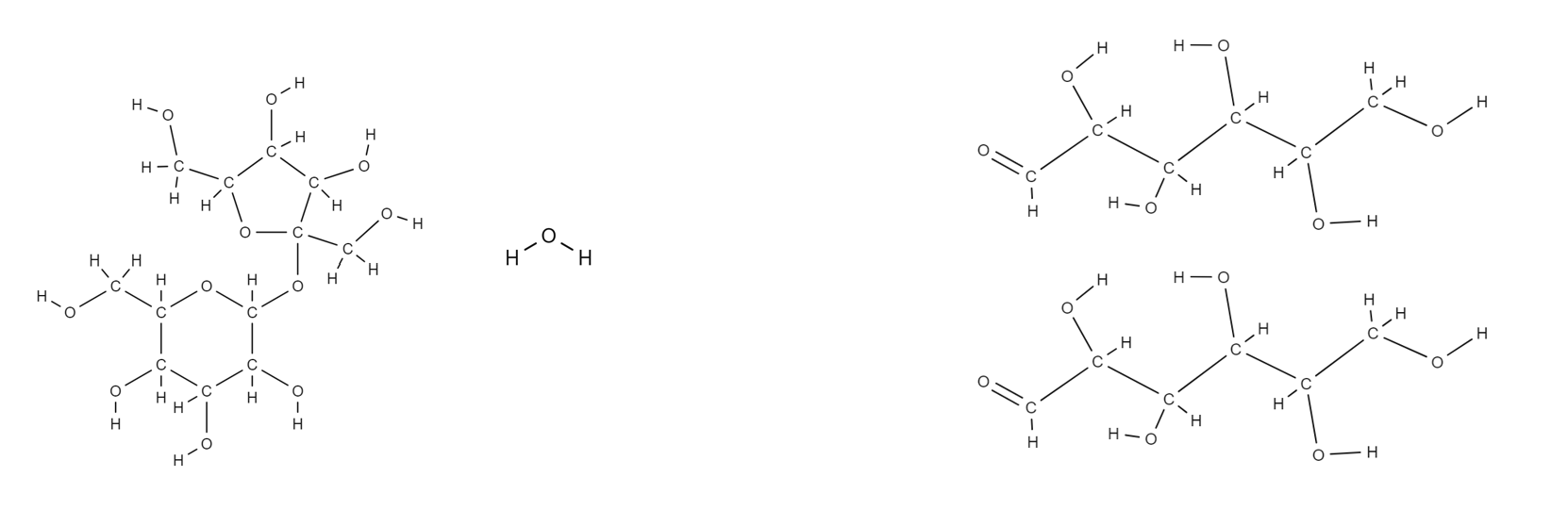
What is the the hydrolysis equation in the fermentation of biomass and draw it
C6H12O6(aq) —> (Zymase) 2C2H5OH(aq) + 2CO2(g)
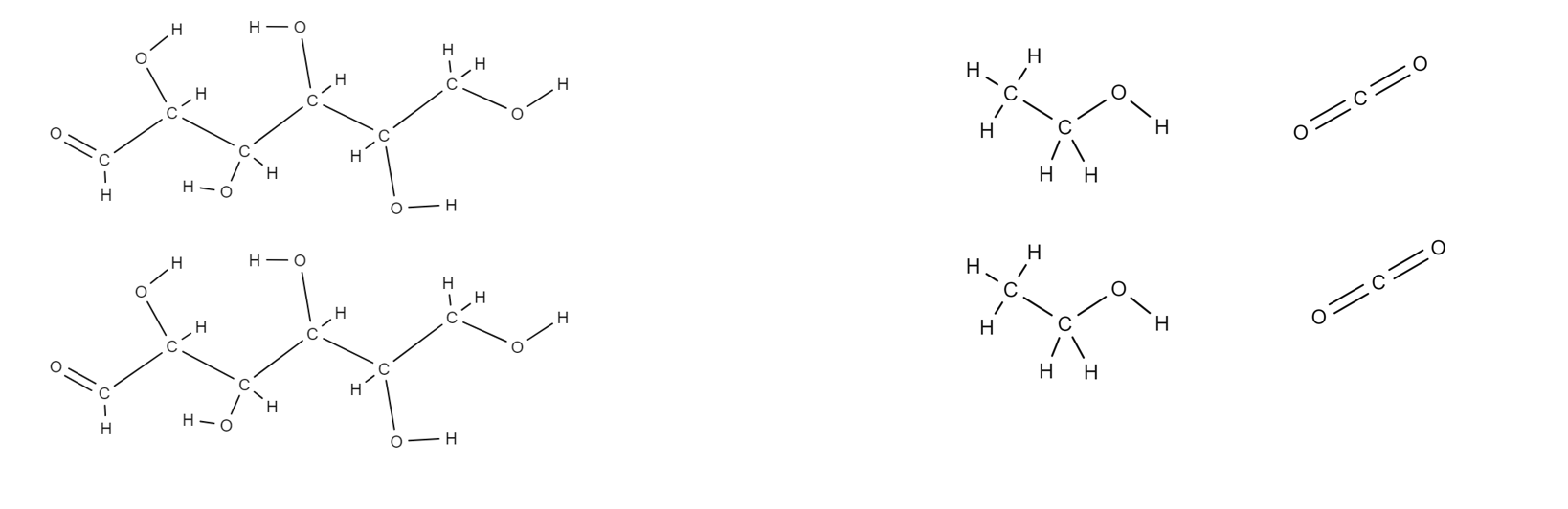
What is the overall chemical equation of the production of ethanol by fermentation of biomass
C12H22O11(aq) + H2O(l) —> (Yeast Enzyme) 4C2H5OH(aq) + 4CO2(g)
What are the reaction conditions for the production of ethanol by fermentation of biomass?
Air is excluded from the process to force the yeast to respire anaerobically so glucose is converted to ethanol
Once ethanol concentration reaches 8-14%, fermentation ceases as the ethanol poisons the yeast
Distillation is used to raise the ethanol concentration to 95%
What is a biodiesal?
A renewable biofuel derived from biological sources
It consists of a long-chain fatty acid ester and is typically made from triglycerides
What is the base-catalysed method of producing biodiesel?
A reaction of a trigylceride with an alcohol forms an estern and glycerol, and the ester formed is a biodiesel.
Before the reaction, biomass (oils or fats containing triglycerides) is pre-treated by filtering off unwanted material and treated to remove water
Sodium or potassium hydroxide used as a catalyst
What is used as the catalyst in producing biodiesel in base-catalysed method?
Sodium hydroxide is used as the catalyst as the presence of any water will lead to the formation of soap (water eliminated from water to prevent water formation)
What happens if the free fatty acids content is high?
Biomass is generally made up of triglycerides, which is glycerol (propan-1,2,3-triol or C3H8O3) and 3 fatty acid chain
However, some fatty acids are already present in their “free” form (not attached to glycerol
Free fatty acid (FFA) content needs to be kept below 4%. If its too high, it will react with NaOH catalyst and form soap instead.
Acid-catalyzed esterification (reaction with methanol using an acid catalyst) is done first
Draw the acid-catalyst pre-treatment of free fatty acids
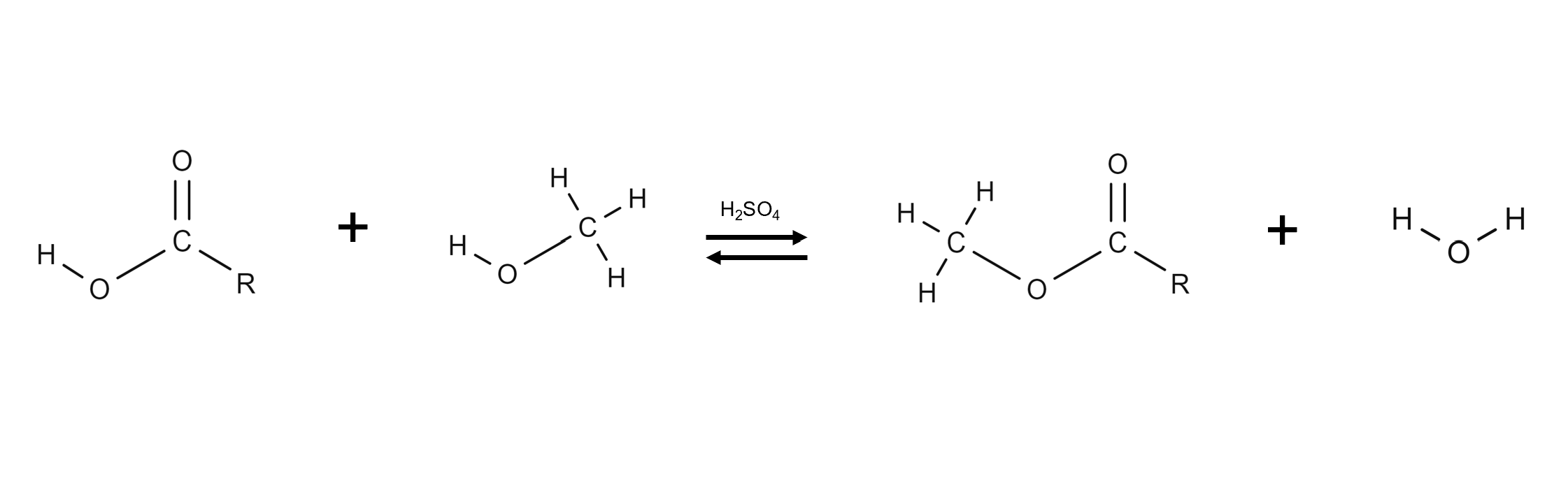
What are the requirements in base-catalysed reaction?
Sodium or potassium hydroxide catalyst
Temperature of reaction vessel kept at 60 degrees to prevent loss of methanol
Methanol reacts with triglycerides at a 3:1 ratio. However a large excess of methanol is used (>6:1) to favor high yield (up to 98%)
By-product of reaction is glycerol, which forms a separate layer.
Draw the structural formula for the base-catalysed reaction of production for biodiesel?
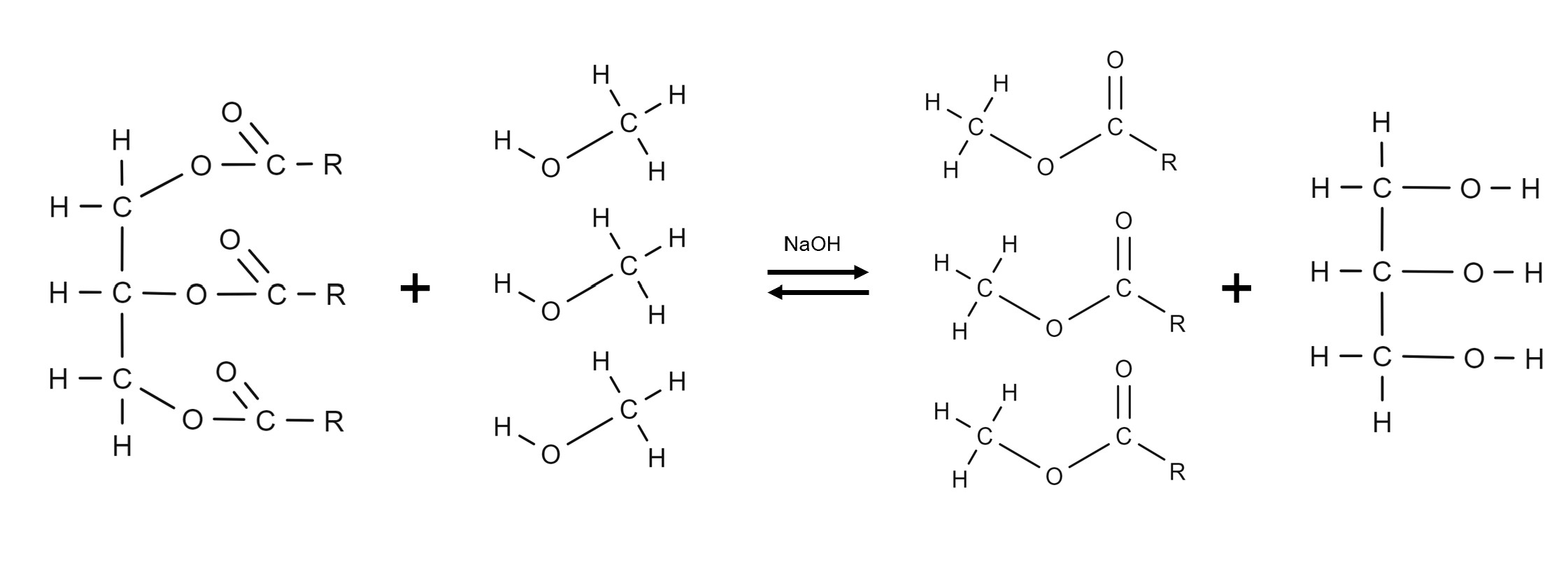
What is lipase catalysed reaction of producing biodiesel?
Method conducted the same way as the base-catalyzed reaction but lipase is used as a catalyst rathe
What are the advantages of lipase catalysed reaction producing biodiesel?
Conducted at milder temperatures and pH. Operating outside these ranges can cause denaturation of enzymes
No treatment of FFA’s needed as they’re converted simultaneously in the process
No NaOH or KOH means no formation of soap as part of the process
Because conducted at low temperature, energy demand is lower
What are some challenges in lipase catalyzed reaction?
Method sue of enzymes is very slow and higher amounts of enzyme require
Lipase catalyst fairly expensive
If methanol or glycerol conc too high, it will inhibit the activity of enzymes so methanol needs to be added gradually.
What are triglycerides?
Triglygerides are organic molecules that are the primary component of lipids, or fats and oils.
They consist of three long alkyl chains connected together using ester links.
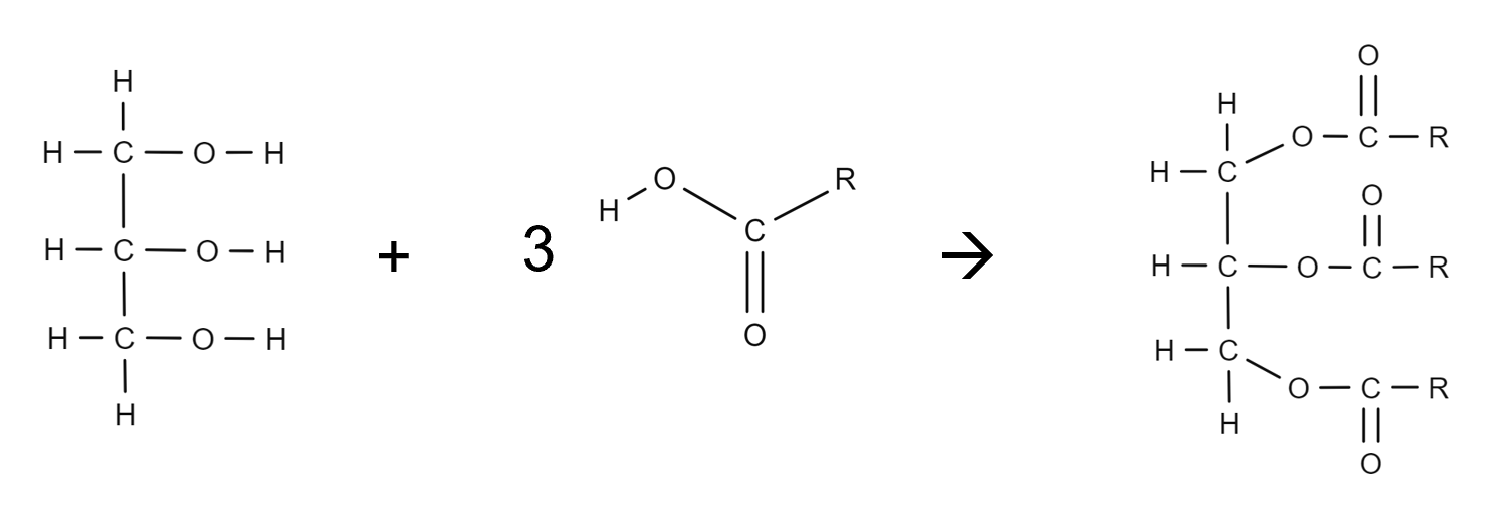
How are triglycerides formed?
•Triglycerides are formed from the reaction of fatty acids with glycerol (1,2,3-propanetriol).
•The fatty acids that are attached determine the type of fat or oil.
•They may be three of the same type or a mixture of different fatty acids.
Draw the equation for triglycerides forming
3H2O is the product
What are some examples of fatty acids?
Saturdated:
-Stearic acid
Unsaturated:
-Oleic acid
What is a fat?
A fat is a triglyceride that is a solid at room temperature.
Examples: margarine, butter, lard
What is an oil?
An oil is a triglyceride that is a liquid at room temperature.
•Examples: olive oil, canola oil, peanut oil.
What is a soap?
A soap is the salt formed from the reaction of a natural fat (triglycerides) or oil with caustic soda.
Soaps consists of a fatty acid salt, with a long non-polar carbon chain and polar carboxylate ion on the other end. The soap ion is bonded to the potassium of sodium ion, making the final structure a potassium or sodium carboxylate salt.
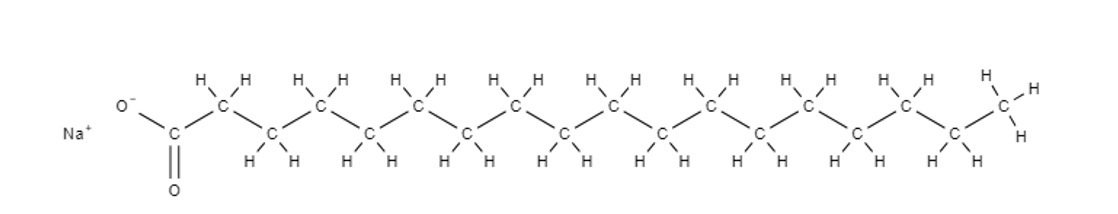
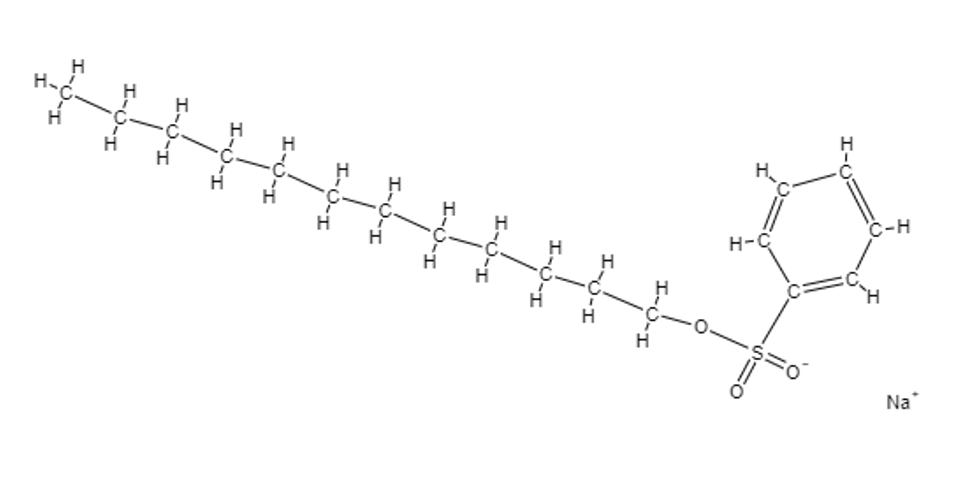
What is detergent?
A detergent is a special form of salt with a sulfonate group, which enhances the compounds properties. They can exist in liquid or powder form.
What is saponification?
The process of soaps being produced by alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils
What is the general equation for saponifcation (draw it)
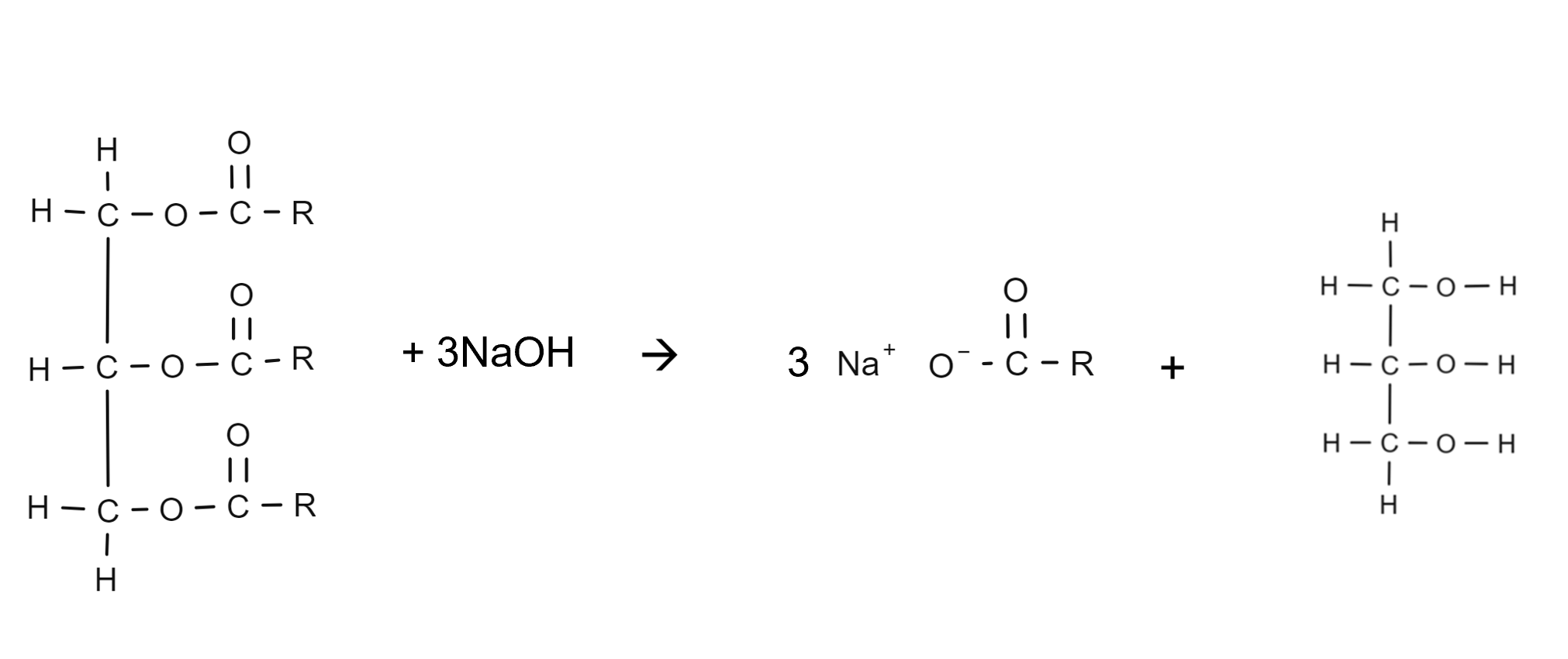
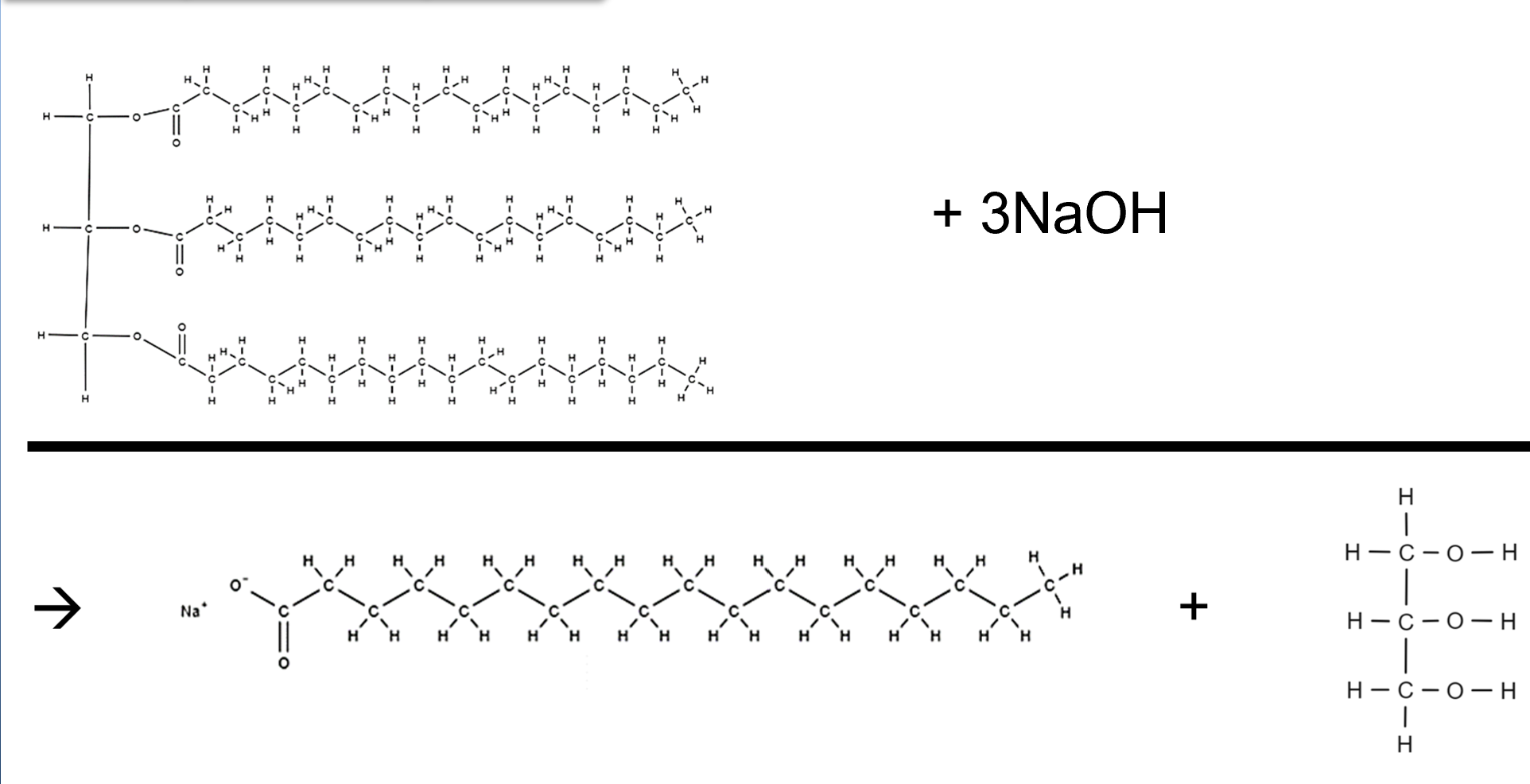
Draw the full saponification equation
What is the polar and non-polar part of a soap and detergent?
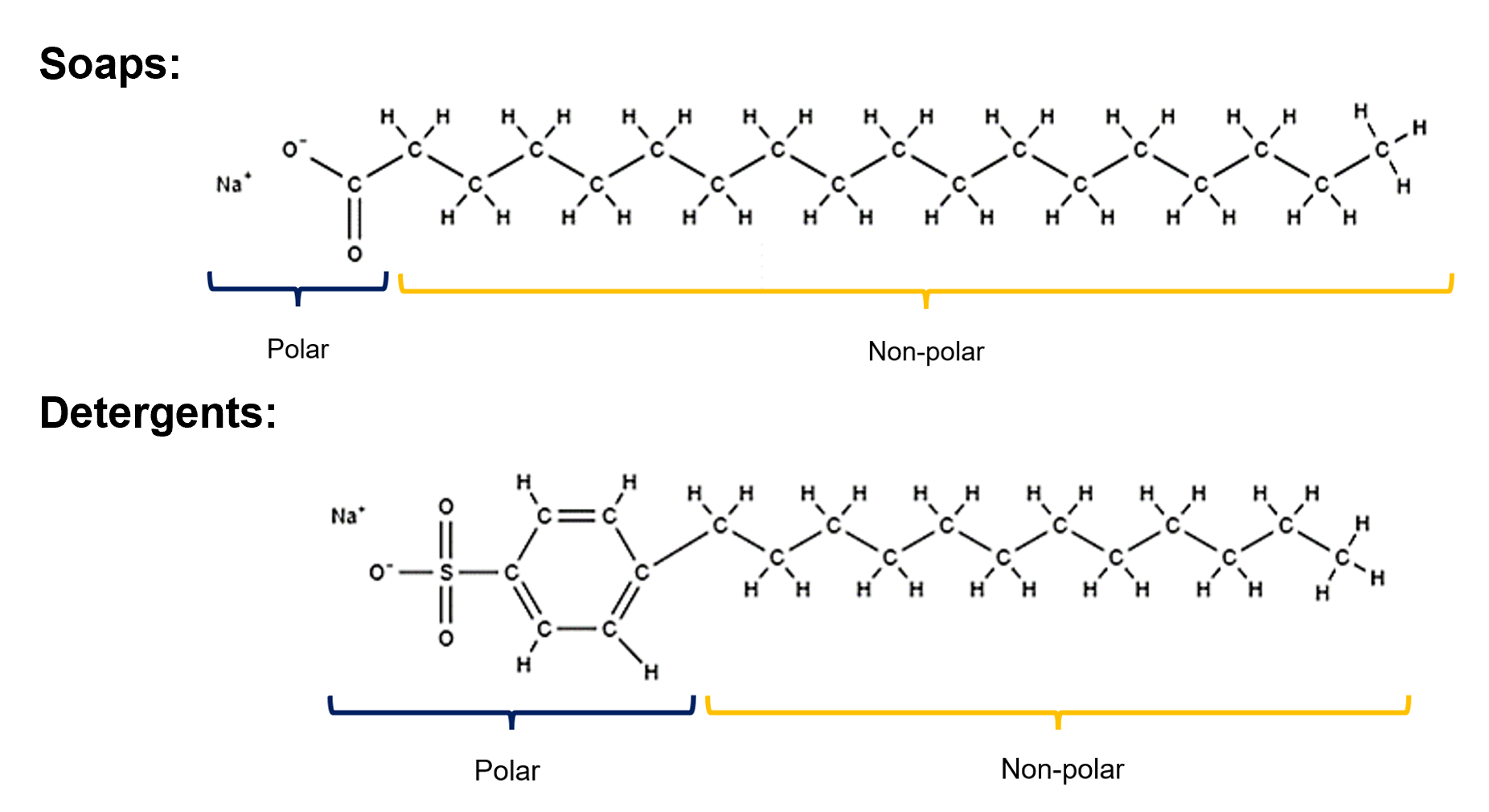
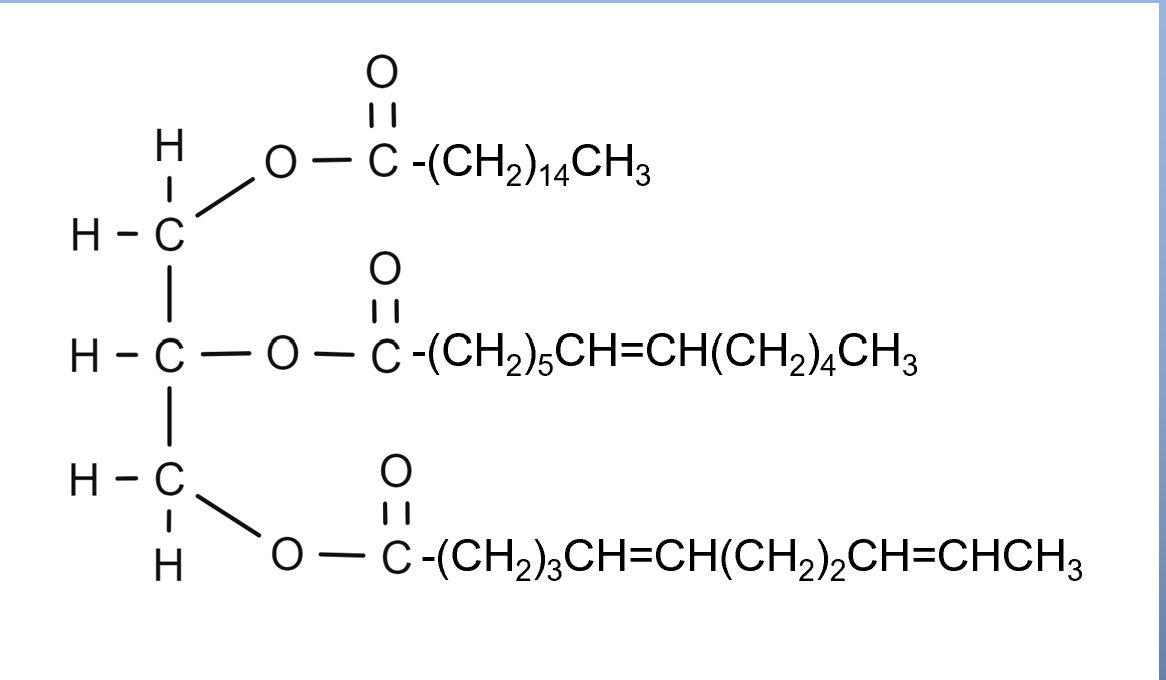
Determine the type of soap that can be made from this equation: