Urban Geography: City Structures, Growth, and Global Systems
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is the primary determinant of land-use patterns in urban areas?
Accessibility, influenced by competition for accessible sites near the city center.
What does 'bid rent' refer to in urban economics?
The price people are willing to pay for accessibility.
What is the Central Business District (CBD)?
The city center traditionally serving as a hub for shops, government, and business offices.
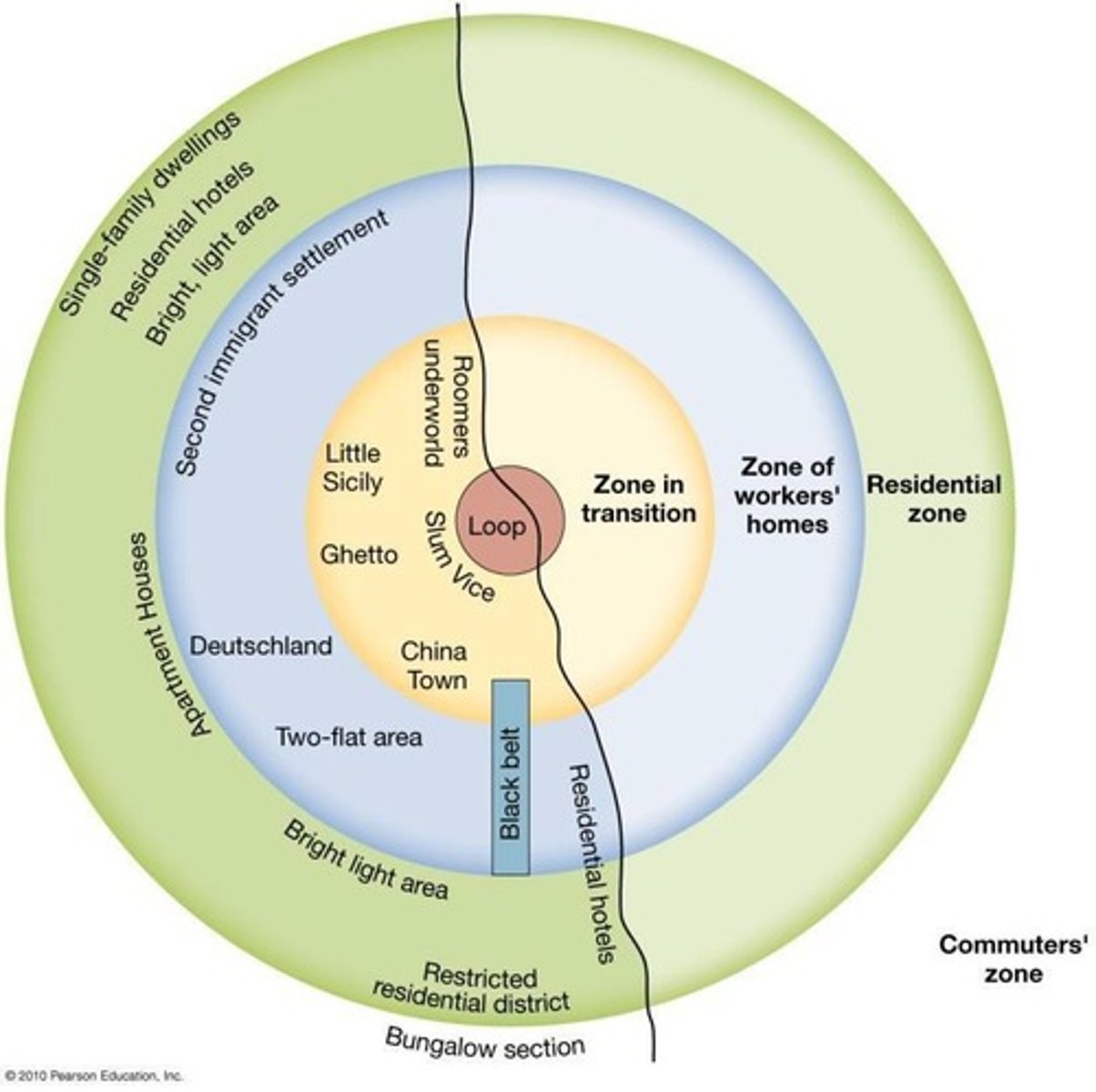
What is urban sprawl?
The expansion away from CBD areas to low-density developments.

What does 'exurb' mean?
Vast sprawling areas with no defined center.
What are some issues that push people out of cities?
Aging infrastructure, environmental quality, crime, and high living expenses.
What is 'gentrification'?
The restoration and upgrading of deteriorated urban property by middle-class or affluent individuals.
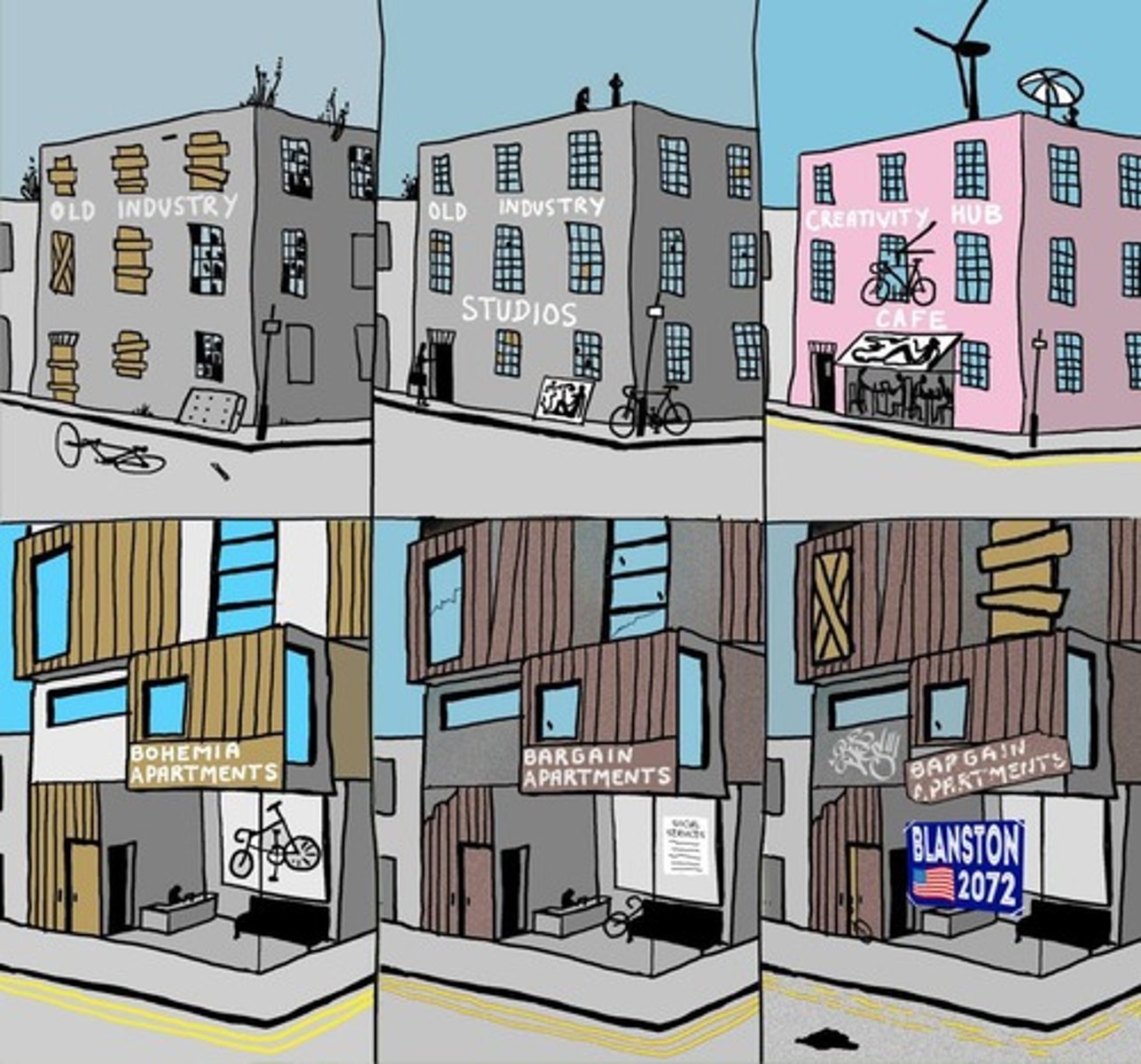

What are the positive aspects of gentrification?
Increases property values, promotes urban renewal, and enhances community services.
What are the negative aspects of gentrification?
Displaces lower-income residents and increases rents, forcing local businesses out.
What is 'neighborhood decay'?
The pronounced poverty and deterioration of inner-city neighborhoods.
What is 'redlining'?
The discriminatory practice of not making loans to high-risk neighborhoods.
What is the cycle of poverty?
The transmission of poverty and deprivation from one generation to another due to domestic circumstances and local conditions.
What does 'congregation' refer to in urban studies?
The territorial clustering of specific groups or subgroups of people.
What is 'spatial segregation'?
The spatial separation of specific subgroups within a wider population.
What are the characteristics of European cities?
Low skylines, lively downtowns, neighborhood stability, and a focus on order and efficiency.
What are the main principles of traditional Islamic city design?
Personal privacy, communal well-being, and compact residential structures.
What is 'metroburbia'?
A condition where suburban areas are interspersed with office employment and retailing.
What is 'smart growth' in urban planning?
A strategy to control growth patterns, discourage urban sprawl, and protect ecologically sensitive areas.
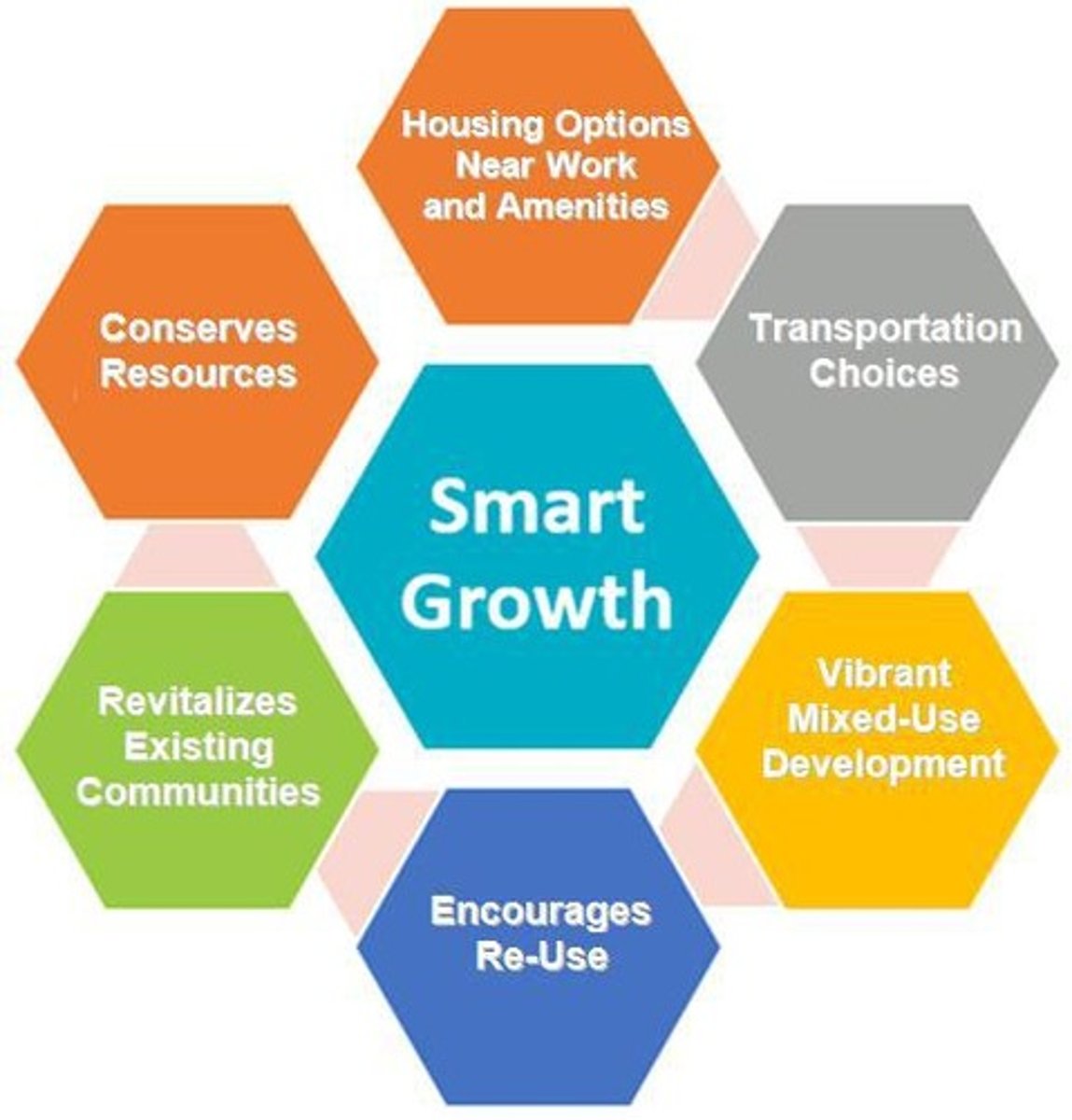
What is zoning in urban planning?
The designation of land parcels for specific uses to control development.
What is 'New Urbanism'?
A form of smart growth that encourages walkable neighborhoods with mixed-use development.
What does 'edge cities' refer to?
Decentralized clusters of office employment and retailing near major transportation routes.
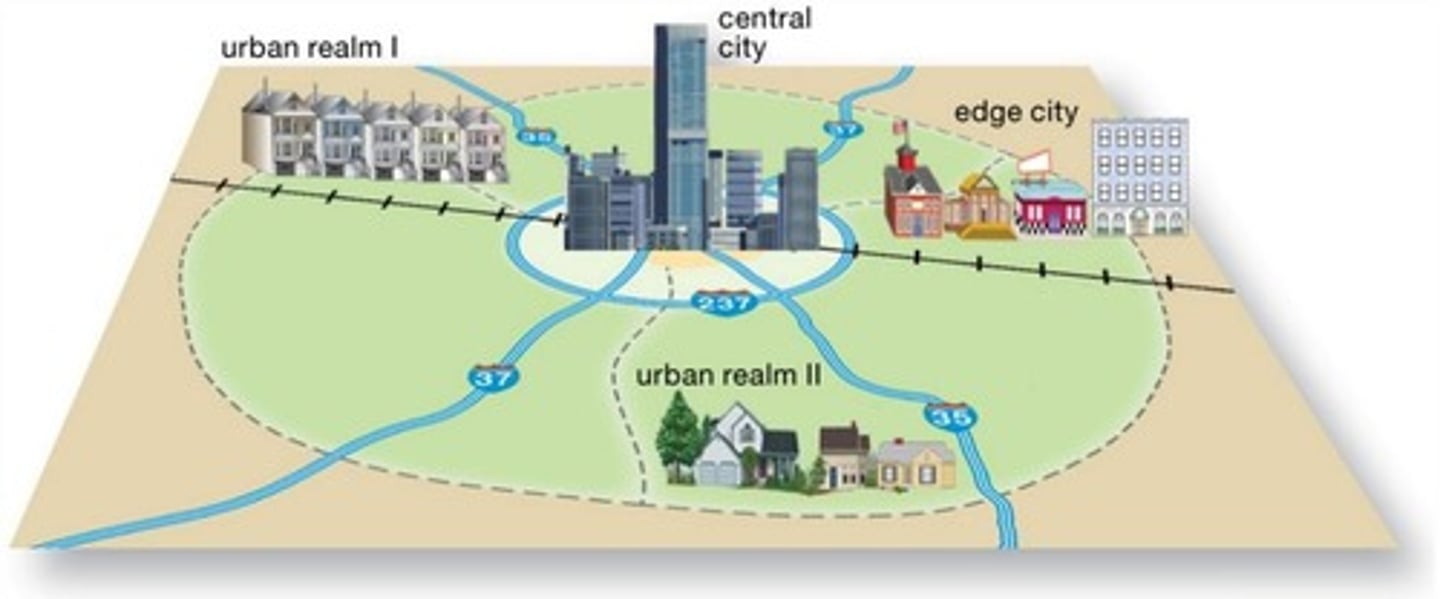
What is the significance of the term 'dualism' in urban geography?
The juxtaposition of formal and informal sectors of the economy in geographic spaces.
What are 'slums' or 'squatter settlements'?
Residential developments made on land that is neither owned nor rented by its occupants.

What is the role of children in the informal economy?
Children often engage in work that contributes to survival, such as garbage picking or street vending.
What is the impact of urban planning on population growth in the U.S.?
It often encourages growth and economic development while overlooking environmental and social consequences.
What are the four phases of urbanization in the U.S. from 1800 to 2006?
1. Rural to large central cities, 2. Central cities to suburbs, 3. North & East to South & West, 4. Cities & suburbs to rural areas.
What is urban geography?
The study of the development of towns and cities around the world, focusing on similarities and differences among urban places.
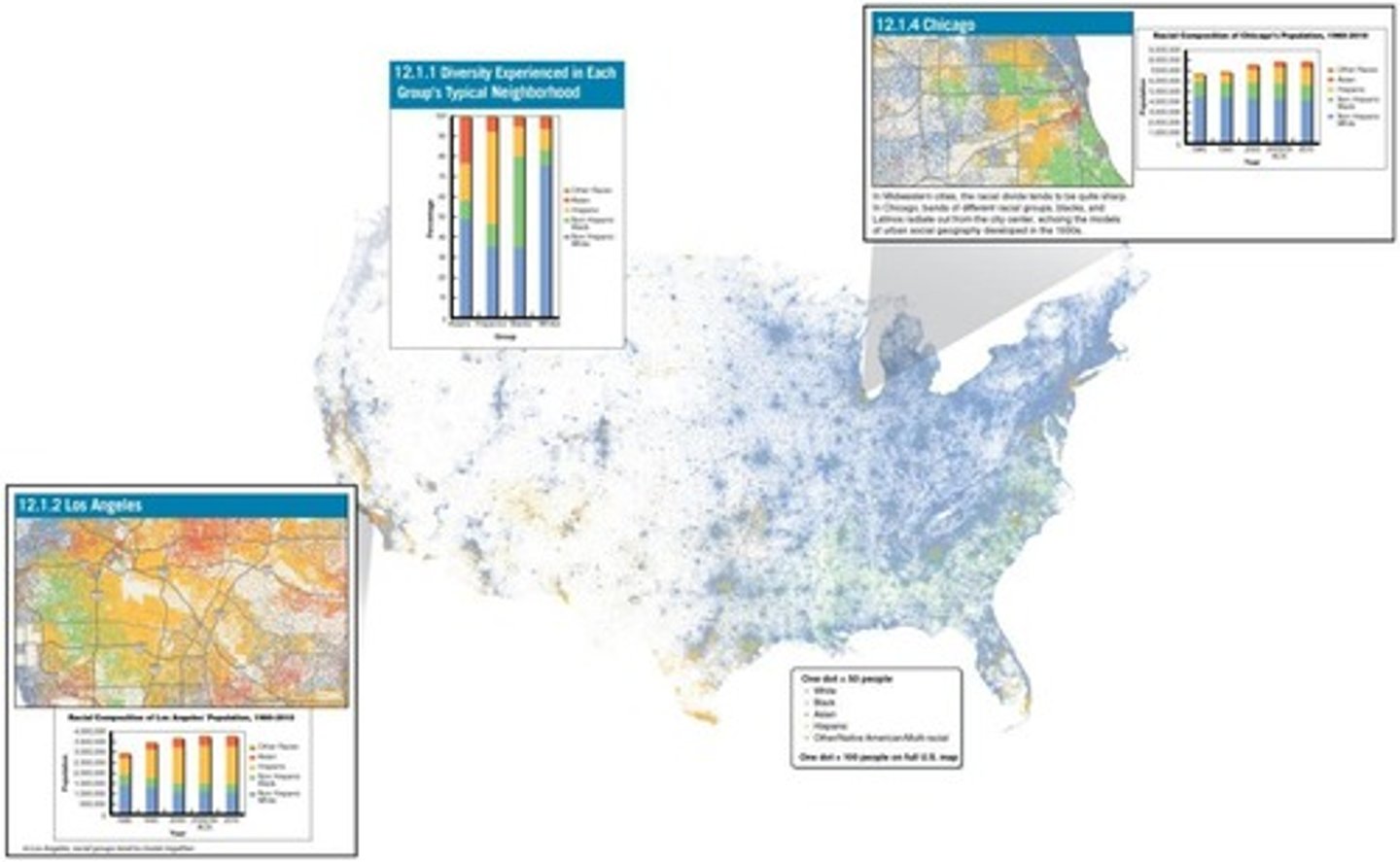
Define urban form.
The physical structure and organization of cities.
What does urban ecology study?
The social and demographic composition of city districts and neighborhoods.
What is urbanism?
People's attitudes and behaviors about the city in which they live.
How is urbanization measured?
As the percentage of people living in urban areas.
What is urban growth?
The rate of increase of urban populations.
What are push factors in urbanization?
Forces that drive people out of rural areas.
What are pull factors in urbanization?
Factors that attract people to cities, giving them hope for a better life.
What is the agglomeration index?
An area is considered urban if it has a population density greater than 150 and access to a settlement of more than 50,000 inhabitants within 60 miles by road.
What is doubling time in urban studies?
The time needed for a city to double in size.
List some functions of urban settlements.
Mobilizing function, decision-making capacity, generative functions, and transformative capacity.
What conditions contribute to the prosperity of cities?
Infrastructure and amenities, social services, environmental quality, equity and social inclusion, and adequate income and employment.
What is the significance of 'buzz' in cities?
It refers to the successful economic development characterized by a large number of people clustering in a small area, creating a busy environment.
What historical system influenced European urban expansion?
Feudalism, where nobility held lands in exchange for military service.
What role did colonialism play in urban development?
It contributed to the establishment of gateway cities that link regions and countries.
What are gateway cities?
Cities that serve as links between one country or region and others due to their physical location.
What was the urban population trend in medieval Europe?
Cities with more than 10,000 residents were uncommon, except in areas like northern Italy and Flanders.
What characterized 'buzz cities'?
Cities that are continuously busy due to diverse activities, such as Los Angeles and New York City.
What percentage of the world's population currently lives in urban areas?
49% of the world's population.
What is the significance of satellite images of Earth at night in urban studies?
They show city lights, indicating the extent of urbanization and major urban areas.
What is the relationship between urbanization and poverty in developing countries?
Rapid urban growth in developing countries often leads to increased centers of poverty.
What is the impact of urbanization on social services?
Urbanization necessitates improved social services to support growing populations.
What does the term 'urban system' refer to?
The interconnectedness of cities, where smaller cities are linked to middle-order cities and then to regional and national metropolises.
What major change in urbanization occurred in the 1800s?
Urbanization became an important issue due to the Industrial Revolution.
Why did people move to cities during industrialization?
They moved for jobs in the manufacturing sector.
What is a 'shock city'?
A modern industrial city that embodies surprising changes in economic, social, and cultural life, such as Chicago and Manchester.
What role do transportation networks play in urban development?
Transportation networks heavily guide how cities develop.
What is the central focus of the urbanization process in Western Europe and North America?
It is centered around agricultural productivity.
What are colonial cities?
Cities created as commercial or administrative centers by colonial or imperial powers.
Give an example of a pure colonial city.
Bombay, Calcutta, Manila, and Hong Kong.
What is Central Place Theory?
It analyzes the organization of central places in hierarchical systems based on consumer behavior.
What is a 'central place'?
A settlement where certain types of products are available.
What does the rank-size rule describe?
The functional interdependency between places within an urban system and the relationship between city population sizes and their ranks.
What is 'primacy' in urban studies?
When the population of the largest city is disproportionately large compared to others.
What are examples of primate cities?
London, Paris, and Mexico City.
What defines world cities?
Cities that play key roles in organizing space beyond their national boundaries.
What are megacities?
Very large cities with a population of over 10 million, characterized by both primacy and centrality.
What is deindustrialization?
The process of reducing industrial activity, often leading to job decentralization.
What is counterurbanization?
The movement of people from cities to rural or smaller cities, resulting in net population loss in urban areas.
What is reurbanization?
The growth of population in central urban cores following a period of decline.
What are brownfield sites?
Former industrial or commercial areas where future use is affected by real or perceived risks.
What are some environmental impacts of cities?
Cities threaten biodiversity, lack greenery, and concentrate pollutants.
How do cities contribute to social issues?
Cities can be centers of poverty and crime and are subject to terrorism.
What is the significance of public-private partnerships in urban redevelopment?
They are used to help redevelop brownfield sites and other areas in decline.