14-15 Enzymes and Membrane Transport
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
What is activation energy (EA)?
The initial input of energy required to break chemical bonds before new bonds can be formed.
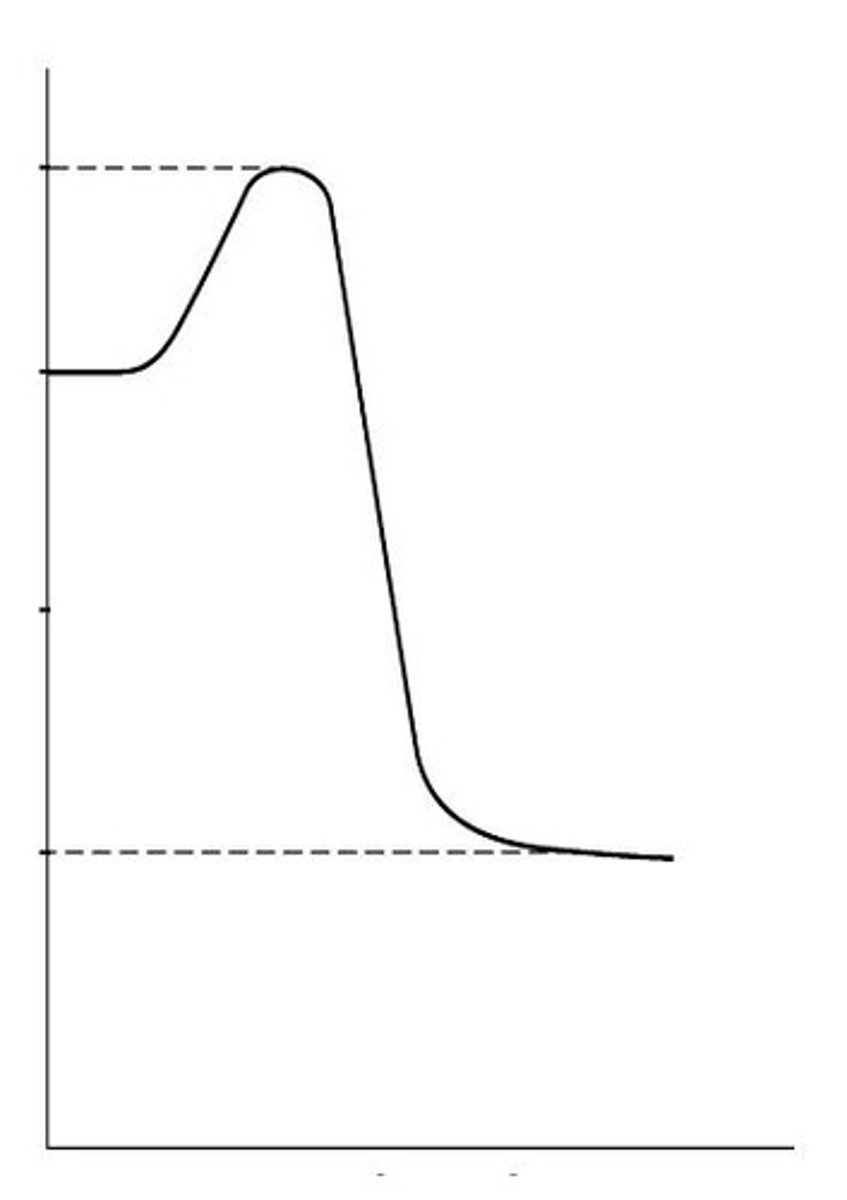
What is the transition state in a chemical reaction?
An intermediate high energy state between reactants and products.
What determines whether a reaction is favorable or not?
The reaction energy (ΔG); if ΔG is negative (< 0), the reaction is possible.
How does activation energy affect the speed of a reaction?
Higher activation energy results in a slower reaction, while lower activation energy leads to a faster reaction.
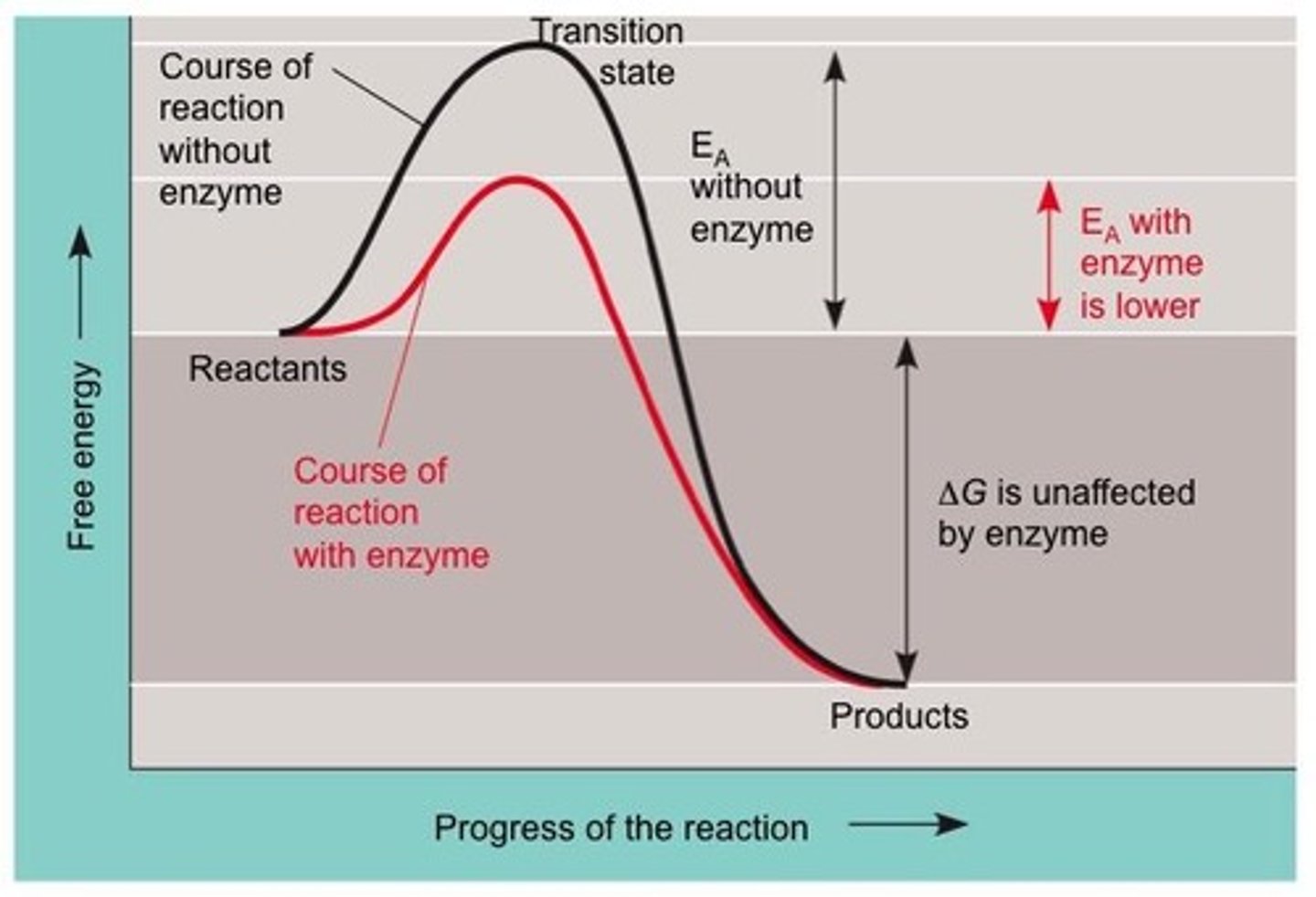
What is the formula for calculating activation energy (EA)?
EA = energy of transition state - energy of substrates.
What is the formula for calculating reaction energy (ΔG)?
ΔG = energy of products - energy of substrates.
What characterizes an energetically favorable reaction?
A reaction with negative reaction energy (ΔG < 0) where free energy is lost in converting reactants to products.
What is a catalyst?
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by reducing the activation energy (EA) without changing the reaction energy (ΔG).
What are enzymes?
Proteins that act as biological catalysts, speeding up reactions by lowering activation energy.
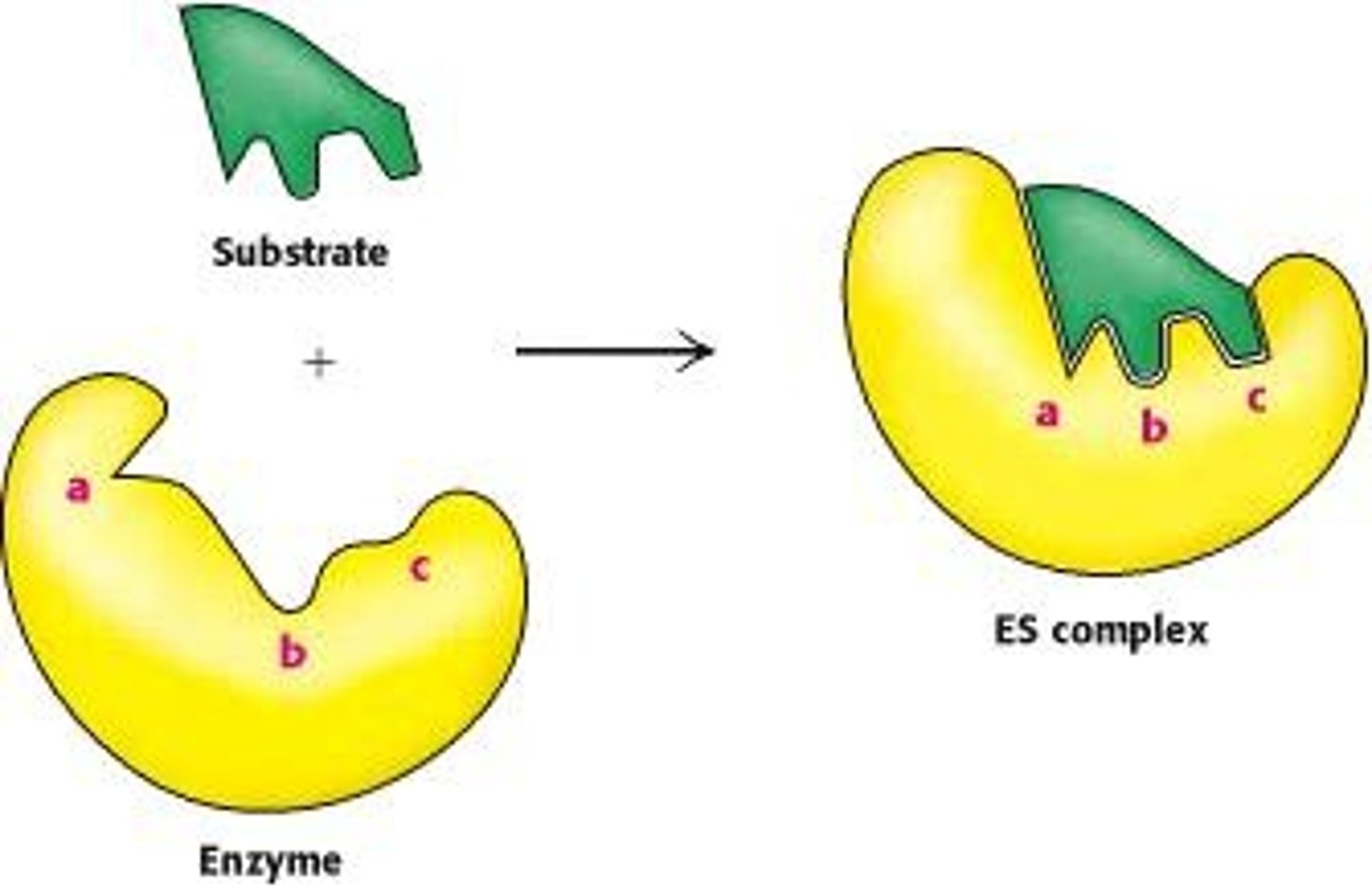
What is substrate specificity in enzymes?
The ability of an enzyme to bind to specific substrates, forming a transient enzyme-substrate complex.
What is the active site of an enzyme?
The region of the enzyme where substrates bind, characterized by a specific shape that accommodates certain substrates.
Do enzymes change the equilibrium of a chemical reaction?
No, enzymes do not change the equilibrium; they only speed up the rate at which equilibrium is reached.
What is the difference between exergonic and endergonic reactions?
Exergonic reactions release energy (ΔG < 0), while endergonic reactions require energy input (ΔG > 0).
What is the significance of the double arrow in chemical reactions?
It indicates that reactions can occur in both directions until equilibrium is reached.
How do enzymes stabilize the transition state?
By forming a transient enzyme-substrate complex that lowers the activation energy required for the reaction.
What happens to the enzyme after a reaction?
The enzyme is not consumed in the reaction and can be reused for subsequent reactions.
What does it mean for a reaction to be maintained far from equilibrium?
It means that the concentrations of reactants and products are kept at levels that favor the direction of the reaction.
What role do enzymes play in living organisms?
Enzymes catalyze all biochemical reactions, making them essential for metabolic processes.
What is the relationship between reaction energy (ΔG) and activation energy (EA)?
ΔG determines if a reaction is favorable, while EA determines the speed of the reaction.
What is a transient enzyme-substrate complex?
A temporary association formed when an enzyme binds to its substrates.
What is the effect of a catalyst on reaction energy (ΔG)?
A catalyst does not change the reaction energy (ΔG); it only lowers the activation energy (EA).
What is the role of the active site in an enzyme?
The active site is designed to bind to specific substrates, facilitating the enzyme's catalytic function.
What is the induced fit model of enzyme action?
The induced fit model suggests that the enzyme changes shape upon substrate binding, forming a complementary shape to the substrate.
How do substrates interact with the active site of an enzyme?
Substrates enter the active site, and the enzyme changes shape to enfold the substrates, stabilizing them through weak interactions.
What is activation energy (EA) and how do enzymes affect it?
Activation energy is the energy required to initiate a reaction. Enzymes lower EA by stabilizing the transition state.
What happens to the enzyme after a reaction occurs?
The enzyme is not consumed in the reaction and is available to catalyze more reactions after products are released.
What environmental factors can affect enzyme activity?
Enzyme activity is sensitive to pH, temperature, and salt concentration, with each enzyme having an optimum range for function.
What are cofactors in relation to enzymes?
Cofactors are non-protein molecules, often metal ions like iron, copper, and zinc, that are necessary for certain enzymes to function.
What is competitive inhibition?
Competitive inhibition occurs when an inhibitor binds to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate for access.
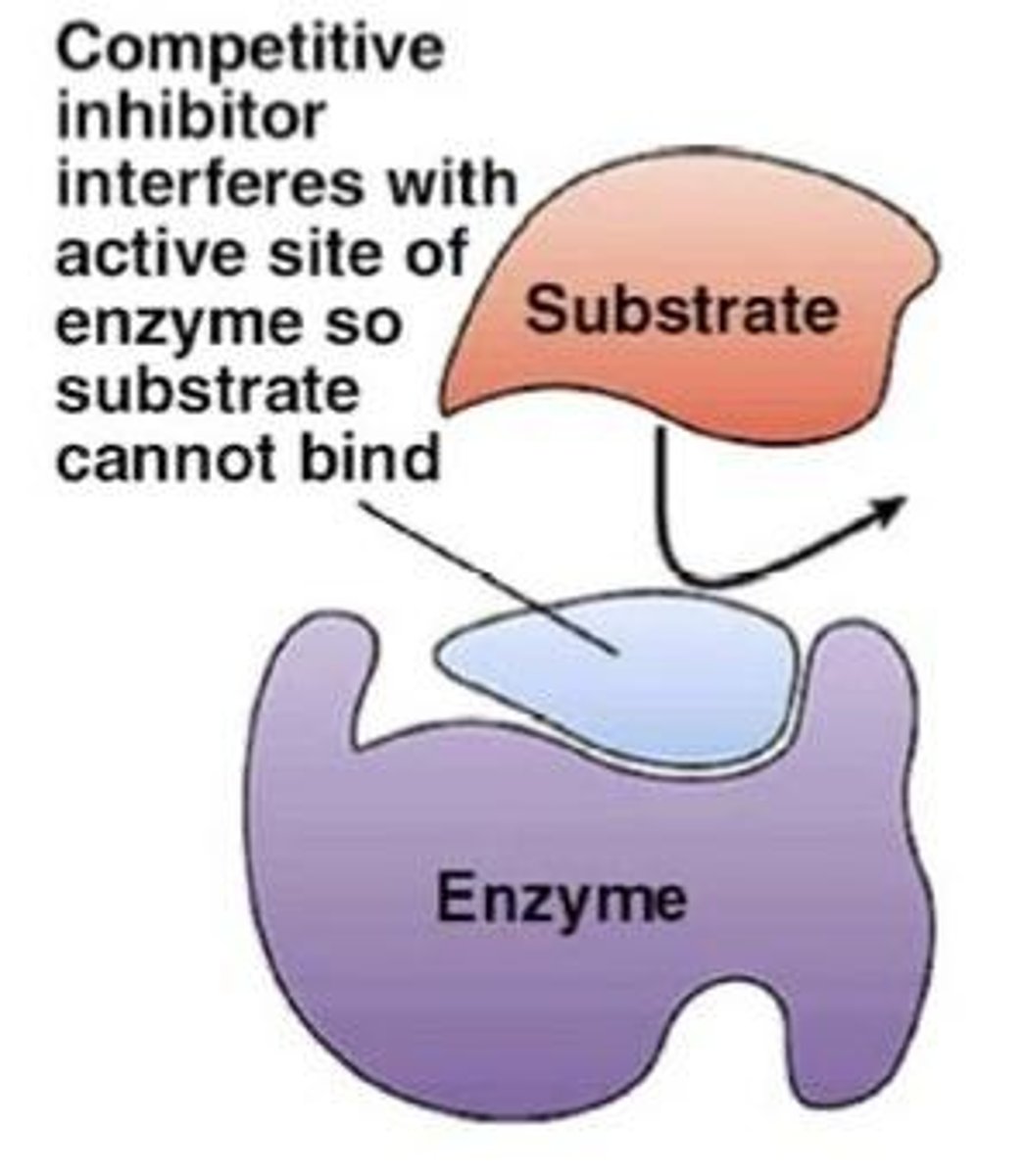
How can competitive inhibition be reversed?
Competitive inhibition can be reversed by increasing the concentration of the substrate, allowing it to out-compete the inhibitor.
What is noncompetitive inhibition?
Noncompetitive inhibition occurs when an inhibitor binds to a site other than the active site, changing the enzyme's shape and reducing its effectiveness.
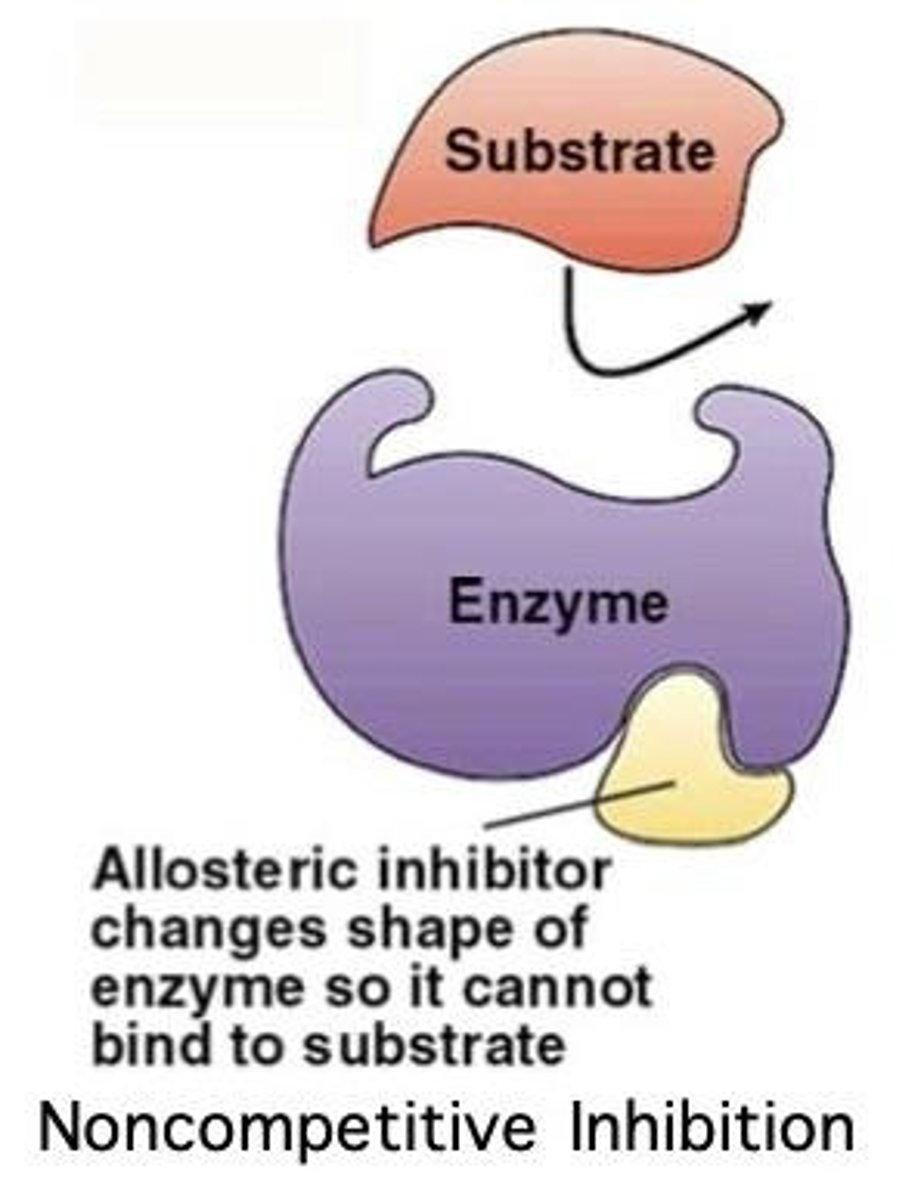
What is allosteric inhibition?
Allosteric inhibition refers to the binding of an inhibitor to a site different from the active site, which alters the enzyme's shape and function.
What is feedback inhibition?
Feedback inhibition is a regulatory mechanism where the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an earlier step, preventing overproduction.
Why are enzymes essential for life?
Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reactions, allowing cellular processes to occur quickly enough to sustain life.
How do enzymes ensure specificity in chemical reactions?
Each enzyme is specific to a particular substrate, directing reactions along specific pathways and avoiding unwanted side reactions.
What is the significance of the enzyme's shape?
The shape of the enzyme, particularly the active site, is crucial for its ability to bind substrates and catalyze reactions.
What types of interactions stabilize substrates in the active site?
Substrates are stabilized in the active site by weak interactions such as hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds.
What is the catalytic cycle of an enzyme?
The catalytic cycle involves the enzyme binding substrates, converting them to products, releasing the products, and being recycled for further reactions.
What is the role of allosteric regulators?
Allosteric regulators can act as activators or inhibitors, changing the enzyme's shape to enhance or reduce its activity.
What is the optimal temperature and pH for most human enzymes?
Most human enzymes work best at around 37°C and a pH close to 7.
What is the primary function of transmembrane proteins in cellular membranes?
To allow transport of specific molecules into and out of the cell and perform other functions.
How do channel proteins facilitate membrane transport?
They provide a tunnel or corridor that allows a specific molecule to cross the membrane.
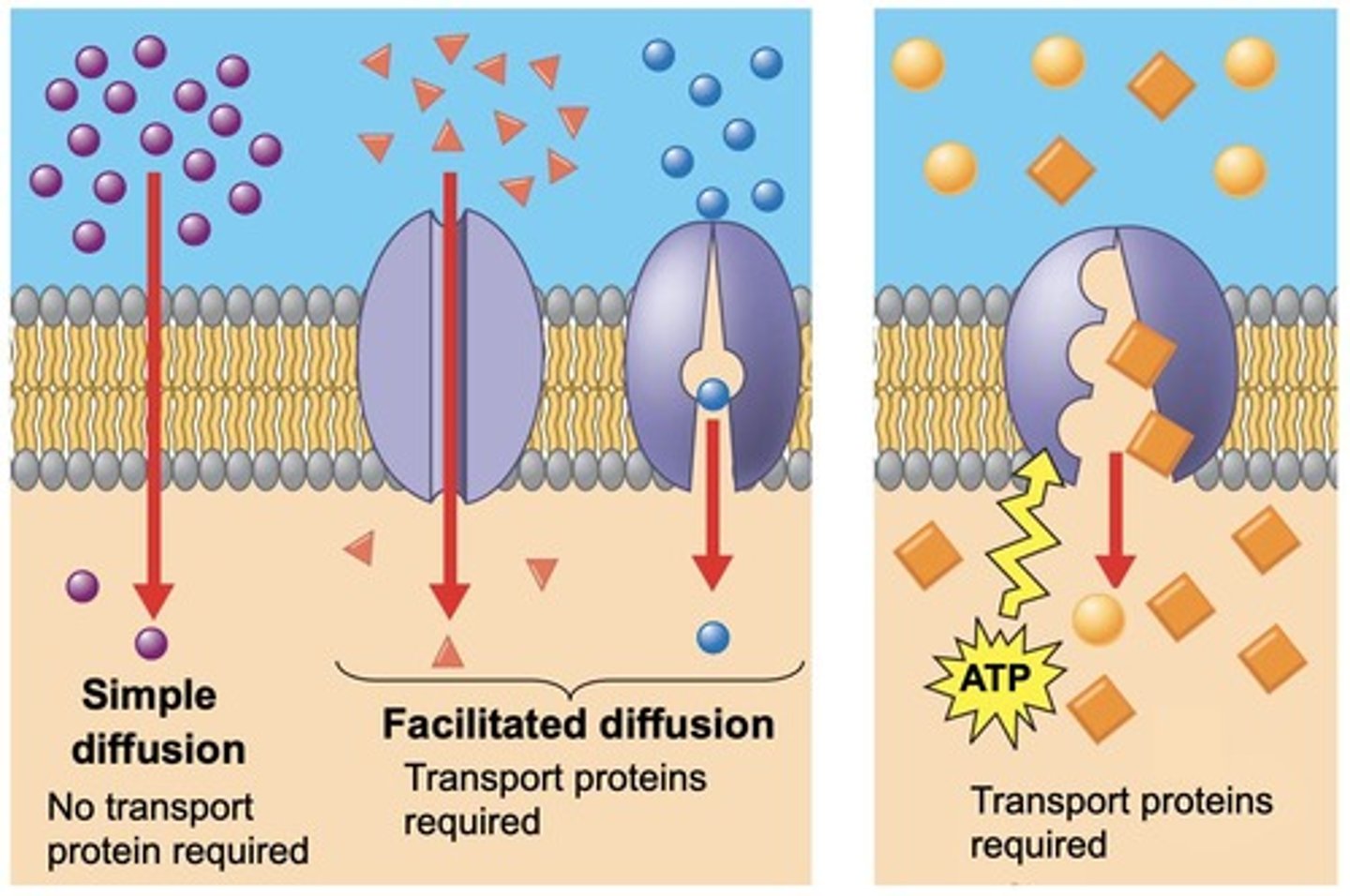
What is the role of carrier proteins in membrane transport?
They bind to the solute molecule and undergo a shape change to translocate the molecule across the membrane.
What type of molecules can pass directly through the phospholipid bilayer?
Small hydrophobic molecules such as O2 and steroid hormones.
What is membrane transport?
The movement of a molecule across a cell membrane, either directly through the phospholipids or via a transport protein.
What does it mean if a membrane is permeable to a molecule?
It means the molecule can pass through the cell membrane by membrane transport.
What is selective permeability in cellular membranes?
The ability of different cells and organelles to have different transport proteins, making them permeable to different materials.
What determines the direction of membrane transport?
The concentration gradient, where molecules move from high concentration to low concentration.
What is diffusion in the context of membrane transport?
The net movement of a substance down its concentration gradient, which can occur with or without transport proteins.
What distinguishes simple diffusion from facilitated diffusion?
Simple diffusion does not require transport proteins, while facilitated diffusion does.
What is active transport?
The movement of solutes against their concentration gradients, requiring energy.
How is active transport coupled to ATP breakdown?
A reaction with a negative DG can drive the active transport process, which has a positive DG.
What is cotransport in membrane transport?
The process where passive transport of one solute drives the active transport of another.
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water down its concentration gradient across a selectively permeable membrane.
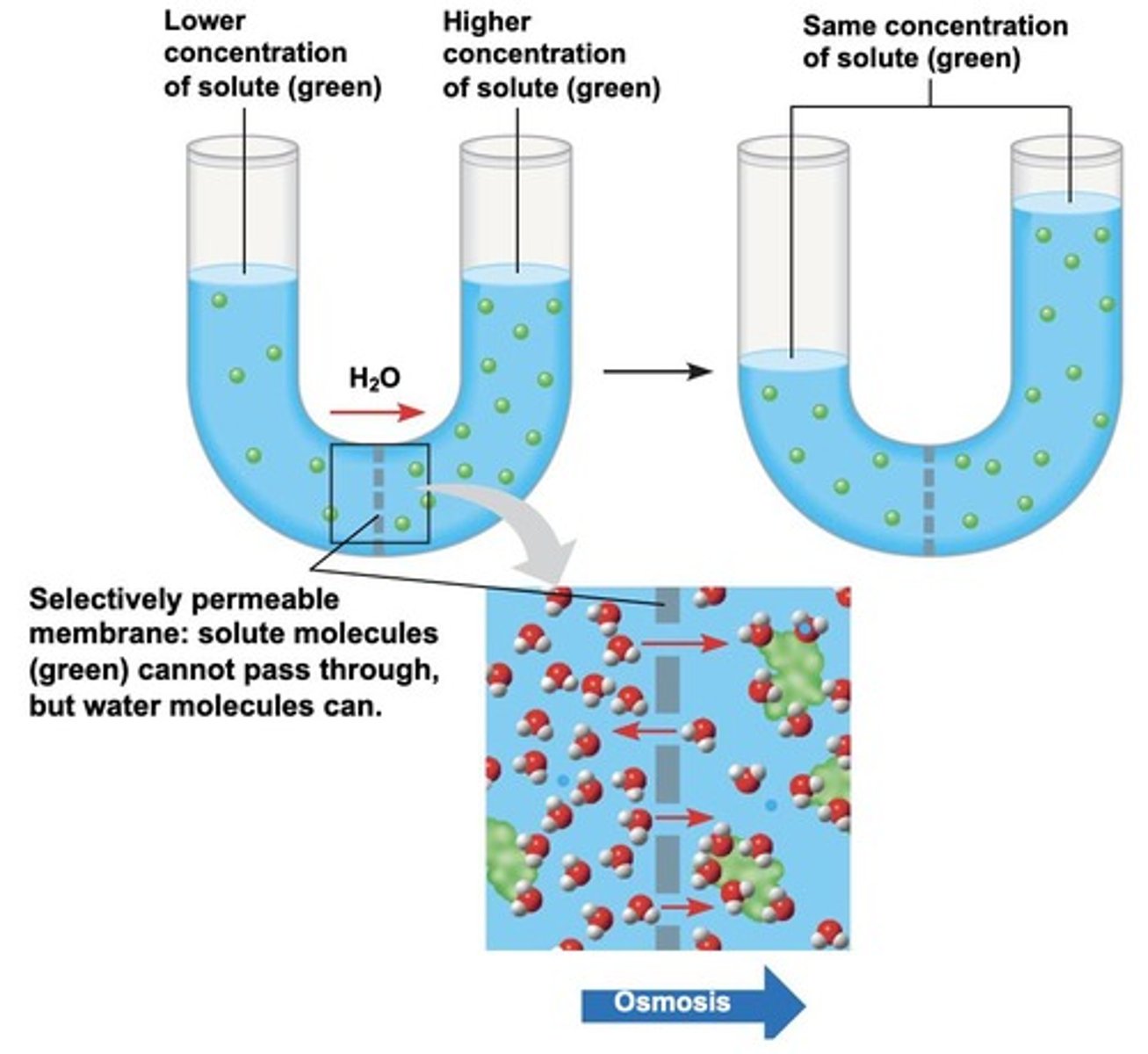
How does the concentration of solute affect the movement of water in osmosis?
Water moves from areas of lower solute concentration to areas of higher solute concentration.
What happens during osmosis when the membrane is impermeable to solute?
Water moves to equalize solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
What is the significance of equilibrium in membrane transport?
It is the state where the net movement of molecules ceases, as concentrations are equal on both sides.
What type of transport is characterized by DG < 0?
Passive transport, which does not require energy.
What is the overall DG for a coupled process involving active transport?
It must be negative for the process to be favorable overall.
What does tonicity describe?
The solute concentration of one solution compared to another.
What is an isotonic solution?
A solution where the solute concentration is the same as that inside the cell, resulting in no net movement of water.
What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution?
The cell loses water because the solute concentration is greater outside the cell.
What occurs to a cell in a hypotonic solution?
The cell gains water because the solute concentration is less outside the cell.
How do animal cells respond to hypotonic solutions?
Animal cells can burst due to the influx of water, necessitating osmoregulation to maintain water balance.
What is osmoregulation?
The control of water balance in cells to maintain integrity, especially in animal cells.
What is turgor pressure in plant cells?
The pressure created by water influx in a hypotonic solution that keeps plant cells turgid and strong.
What is the role of the contractile vacuole in Paramecium?
It acts as a pump to expel excess water that enters by osmosis in freshwater environments.
What is the significance of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump?
It maintains membrane potential by pumping 3 Na+ out of the cell and 2 K+ into the cell for each ATP used.
What is membrane potential?
The charge difference across a membrane due to the partition of electrically charged ions, typically between -50 to -200 mV.
What is an electrochemical gradient?
The combined effect of the concentration gradient and the membrane potential on the movement of ions.
How does the Nernst equation relate to electrochemical gradients?
It is used to calculate the electrochemical gradient by considering both chemical and electric gradients.
What happens to glucose and fructose in a dialysis bag model?
Glucose moves out of the bag, fructose moves into the bag, and there is no net movement of sucrose.
What is the effect of a plant cell being placed in a hypertonic solution?
The plant cell becomes plasmolyzed as it loses water and the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall.
What is the preferred solution for plant cells?
Plant cells prefer a hypotonic solution to maintain turgor pressure.
What adaptation do unicellular protists have for osmoregulation?
They have specialized mechanisms, such as contractile vacuoles, to manage water balance in different environments.
What is the net movement of water in relation to sucrose in a dialysis bag?
Water moves into the bag because sucrose is at a higher concentration inside the bag, creating a lower concentration of water inside.
What is the outcome for an animal cell in an isotonic solution?
The animal cell remains normal with no net movement of water.
What happens to plant cells in an isotonic solution?
Plant cells become flaccid as they do not have turgor pressure.
What is the role of ion gradients in cellular processes?
Ion gradients are used as a source of energy for processes like cotransport.