L11 How plate tectonics & Cliamte shaped ireland part 1
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Geological period
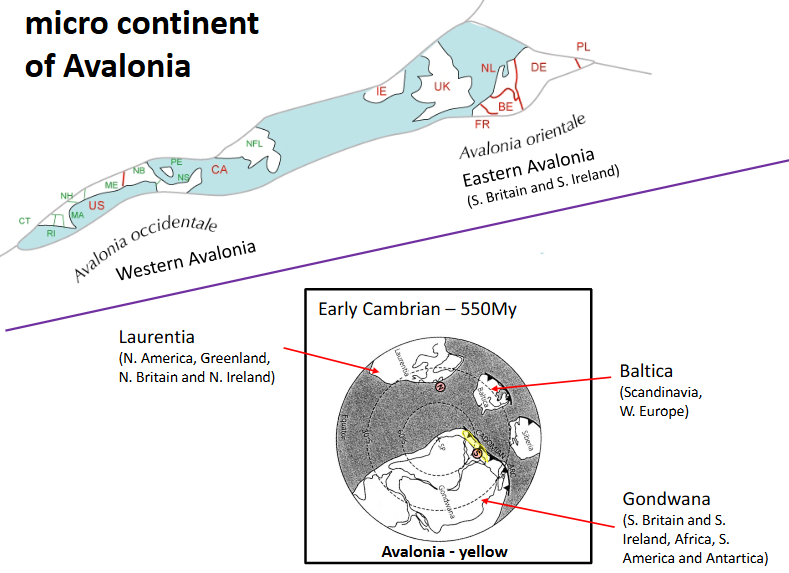
Micro continent of ______?
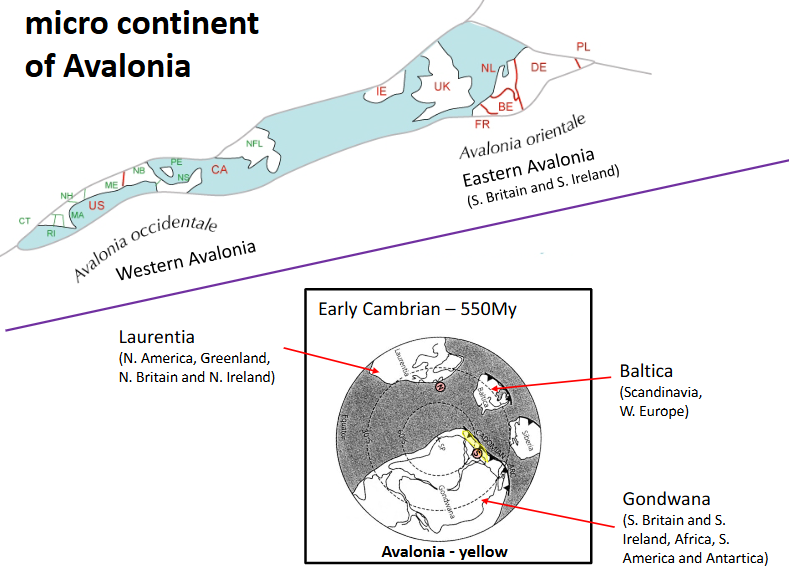
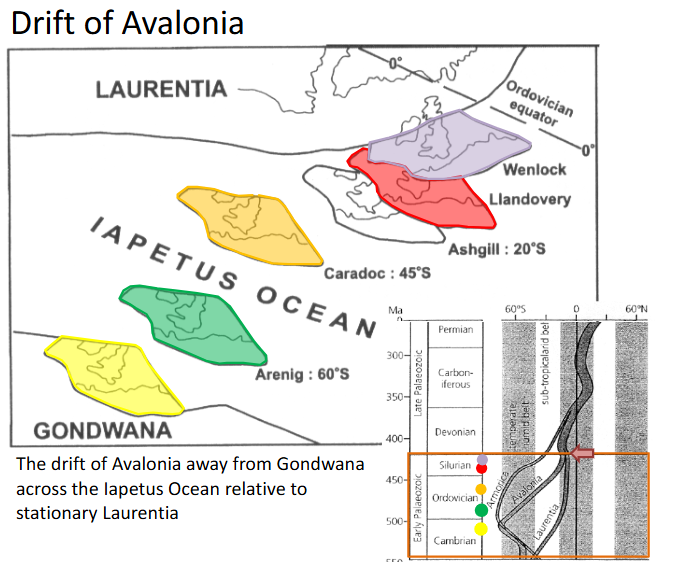
Drift of Avalonia
The drift of Avalonia away from Gondwana across the Lapetus Ocean relative to stationary Laurentia
The Caledonian- Appalachian Orogeny
Continuity of Caledonian/Acadian mountain belt chains in the Early Devonian (420My)
Collison zone between North and South of Ireland
Collision took place 400My ago - contains island arcs, seamounts, microcontinents from lapetus ocean.
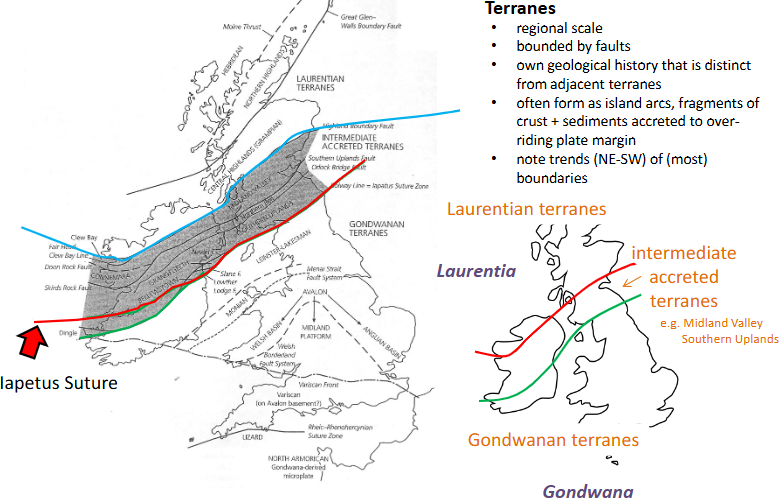
Terranes
regional scale
bounded by faults
own geological history that is distinct from adjacent terranes
often form as island arcs, fragments of crust + sediments accreted to over-riding plate margin
note trends (NE-SW) of (most) boundaries
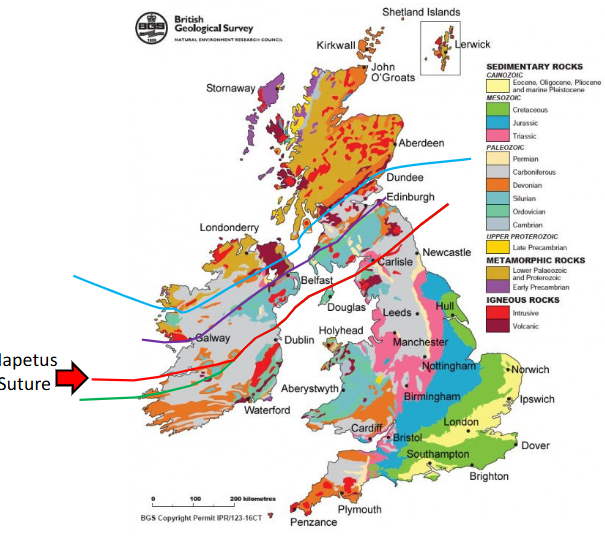
The geological map of Britain and Ireland
The lines are indication of terrains around these two countries.
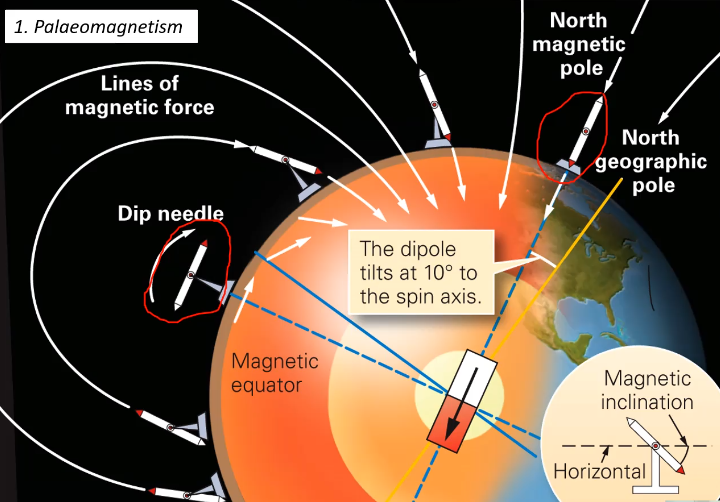
Palaeomagnetism
orientation of the magnetic field can be retained in rocks in any form.
Igenous rocks
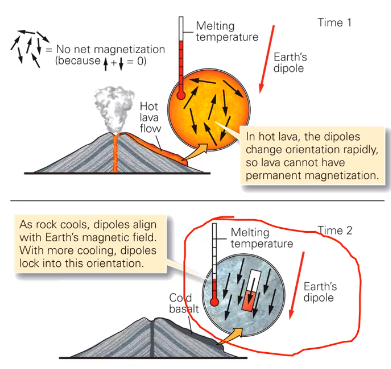
Thermo-remanent magnetization
magnetic minerals become aligned in igneous rocks as they cool
Sedimentary rocks
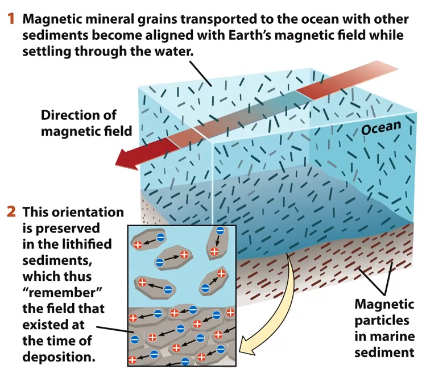
Depositional remanent magnetization
Detrital magentic minerals settle out during deposition symapthetic to the orientation of the magnetic field.
Faunal Provincialism
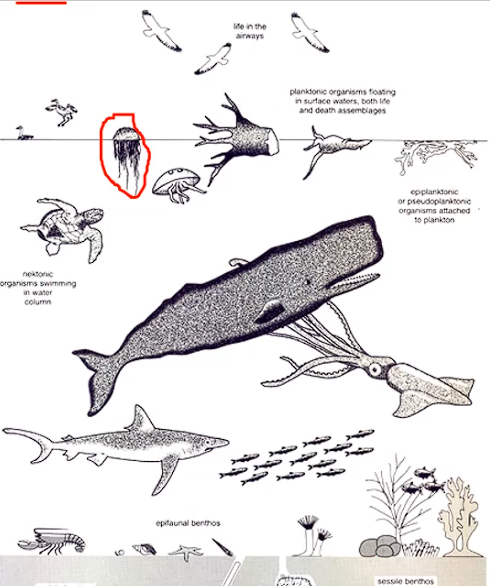
Ecology of marine
benthic = living on or within floor of sediment column
pelagic = water not at/cloose to floow of sediment body, nor its margins (e.g. shore)
planktonic = drift or swim weakly
nektonic = free-swrimming in water column
epifaunal = living on surface of sediment column
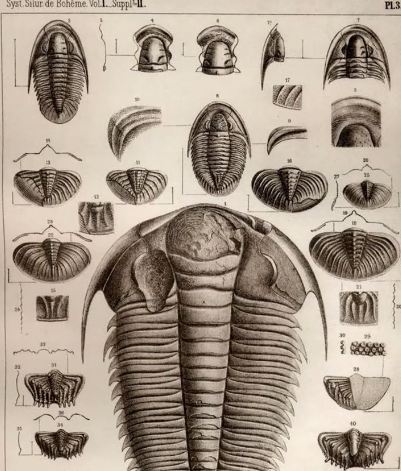
Trilobites
Marine arthropods (Phylum arthropoda)
Shed exoskeleton
Extincy
Cambrian to Permian
Graptolites
Phylum Hemichordata
Colonila, marine, invertebrates
M. Cambrian - U. Carboniferous
Organic outer protective layer (periderm)

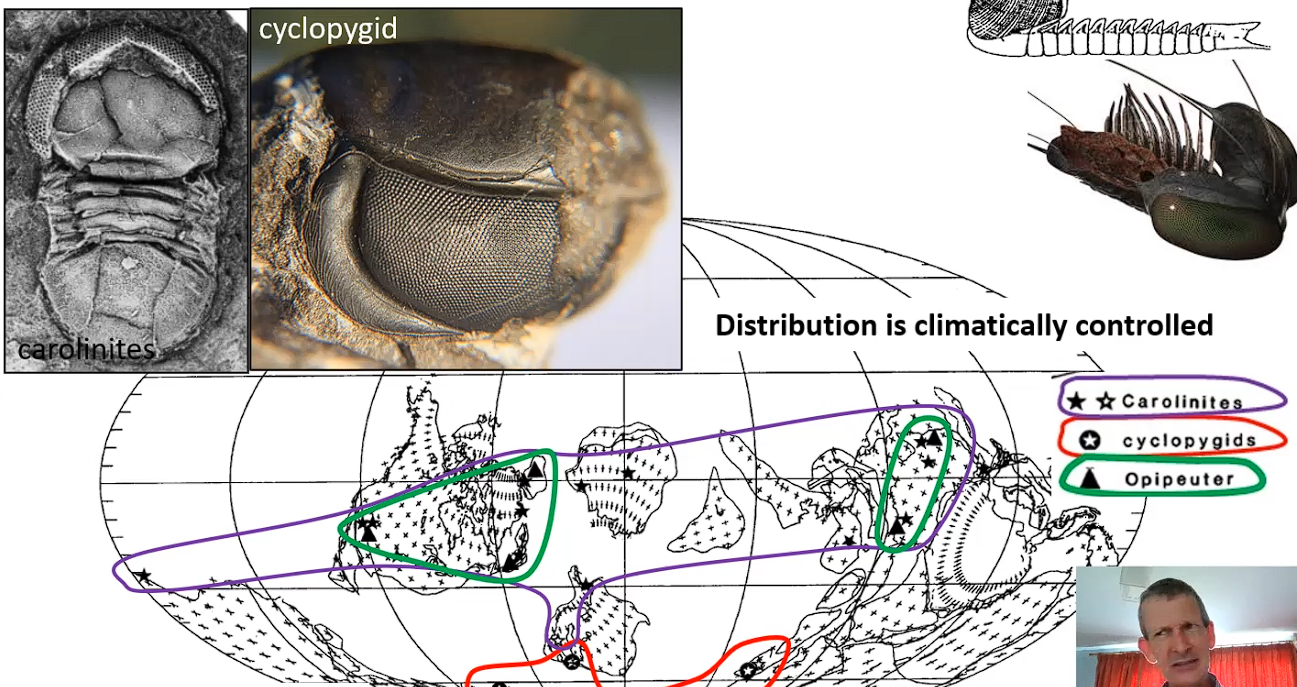
Early Ordovician pelagic trilobites - strong latiduinal control
Cyclopygid trilobites: High southerly (palaeo) latitudes - enlarged eyes with wide angle of view, both horizontal and vertical
Opipeuter: Low latitudes - note visual adaption for nektonic lifestyle
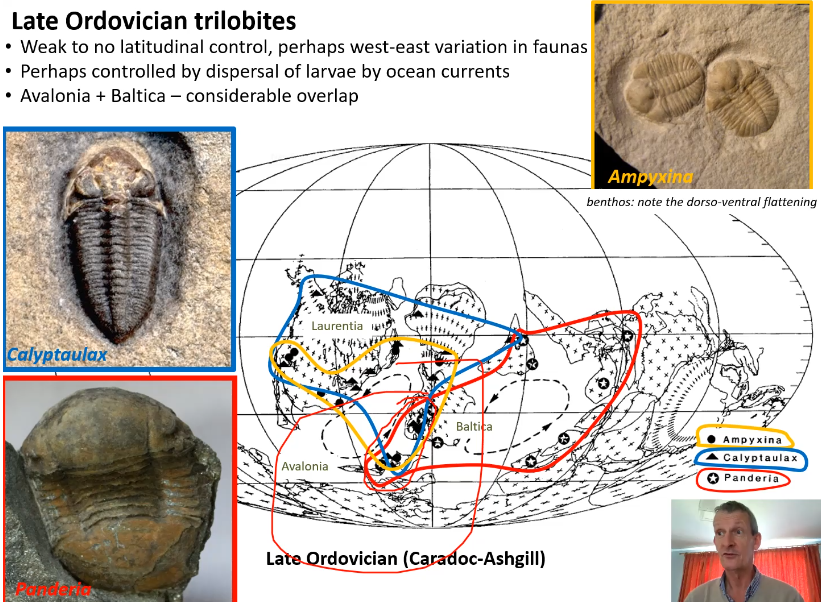
Late Ordovician trilobites
Weak to no latitudinal control, perhaps west-east variation in faunas
Perhaps controlled by dispersal or larvae by ocean currents
Avalonia + Baltica - considerable overlap
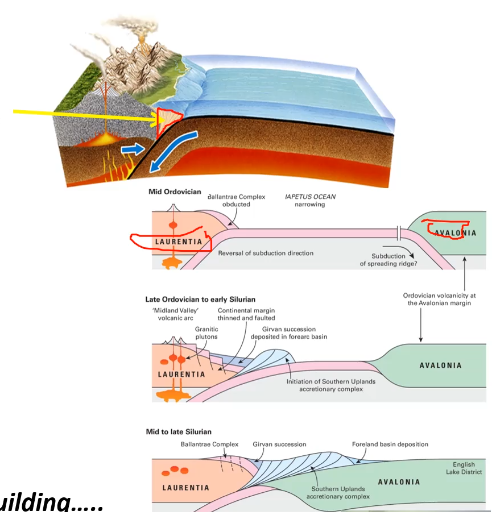
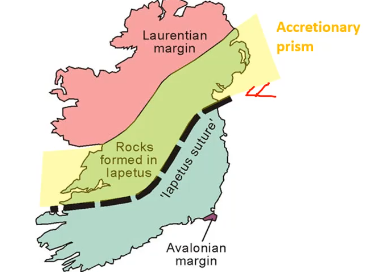
Accretionary wedge
deep marine sediments
greywackes (muddy sandstones)
deposited as event beds from turbidity currents
associated with black shales and cherts (open oceanic sediments)
orogneic events during closure of lapetus collectively the caledonian orogeny
accretionary wedge is developed to the north of suture.