Bernoulli's Principle
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Kinetic Energy Term
(1/2)ρv² → (Represents the energy per unit volume due to the fluid’s motion)
Gravitational Potential Term
ρgh → (Represents the energy per unit volume due to the fluid’s height in a gravitational field)
p1 + ρgh1 = p2 + ρgh2
The Bernoulli’s equation in static fluids (v1 = v2 = 0)
p2 = p1 + ρgh1
Bernoulli’s equation for static fluids simplified if we set h2 = 0 as the reference height.
p = ρgh (Formula for pressure in a static fluid column)
In the simplest static case, if p1 = 0 at the fluid surface, what relation do we get?
ΔUg = -mgh
Formula for the Gravitational potential energy
That the pressure change due to fluid weight is ρgh, consistent with the gravitational potential energy.
What fundamental fact about fluids does Bernoulli’s equation confirm in static cases?
When h1 = h2 (that means the fluid depth remains the same)
What condition defines Bernoulli’s equation for constant depth?
p1 + (1/2)ρ(v1)^2 = p2 + (1/2)ρ(v2)^2
Bernoulli’s equation for the constant depth
Bernoulli’s Principle
What is Bernoulli’s equation called when applied to constant depth flows?
That the pressure decreases as the fluid speed increases.
What does Bernoulli’s principle reinforce about pressure and speed?
p2 < p1, in order to keep the energy balanced.
If v2 > v1, how must the pressure compare?
Entrainment
The process where high-velocity fluid creates low pressure that pulls another fluid into the stream.
Historical use of the entrainment devices.
As pumps to raise water small heights for draining swamps, fields, and low-lying areas.
Entrain
(Verb) To make something part of a liquid or flow of something and carry it along.
Entrainment Device Principle
Increased fluid speed → reduced pressure → one fluid entrains another.
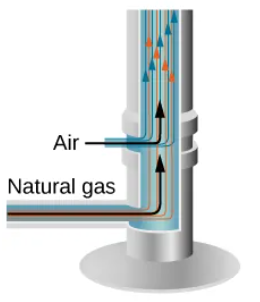
Its gas nozzle entrains air for proper combustion.
How does a Bunsen burner use entrainment?
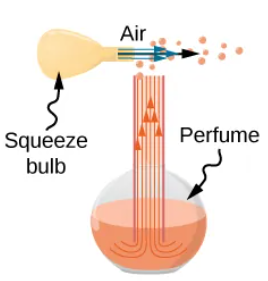
A squeeze bulb makes a jet of air that entrains drops of perfume
How does an atomizer apply entrainment?
Carburetor
A device in an internal combustion engine for mixing air with a fine spray of liquid fuel.
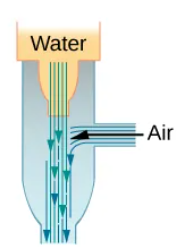
A high-speed stream of water creates low pressure for suction in dentistry, surgery, or draining basements.
How does a common aspirator use entrainment?
It draws in air through the pipe leading out the ceiling.
How does a water heater chimney use entrainment?

v1 = 0
(i)
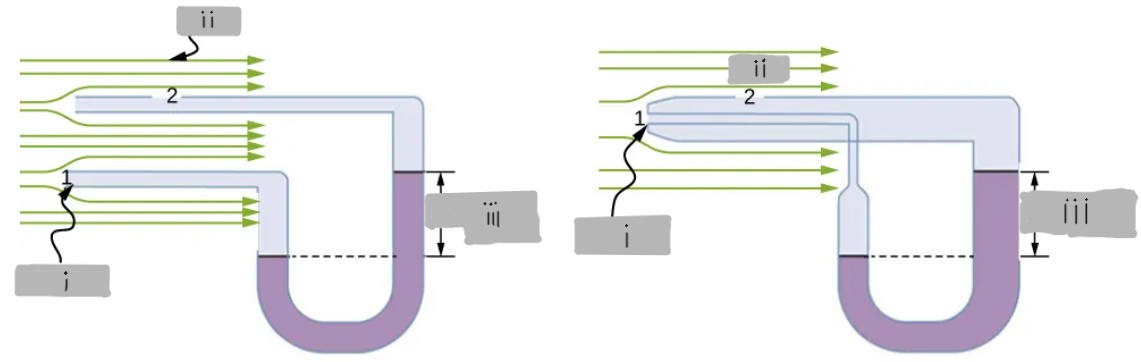
v2
(ii)
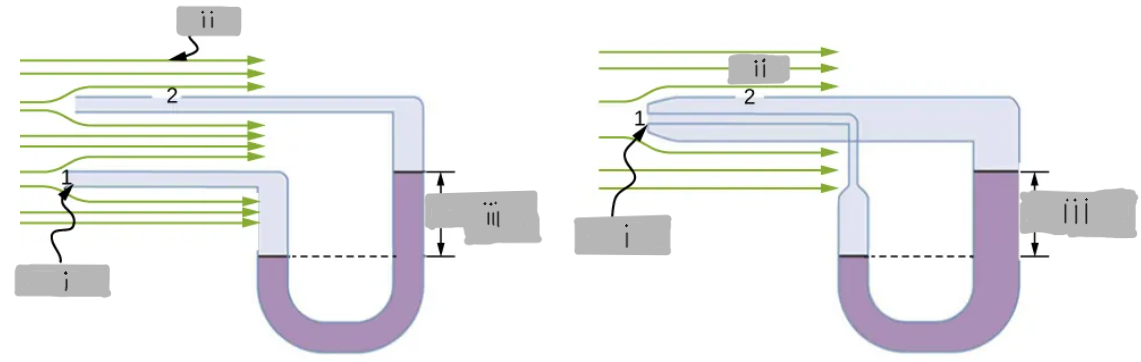
h ∝ (1/2)ρ(v2)^2
(iii)

The fluid comes to rest at the opening, creating a stagnation point where velocity is zero (v1 = 0)
What happens at the tube of a manometer that directly faces the oncoming fluid?
The fluid has velocity v2, which reduces the pressure at that opening.
In the second tube of the manometer, which is exposed to moving fluid, what is the velocity?
p1 = p2 + (1/2)ρ(v2)^2
Bernoulli’s relation for the manometer tubes
By (1/2)ρ(v2)^2
By how much is the pressure reduced at the second tube’s opening?
h ∝ (1/2)ρ(v2)^2, which is the pressure difference due to the fluid speed
What does the manometer height difference (h) represent in this setup?
v2 ∝ (h)^1/2
How is fluid velocity related to the manometer height difference?
Prandtl tube
A manometer that measures the fluid velocity using the Bernoulli’s principle. Utilized as an air-speed indicator in the aircraft.
Pilot tube
Another name for “Prandtl tube”
Because the water must rise uphill and its speed increases in the nozzle.
Why is the pressure in the nozzle of a fire hose less than at ground level?
The water’s kinetic energy allows it to deliver a strong impact force.
Even with lowered pressure at the nozzle, how can water still exert a large force when it hits something?
It becomes equal to atmospheric pressure.
What happens to the pressure in the water stream once it exits the nozzle into the air?
Because the water discharges directly into the atmosphere without any condition changes.
Why does nozzle pressure equal atmospheric pressure at the exit?