Halogenoalkanes
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is the general formula of a halogenoalkane?
CnH2n+1X often shortened to R-X.
Why are halogenoalkanes polar?
The halogens are more electronegative than carbon.
Why are halogenoalkanes insoluble in water?
the C-X bond isn't polar enough & they can't form hydrogen bonds
What are halogenoalkanes soluble in?
Non polar solvents such as cyclohexane
What are the main intermolecular forces of attraction in halogenoalkanes?
dipole-dipole attractions and van der waal forces
What are some uses of halogenoalkanes?
refrigerants, solvents, pharmaceuticals
When halogenoalkanes mix with hydrocarbons what can they be used as?
dry-cleaning fluids and to remove oily stains
What increases boiling point in halogenoalkanes?
Increased chain length
Boiling point ________ going down the halogen group
Increases
Why do halogenoalkanes have higher boiling points than alkanes with similar chain lengths?
They have higher relative molecular masses and they are more polar
What are the two factors that determine how readily the C-X bond reacts?
the c-x bond polarity and the c-x bond enthalpy
What is a nucleophile?
An electron pair donor
Why can the carbon atom bonded to halogen in a halogenoalkane be attacked by a nucleophile?
It has a partial positive charge - it is electron deficient
Why is the C-F bond the most reactive if bond polarity was the only factor?
Most polar, carbon atom has the most positive charge therefore is most easily attacked by a nucleophile
Why is the C-I bond the least reactive if bond polarity was the only factor?
Least polar
The C-X bonds get _______ going down the halogen group
weaker
Why is the C-F bond the strongest?
It has the highest bond enthalpy
Why does the C-F bond have the highest bond enthalpy?
Fluorine is the smallest halogen and the shared electrons in the C-F bond are strongly attracted to the fluorine nucleus, making a strong bond.
Is bond enthalpy or bond polarity more important in determining reactivity of halogenoalkanes?
Bond enthalpy
Are C-F bonds more or less reactive than C-I bonds and why?
C-I bonds are more reactive as they have a lower bond enthalpy
What is a primary halogenoalkane?
When one carbon is attached to the carbon atom adjoining the halogen
What are some common nucleophiles?
OH-, NH3, CN-
What is nucleophilic substitution?
A reaction where a nucleophile donates a lone pair of electrons to δ+ C atom, δ− atom leaves molecule (replaced by nucleophiles)
What is the halide ion called in nucleophilic substitution?
The leaving group
What are nucleophiles attracted to?
Electron deficient carbon atoms
Why do halogenoalkanes need to be dissolved in aqueous ethanol for nucleophilic substitutions?
They are insoluble in water
What are the products of the nucleophilic substitution reaction using a hydroxide ion?
An alcohol and a halide ion
What is the overall equation of the nucleophilic substitution reaction using a hydroxide ion?
R-X + OH⁻ → ROH + X⁻
What are the products of the nucleophilic substitution reaction using a cyanide ion?
A nitrile and a halide ion
What are the products of the nucleophilic substitution reaction using ammonia?
Primary amine and ammonium halide
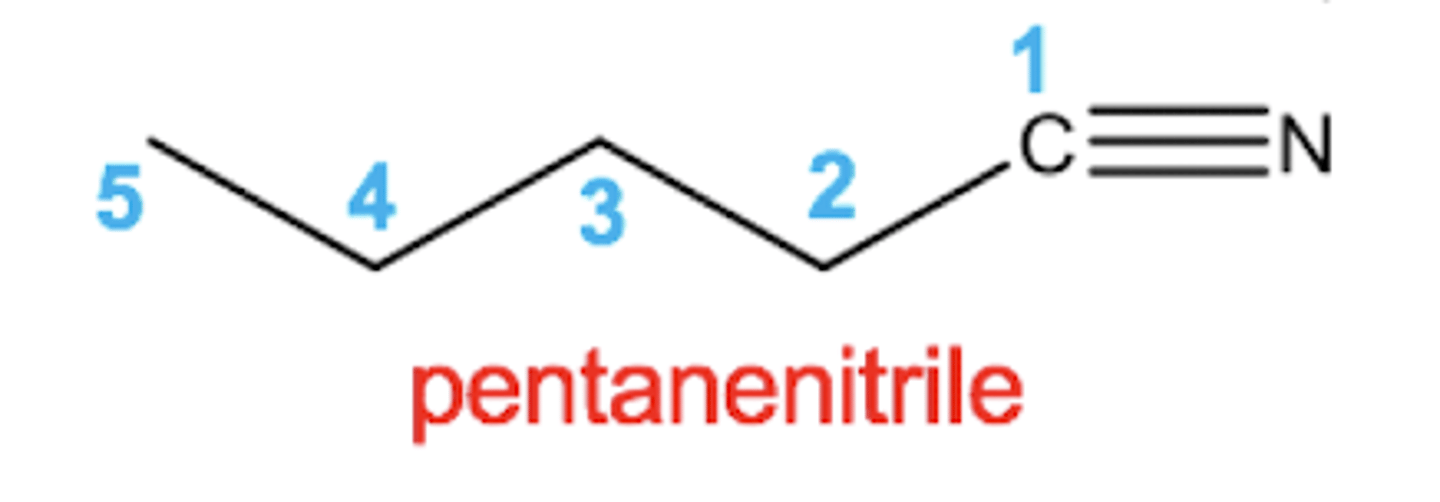
What is one important thing to remember when naming nitriles?
Nitrile groups have to be at the end of a chain. Start numbering the chain from the C in the CN.
Why is the nucleophilic substitution reaction using ammonia carried out in a sealed tube?
Increases the pressure of the reaction and prevents the ammonia escaping as a gas.
What is the overall reaction for the nucleophilic substitution reaction using ammonia?
R-X + 2NH₃ → RNH₂ + NH₄X
Why is an excess of ammonia used in nucleophilic substitution reactions between halogenoalkanes and ammonia?
To prevent further substitution reactions between the halogenoalkane and the amines formed
How do we increase the rate of nucleophilic substitution?
By heating the reaction under reflux
What happens if you warm a halogenoalkane with hydroxide ions dissolved in ethanol instead of water?
An elimination reaction occurs
Why are nucleophilic substitution reactions useful?
They can convert halogenoalkanes into alcohols, amines and nitriles.
What is an elimination reaction?
Removal of a small molecule from a larger one
What are the products of elimination reactions?
alkenes
What do hydroxide ions act as in an elimination reaction?
Bases
What are the conditions for elimination?
hot and ethanolic
What are the steps in an elimination reaction?
1. The lone pair on the hydroxide ion forms bond with H atom on a carbon atom adjacent to the carbon with the halogen
2. The electrons from the carbon-hydrogen bond form a carbon-carbon double bond
3. The bromine takes the pair of electrons from the carbon-bromine bond to leave as a bromide ion
Hydroxide ions at room temperature, dissolved in water (aqueous) favour...
substitution
Hydroxide ions at high temperature, dissolved in ethanol favour...
elimination
What do primary halogenoalkanes tend to react by?
substitution
What do tertiary halogenoalkanes tend to react by?
elimination