Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Contains: Chapter 44, Chapter 45, and Chapter 47
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
Ecology
The study of organisms and how they interact with the environment around them.
2
New cards
What are abiotic factors?
The **nonliving** part of the ecosystem
3
New cards
What are biotic factors?
The **living** part of the ecosystem
4
New cards
List the levels of organization from smallest to greatest
Organisms → Populations → Communities → Ecosystems → The Biosphere
5
New cards
Organismal Ecology
Study adaptations that enable individuals to live in specific habitats. These adaptations can be morphological, physiological, and behavioral.
6
New cards
Population Ecology
Focus on the number of individuals in an area and how and why population size changes.
7
New cards
Community Ecology
Study the processes driving interactions between species, as well as their consequences.
8
New cards
Ecosystem Ecology
Study the storage and movement of nutrients and energy among organisms and the surrounding atmosphere, soil, and water.
9
New cards
Biosphere
all of the parts of Earth inhabited by life
10
New cards
What is the difference of community biology and population biology
Population biology is one type of organisms while community includes multiple types of organisms.
11
New cards
__**What is the biome?**__
Temperature: Day: Hot!! Night: Cold
Precipitation: Low precipitation
Plants: Xerophytes
Temperature: Day: Hot!! Night: Cold
Precipitation: Low precipitation
Plants: Xerophytes
Desert
12
New cards
__**What is the biome?**__
Temperature: Warm
Precipitation: Seasonal droughts
Plants: Mainlly grasses and spars trees
Temperature: Warm
Precipitation: Seasonal droughts
Plants: Mainlly grasses and spars trees
Grass lands
13
New cards
__**What is the biome?**__
Temperature: Moderate
Precipitation: Rainy winters and dry summers
Plants: Dry wood shrubs regrow quickly
Temperature: Moderate
Precipitation: Rainy winters and dry summers
Plants: Dry wood shrubs regrow quickly
Shrubland/chaparral
14
New cards
__**What is the biome?**__
Temperature: Cold
Precipitation: A small amount of precipitation
Plants: Coniferous trees
Temperature: Cold
Precipitation: A small amount of precipitation
Plants: Coniferous trees
Coniferous forest (Tiga)
15
New cards
__**What is the biome?**__
Temperature: Hot
Precipitation: A lot!
Plants: Epipyltes, tall trees, and undergrowth
Temperature: Hot
Precipitation: A lot!
Plants: Epipyltes, tall trees, and undergrowth
Tropical Rainforest
16
New cards
__**What is the biome?**__
Temperature: Freezing
Precipitation: Little precipitation
Plants: Small, close to the ground
Temperature: Freezing
Precipitation: Little precipitation
Plants: Small, close to the ground
Tundra
17
New cards
__**What is the biome?**__
Salinity: High
Diversity: Very high
Salinity: High
Diversity: Very high
Coral reef
18
New cards
Climate
refers to the long-term, predictable atmospheric conditions of a specific area.
19
New cards
Weather
refers to the conditions of the atmosphere during a short period of time.
20
New cards
Milankovitch cycles
the effects of slight changes in the Earth’s orbit on Earth’s climate
21
New cards
Solar intensity
the amount of solar power or energy the sun emits in a given amount of time
22
New cards
Haze-effect cooling
a global phenomenon that occurs when dust, ash, or other suspended particles block out sunlight and trigger lower global temperatures as a result
23
New cards
**Greenhouse gases**
trap the heat in the atmosphere
24
New cards
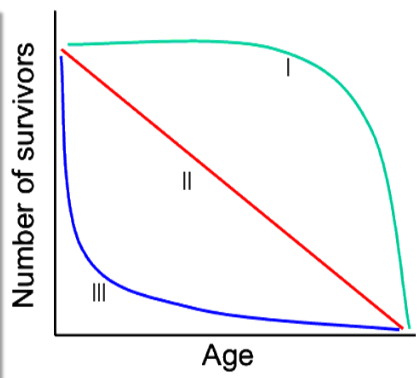
What organism is an example of type 1 survival ship curve?
Humans
25
New cards
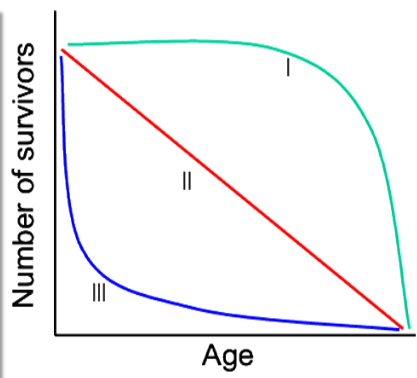
What organism is an example of type 2 survival ship curve?
Birds
26
New cards
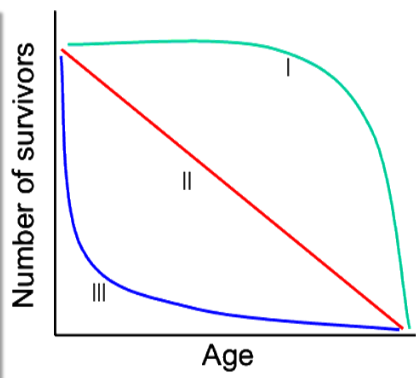
What organism is an example of type 3 survival ship curve?
Fish
27
New cards
Census
Count all members of the population
28
New cards
Quadrat
Sectioning off a section of the area and counting the organism (For immobile organisms such as plants)
29
New cards
Mark and recapture
Individuals are is captured, counted, and marked. Then they are released back into the population.
30
New cards
Transect
A-line, laid on the forest floor, that is used to make sure the points or plots are distributed evenly throughout the forest stand.
31
New cards
R-selected
produce large numbers of offspring at a time with a low amount of parental care
32
New cards
K-selected
produce small numbers of offspring at a time with a high amount of parental care
33
New cards
Life tables
A divide the population into age groups and often sexes and show how long a member of that group is likely to live
34
New cards
Density-dependent factors
Factors that determine a population size that depend on the density of the population. (ex. disease)
35
New cards
Density- independent Factors
any force that affects the size of a population of living things regardless of the density of the population (ex. food)
36
New cards
Commensal relationship
one species benefits, while the other neither benefits nor is harmed.
37
New cards
Mutualism
two species benefit from their interaction.
38
New cards
Parasitism
one organism that lives in or on another living organism and derives nutrients from it; the parasite benefits, but the host is harmed.
39
New cards
Mass extinction
a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth.
40
New cards
Keystone species
Species hold together the complex web of relationships in an ecosystem (ex. otters)
41
New cards
Four Types of Ecosystem Services
provisioning, regulating, cultural and supporting services
42
New cards
What is an example of a provisioning service?
Food, water, and fuel
43
New cards
What is an example of a regulating service?
Climate, air quality, and pollination
44
New cards
What is an example of a supporting service?
Nurturance cycling, soil formation, and photosynthesis.
45
New cards
What is an example of a cultural service?
Ethical values, recreational, ecotourism.
46
New cards
What are some examples of threats to biodiversity?
habitat loss, pollution, overexploitation, invasive species, and climate change