Terminologies for Aqueous Solutions in Animals
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What does blood serum mean?
A clear yellowish liquid part in blood that remains after blood cells and clotting protein have been removed
Acidemia
The state of having low blood pH (acidic) where the pH level is below 7
It is the result of acidosis
Acidosis
What
How it happens (3)
Can be classified as
What: The process that causes the body to become more acidic
How it happens:
When there is an increase in acid production
Decrease in bicarbonate (a base)
Failure to remove enough CO2
Classifications:
Metabolic acidosis
Respiratory acidosis
What is respiratory acidosis and give examples and the compensatory mechanism
A condition where the body’s blood becomes more acidic due to an excess of CO2 due to impaired lung function
EX:
Chronic lung disease
Pneumonia
Pulmonary fibrosis
Pulmonary oedema
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
High [CO2]
Compensatory mechanism:
Increase excretion of acid in urine
What is metabolic acidosis and give examples and the compensatory mechanism
A condition where the blood becomes too acidic due to a decrease in bicarbonate (HCO3-), occurs when there is an imbalance in body’s metabolism causing excess acid production or loss of base
EX:
Diarrhoea
Diabetes mellitus
Starvation
Lactic acidosis
Renal failure
Ruminal acidosis
Compensatory mechanism:
Increased breathing rate to expel CO2
Alkalemia
A condition where the blood pH is abnormally higher, meaning that it has become too alkaline (basic) with a pH above 7
Alkalosis
What
Classifications
Results to, BUT
What: The process that increases the body’s pH toward alkaline levels
Classifications:
Respiratory alkalosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Can results to: Alkalemia BUT not all cases do, if the body can compensate well enough
What is respiratory alkalosis and give examples and give the compensatory mechanism
A condition where the blood becomes too alkaline (basic) due to excessive loss of CO2 due to hyperventilation
EX:
High fever (hyperventilation)
Inflammation/disease of brain
Compensatory mechanism:
Increase excretion of alkali in urine
What is metabolic alkalosis and give examples and give compensatory mechanisms
A condition where the blood becomes too alkaline (basic) due to
Increase in bicarbonate (HCO3-) OR
Decrease of acids
EX:
Vomiting
Ingestion of alkaline salts
GI obstruction
Furosemide
Compensatory mechanism:
Decreased breathing rate to retain CO2
Buffer
A solution that maintains pH and brings it back to its optimal value by addition or removal of hydrogen ion
Give examples of extracellular buffers
Bicarbonate/carbonic acid buffer system
Plasma proteins
Give examples of intracellular buffers
Hemoglobin buffer
Phosphate
Intracellular protein
Buffer systems can be achieved through 3 main mechanisms, name them
Neutralisation by buffer systems (seconds to minutes)
Exhalation by respiratory system (minutes to hours)
Clearance by renal system (hours to days)
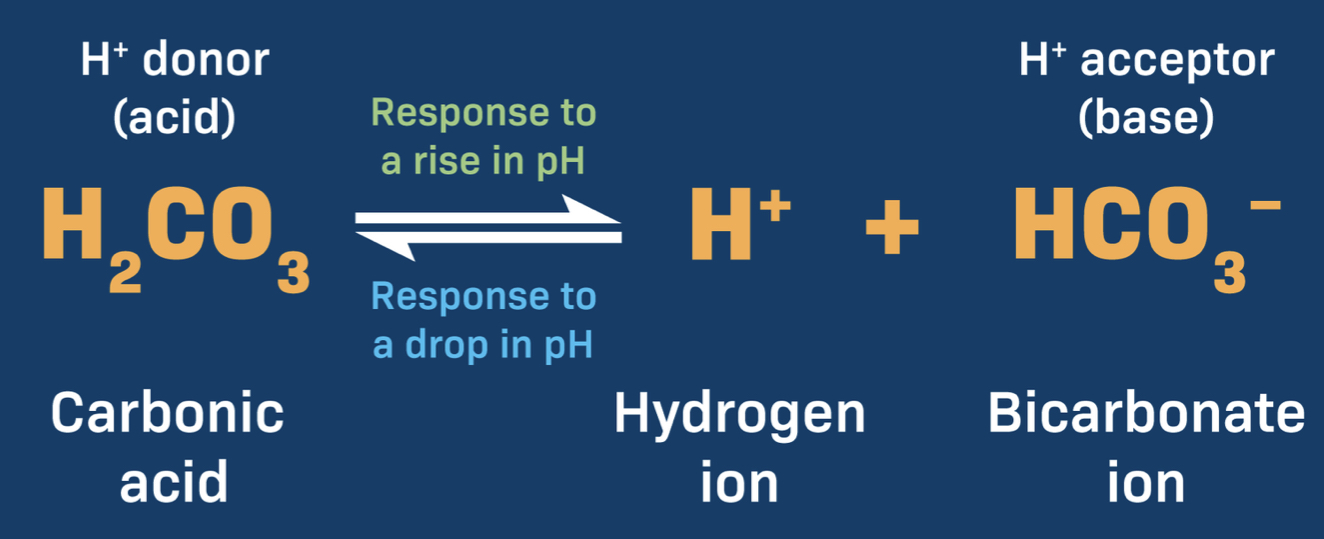
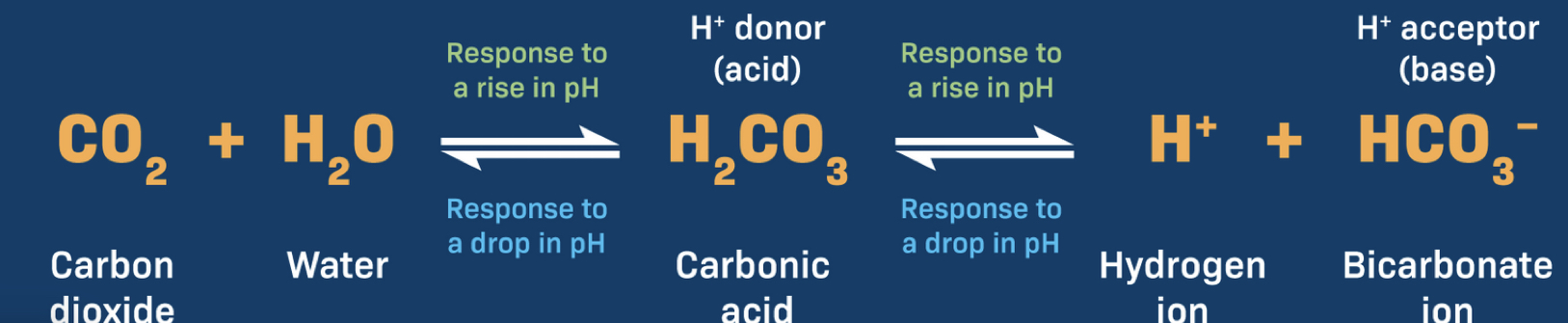
An example of a buffer system is carbonic acid-bicarbonate, how does it work?
Decrease in H ions causes carbonic acid to dissociate —> H ions and bicarbonate ions, resulting in the release of H ions
Increase in H ions, combines with bicarbonate to make carbonic acid
How does the respiratory system act as a buffer system?
It controls the release of CO2 from the body through breathing rate
How does the urinary system act as a buffer system?
Regulates the levels of bicarbonate ions in blood by absorbing or excreting them
Hypoxia
Deficiency in the amount of oxygen reaching tissues
Tachycardia
Increased heart rate
Bradycardia
Decreased heart rate
Tachypnea
Abnormally rapid breathing
Bradypnea
Abnormally slow breathing
Acid
What
So is it a proton donor or acceptor
pH level
Turns blue litmus paper into
Examples
Ionisation of strong acid in water
Ionisation of weak acid in water
What: A substance that releases hydrogen ions in solution
Proton: Donor
pH level: Below 7
Turns blue litmus paper into: Red
Examples:
HCl
Acetic acid
Lactic acid
Ionisation of strong acid in water: Completely ionized
Ionisation of weak acid in water: Partially ionized
Base
What
So is it a proton donor or acceptor
pH level
Examples
Ionisation of strong base in water
Ionisation of weak base in water
What: Substance that accepts hydrogen ions in solution
Proton: Acceptor
pH level: Above 7
Examples:
Sodium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide
Ammonia
Ionisation of strong base in water: Completely ionised
Ionisation of weak base in water: Partially ionised
Compensatory
Refers to how the body adjust to disturbances in internal balance like in pH levels to restore homeostasis
Homeostasis
A self-regulating process by which biological system tend to maintain internal stability
Ionized
A process in which an molecule acquires a positive/negative charge by losing or gaining electrons