Understanding Stressors and Coping Mechanisms in Teens
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Stress
Natural response to pressure from challenges.
Stressors
Stimuli causing feelings of stress.

Eustress
Positive stress that motivates and focuses energy.
Distress
Negative stress causing anxiety and concern.
Acute Stressors
Immediate threats or pressures causing stress.
Chronic Stressors
Long-term stress from ongoing challenges.
Episodic Stressors
Frequent acute stress episodes.
Mental Disorders
Conditions affecting mental health, prevalent in teens.
Depression
Leading cause of illness among adolescents.
Anxiety Disorders
Common mental health issues in teenagers.
Behavioral Disorders
Disruptive behaviors impacting daily functioning.
Suicide
Fourth leading cause of death in 15-19 year-olds.
Healthy Sleep Patterns
Regular sleep habits promoting mental well-being.
Coping Skills
Strategies to manage stress and emotions.
Problem-Solving Skills
Abilities to find solutions to challenges.
Interpersonal Skills
Skills for effective communication and relationships.
Protective Environments
Supportive settings promoting mental health.
American Psychological Association
Conducted survey on teen stress levels.
World Health Organization
Reported on global adolescent mental health issues.
Physical Sensations
Bodily responses contributing to stress perception.
Social Resources
Support systems available to individuals.
Lazarus' Definition of Stress
Perception of demands exceeding available resources.
Episodic Stress
Frequent disturbances causing constant worry and confusion.
Chronic Stress
Long-lasting stress from unresolved difficult circumstances.
Fight or Flight Response
Physiological reaction to perceived threats or stress.
Physiological Arousal
Physical symptoms like headaches and hypertension.
Defense Mechanisms
Psychological strategies to protect against anxiety.
Compensation
Overachieving in one area to offset failures elsewhere.

Denial
Refusal to acknowledge reality to avoid anxiety.
Displacement
Redirecting feelings to a substitute target.
Introjection
Internalizing others' standards and beliefs.

Projection
Attributing one's own thoughts to others.

Rationalization
Justifying unacceptable behavior with logical explanations.
Reaction Formation
Expressing opposite feelings to hide true emotions.

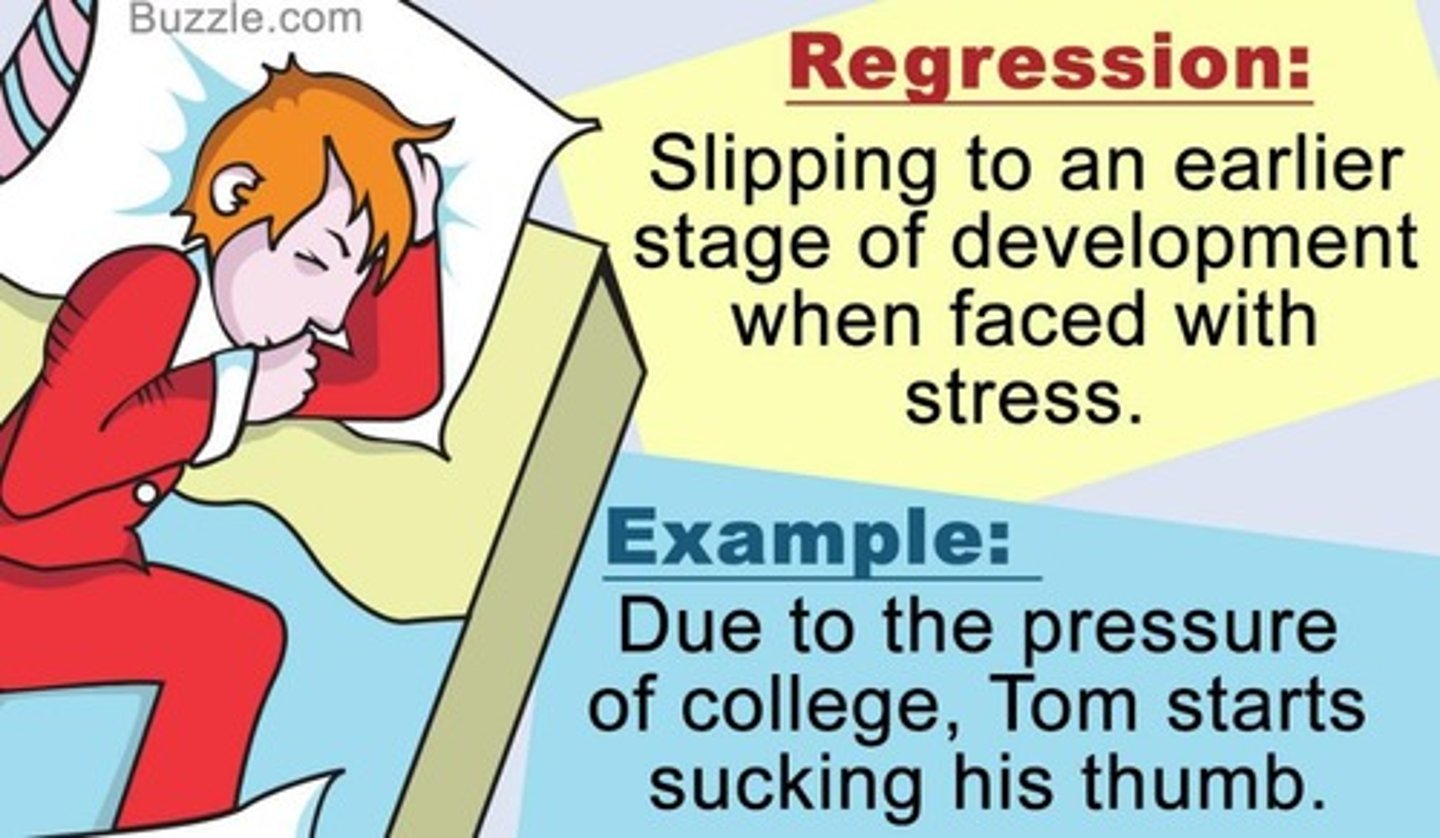
Regression
Reverting to earlier developmental stages under stress.
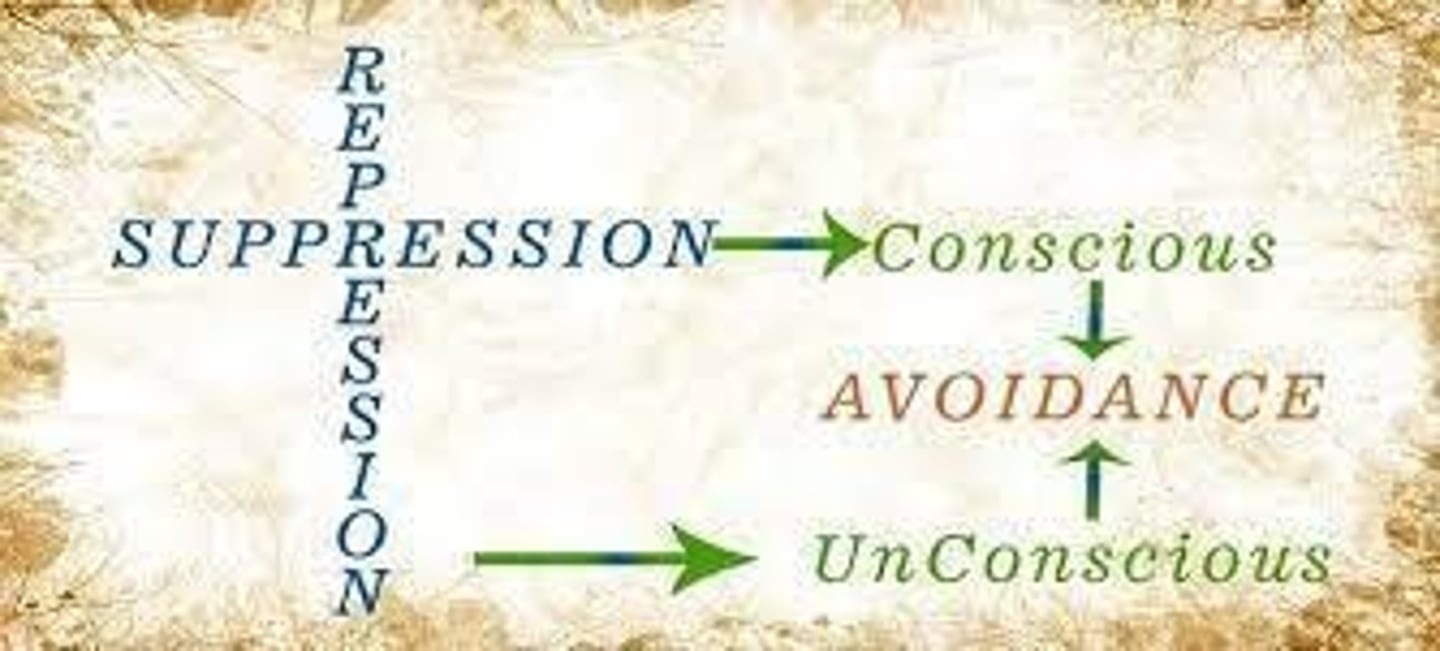
Suppression
Consciously avoiding thoughts of unpleasant memories.
Repression
Unconsciously blocking unpleasant thoughts from awareness.
Sublimation
Transforming unacceptable impulses into socially acceptable actions.
PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder from traumatic experiences.
Health Concerns
Issues affecting physical well-being and stress levels.
Relationship Problems
Difficulties in personal relationships causing stress.
Money Problems
Financial issues leading to chronic stress.
Family Problems
Conflicts within family contributing to stress.
Traumatic Events
Significant incidents causing long-term psychological effects.
Altruism
Goodwill act satisfying internal needs through helping others.
Conversion
Anxiety transformed into physical complaints like paralysis.

Fantasy
Creating a make-believe world instead of reality.
Humor
Finding funny aspects to endure uncontrollable situations.
Humility
Lowering self-importance and focusing on others.
Intellectualization
Viewing emotionally charged issues in cold, rational terms.

Coping
Efforts to manage or endure stressors effectively.
Problem-focused coping
Strategies aimed at altering the stress-causing problem.
Emotion-focused coping
Regulating emotional responses to stressors instead of altering them.
Avoidance strategies
Avoiding stress by withdrawing or engaging in distractions.
Task-oriented strategy
Immediate actions taken to improve stressful situations.
Emotion regulation
Alleviating emotional distress related to stressors.
Reframing
Changing perception of issues to reduce negative emotions.
Strong faith
Belief in God providing emotional support during stress.
Sense of self-worth
Personal value aiding in emotional coping.
Gardening
Activity used to avoid stressful situations.
Listening to music
Distraction technique to cope with stress.
Watching drama series
Engaging in entertainment to escape stress.
Coping mechanisms
Unconscious strategies used to manage stress.
Folkman and Moskowitz
Defined coping as managing emotional and stress responses.
Lazarus and Folkman
Distinguished problem-focused and emotion-focused coping strategies.
Avoidance coping
Withdrawing from stressors instead of confronting them.