EXAM 1 Objectives (Week 1)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Define overview of neuro rehabilitation
Branch of rehabilitation that focuses on
-Increasing and restoring participation
-Improve Function
-Make movement fun
-Identify movement priorities
and improve Overall quality of life
Identify therapy classifications and treatment strategy categories
Treatments can be classified into restorative, impairment-specific, neurofacilitation techniques, and compensatory strategies.
Recovery vs. Compensation
Recovery: Restoration of normal movement patterns.
Compensation: Adaptations using alternative movement strategies to perform tasks.
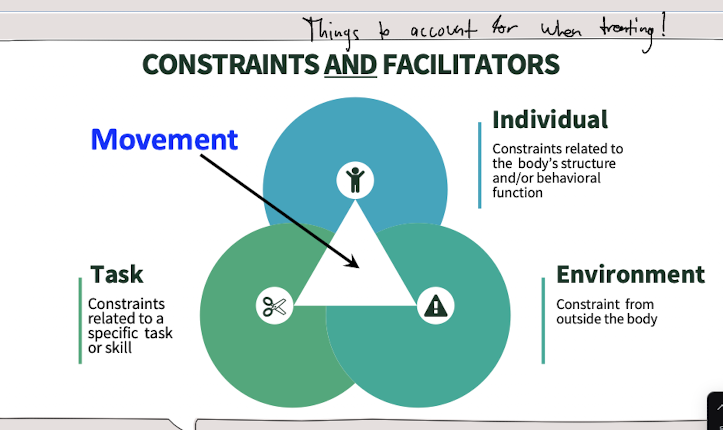
Components of Movement
Movement is influenced by the individual (cognition, perception, motor abilities), task (stability, mobility, manipulation), and environment (regulatory and non-regulatory conditions).
Timeframe of Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity can occur across a lifetime but is most pronounced in the acute phase after injury.
-Motor improvements can occur after 1 year post stoke and are influenced by rehabilitation.
Neuroplasticity can occur across a lifetime but is most pronounced in the acute phase after injury.
Acute phase: High potential for neural reorganization.
Chronic phase: Slower but still possible with appropriate interventions.
True Lack of Potential vs. Intervention-Induced Plateau
A true lack of potential suggests neurological limitations.
A plateau is often a sign of suboptimal interventions or insufficient challenges.

Moving Past a Plateau
Requires task-specific training, increased intensity, and variability in practice.
Peep Picture *
Clinical Decision-Making Process (HOAC Model)
The Hypothesis-Oriented Algorithm for Clinicians (HOAC) guides therapists through structured assessment and intervention planning.
-Helps as a guide for the documentation process
Contrast models of function and disablement
Disablement model: Focuses on pathology and its impact on a person’s ability to perform daily activities
Example: An underlying disease or injury such as a meniscus tear
Function model: focuses on Function and participation and contextual factors affecting a person’s ability to engage in life activities
-Think ICF
Identify values utilized in clinical decision making
Decisions are guided by Evidence, patient preferences, clinician expertise, and ethical considerations.
-Think EBP (BIG 3)
Patient-Centered Care & Patient-First Language
Focuses on respecting patient autonomy, shared decision-making, and emphasizing abilities over disabilities.
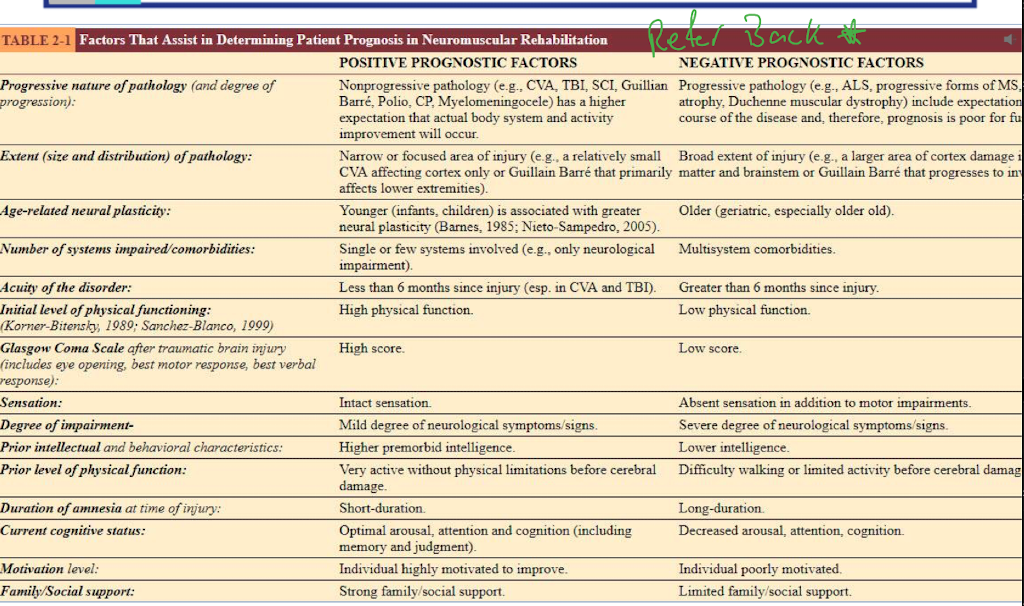
Guiding Principles for Prognosis
Based on injury severity, comorbidities, age, motivation, and neuroplastic potential
Go over the picture *

Identify key components of the intervention
Patient centered care
3 parts
Coordination, communication, documentation
Patient/client related instruction/education
Procedural intervention
Compare and contrast current neurorehabilitation practices with evidence in best
practice
While current neurorehabilitation practices incorporate effective strategies, evidence-based best practices emphasize early, intensive, and task-specific training with a focus on neuroplasticity, technology, and holistic care. Bridging the gap between research and clinical application requires continued education, improved accessibility to technology, and a shift towards more functional, patient-centered approaches.
Key Components of Best Practice
Task specificity, high repetition, patient engagement, intensity, and variability.
Big 2 Intensive therapy and Task Specificity
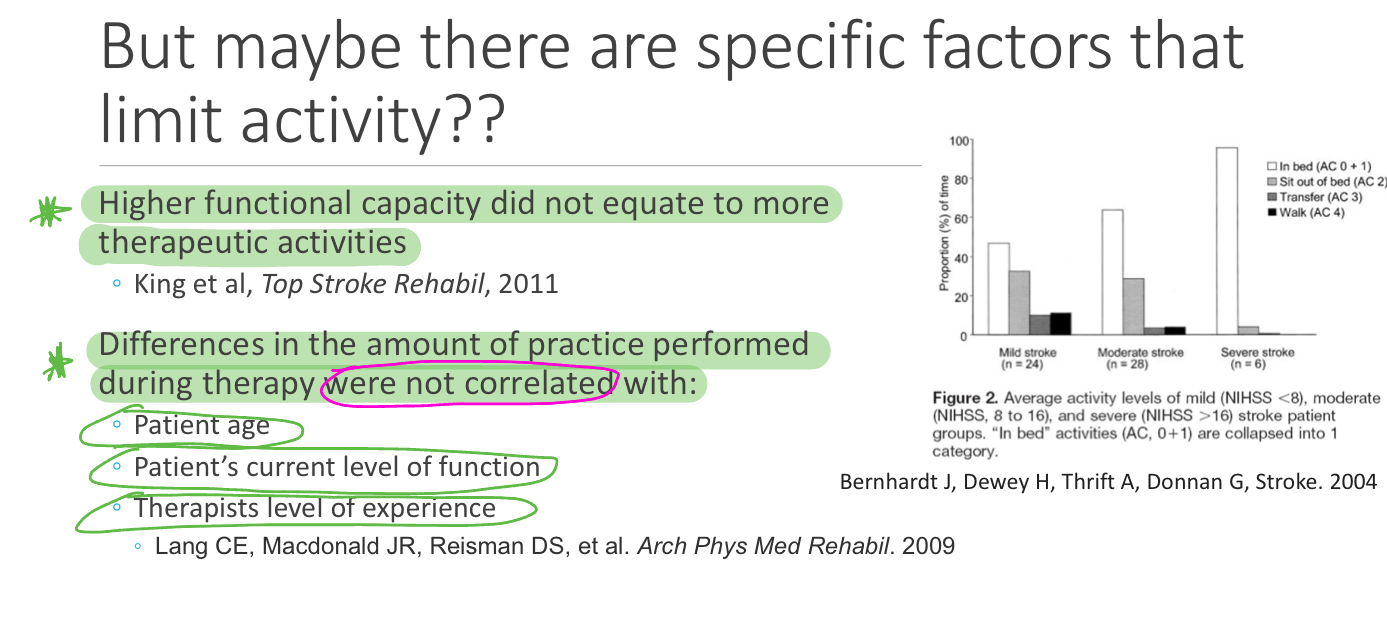
Describe current practice based on the evidence
Lack of EBP with our interventions, not consistently applying it (CURRENT)
They Use of approaches that don’t focus on motor learning and Neuroplasticity
Peep both Screenshots *

Identify factors which impact motor learning and how to manipulate these to maximize motor learning
Motor learning: Acquisition and modification of movement, also is the retention ad transfer of that behavior
Factors: Practice type, feedback, motivation, and environmental conditions.
Strategies: Blocked vs. random practice, external focus of attention, and task-specific exercises.
Discuss the three key components of the optimal theory and its impact on motor
learning
Autonomy, enhanced expectancies, and external focus of attention, all contributing to improved motor learning.
Autonomy- Person is allowed to control or choose some aspects of practice or performance conditions (increases sense of ownership)
Enhanced expectancies- focuses on giving positive feedback (has positive effect on self efficacy and learning)
Focus on attention-External-concentration on movement affect (focusing on the back on the rim while shooting). External is better for learning snd automaticity. Internal- concentration on body movements (focusing on the flick of the wrist)
Organize interventions by type: restorative, impairment specific, neurofacilitation techniques, compensatory
Restorative: Recovery-based.
Impairment-specific: Address specific deficits.
Neurofacilitation: Guides normal movement patterns.
Compensatory: Uses alternative strategies that achieve the same goal
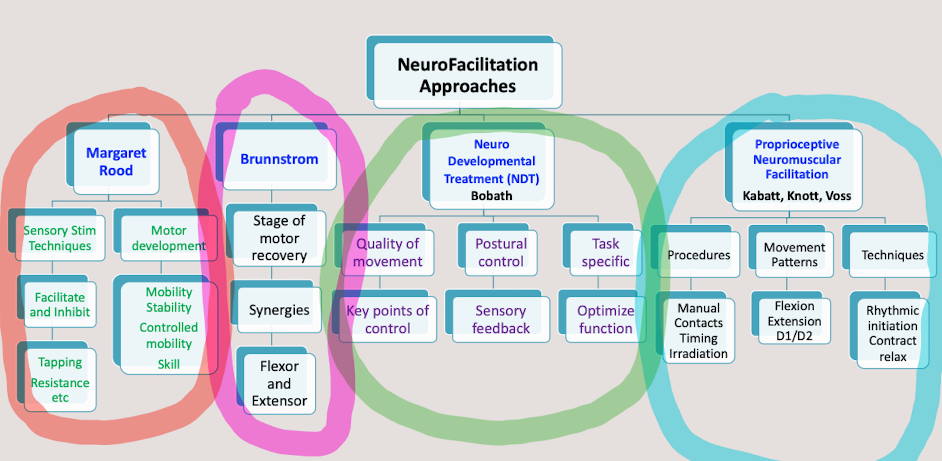
Common Neurofacilitation Techniques
Rood, Brunnstrom, NDT, PNF

Rood Sensory stimulation techniques
Rood Sensory stimulation techniques
Peep the image*
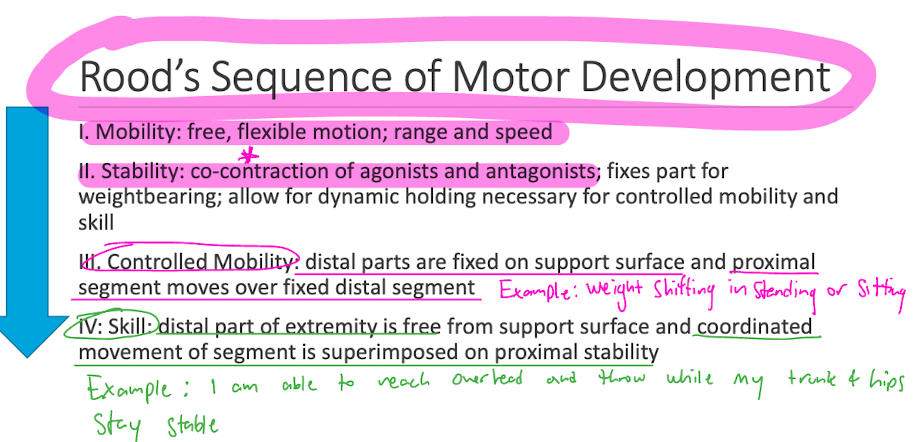
Rood Sequence of motor development
Rood Sequence of motor development
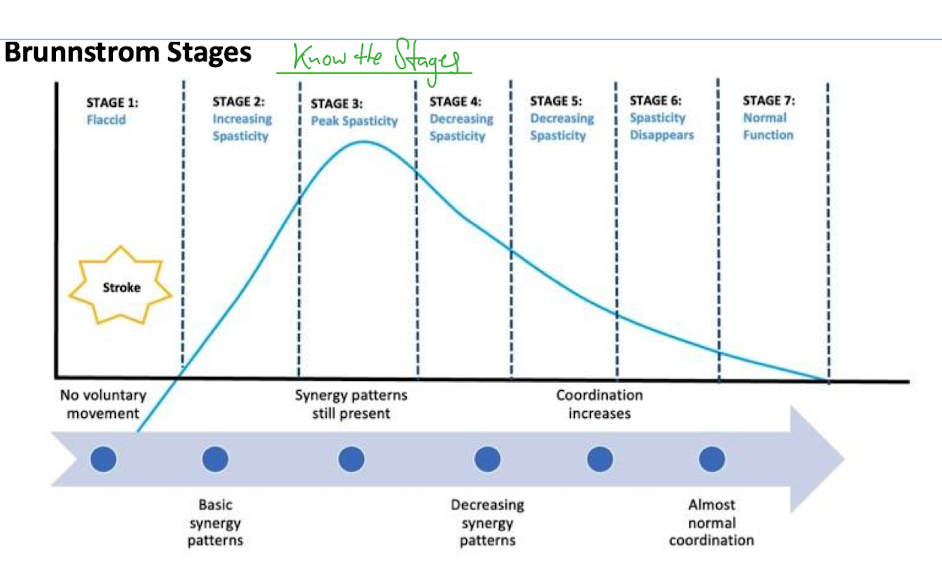
Brunnstrom
Focuses on abnormal synergistic patterns and stages of motor recovery following stroke
Flexion synergy (upper extremity and more common) flexion of the spine while typing this
Extension Synergy (Lower Extremity) sit to stand- gotta extend lol
Neurodevelopment treatment (NDT)
-KEY POINTS OF CONTROL
-Motor control theories
-Purpose: Core stability and alignment, guiding patients to more normal posture and movement
Define continuum of care
-Post acute care (PAC)
-Refers to care received after an acute hospitalization
Long term Acute Care Hospital (LTACH)
Patients who require complex, intensive care. This can include ventilator needs or any significant nursing requirement
Inpatient rehab facility (IRF)
Patient can tolerate 3 hours of therapy and requires at least 2/3 disciplines (PT/OT/SLP). Requires CMS-13 dx (neuro, burn. trauma)
Skilled Nursing Facility
Patient continues to require therapy but cannot tolerate 3 hours. Receives 1.5 hours of therapy
Long Term care / Nursing Home (LTC/NM)
Patient is unable to return home and requires continued supervision. May continue to receive some Maintenance Therapy
Home Health (HH)
Patient is able to be discharged home but is unable to tolerate leaving the house for therapy or needs nursing
Outpatient (OP) (Team Rehab lol)
Patient continues to require therapy but is able to leave the house and get transportation

Key to coordination
Read screenshot *
Need a TEAM and for all of the members be on the same page
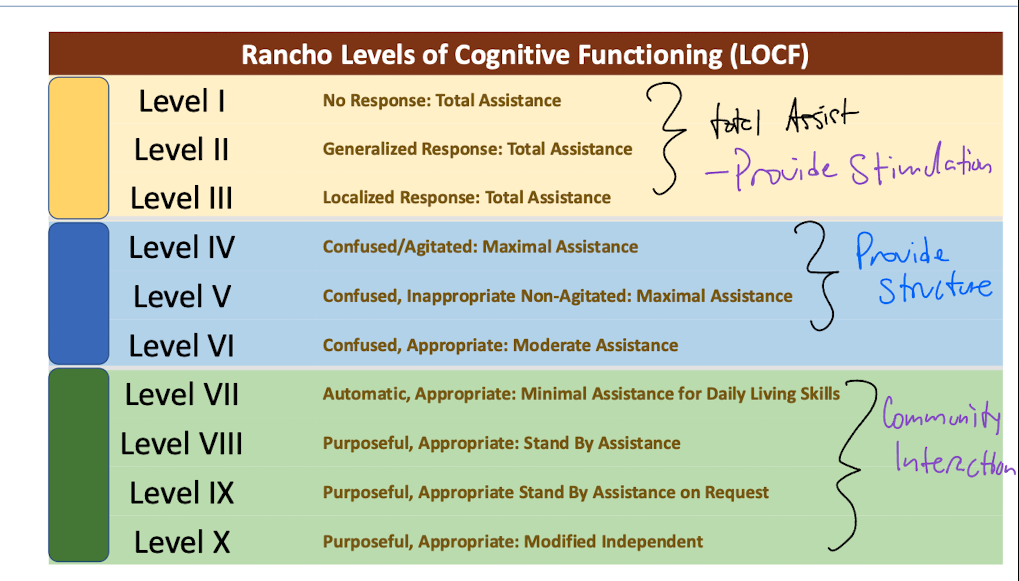
Describe the purpose of the Rancho Levels of Cognitive Functioning
-Framework for assessing cognitive and behavioral recovery after brain injury.
-8 levels
-Focus on each group (3) and what us as PT’s need to focus on for our intervention
Expressive (Broca’s Aphasia)
Comprehension is not impaired, however Language expression is impaired
Treatment: Green and red, cards, yes/no
Receptive (Wernicke’s Aphasia)
Language comprehension impaired
Treatment: Simon says, focus on contextual cues

Aphasias Cont.
Peep the screenshot *
Dysarthria
Speech Disorder caused by muscle weakness
-slurred speech
-it makes sense, just very hard to understand (XL on the panthers)
Apraxia
-affects motor planning
-a disorder of the brain and nervous system in which a person is unable to perform tasks or movements when asked, even though: The request or command is understood.
Dysphagia & Its Signs/Symptoms
Difficulty swallowing, coughing during eating, aspiration risk, and malnutrition.