Session 10: The Pre-embryonic Period and Gastrulation
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Embryogenesis lasts how many weeks
8 weeks
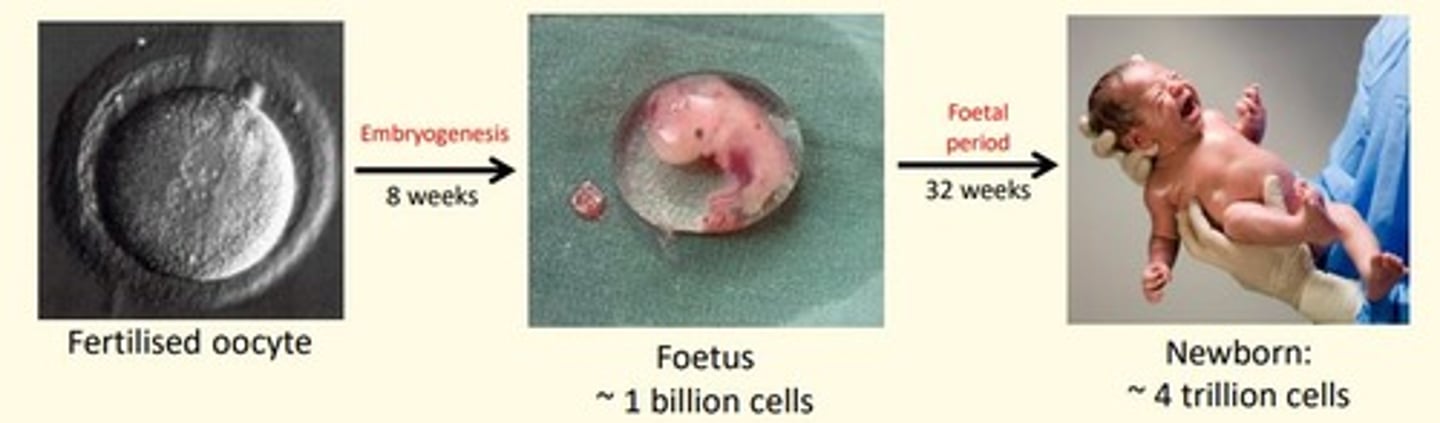
Foetal period lasts how many weeks
32 weeks
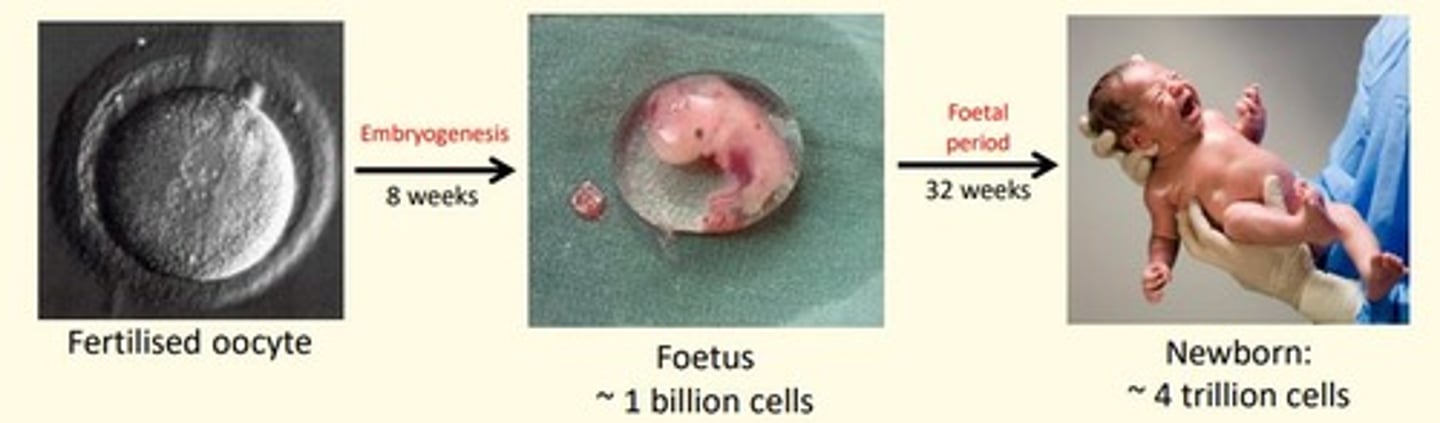
Average gestation period in humans is ___ weeks
40 weeks
- First 8 weeks = embryogenesis
- Week 9-40 = foetal period
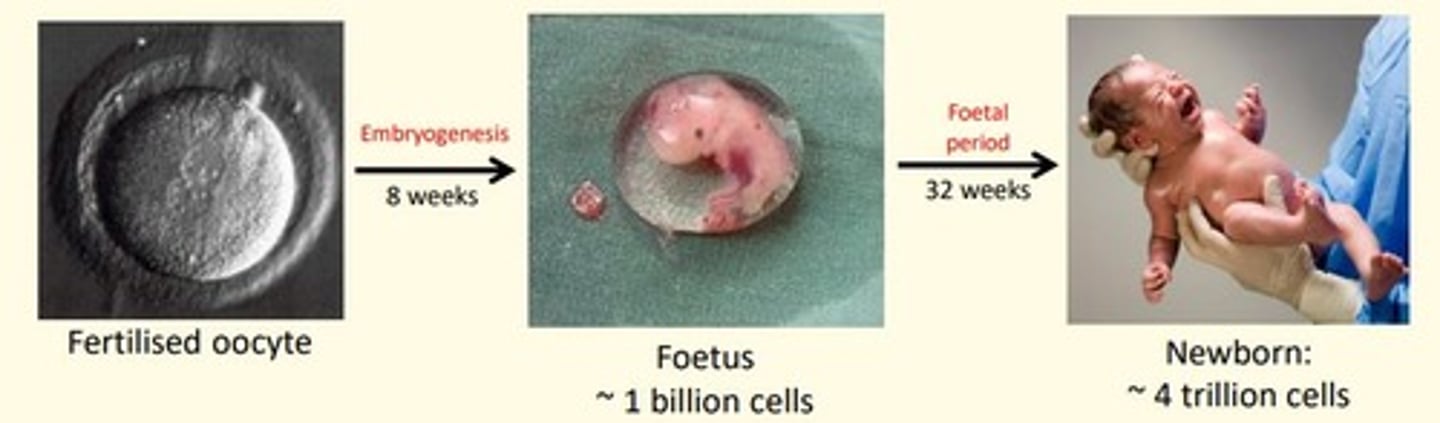
First trimester
0-12 weeks
What is spermatogenesis triggered by?
Testosterone produced by Leydig cells of testis during puberty
Testosterone is produced by what cells?
Leydig cells of testis
Testosterone production is under the control of what hormone?
Pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH)
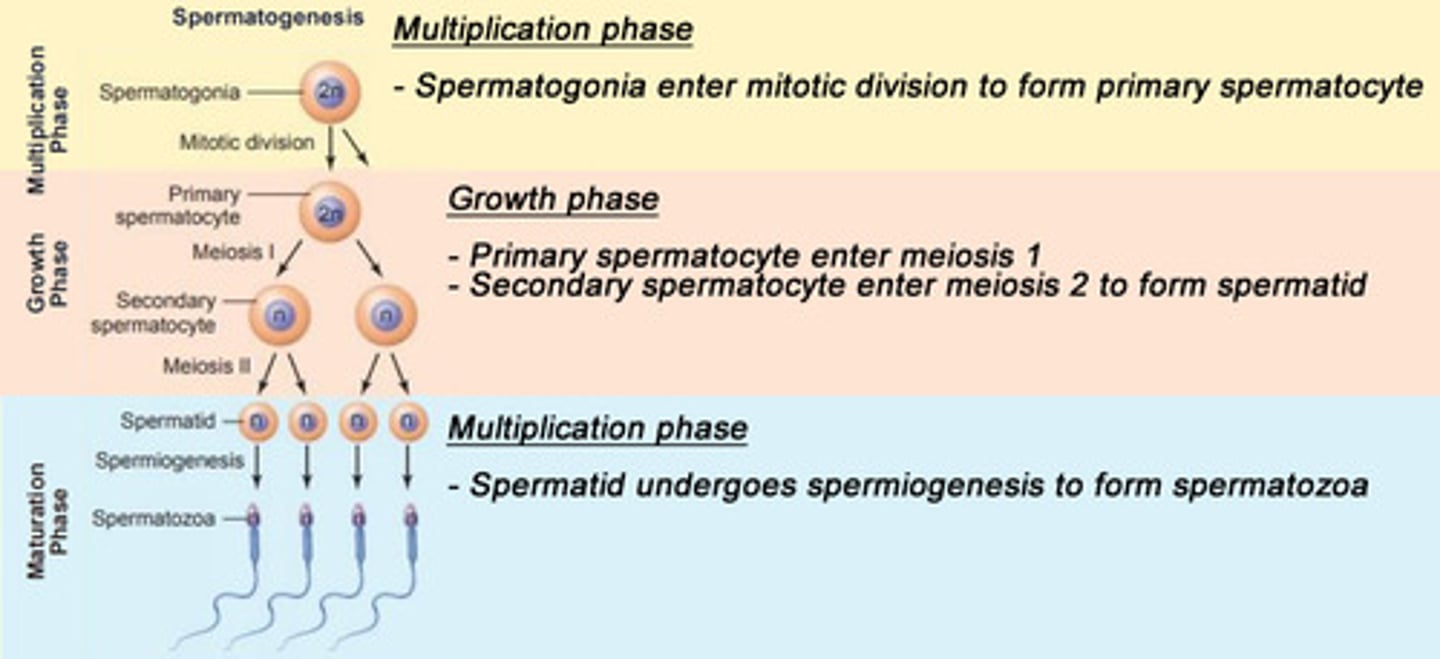
Spermatogenesis process
1) Multiplication Phase
- Spermatogonia enter mitotic division to form primary spermatocyte
2) Growth Phase
- Primary spermatocyte enters meiosis 1
- Secondary spermatocyte enters meiosis 2 to form spermatid
3) Maturation Phase
- Spermatid undergoes spermiogenesis to form spermatozoa
Spermatogonia → primary spermatocyte → secondary spermatocyte → spermatid → spermatozoa
Oogenesis process
Foetal Life
- Oogonia enter mitotic division to form primary oocyte
- Primary oocyte enters meiosis 1
- Primary oocytes arrest at prophase 1 stage of meiosis 1 until puberty (beginning of menstrual cycle)
Beginning of Menstrual Cycle
- Primary oocyte becomes a secondary oocyte
- Secondary oocyte arrests at metaphase 2 of meiosis 2 until fertilisation occurs
Fertilisation
- Secondary oocyte undergoes completion of meiosis 2 to form an Ovum
Oogonia → primary oocyte → secondary oocyte → ovum

Primary oocytes arrest at what stage of meiosis 1 until beginning of menstrual cycle?
Prophase 1
Secondary oocytes arrest at what stage of meiosis 2 until fertilization takes place?
Metaphase 2
Sperm vs Ovum
Sperm
- 55µm (smaller)
- Motile (tail)
- Acrosome head full of enzymes for penetrating ovum
- Lots of mitochondria for energy (motility of sperm tail)
Ovum
- Larger (~0.1 mm) - largest cell in human body
- Immotile
- Two protective membranes = corona radiata (outermost) and zona pellucida (innermost)
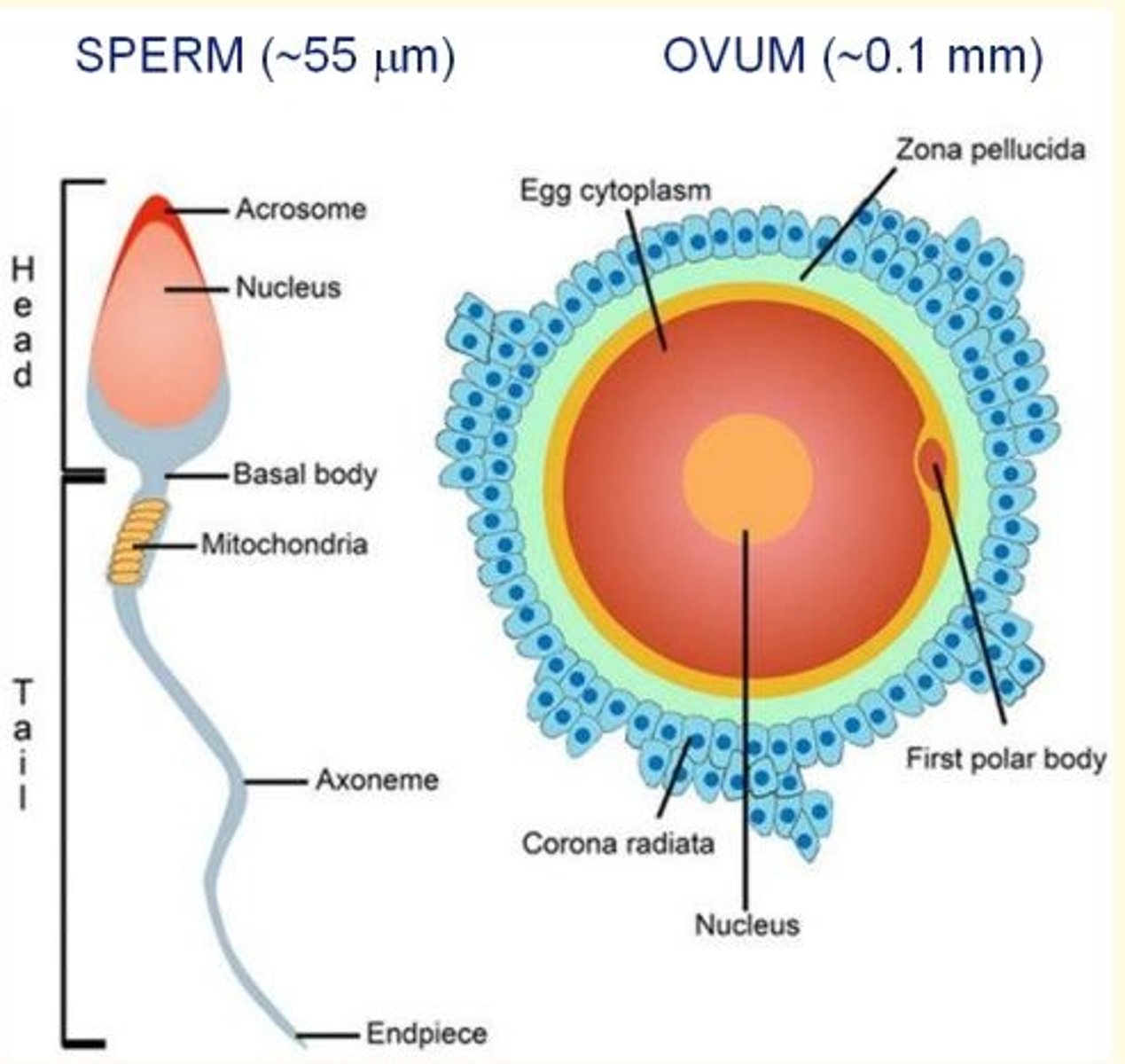
First (outer) protective membrane of the ovum
Corona radiata - follicular cells
Zona pellucida is made of ___
proteoglycans
Second (inner) protective membrane of the ovum
Zona pellucida - proteoglycans
Corona radiata is made up of ___ cells
follicular
Fertilisation
Fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote
In order to fertilise the egg, the sperm must undergo ___
Capacitation
This is a conditioning process where glycoprotein coat and seminal plasma proteins (from sperm membrane) are removed - this exposes the acrosome (enzymes) allowing penetration of ovum to take place
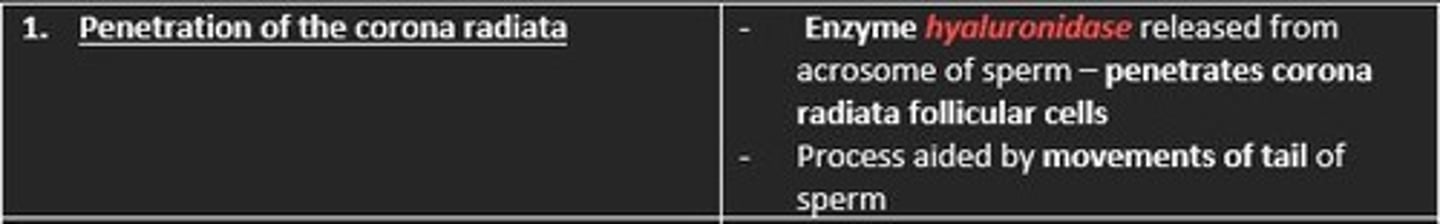
Describe the first phase of fertilisation
Penetration of the corona radiata
The enzyme hyaluronidase released from acrosome of sperm penetrates the corona radiata (outermost membrane of ovum) which is made of follicular cells
This process is aided by movements of the tail of the sperm
Describe the second phase of fertilisation
Penetration of the zona pellucida
Acrosome reaction
Release of proteolytic enzymes including acrosin that causes lysis of the zona pellucida (innermost membrane of ovum)
This allows sperm to come into contact with ovum plasma membrane

Describe the third phase of fertilisation
Fusion of the plasma membrane of ovum and sperm
Zona reaction
The fusion of plasma membrane of ovum and sperm leads to the hardening of zona pellucida
This hardening prevents other sperm from entering ovum

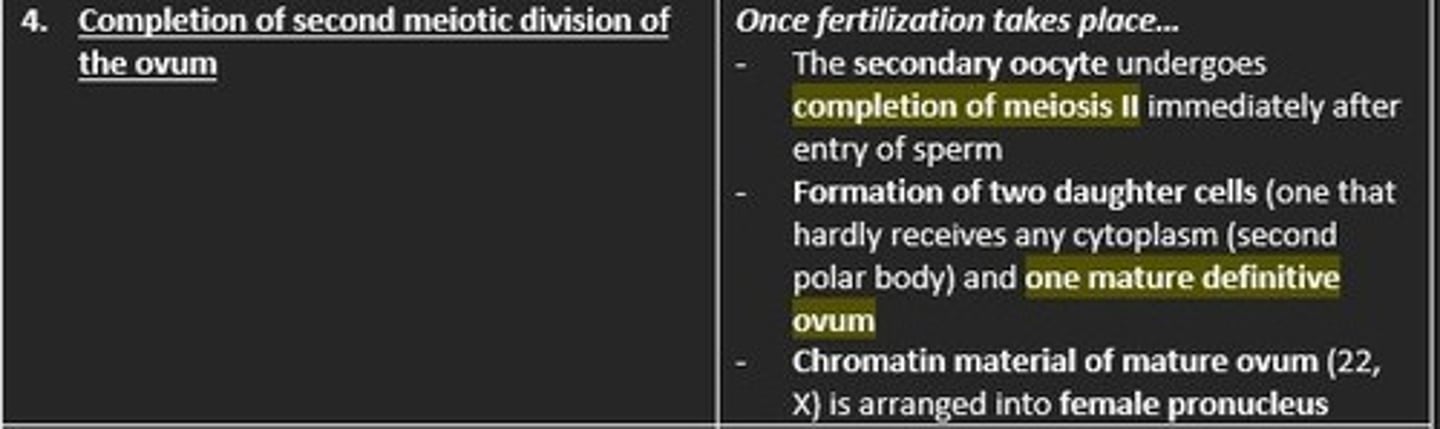
Describe the fourth phase of fertilisation
Completion of second meiotic division of the ovum
Secondary oocyte undergoes completion of Meiosis 2
Formation of two daughter cells which include = second polar body (hardly receives cytoplasm) and one mature definitive ovum
Chromatin material of the mature ovum (22, X) is arranged into the female pronucleus
Describe the fifth phase of fertilisation
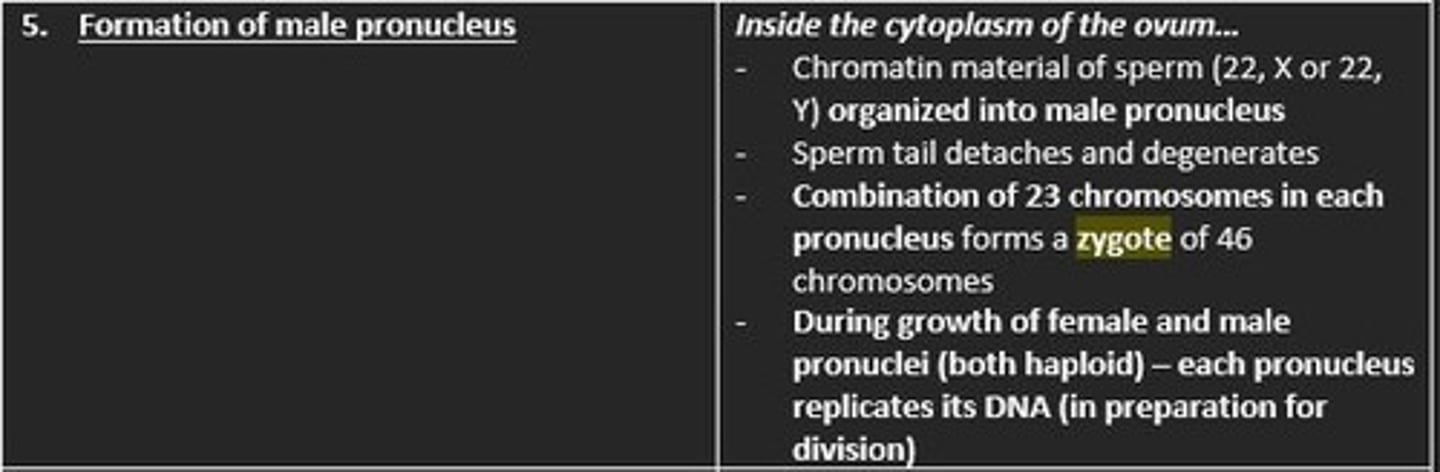
Formation of the male pronucleus
Chromatin material of the sperm is organised into the male pronucleus
Sperm tail detaches, degenerates
Combination of 23 chromosomes in each pronucleus forms a zygote of 46 chromosomes
DNA replication occurs in each pronucleus - in preparation for division of zygote
Describe the sixth and final phase of fertilisation
Metabolic activation of the ovum
Breakdown of pronuclear membranes and the mixing of maternal and paternal chromosomes
Chromosomes organised onto a spindle in preparation for normal mitotic division

The first cleavage of the zygote occurs roughly ___ hours after fertilisation
30
Labelled diagram showing the second polar body which disappears slowly

What are the consequences of fertilisation process?
Describe four consequences
1) Secondary oocyte completes meiosis 2 producing a second polar body
2) Restoration of normal diploid number of chromosomes (2n = 46 chromosomes) in zygote
3) Variation in human species through mingling of paternal and maternal chromosomes - fertilisation is RANDOM!
4) Determination of the chromosomal sex of the embryo
Dizygotic twins
Fraternal twins
These siblings result from two separately fertilized eggs
Two separate placentas
Different genetic material (non-identical)
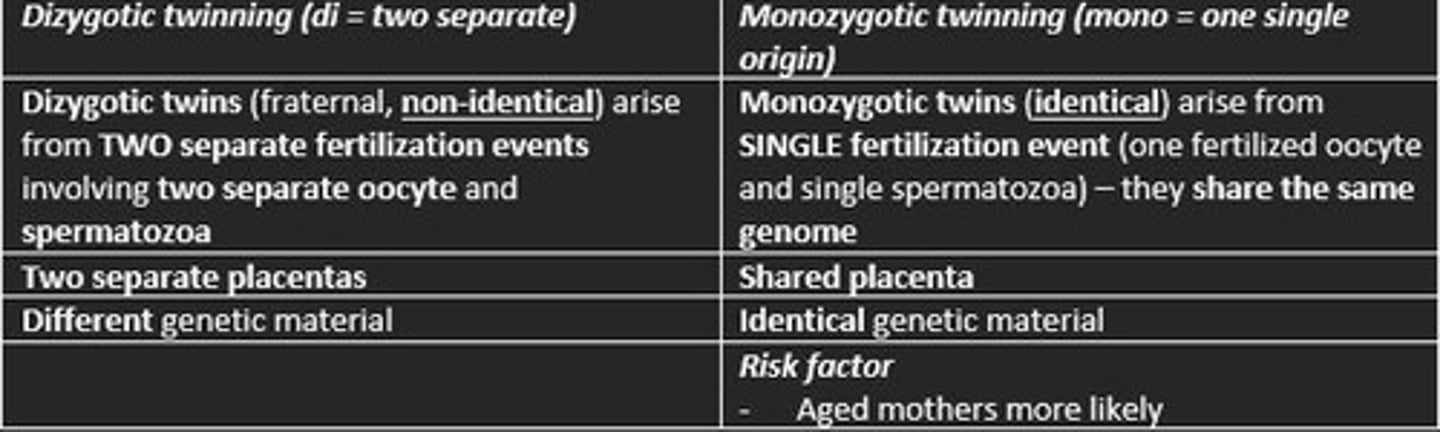
Monozygotic twins
Identical twins
These arise from single fertilisation event
Shared placenta
Identical genetic material
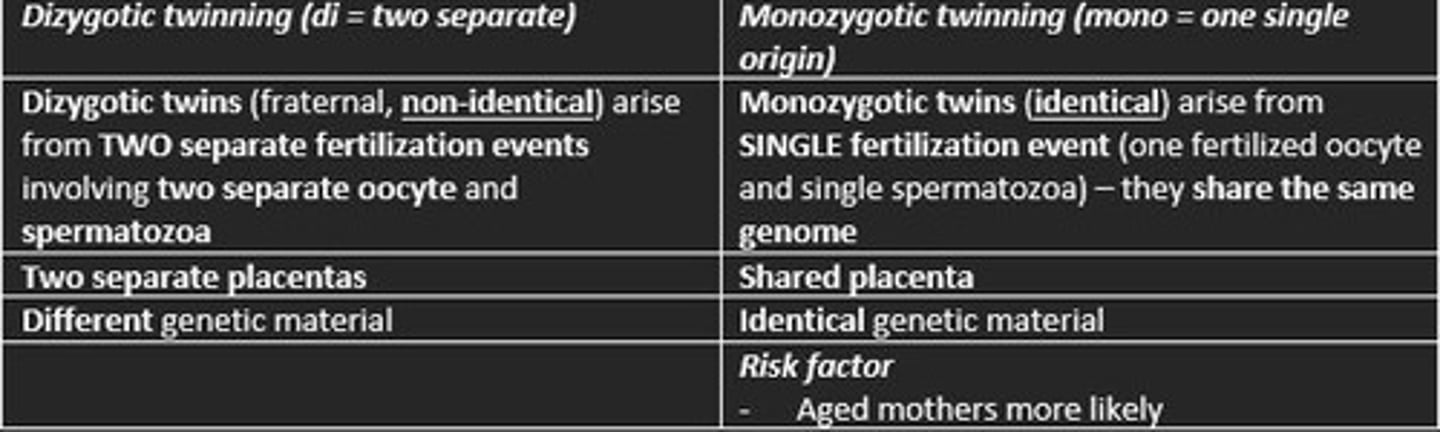
Risk factor in mothers for monozygotic twins
Older mothers (ageing)
What is the cleavage process of the zygote?
Series of repeated mitotic divisions of the zygote which features a rapid increase in the number of blastomere cells (totipotent cells)
After the ___ cleavage of the zygote = the compaction process takes place
After the third cleavage of the zyogte = the compaction process takes place
Compaction of a zygote
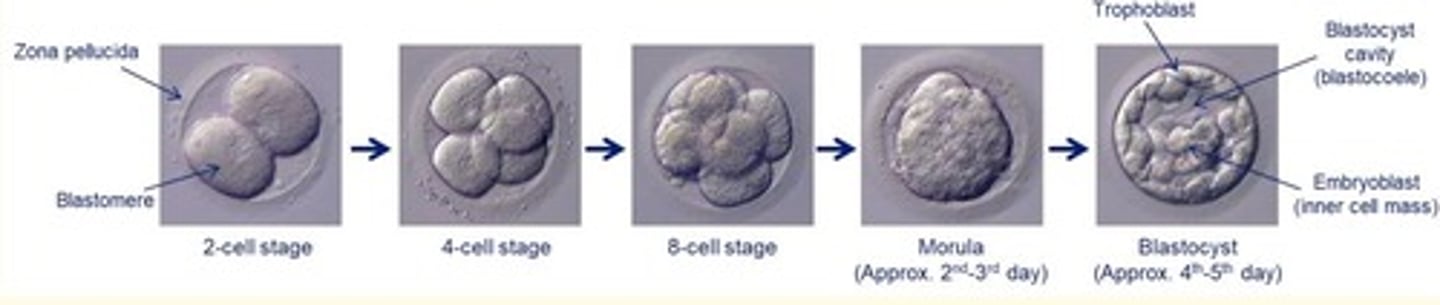
Three days after fertilisation - what is the name of the structure formed from dividing zygote?
16-cell morula
In the morula - all cells are the SAME and undifferentiated
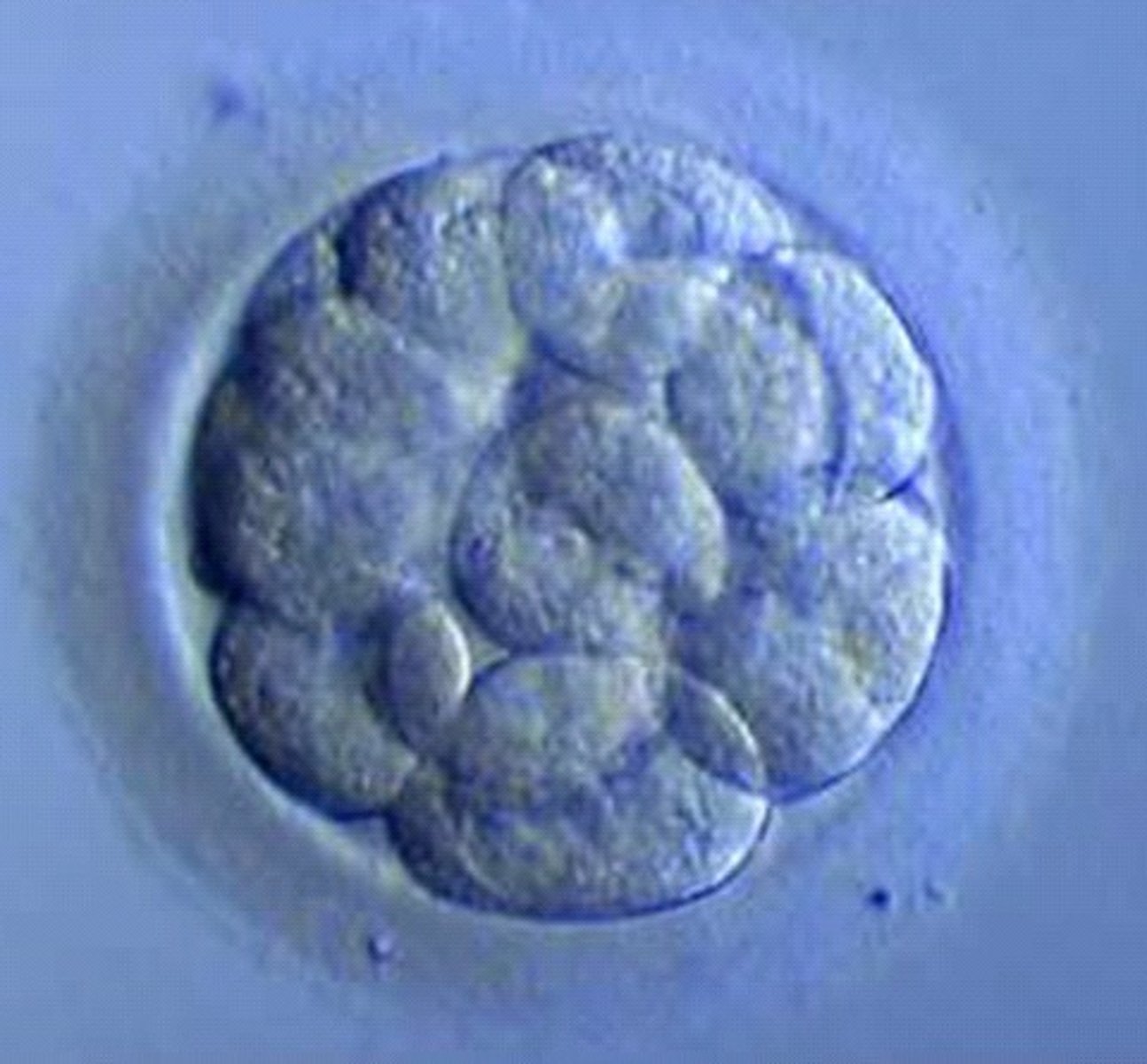
Four days after fertilisation - what is the name of the structure formed from dividing zygote?
Blastocyst
In the blasocyst, cells are not the same - they are differentiated
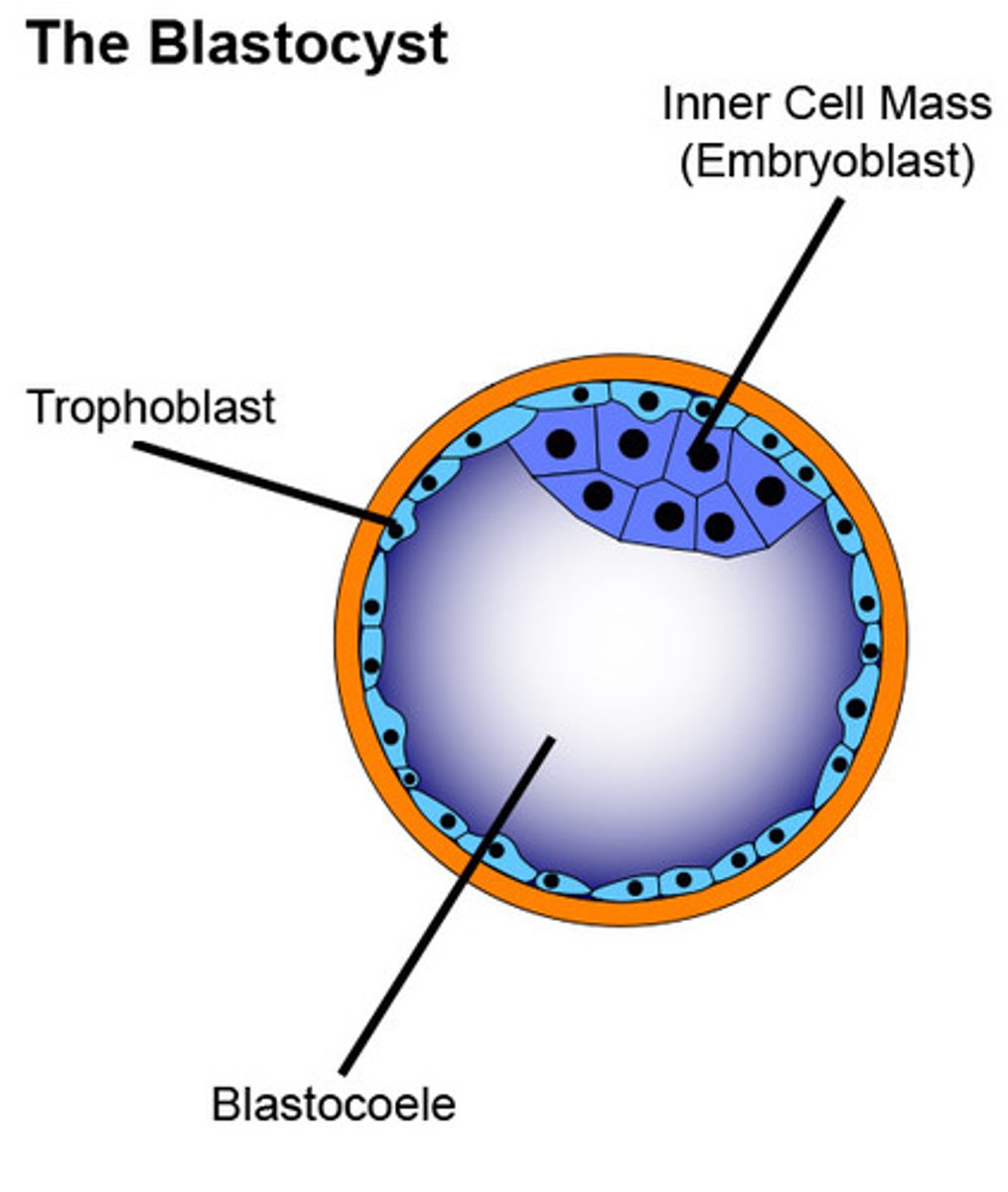
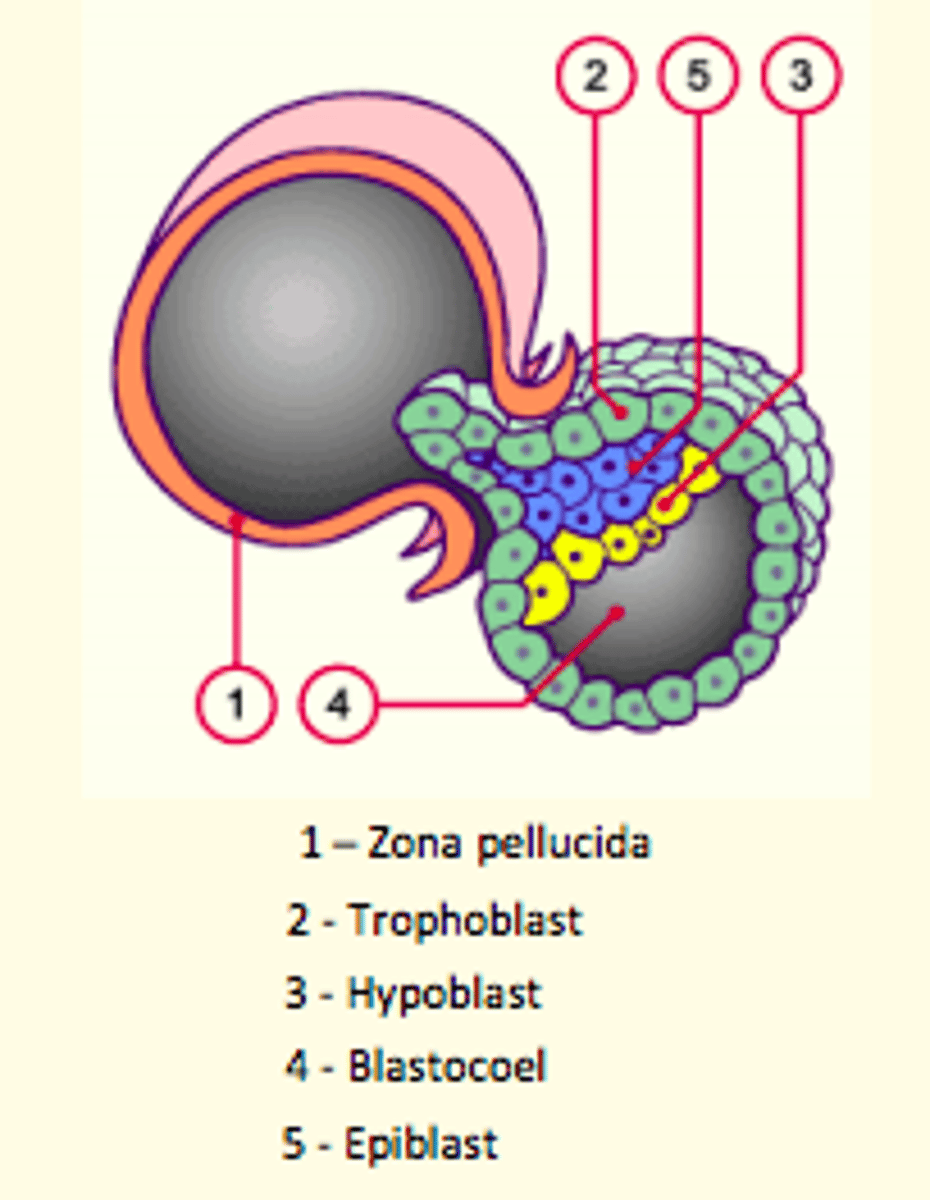
Structure of a blastocyst
- Outer = trophoblast surrounding embryo
- Inside cavity = blastocoele
- Inner cell mass (ICM) = give rise to embryo (embryoblast)
The inner cell mass (ICM) is where stem cells are extracted. These embryonic stem cells are ___
Pluripotent
Pluripotent
Able to give rise to multiple, but not all, cell types.
Embryo hatching
5 days after fertilisation
Embryo liberates itself from the zona pellucida shell, leaving it behind
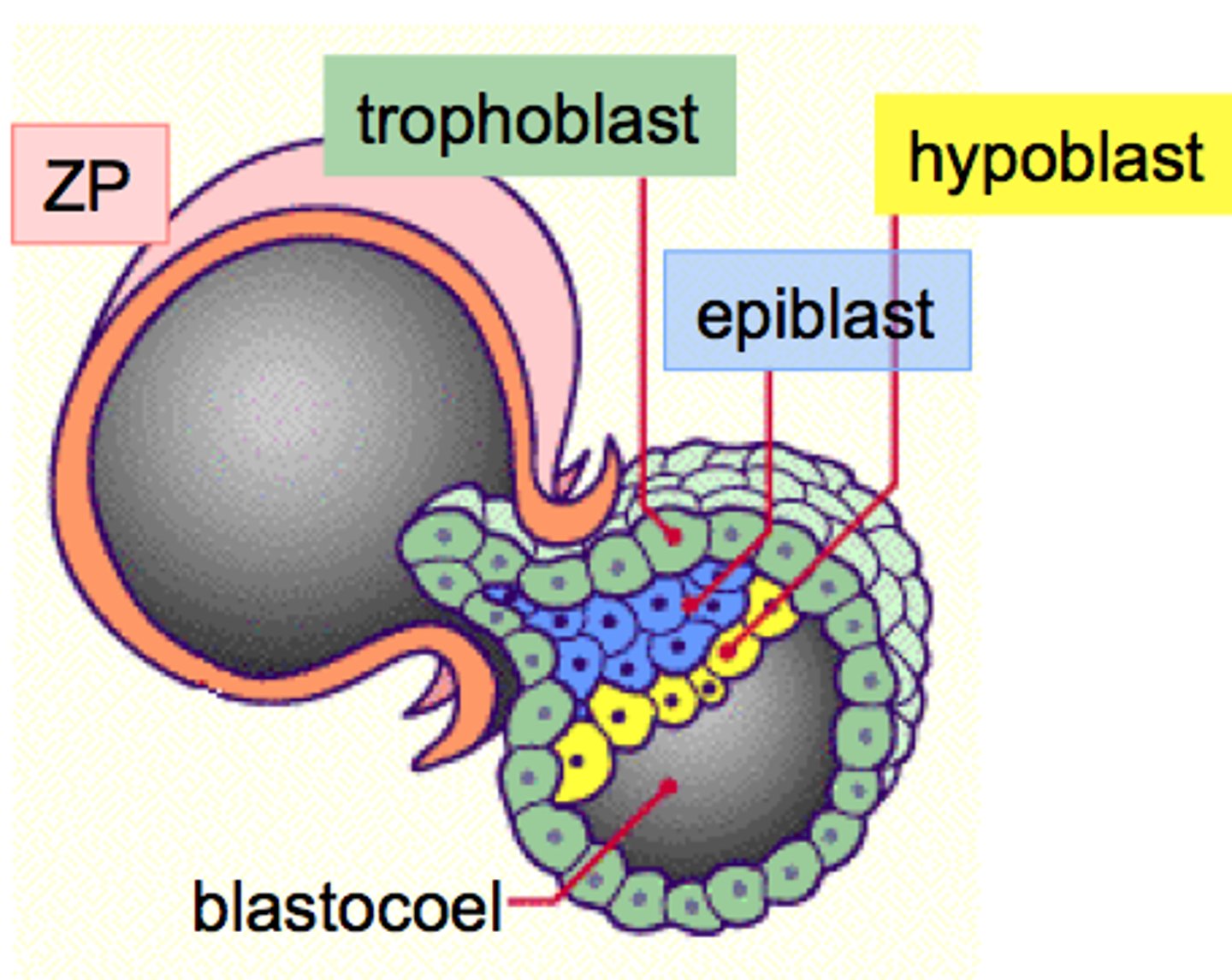
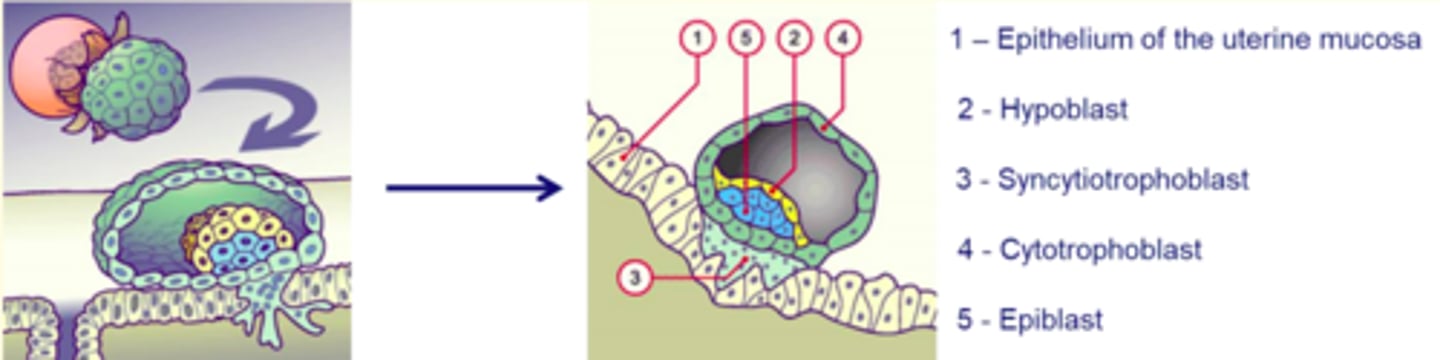
Implantation of the embryo
6 days after fertilisation
- The hatched blastocyst attaches itself to the endometrial epithelium (decidua)
- Trophoblast outer layer rapidly proliferates and differentiates into = cytotrophoblasts and synctiotrophoblasts
Synctiotrophoblasts erode maternal endometrium, enabling embryo to burrow and implant securely
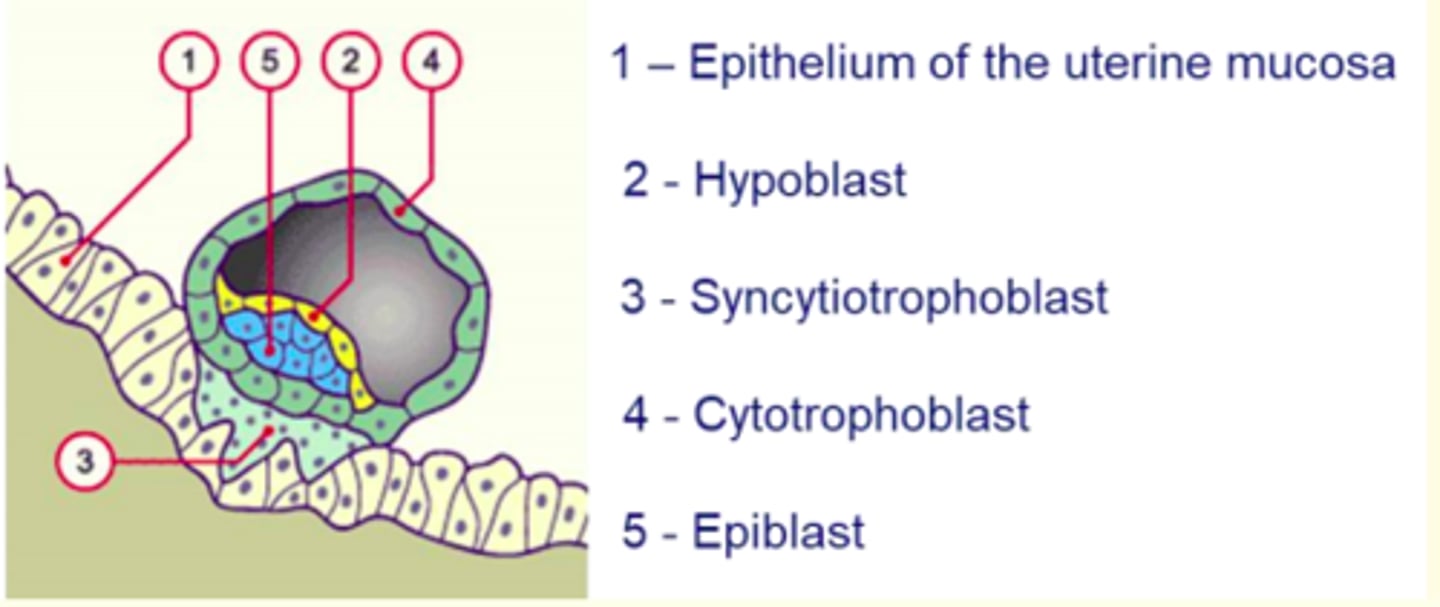
What feature of synctiotrophoblasts allow them to burrow into the maternal endometrium?
Synctiotrophoblasts produce proteolytic enzymes that erode the maternal tissue which enables the embryo to burrow and implant securely into the endometrium
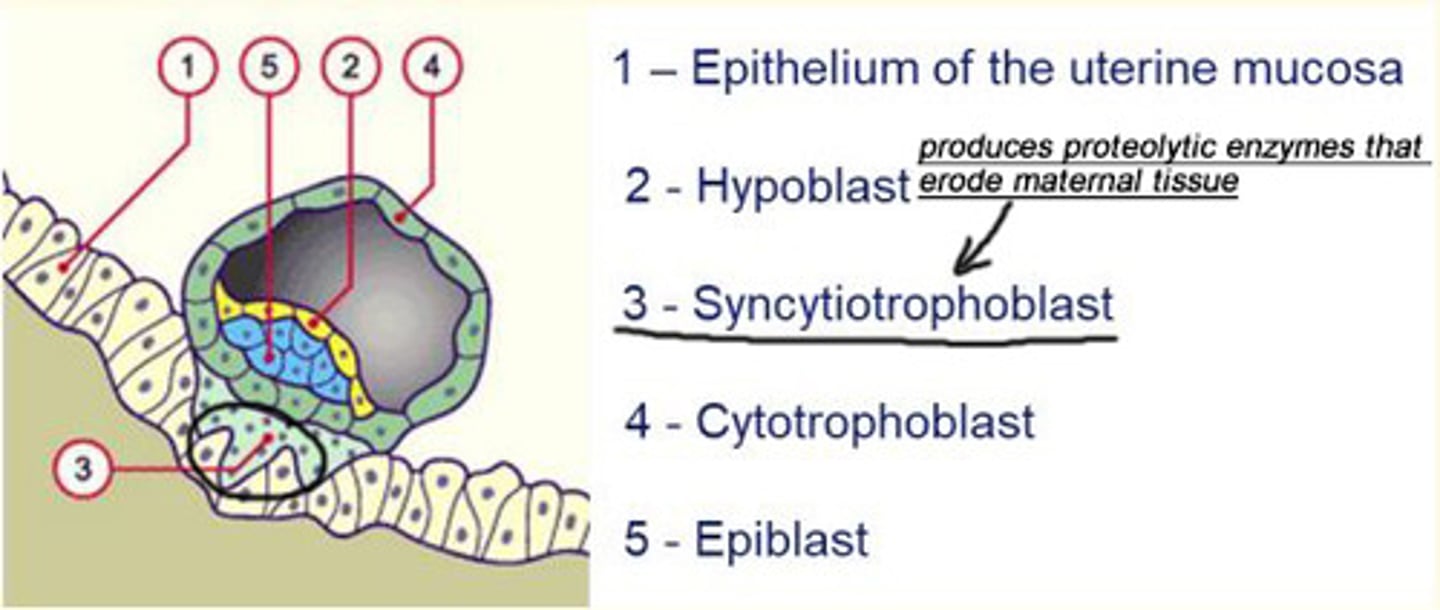
The second week post-fertilisation is characterised by the formation of what structure?
Formation of the bi-laminar embryonic disc
- Differentiation of the inner cell mass (ICM) into flat, bilaminar embryonic disc consisting of epiblast and hypoblast cells
Epiblast eventually gives rise to the...
embryo
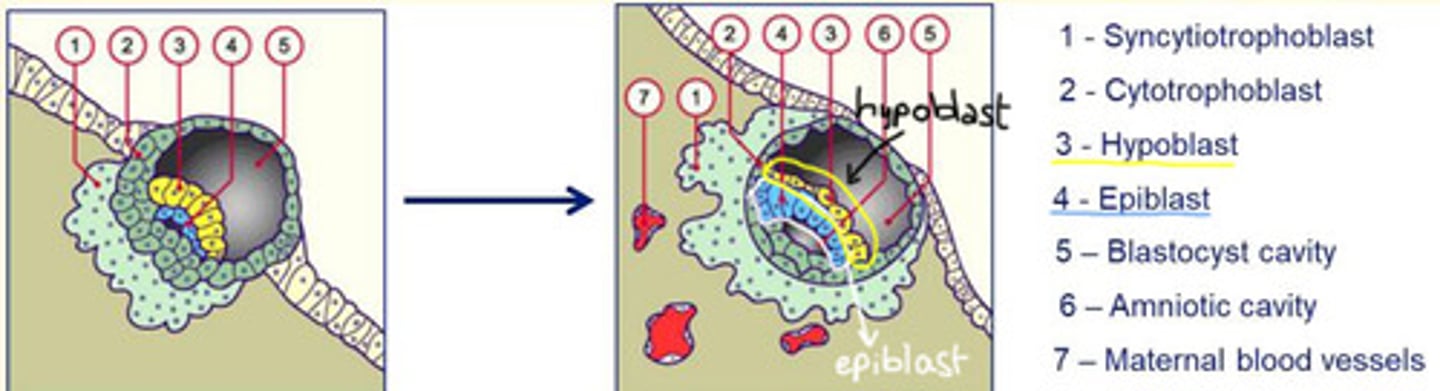
Day 9-10 post-fertilisation
Implantation continues with the formation of a ___ plug.
The appearance of vacuoles in the synctiotrophoblasts join to form ___.
These ___ soon reach capillaries of maternal tissue and become filled with blood, allowing for the exchange of nutrients/gases.
Amnioblast cells separate from the epiblast and organise to form the ___ (a thin membrane that encloses the amniotic cavity).
Hypoblast cells proliferate to form the primary ___ sac.
Day 9-10 post-fertilisation
Implantation continues with the formation of a fibrin plug.
The appearance of vacuoles in the synctiotrophoblasts join to form lacunae.
These lacunae soon reach capillaries of maternal tissue and become filled with blood, allowing for the exchange of nutrients/gases.
Amnioblast cells separate from the epiblast and organise to form the amnion (a thin membrane that encloses the amniotic cavity).
Hypoblast cells proliferate to form the primary yolk sac.
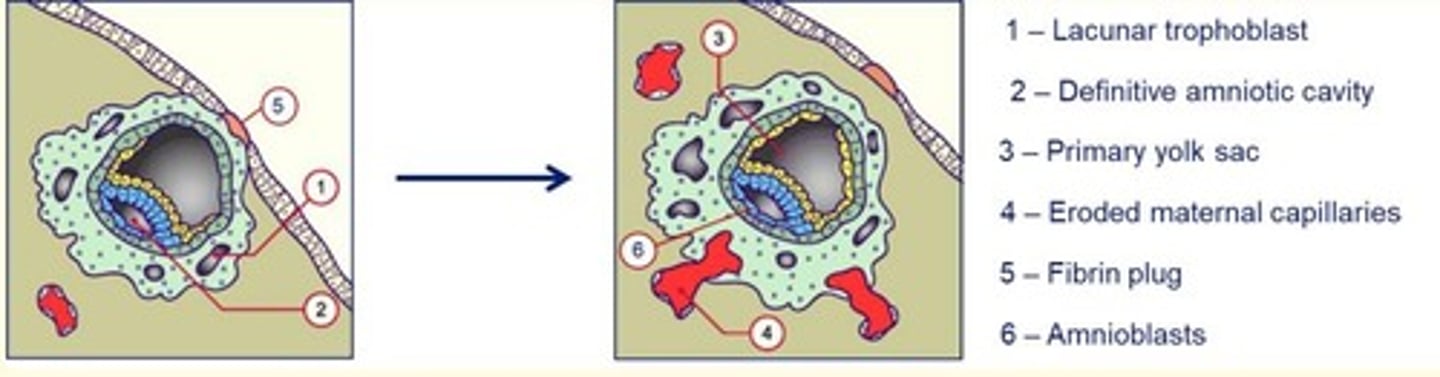
Day 11-13 post-fertilisation
The hypoblast gives rise to extraembryonic ___ which splits to form the ___ cavity.
Transformation of the primary yolk sac to the ___ yolk sac.
Beginning of utero-placental circulation occurs as the lacunae fill with maternal blood.
Day 11-13 post-fertilisation
The hypoblast gives rise to extraembryonic mesoderm which splits to form the chorionic cavity.
Transformation of the primary yolk sac to the secondary yolk sac.
Beginning of utero-placental circulation occurs as the lacunae fill with maternal blood.
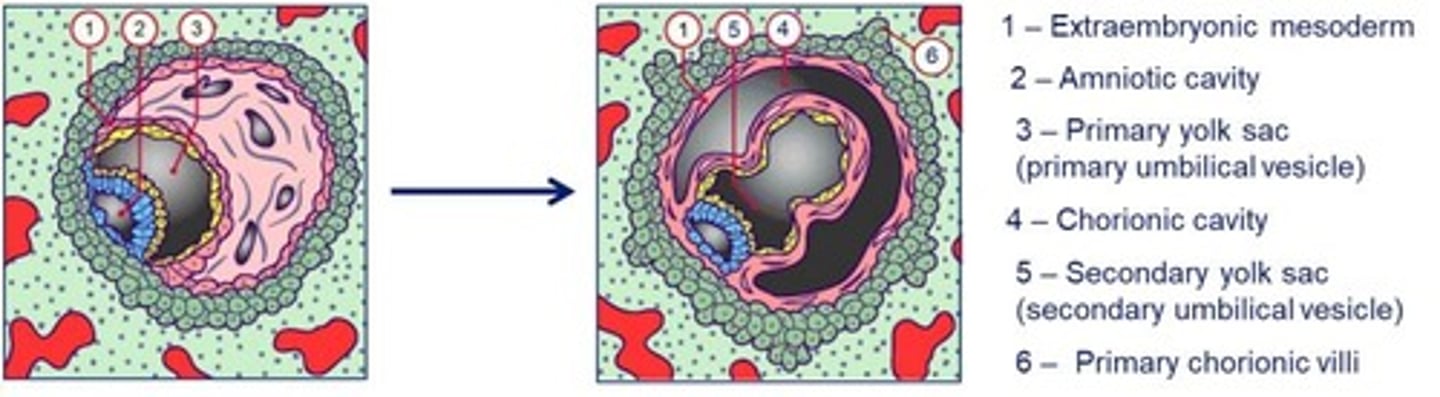
The chorion eventually gives rise to the fetal part of the ___
placenta
WEEK 2
The hypoblast becomes...

WEEK 2
The epiblast becomes...

Name two abnormalities that can occur during week two post-fertilisation in the developing embryo
Ectopic pregnancy
- Abnormal implantation (uterine tube or outside uterus)
Molar pregnancy (Hydatidiform Mole)
- Occurs when only the trophoblast layers of embryo proliferate and epiblast layer FAILS to proliferate. No embryo forms as a result

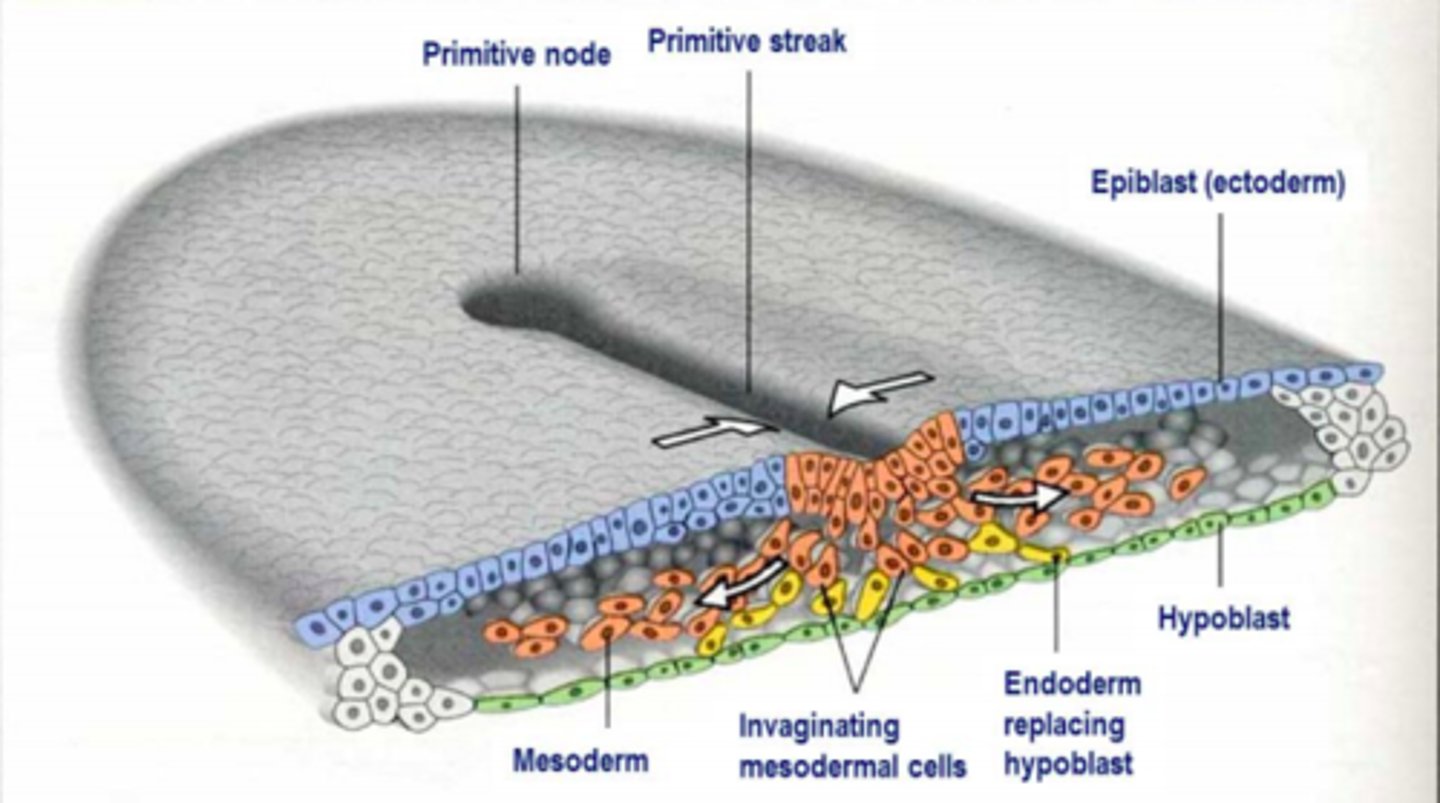
Gastrulation occurs during the third week of embryonic development.
What is gastrulation?
Gastrulation is the process by which bi-laminar embryonic disc is converted to a tri-laminar embryonic disc which has three germ layers...
Ectoderm (outer)
Mesoderm (middle)
Endoderm (inner)
Gastrulation is the beginning of ___ (the formation and structure of various organs/parts of the body)
Morphogenesis
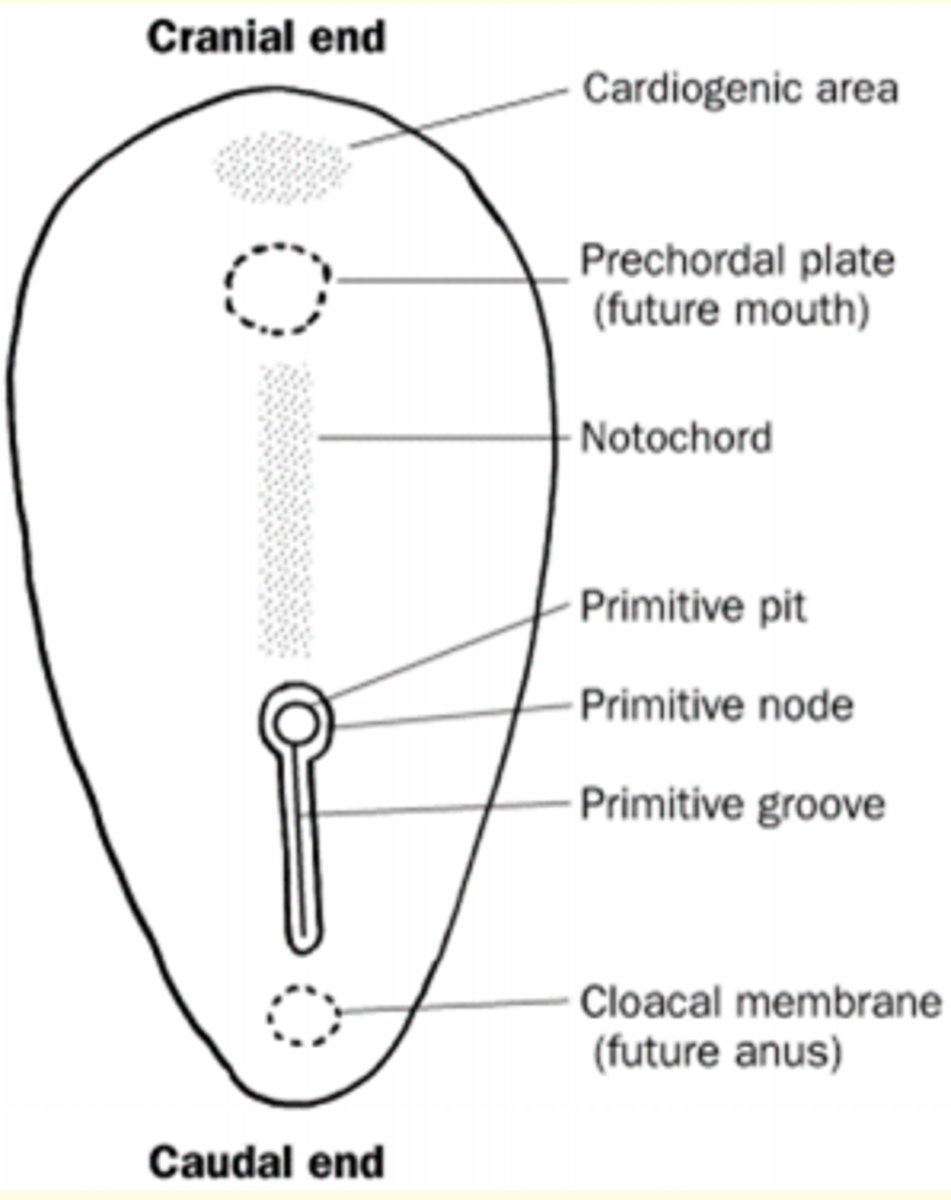
The beginning of gastrulation is marked by the formation of a transient structure formed from epiblast cells called the ___ ___ on day 15
Primitive streak
Primitive streak formation
Primitive streak begins in caudal end of embryo (butt) and moves towards cranial end (head) elongating to form a primitive groove.
At the cranial end - epiblast cells form circular cavity known as the primitive pit
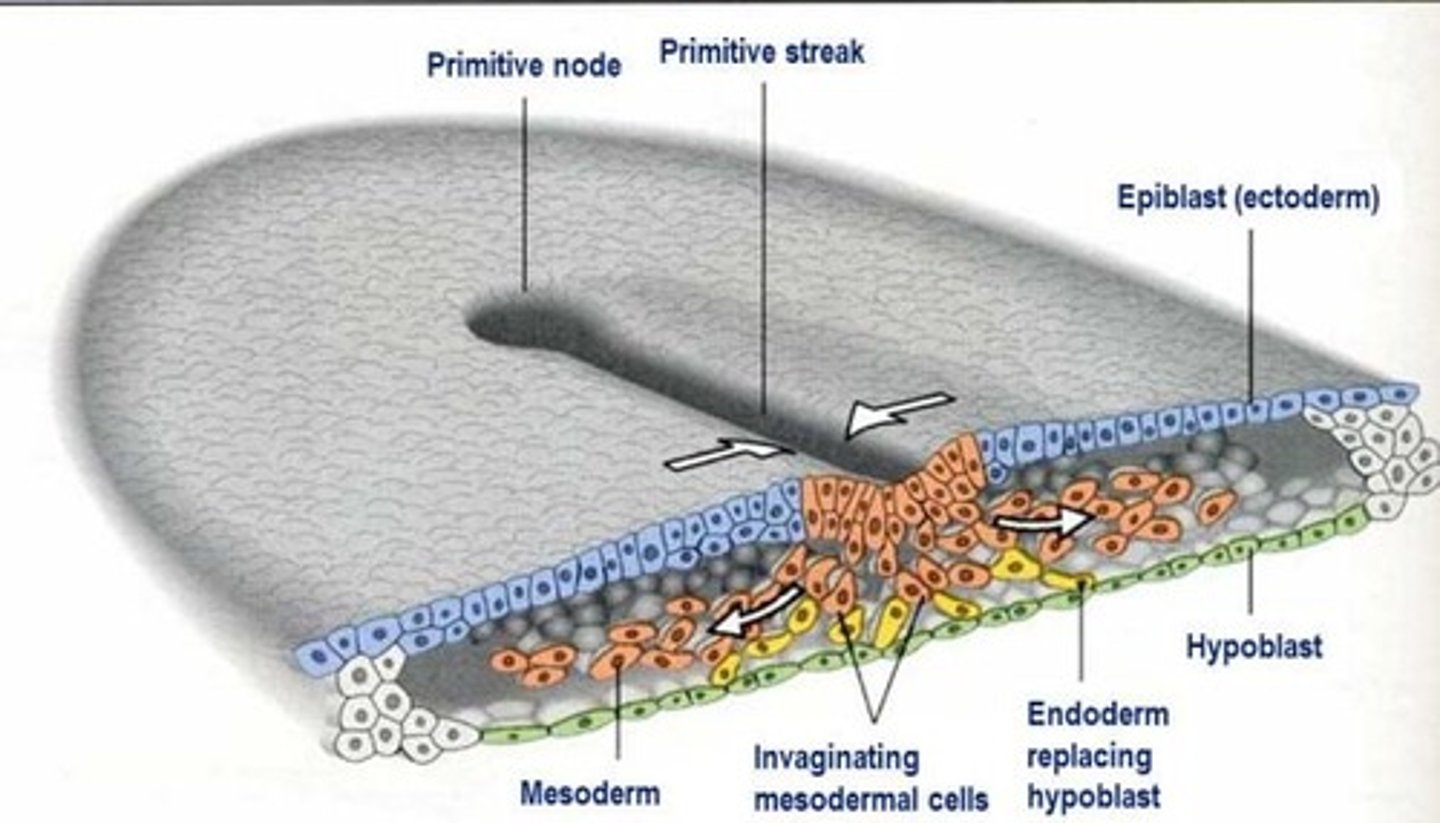
Gastrulation process
Epithelial cells at the lateral edge of the epiblast undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal (EMT) transition
Invagination of ingression of mesenchymal cells - cells migrate down into the primitive streak.
The first set of cells to move down which integrate into hypoblast layer become the endoderm (innermost)
The second set of cells to move down primitive streak become the mesoderm (middle)
The last set of cells to move down primitive streak become the ectoderm (outer)
The consequence of gastrulation process is the formation of a ___ map
Fate map
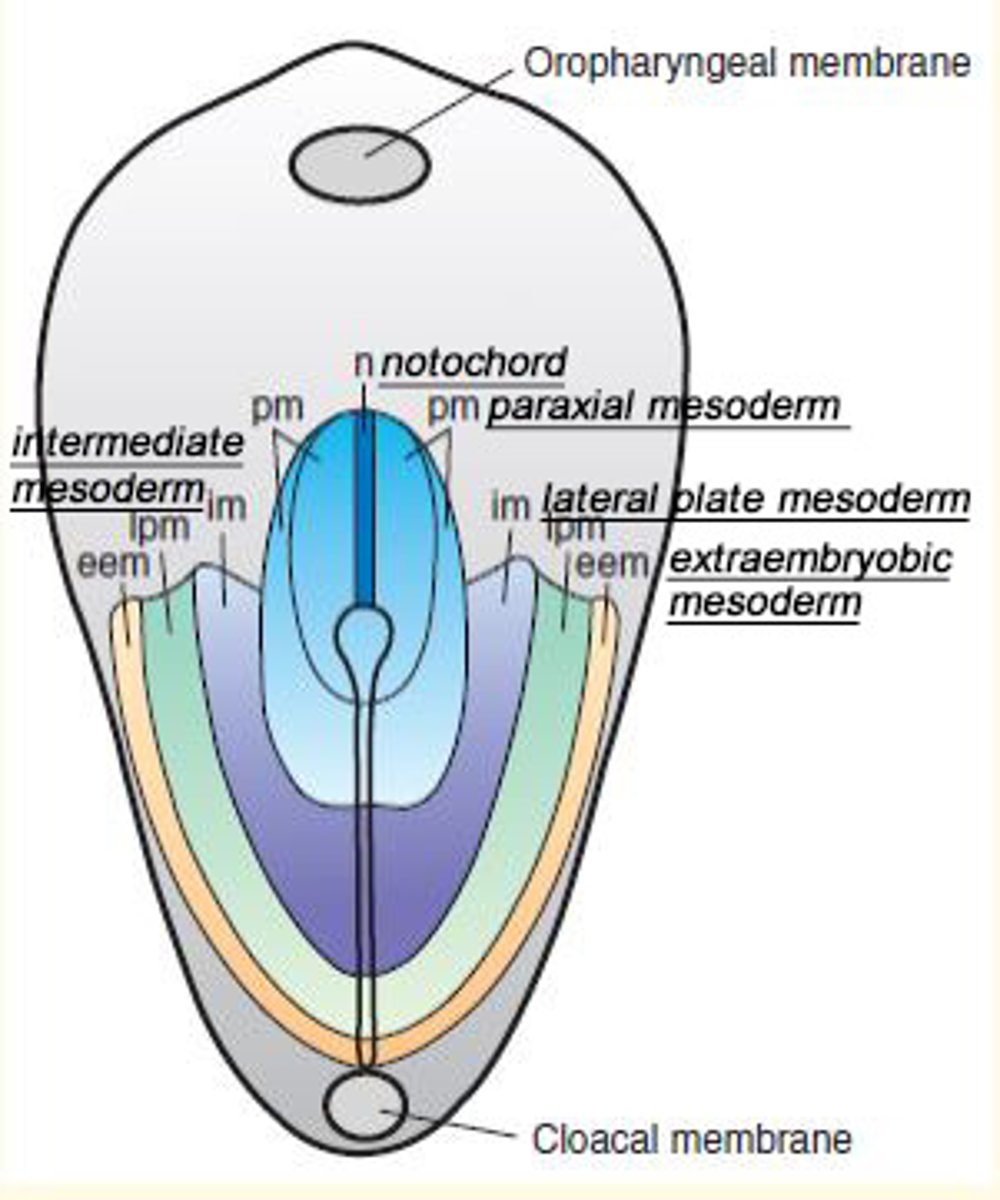
All our tissues and structures derive from these three important layers...
Endoderm (inner)
Mesoderm (middle)
Ecotoderm (outer)
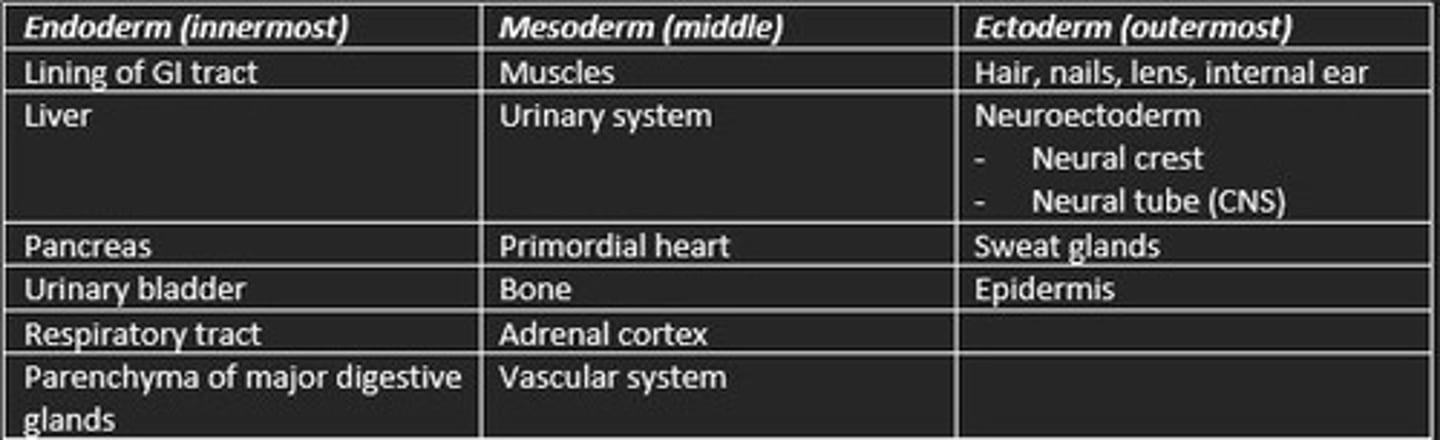
Derivatives of the three germ layers
Endoderm (inner)
- Respiratory tract
- Lining of GI tract
- Parenchyma of major digestive glands
Mesoderm (middle)
- Muscle
- Bone
- Urinary system
- Vascular system
Ectoderm (outer)
- Nervous tissue
- Sweat glands
- Epidermis
Name TWO abnormalities arising during gastrulation process
1) Caudal dysgenesis (sirenomelia)
- Insufficient mesoderm in caudal-most region of embryo
- Abnormalities of lower limbs/urogenital system
2) Sacrococcygeal teratomas
- Primitive streak persists and results in tumour in sacrococcygeal region
- Most common newborn tumour
Most common tumour found in newborns arising from persistence of the primitive streak
Sacrococcygeal teratomas
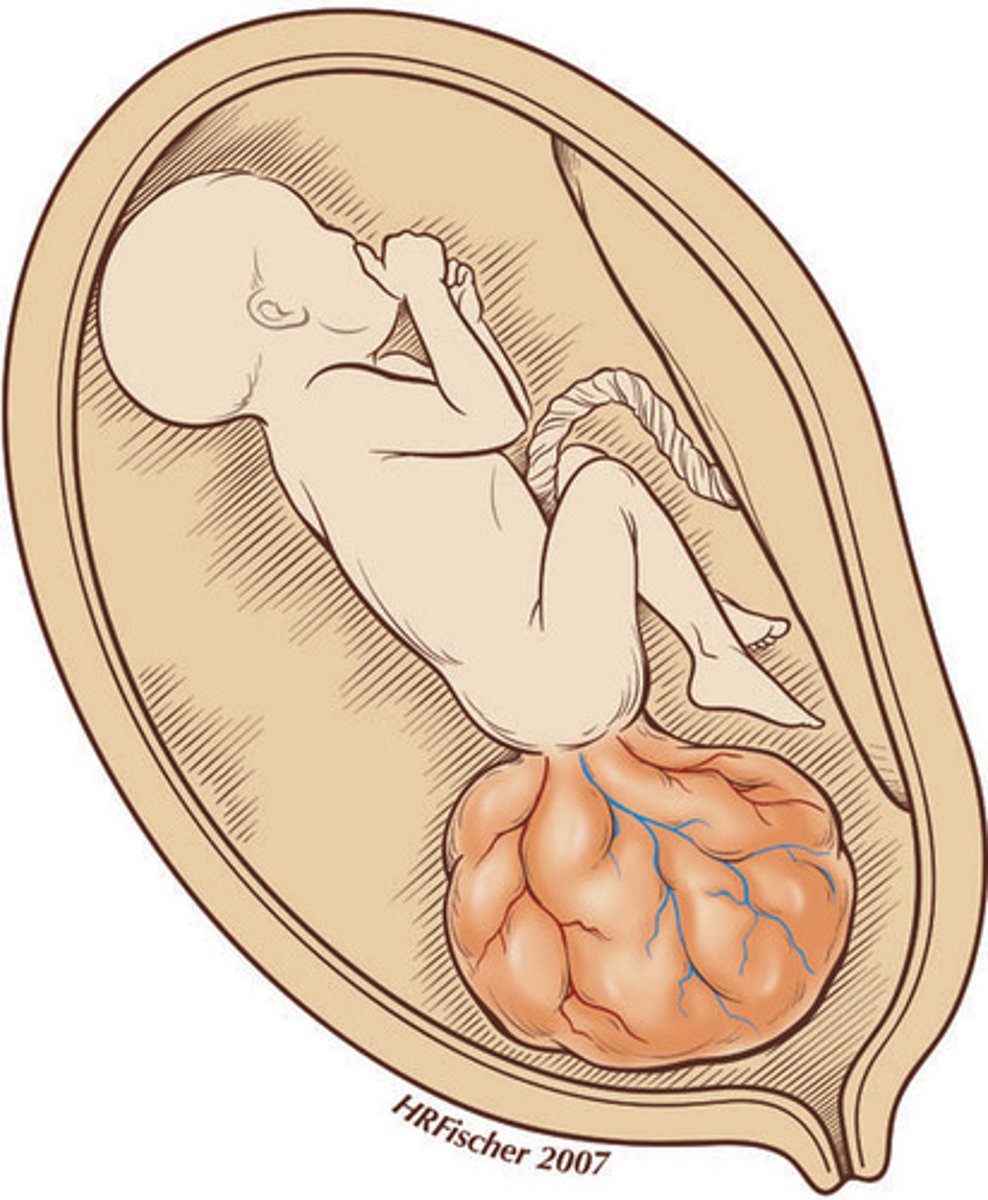
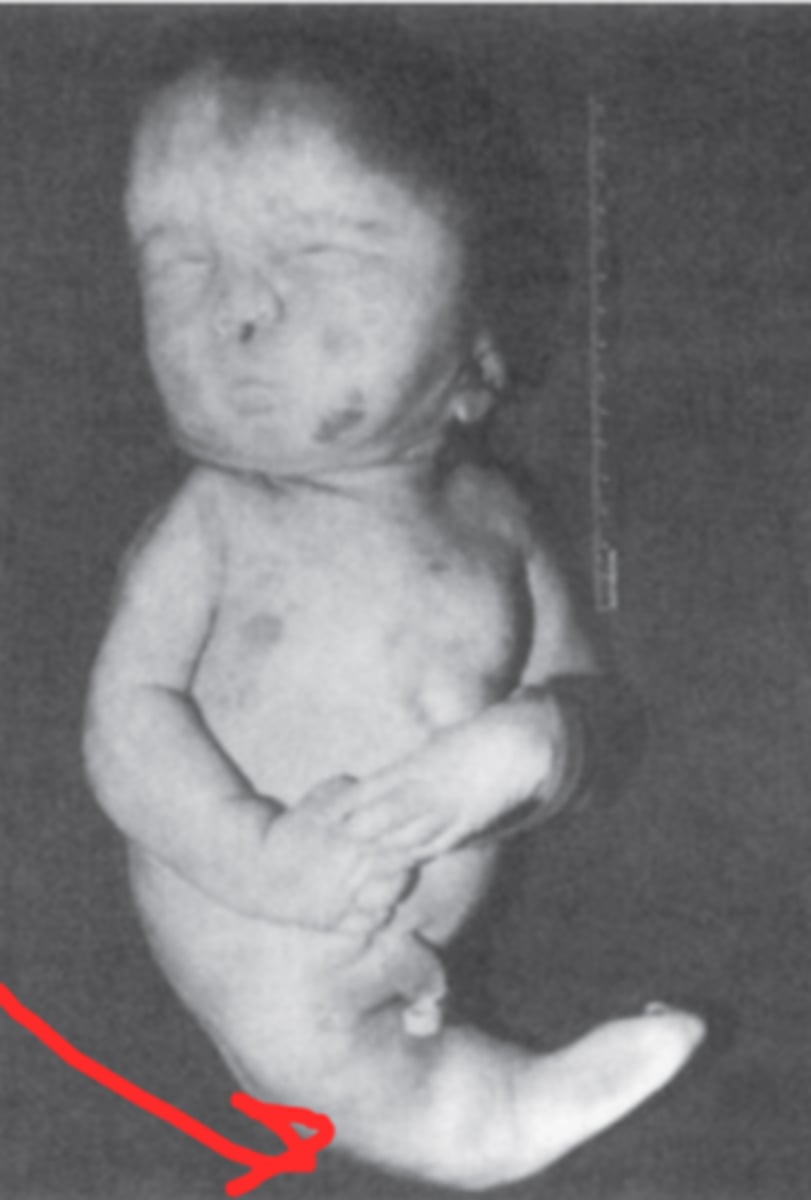
Caudal dysgenesis (sirenomelia)
Insufficient mesoderm in caudal-most regions of embryo
Abnormalities of lower limb and urogenital region
Some causes of male infertility
- Reduced motility of sperm
- Having low levels of sperm
- Having abnormally shaped sperm
Link to previous lecture = Kartagener′s syndrome causes immotile sperm leading men to be sterile
Some causes of female infertility
- Problems with ovulation
- Thickening of cervical mucus
- Scarring of ovarian tubes or cervix from surgery
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
The translucent glycoprotein shell surrounding the oocyte that dissolves prior to implantation
Zona pellucida
What is the outcome of the first cleavage of the zygote?
Two blastomeres of equal size
What is the specific name for the embryo at the 16 cell stage?
A morula
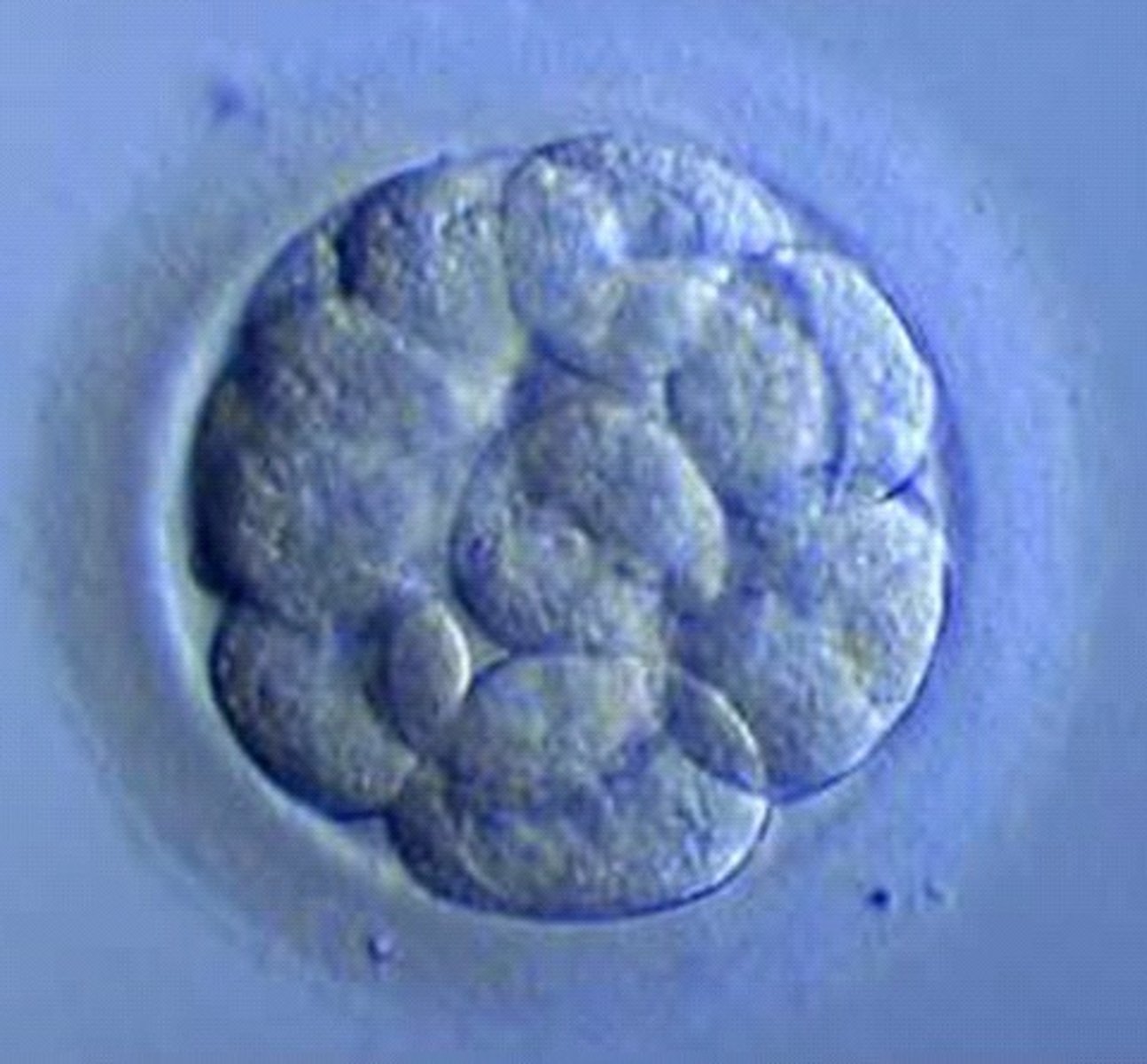
Each cell is totipotent at the 16 cell stage. What does this mean?
Cells have the potential to become any cell type
When does fate become more restricted to many rather than all lineages?
Following compaction (when cell becomes blastocyst)
What structure forms following compaction?
The blastocyst
What is the fate of the inner cell mass?
It forms the embryo and some extraembryonic structures.
The key event following implantation is the transition from histiotrophic to haemotrophic nutrition.
How is this achieved?
Establishment of maternal blood flow
Name the disorder
Poor growth of foetus due to, for example, poor supply of oxygen and nutrients.
Intra-uterine growth restriction (IUGR)
Name the disorder
An obstetric complication arising from implantation in the lower uterine segment.
Placenta praevia
Name the disorder
Incomplete differentiation of cytotrophoblast cells into endothelium results in poor blood supply to the embryo, one consequence of which is maternal hypertension.
Pre-eclampsia
A potentially life-threatening disorder resulting from implantation outside the womb.
Ectopic pregnancy
From which collection of cells does the primary yolk sac form?
Extraembryonic mesoderm
How long is the pre-embryonic period?
Two weeks
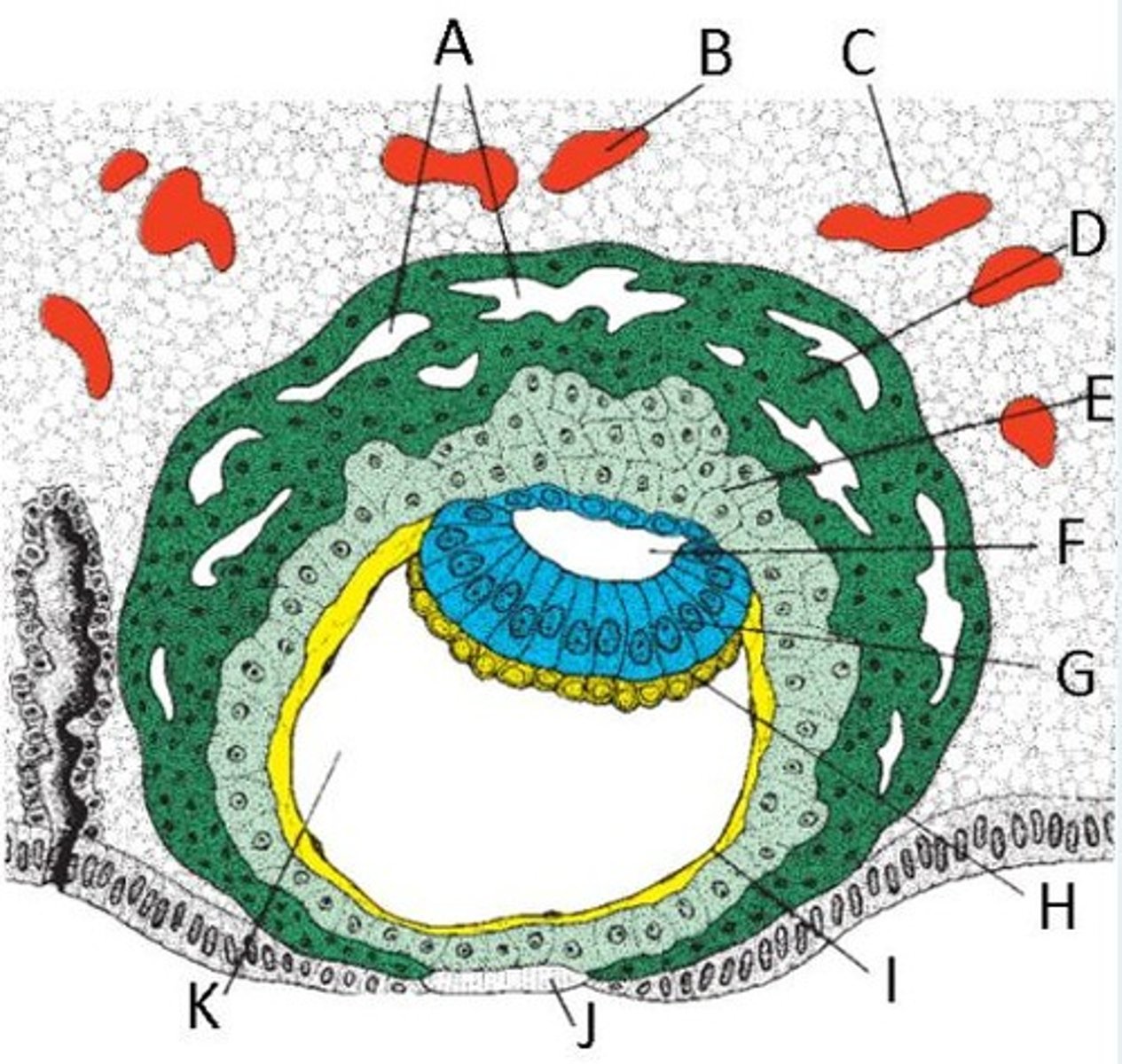
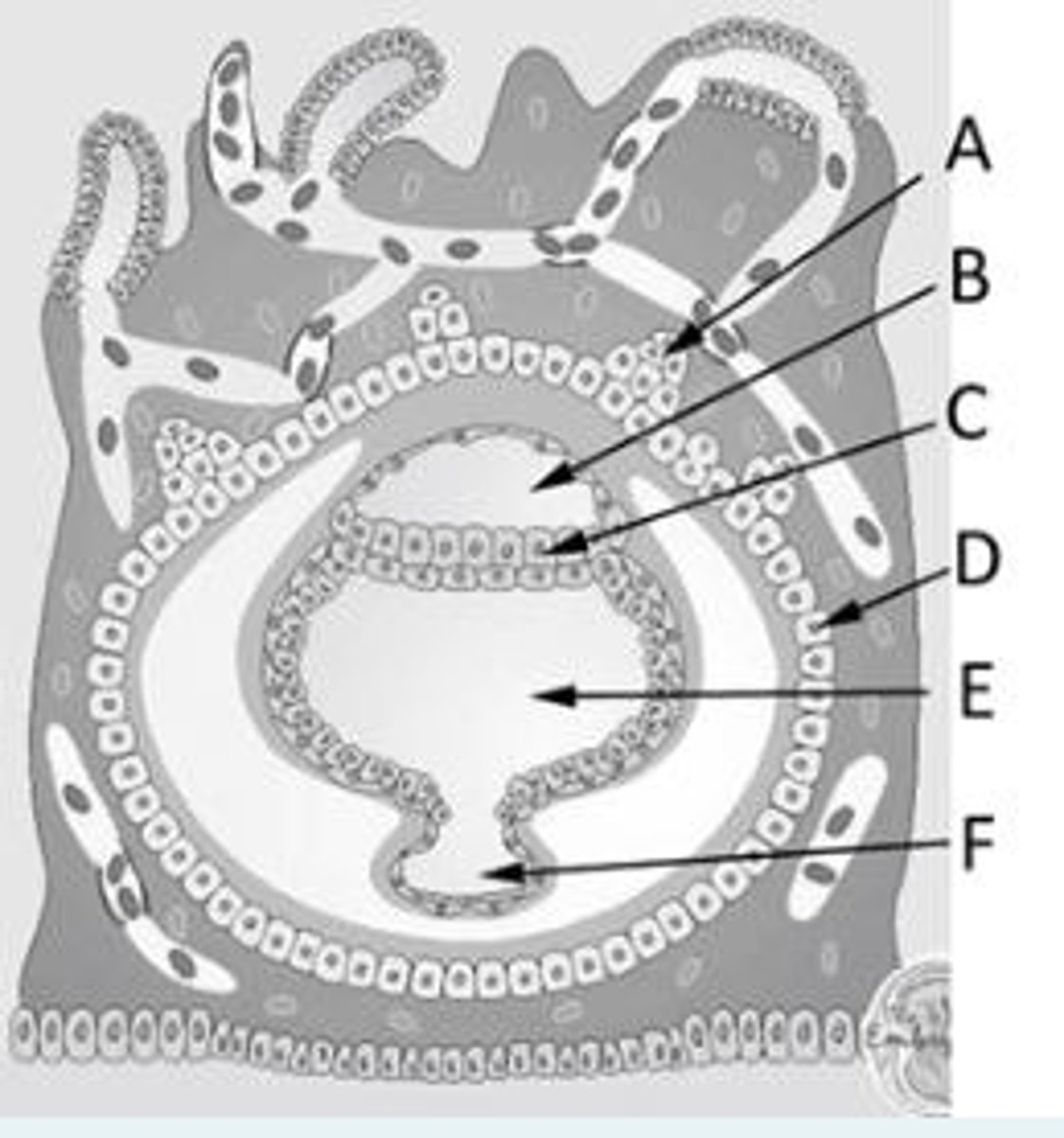
Identify the following structure in a day 9 embryo.
A = Trophoblast lacunae
B and C = Enlarged blood vessel
D = Synctiotrophoblast
E = Cytotrophoblast
F = Amniotic cavity
G = Epiblast
H = Hypoblast
I = Exocoelomic membrane
J = Fibrin plug
K = Primitive yolk sac
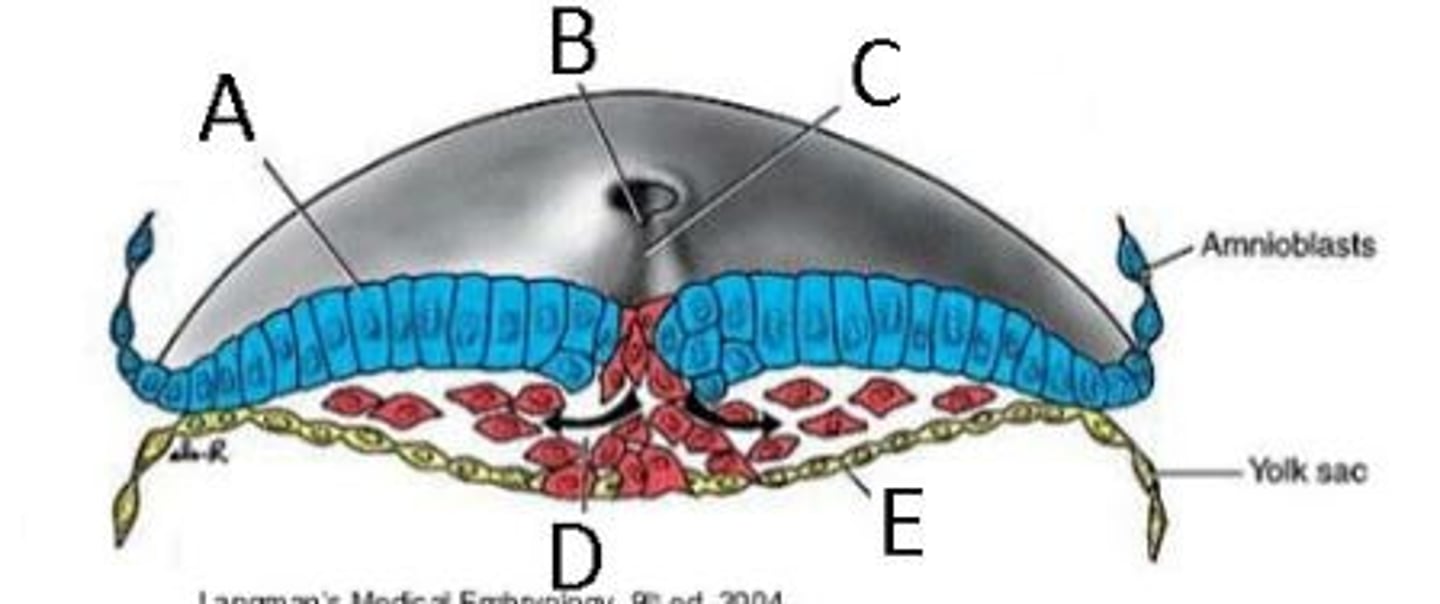
Identify the structures in this image depicting gastrulation
A = Epiblast
B = Primitive pit
C = Primitive streak
D = Invaginating mesodermal cells
E = Hypoblast
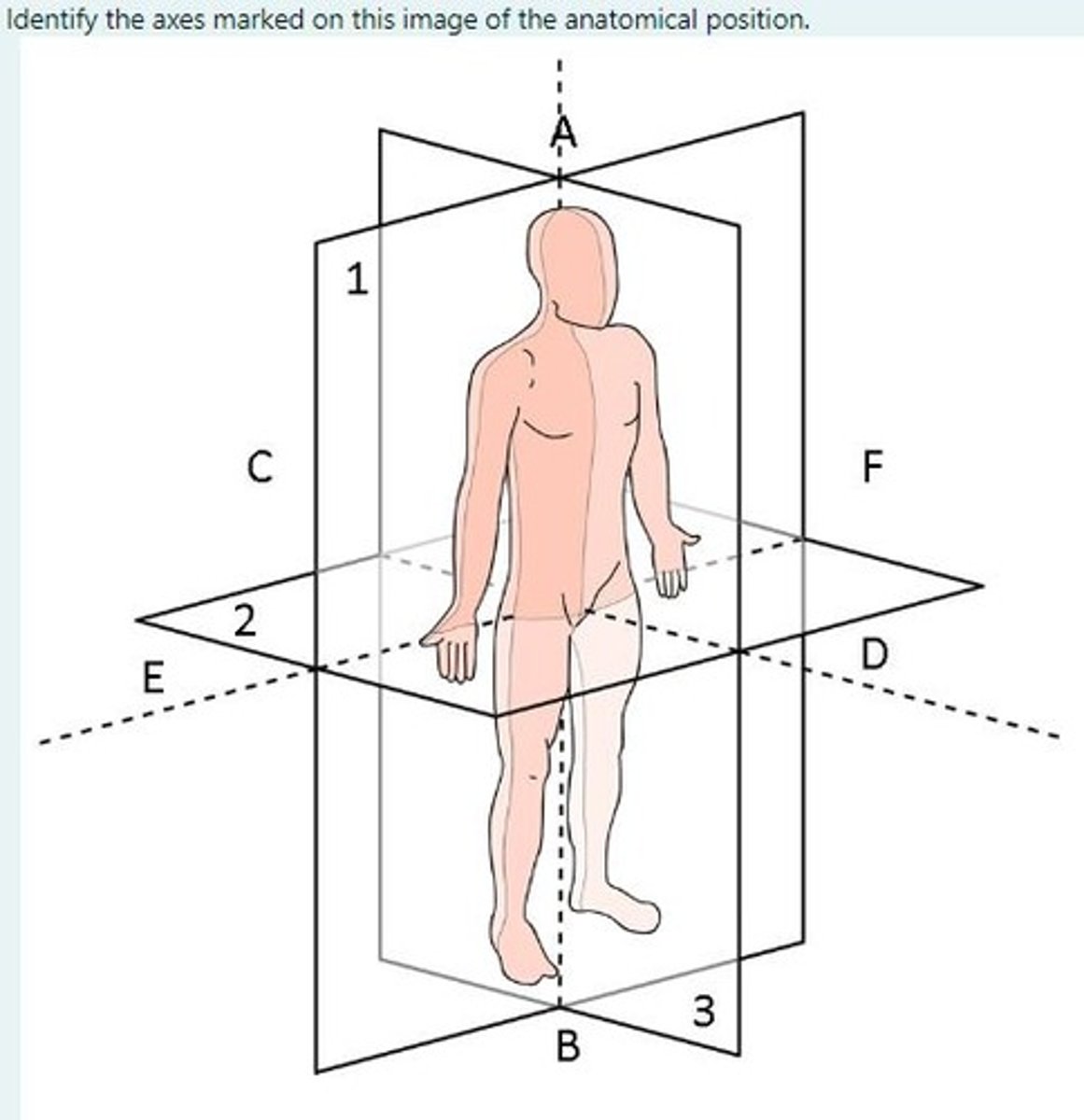
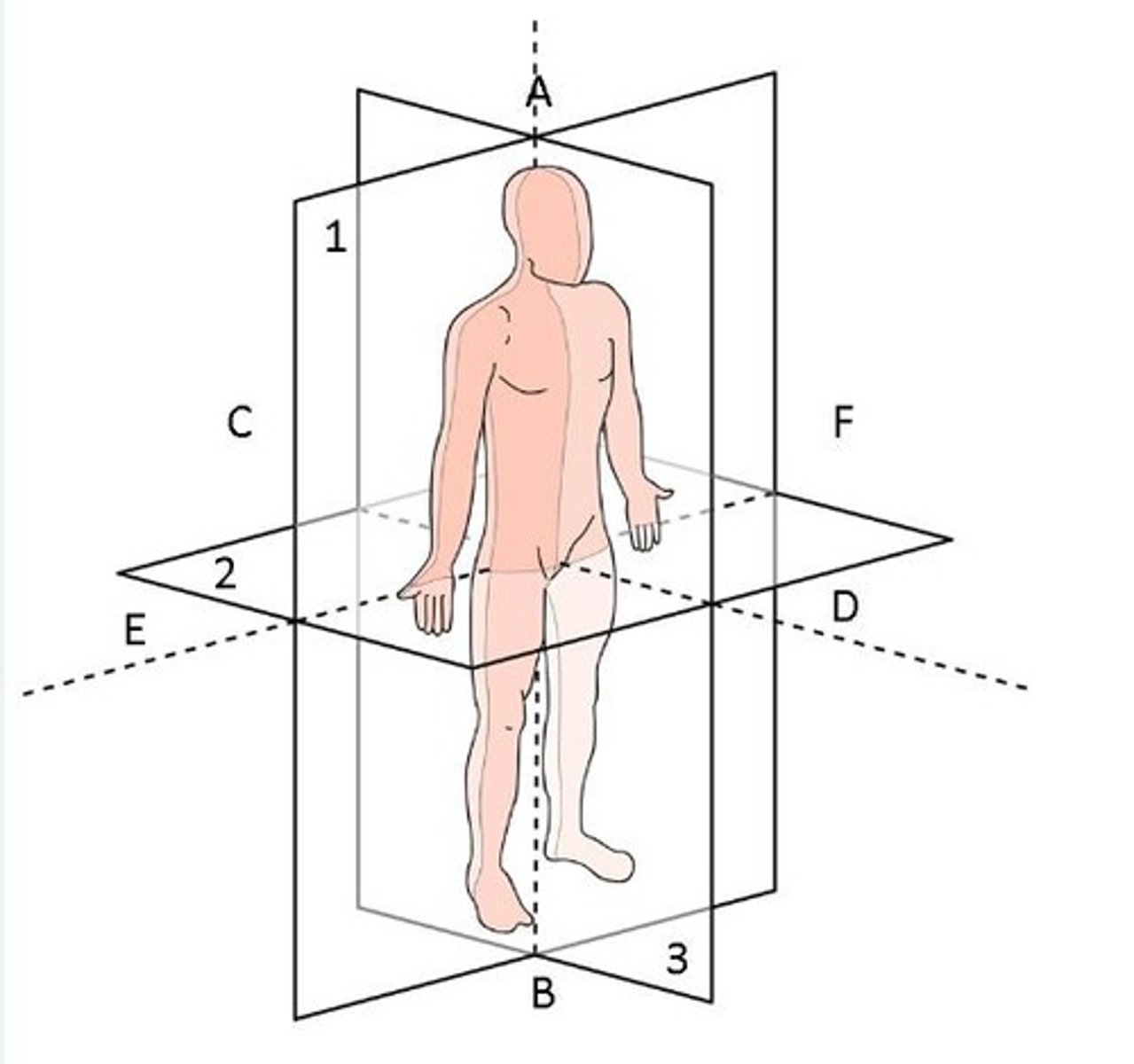
Identify the axes marked on this image of the anatomical position
C-D = Posterior-anterior
A-B = Cranial-caudal
E-F = Right-left
Name a disorder that is routinely detected by pre-implantation screening?
Cystic fibrosis
From which cell layer is the notochord derived?
Epiblast
Identify the transverse, coronal and sagittal planes
Coronal = Plane 1
Transverse = Plane 2
Sagittal = Plane 3
Cognitive impairment caused by teratogen...
Alcohol
Multiple defects including microcephaly, visual impairment, cognitive impairment is caused by the teratogen...
Maternal cytomegalovirus infection
Shortened limbs is caused by the teratogen...
Thalidomide
Toxoplasmosis from poorly cooked meat leads to what developmental outcome?
Hydrocephalus
Most common site for implantation
Stroma of posterior uterine wall
Which highly-invasive layer of the embryo interacts with the connective tissue of the endometrium to facilitate implantation?
Synctiotrophoblast
Identify the structures in the following diagram showing an embryo at day 13 following fertilisation.
A = Primary chorionic villi
B = Amniotic cavity
C = Epiblast
D = Cytotrophoblast
E = Secondary yolk sac
F = Remnant of primary yolk sac
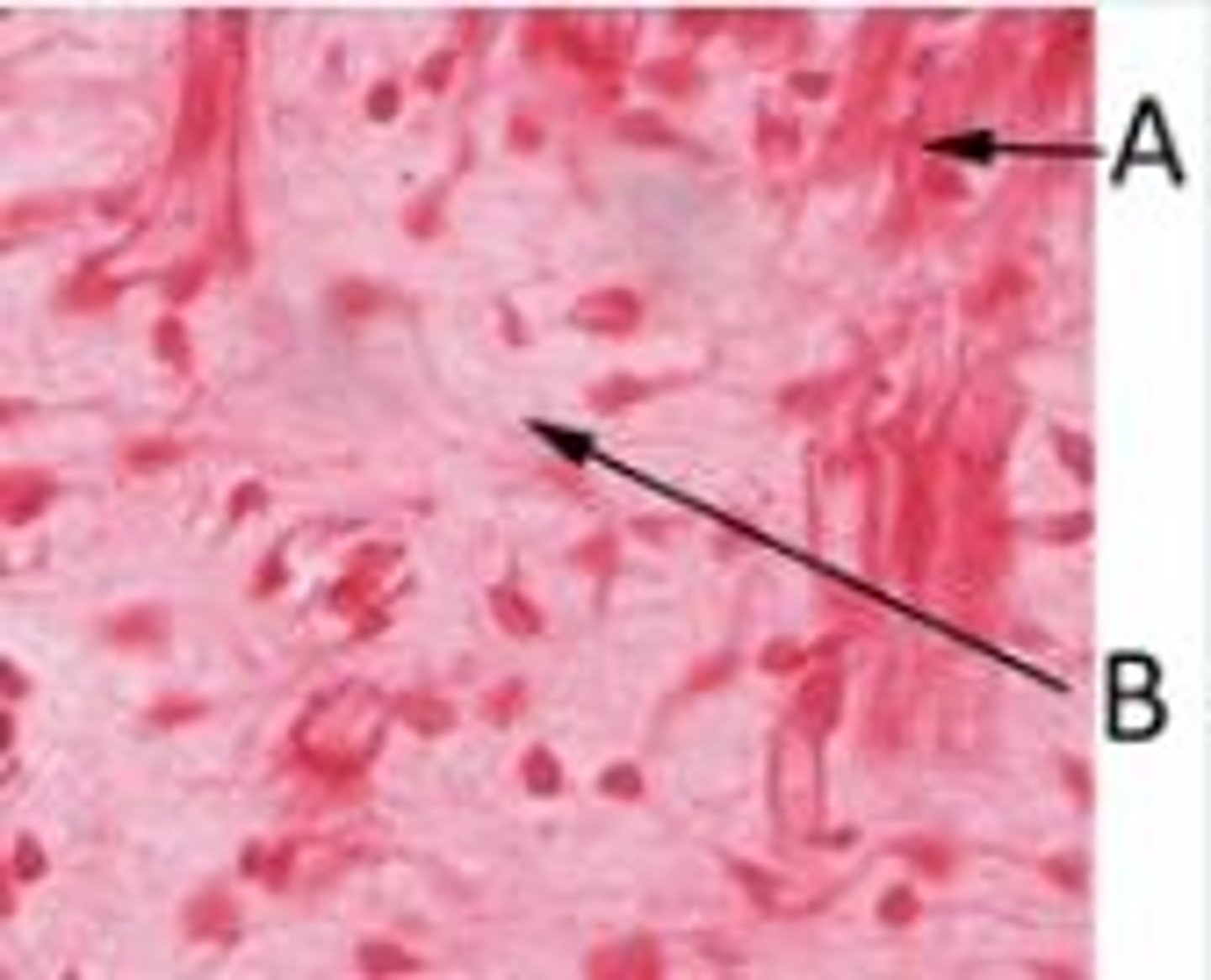
In the following photomicrograph of a histological section of developing tongue, myotubes are labelled A. What type of tissue is labelled B?
Mesenchymal connective tissue
Which of one of the following is not a common source of DNA to allow genetic testing for foetal abnormalities in a pregnant woman?
A) Amniocentesis
B) Foetal DNA in the mother's blood stream
C) A chorionic villus sample
D) An isolated cell at the morula stage
An isolated cell at the morula stage
3 multiple choice options
What stage of embryogenesis does this image represent?
Embryo hatching
What stage of embryogenesis does this image represent?
Implantation of the embryo
Day 7-8 post-fertilisation
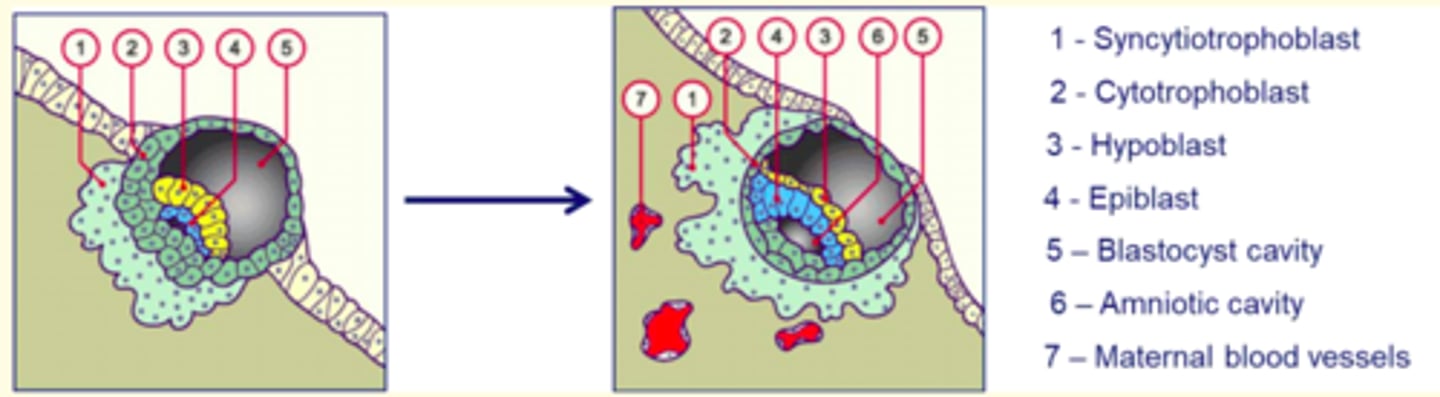
Day 9-10 post-fertilisation
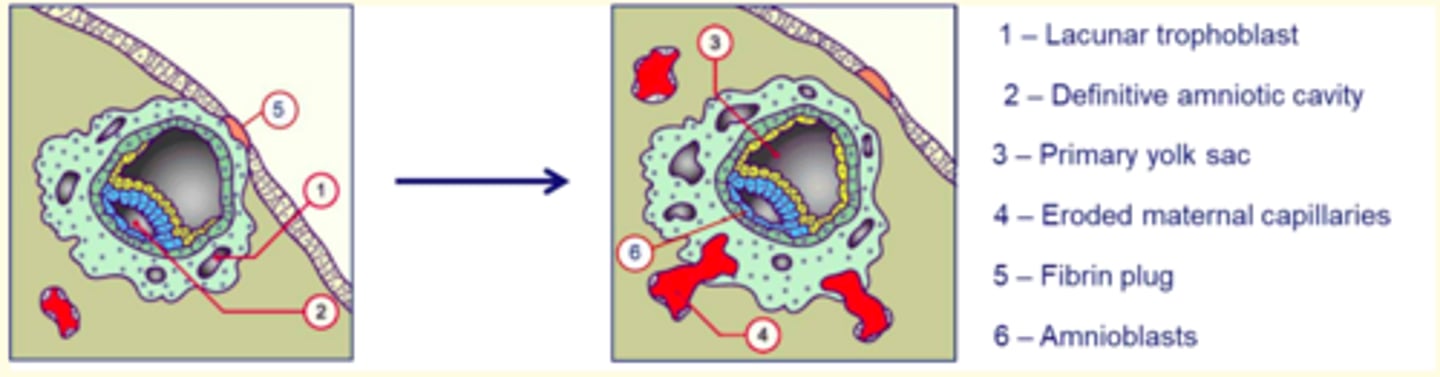
Day 11-13 post-fertilisation
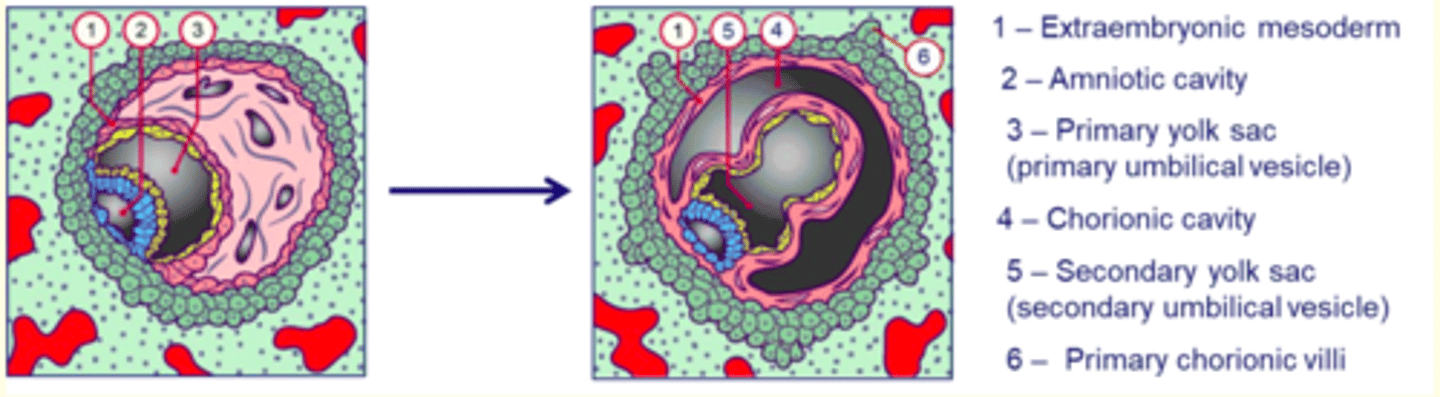
Formation of the tri-laminar disc during gastrulation
The beginning of gastrulation is marked by formation of transient structure from epiblast cells called the primitive streak (day 15)
- Starts at caudal end
- Moves to cranial end, elongating to form primitive groove
- At cranial end = epiblast cells form circular cavity called primitive pit
- Primitive pit cells enlarge to form primitive node
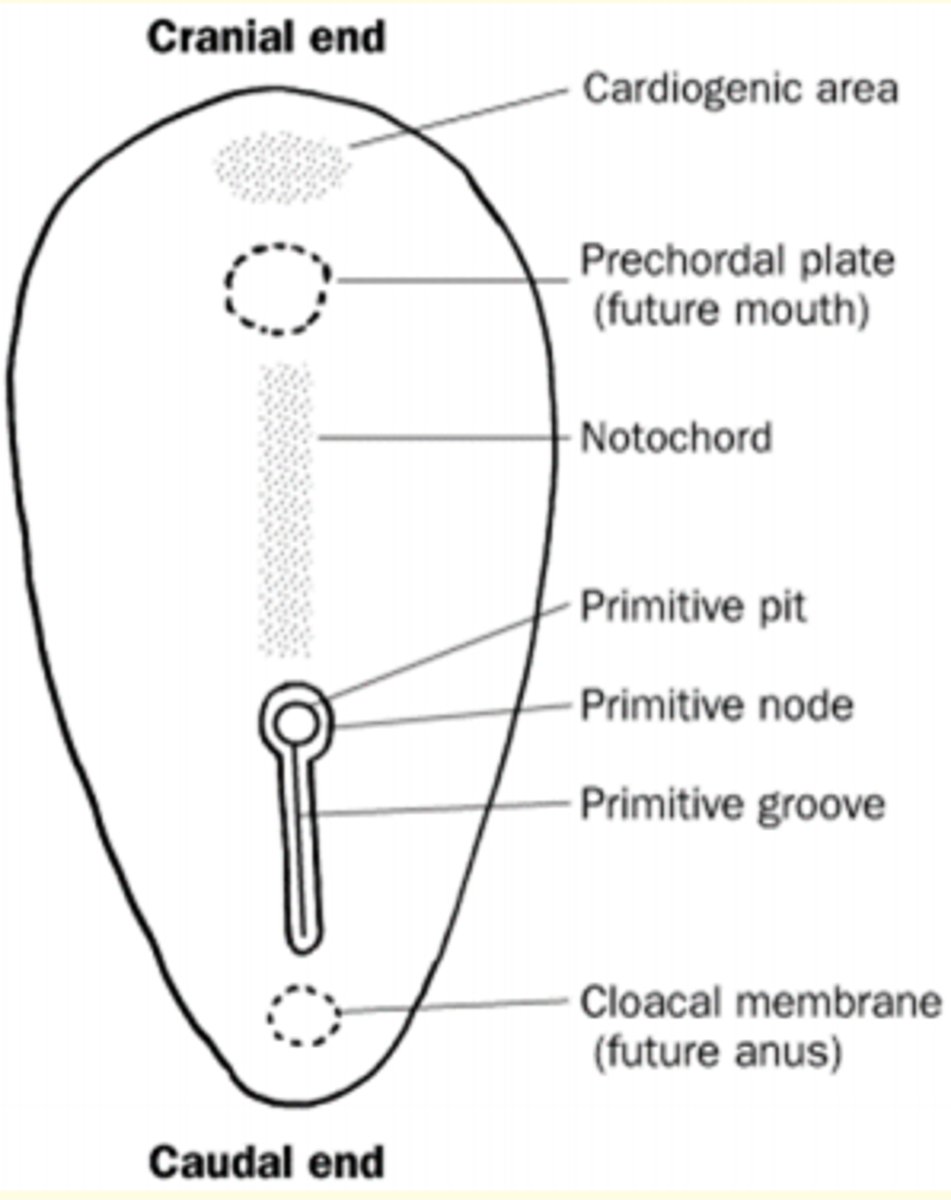
What is occurring in this image taken during gastrulation?
Epithelial cells at the lateral edge of epiblasts undergo 'epithelial-to-mesenchymal' (EMT) transition
- Invagination or ingression = cells become flask-shaped and move down into the primitive streak
- First set to move down = endoderm (innermost)
- Second set = mesoderm
- Third set = ectoderm (outermost)