Organic Chemicals
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Polymers
large molecules that are made up of the same/similar small molecules
monomers
small molecules that make up polymers
dehydration synthesis
the building of large molecules by bonding together smaller molecules and the removing of water per bond formed
hydrolysis
the breaking down(digestion) of a large molecules to created small molecules, requires one water molecule per bond
what is the monomer of carbohydrates
monosaccharide
what is the monomer of lipids
fatty acids/ glycerol
what is the monomer of proteins
amino acids
what is the monomer of nucleic acids
nucleotides
what is the polymer of carbohydrates
polysaccharides
what is the polymer of lipids
triglycerides
what is the polymer of proteins
polypeptides
what is the polymer of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
CHONPS
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur
what are foods that contain carbs
sugars, starches, fiber
what are the elements present in carbs
C, H, O
what is the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen
2:1
What is the functions of carbs
energy storage
What are the other properties of carbs
Hydrophilic and contains the -OH group
What are examples of monosaccharides
glucose (C6H12C6)
What do you get combining two monosaccharides by dehydration synthesis
disaccharides
What are examples of disaccharides in living organisms
maltose: glucose+glucose
sucrose: glucose+glucose
What do you get breaking down disaccharide by hydrolysis
monosaccharides
how are polysaccharides made
combining many monosaccharides by dehydration synthesis
Starch
straight chains; carb storage in plants
glycogen
branched chains; carb storage in animals
cellulose
tightly packed; makes up cell wall in plants, indigestible by most animals
Polysaccharide →disaccharide→monosaccharide what do the arrows represent?
hydrolysis
monosaccharide→disaccharide→polysaccharide what do the arrows represent?
dehydration synthesis
foods that contain lipids
fats oils waxes
elements present in lipids
CHO
building blocks of lipids
fatty acids, glycerol
functions of lipids
energy storage, warmth, protection
other properties of lipids
hydrophobic
saturated fats
solid fats made by animals
unsaturated fats
liquid fats: plant and fish oils
What are most lipids that are made up of fatty acids
glycerol
what is the carboxyl group “acid”
separated from the rest
hydrocarbon chain
makes nonpolar
triglycerides
made up of 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol molecule; make up fats and oils; the more unsaturated fatty acids, the more fluid
phospholipids
made up 2 fatty acids, 1 glycerol molecules, and 1 phosphate group
steroids
not made of fatty acids and glycerol; made of 4 hydrocarbon rings bonded together; make up some hormones and cholesterol
foods that contain proteins
meat, eggs, peanuts
elements present in proteins
CHON
monomer of proteins
amini acids
functions of proteins
so so so many
other properties of proteins
hydrophilic; R group is different in each amino acid; 20 amino acids
what is an essential amino acid
one we cannot make
what is a nonessential amino acid
ones we canmake
properties of the R groups of amino acids
ionic, positive, negative, hydrophobic
dipeptide
two amino acids bonded together by dehydration synthesis
The bond between C-N that holds the amino acids together is
a peptide bond
polypeptide
many amino acids bonded together by dehydration synthesis
What are examples of nucleic acids
DNA and RNA
elements present in nucleic acids
CHONP
monomer of nucleic acids
nucleotides
functions of nucleic acids
replication; protein synthesis
other properties of nucleic acids
hydrophilic; carries genetic information
RNA
single stranded molecule that helps in protein synthesis and gene expression
DNA
shaped like a double helix, this double strangled molecule carries all of our genetic information and is passed from parent to offspring during reproduction
polymer
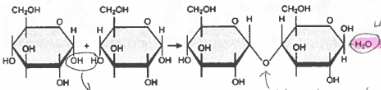
dehydration synthesis
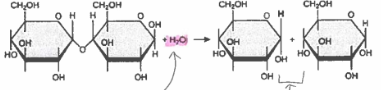
hydrolysis
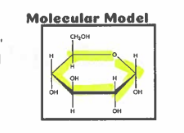
molecular model
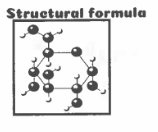
structural formula
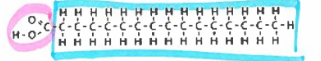
saturated fatty acid
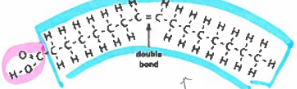
unsaturated fatty acid
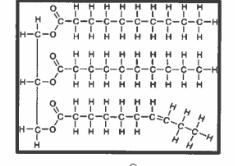
lipids
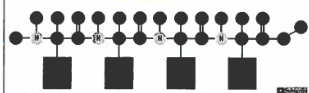
polypeptide chain
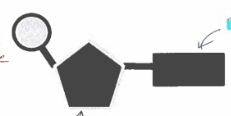
nucleotide