C2.2.1 - C2.2.7 : SL (Neural Signalling)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
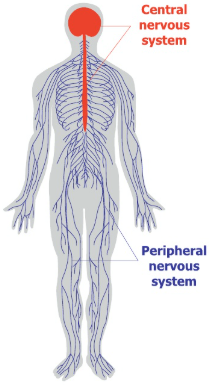
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The body’s processing center
Made up of the brain and spinal cord
Neuron
Individual cell that carries electrical impulses from one point in the body to another very quickly
Nerve
Many individual neurons grouped in a single structure
Peripheral Nerves
Made up of nerves and branches that enter and leave the spinal cord and brain stem
Sensory neurons = carry response to CNS
Motor neurons = carry response information to muscles
3 Basic Neuron Components
Dendrites
Axon
Soma
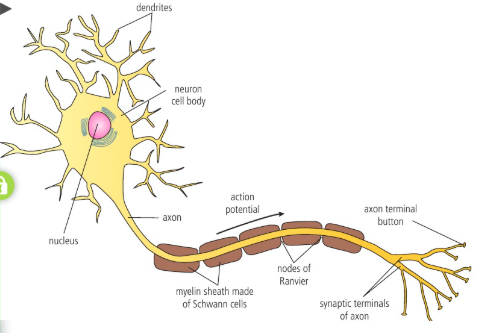
Dendrites
Short-branched fibers that convert chemical info from other neurons or receptor cells into electrical impulses
Axon
An elongated fiber that transmits the electrical signals to terminal regions for communication with other neurons or effectors
Soma
Cell body containing nucleus and organelles where essential metabolic processes occur to maintain cell survival
Synaptic terminal of axon
The end part of a neuron’s axon that releases neurotransmitters to communicate with another neuron, muscle, or gland across a synapse
Action potential
Sequence of events that allow an impulse to travel through a neuron
Polarized (neuron)
When a neuron is ready to send an impulse
→ Has a resting potential across membrane
Resting potential
Difference in charge across membrane when not firing
Created by Na+ (out) and K+ (in) through active transport (sodium-potassium pump = 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in)
→ Outside is more positive relative to inside
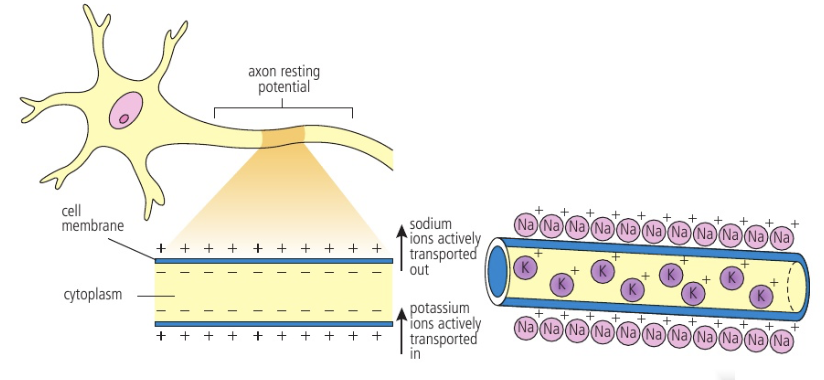
Membrane potential
Potential difference in charge across cell membrane
Myelin sheath
Collection of surrounding membrane on axon
→ One of the factors which affect speed of action potential
It speeds up nerve impulses by allowing action potentials to “jump” from one node of Ranvier to another, skipping the long process of ion movement under insulated myelin
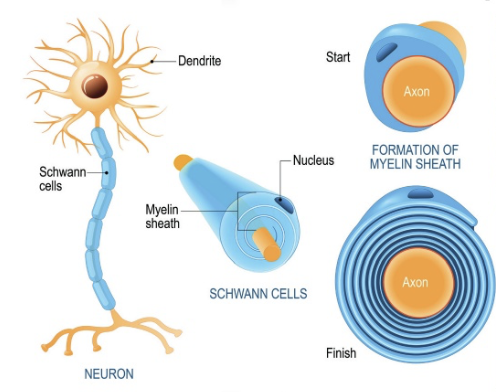
Schwann cells
Cells that wrap themselves around nerve fiber (axon) and acts as insulators
There is no ion movement when axon is covered
Nodes of Ranvier
Small, even gaps between Schwann cell

Synapses
Physical gaps that separate neurons from other cells
→ neurons align, so that synaptic terminals are next to dendrites of another neuron
Neurotransmitter
Chemicals that allow neurons to communicate
Always released from synaptic terminal buttons of first neuron → results in the continuation of the impulse when neurotransmitter is received by dendrites of the second neuron
Presynaptic neuron
Neuron that releases neurotransmitter
Postsynaptic neuron
Neuron receiving neurotransmitter
Synaptic cleft
Very small gap (20nm) between two neurons
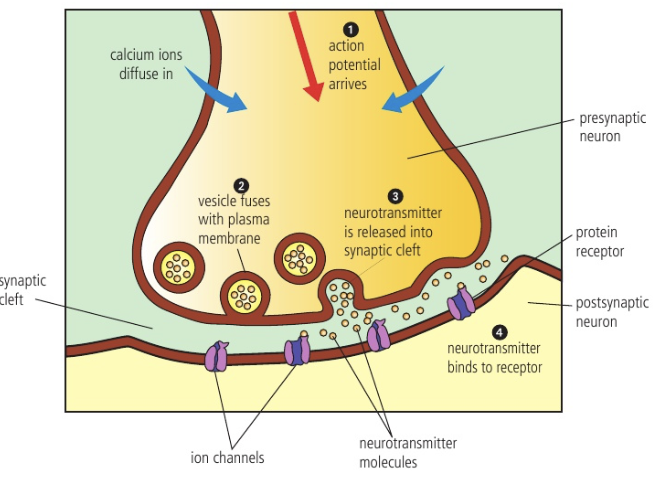
Neurotransmission process steps
Action potential reaches axon terminal → opens voltage-gated calcium channels (depolarization of presynaptic membrane and uptake of Ca2+ into terminal)
Ca2+ acts as a signaling chemical → makes vesicles with neurotransmitters, move to the presynaptic membrane and fuse
Neurotransmitter is released from vesicles into the synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitter binds to protein receptor on postsynaptic membrane
Binding opens ion channels → Na+ diffuse through
This starts action potential → causes electrical signal (depolarization)
Neurotransmitter on protein receptor is released back → the grades and synaptic cleft by enzymes (into two or more fragments)
Ion channel in postsynaptic membrane closes to Na+
Neurotransmitter fragments diffuse back across synaptic cleft → reassembled in terminal buttons of presynaptic neuron
Acetylcholine
Common neurotransmitter found at synapses between two neurons or between a neuron and a muscle cell (neuromuscular junction)
→ causes muscle to contract
Acetylcholinesterase
Enzyme in synaptic cleft and breaks down acetylcholine in fragments
Allows for the transmission of the action potential to only happen once