Intro practical clinical skills
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Normal BG
4-5.9 mmol/L
Fasting blood glucose >7 mmol
It is abnormal but further testing is required
How to use peak flow
Practise explaining…
1. Pull the counter (the red arrow) back as far as it will go to the top.
2. Stand or sit upright
3. Take the deepest breath you can.
4. Make sure your mouth makes a tight seal around the mouthpiece.
5. Blow as hard and fast as you possibly can into the meter.
6. Write down your score
7. Do this three times in a row, with a short rest in between.
8. Use the highest of these scores to fill in your peak flow diary.
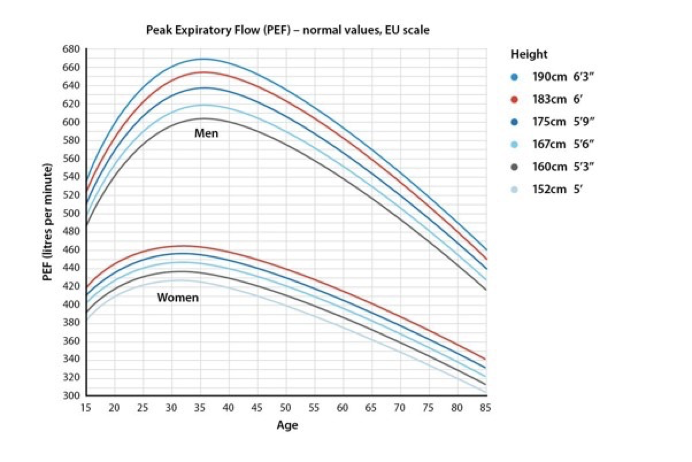
Which parameters are important for peak flow
Height, age, sex
always measure best of 3 to compare baseline
What else do we use to support asthma diagnosis
Peak expiratory flow variability
Amplitude percentage >= 20%
What does BTS/NICE/SIGN say about monitoring
Do not use regular peak expiratory flow to assess asthma control
What would should a patient do if they have a best-of-three result that is:
•80% of personal best
•70% of personal best
•≤50% of personal best ? call ambulance, give treatment
blood glucose kit
Contains lancet and cotton wool/gauze
Gloves
Sharps bin nearby
Stages in taking blood glucose reading
wash with warm water to promote blood flow
‘milk the finger’ to increase blood flow
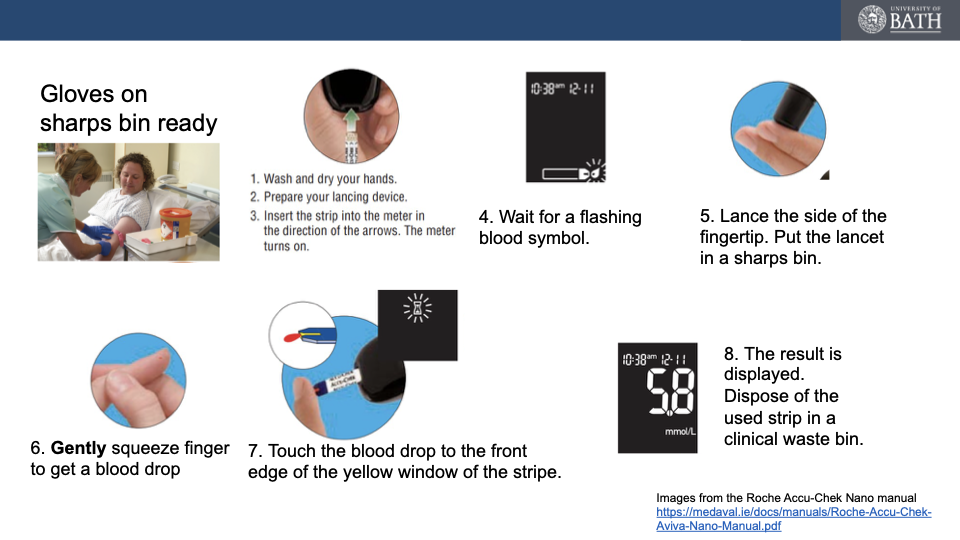
What do we do with fingerprick test
We don’t diagnose diabetes based on test
But it can prompt further investigation
Can be used for self-monitoring e.g. hypoglycemic episodes, driving, operating, pregnant, planning pregnancy
Urinalysis

What is the normal color range of urine?
Colourless to dark yellow.
What are some pathological causes of brown urine?
Bile pigments, myoglobin.
What are some food and drug causes of brown urine?
Levodopa, metronidazole, nitrofurantoin, some antimalarial agents, fava beans.
What are some pathological causes of brownish-black urine?
Bile pigments, melanin, methaemoglobin.
What are some food and drug causes of brownish-black urine?
Cascara, levodopa, methyldopa, senna.
What are some pathological causes of green or blue urine?
Pseudomonal urinary tract infection (UTI), biliverdin.
What are some food and drug causes of green or blue urine?
Amitriptyline, indigo carmine, IV cimetidine, IV promethazine, methylthioninium chloride, triamterene.
What are some pathological causes of orange urine?
Bile pigments.
What are some food and drug causes of orange urine?
Phenothiazines, phenazopyridine, rifampicin, hydroxocobalamin.
What are some pathological causes of red urine?
Haematuria, haemoglobinuria, myoglobinuria, porphyria.
What are some food and drug causes of red urine?
Beetroot, blackberries, rhubarb, phenolphthalein, rifampicin.
What are some causes of yellow urine?
Concentrated urine (orange to gold in dehydration), carrots, cascara.
What are some possible causes of cloudy urine?
Contamination with vaginal mucus or epithelial cells, excess phosphate crystals in alkaline urine, pyuria due to infection, chyluria (secondary to filariasis), hyperuricosuria from a purine-rich diet, lipiduria, hyperoxaluria.
What is the normal odour of urine?
Described as urinoid.
What conditions cause urine to have an abnormal odour?
Alkaline fermentation (ammoniacal smell), diabetic ketoacidosis (sweet or fruity odour), cystine decomposition (sulphuric smell), gastrointestinal-bladder fistulae (faecal smell), medications (e.g., vitamin B6), diet (e.g., asparagus).
Signs of uti
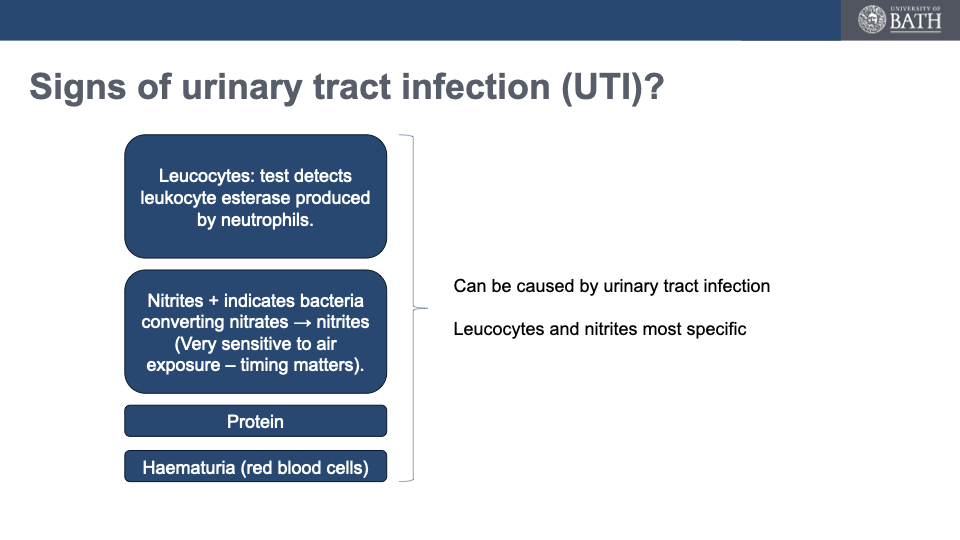
Who do we not use dipsticks for
in older people they have asymptomatic bacteriuria that doesn’t need treatment so don’t use it
•Men <65 years
•do not use urine dipsticks to rule out UTI in men
•Children
•Pregnant women
•People with catheters
•Recurrent UTIs
what can be present in urine
Haematuria
GLucose
Ketones
Visible and non-visible haematuria
Visible (macroscopic) haematuria: Pink, red, or rusty/cola colour.
Non-visible (microscopic) haematuria: Reagent detects: red blood cells, haemoglobin, myoglobin.
but also consider contamination with menstrual blood
Glucosuria
Glucose in urine
Indicates diabetes, renal tubular disease, SGLT2i
Ketones
Breakdown product of fatty acid metabolism
Usually absent
Indicates lack of carbohydrates e.g. ED
Poorly controlled diabetes
RED FLAG: Diabetes, glucose, ketones
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Cause: Insulin deficiency, lipolysis, ketones, metabolic acidosis
Symptoms: Thirst, frequent urination, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhoea, acetone breath
If you find ketones doesn’t mean DKA but do further investigation
Vaccinations: Who should not have vaccines
Anyone with previous anaphylactic reaction to the vaccine
Acutely unwell
Live vaccines: contraindicated if pregnant or immunosuppressed
Intranasal
Live attenuated flu vaccine for children
Subcutaneous and intradermal
Subcutaneous: 45 degrees
Intradermal: 15 degrees
Bleeding disordor
For people with bleeding disorders, vaccines are given by deep subcutaneous injection not intramuscular.
Needle kit
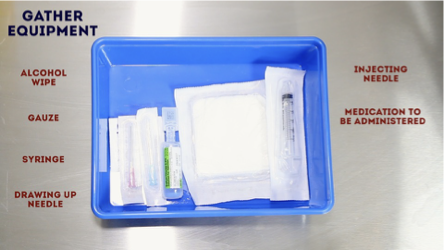
What dangers
Deltoid muscle prefered site
If you touch shoulder risk of injury
Lift arm, feel for dimple = acronium process
Too high risk : sciatic nerve
Too low risk of nerve damage axillary or radial nerve
Don’t inject buttock