FIRST SEMESTER FINAL EXAM 2024
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
Renewable resource
A resource that can be replaced
Nonrenewable resource
A resource that cannot be replaced in a reasonable amount of time
Deforestation
destruction of forests
Smog
Haze caused by chemical reactions from pollutants in the air that form ozone
Greenhouse Gases
Gases in the atmosphere that trap heat. Examples - Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor
Biodiversity
The total variety of all living organisms
Habitat fragmentation
Splitting ecosystems into pieces
Climate Change
A change in global or regional climate patterns due to human impact
Greenhouse effect
When the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap the heat to maintain Earth's temperature range
Ocean acidification
Chemical changes in the ocean as a results of carbon dioxide emissions - causing a sharp decline in populations of shelled organisms
Coral bleaching
coral expel their algae and turn white, and eventually die. Caused by the warming of the ocean and ocean acidification
Drought
Extended period of dry weather caused by a lack of snow and rain
Sustainability
The use of natural resources in such a way that does not cause long-term environmental harm
ecological footprint
the impact of a person or community on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use of natural resources.
Desertification
the process by which fertile land becomes desert, typically as a result of drought, deforestation, or inappropriate agriculture.
Heterotroph
A living thing that needs to eat other living things for energy
Cellular Respiration
A process that makes ATP by breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen
Mitochondria
The cell organelle where cellular respiration takes place
ADP
Molecule with only 2 phosphates that has very little energy
Carbon dioxide
Gas released by animals, after burning fossil fuels, fires, and factories and taken up by plants
Oxygen
Gas released by plants and taken up by animals
Thylakoid
saclike photosynthetic membranes found in chloroplasts. Where the light reaction happens
Stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; where the calvin cycle happens
quantitative
Data that is in numbers

qualitative
Data in the form of recorded descriptions rather than numerical measurements.

data
Facts, figures, and other evidence gathered through observations.
independent variable
The experimental factor that is changed; the variable whose effect is being studied.
dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that is measured or observed
hypothesis
A prediction that can be tested. Typically an If/Then statement

procedure
A way of organizing & writing detailed steps to complete the experiment.

conclusion
A summary based on evidence or facts collected in the experiment
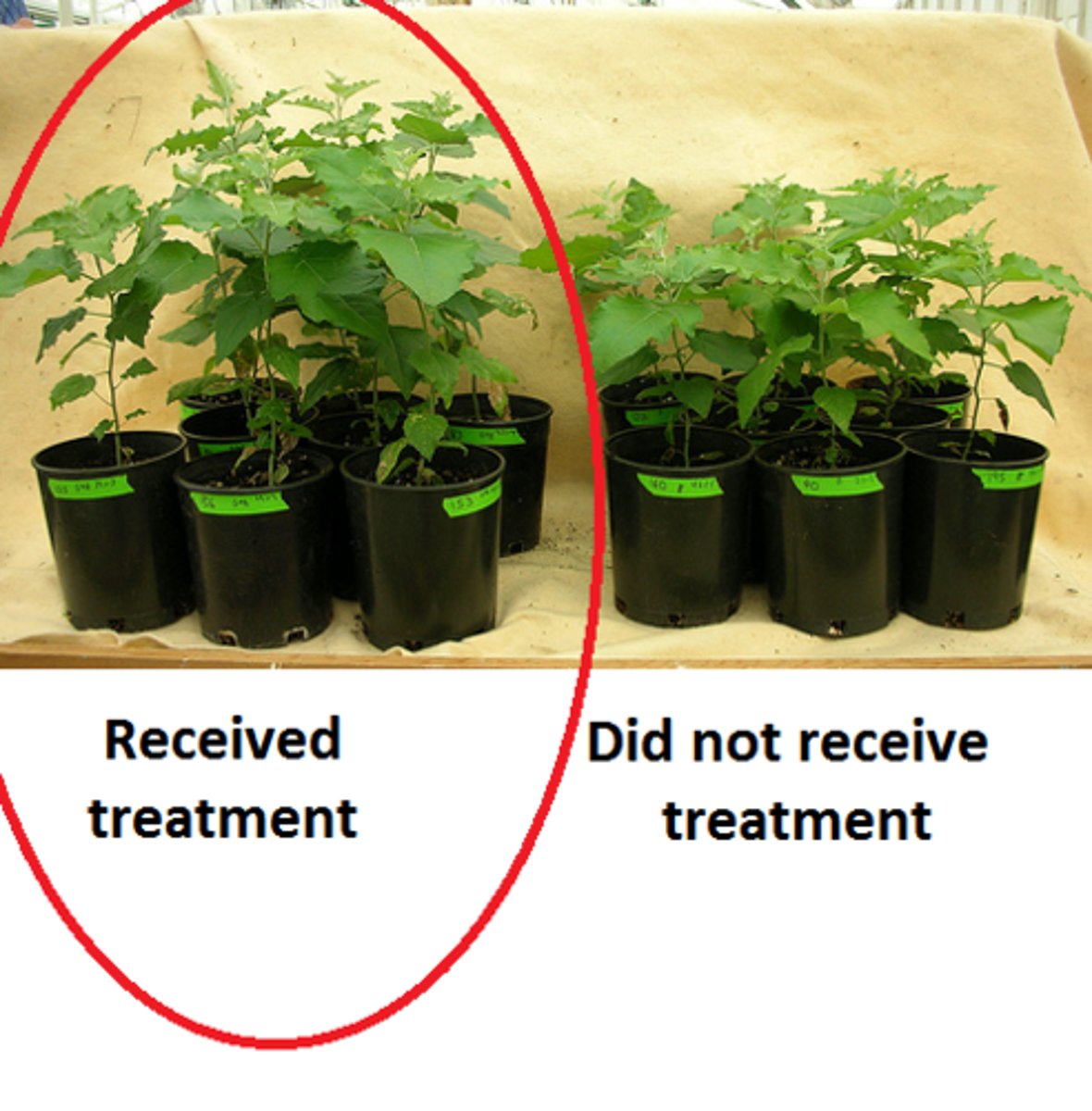
experimental group
In an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.

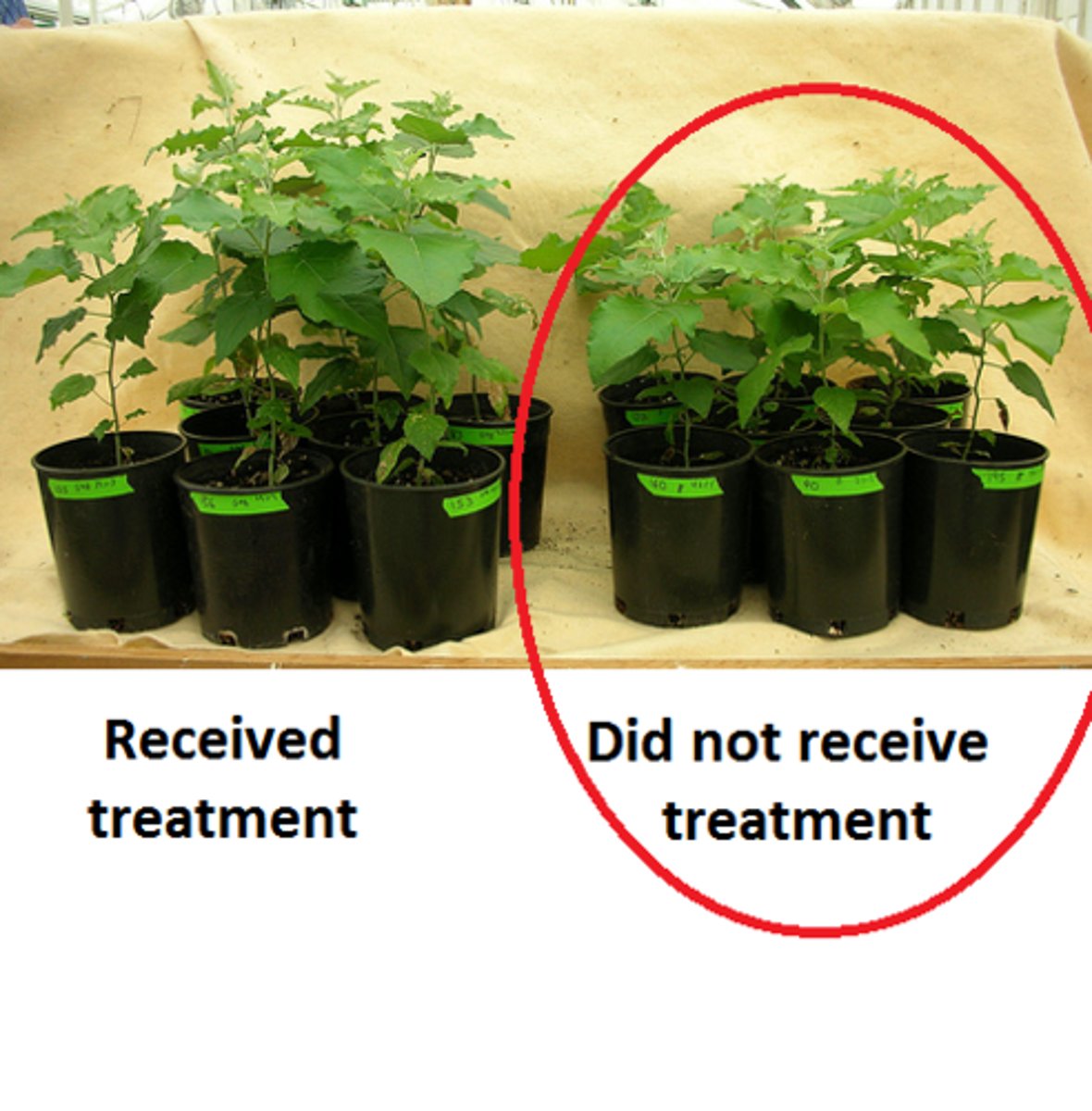
control group
the group that does not receive the experimental treatment.
Contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.

constants
A values that do not change and are the same for all of the tested groups
You water some plants with 4 different types of water (salt water, regular water, sugar water and distilled water). After a two-week period, the height of the plants is measured. What is the independent variable?
Type of water
You water some plants with 4 different types of water (salt water, regular water, sugar water and distilled water). After a two-week period, the height of the plants is measured. What is the dependent variable?
the height of the plants
Inside a greenhouse, maple trees are kept at 3 different humidity levels. These are left for 3 years. One tree is left outside in normal conditions. The heights of the trees are measured once a week. What is the independent variable?
humidity levels
Inside a greenhouse, maple trees are kept at 3 different humidity levels. These are left for 3 years. One tree is left outside in normal conditions. The heights of the trees are measured once a week. What is the dependent variable?
The height of the maple trees
Inside a greenhouse, maple trees are kept at 3 different humidity levels. These are left for 3 years. One tree is left outside in normal conditions. The heights of the trees are measured once a week. What is the control group?
The tree left outside in normal conditions
One tank of goldfish is fed the normal amount, which is once a day; a second tank is fed twice a day; and a third tank is fed four times a day during a six-week study. The fishes' body fat is recorded daily. What is the independent variable?
How much they are fed
One tank of goldfish is fed the normal amount, which is once a day; a second tank is fed twice a day; and a third tank is fed four times a day during a six-week study. The fishes' body fat is recorded daily. What is the dependent variable?
The fishes' body fat
One tank of goldfish is fed the normal amount, which is once a day; a second tank is fed twice a day; and a third tank is fed four times a day during a six-week study. The fishes' body fat is recorded daily. What is the control group?
The goldfish fed the normal amount
You decide to clean the bathroom. You notice that the shower is covered in a strange green slime. You decide to try to get rid of this slime by adding lemonade juice. You spray half of the shower with lemonade juice and spray the other half of the shower with water. After 3 days of "treatment", there is no change in the appearance of the green slime on either side of the shower. What is the independent variable?
lemonade juice
You decide to clean the bathroom. You notice that the shower is covered in a strange green slime. You decide to try to get rid of this slime by adding lemonade juice. You spray half of the shower with lemonade juice and spray the other half of the shower with water. After 3 days of "treatment", there is no change in the appearance of the green slime on either side of the shower. What is the dependent variable?
The appearance of slime
1) You decide to clean the bathroom. You notice that the shower is covered in a strange green slime. You decide to try to get rid of this slime by adding lemonade juice. You spray half of the shower with lemonade juice and spray the other half of the shower with water. After 3 days of "treatment", there is no change in the appearance of the green slime on either side of the shower. What is the control group?
the half of the shower that gets sprayed with water
What is the first step of the scientific method?
Make an observation and ask a question
What is the next step in the scientific method after you have made an observation and asked a question?
Create a hypothesis
What is the next step in the scientific method after you have made hypothesis?
Design an experiment
What is the next step in the scientific method after you have conducted an experiment?
collect data
What is the next step in the scientific method after you have analyzed data?
come to a conclusion
Independent Variable
The variable that is changed in an experiment
Dependent Variable
The variable that is measured in an experiment
Error
A mistake that could have been made during an experiment
Conclusion
The end results of the experiment and how the results relate to the hypothesis
Procedure
Steps involved in performing an experiment. (directions)
Experimental Group
In an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment or the independent variable
X-Axis
Horizontal line of the graph
Y-Axis
Vertical line of the graph
Line Graph
A graph used to show how data changes over a period of time
Bar Graph
A type of graph used to compare data in categories or groups
Title
A detailed name for the graph
Labels
A name for the X and Y axis
Units
The value that something is measured in (Ex: grams, milliliters, centimeters) All numbers require this
Key
If a graph has two or more types of data, an illustration of what each line represents is needed. (different colors, shapes, or lines)
Graph
A visual display of information or data
Horizontal
Line at the bottom of the graph going left and right. This is the X-Axis
Vertical
Line on the side of the graph going up and down. This is the Y-Axis
Data Point
A point on a graph showing the location of a piece of data.
Ecology
The study of interactions between organisms and their environment.
Ecosystem
All of the organisms and the physical environment in the same area. (All biotic and abiotic factors)
Biotic Factor
Any living part of the environment. (ex: plants, animals, bacteria)
Abiotic Factor
Non living physical factors that shape an ecosystem. (ex: rocks, water, air, dirt)
Water Cycle
The process in which water is recycled between oceans, land, and the atmosphere.
Evaporation
Liquid to gas
Condensation
Gas to liquid
Transpiration
Evaporation from plants
Surface runoff
Water flowing off the land into bodies of surface water.
Seepage
Water leaking through soil into the groundwater
Groundwater
Water that is beneath Earth's surface
Precipitation
Rain, snow, sleet, hail
Food Chain
A series of steps in an ecosystem in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten.
Food Web
An network of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationships between the various organisms in an ecosystem. (Many food chains intertwined together)
Limiting factor/nutrient
Any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence, numbers, reproduction, or distribution of organisms.
Autotroph
An organism that produces its own food by capturing energy from the sun or chemicals. Also called a producer
Producer
An organism that produces its own food that is used by other organisms for energy. Also called an autotroph.
Photosynthesis
The process where autotrophs use sunlight energy is used to produce food.
Heterotroph
An organism that has to consume other living things for food. Also called a consumer.
Consumer
An organism that relies on other organisms for its energy and food. Also called a heterotroph.
Omnivore
An organism that eats both plants and animals
Herbivore
An organism that only eats plants.
Detritivore
Organism that feeds on decaying plant and animal remains and other dead matter.
Carnivore
An organism that only eats other animals.
Decomposer
Organism that breaks down organic matter.
Scavenger
Animals that consume the carcasses of other animals that have already died.
Autotroph
A living thing that can capture energy from sunlight or chemicals to make its own food.
Photosynthesis
A process by which plants use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and sugar
Chlorophyll
A pigment in plants that absorbs red and blue light and reflects green
Chloroplast
A plant cell organelle where photosynthesis takes place
Reactants of Photosynthesis
Water, Carbon Dioxide, and Sunlight Energy
Products of Photosynthesis
Glucose and Oxygen