Intro to Psych (Pitt) Exam 3
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Secure Attachment
Healthy and consistent emotional tie with another person
Instinct
Complex, unlearned behavior; patterned through a species
Set Point
Your body drops into "starvation mode" when you go below this point
Basal Metabolic Rate
Body's resting rate of natural energy usage
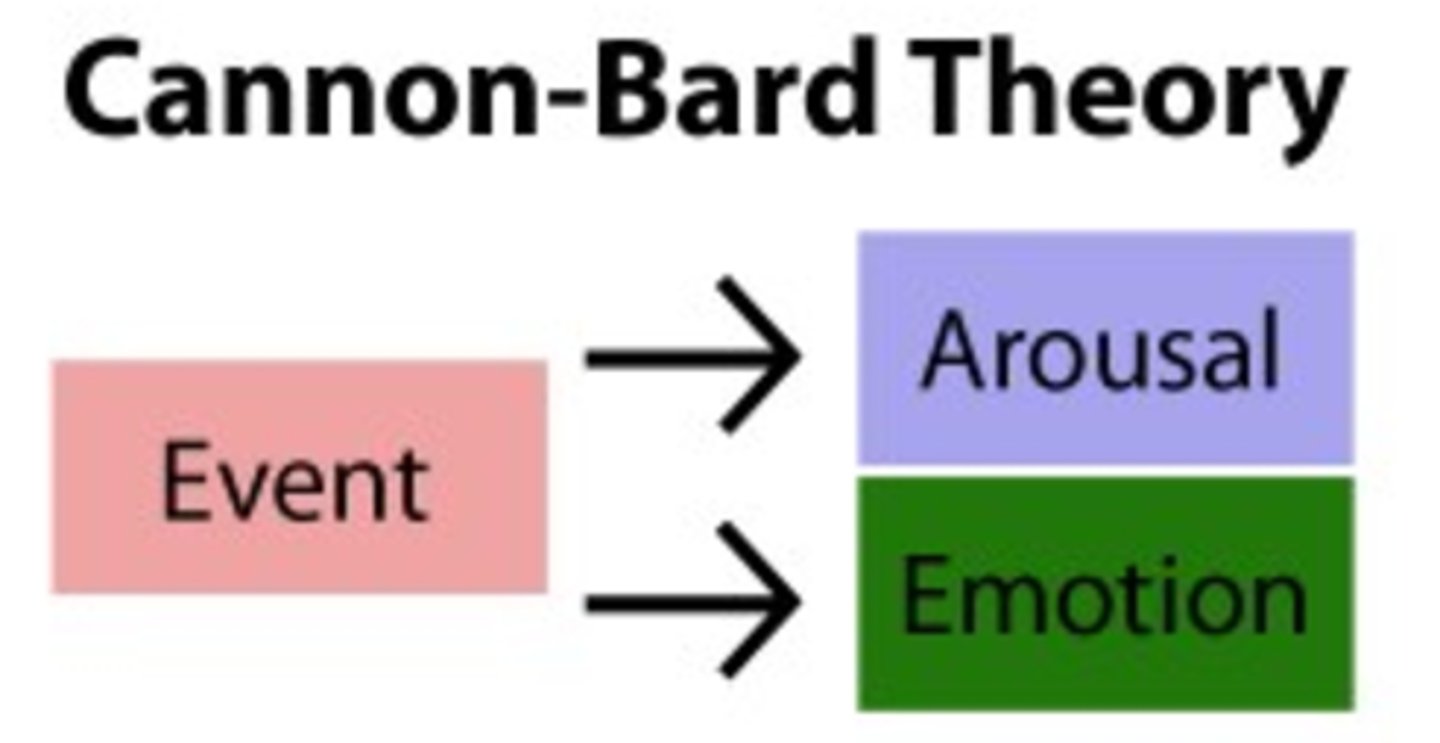
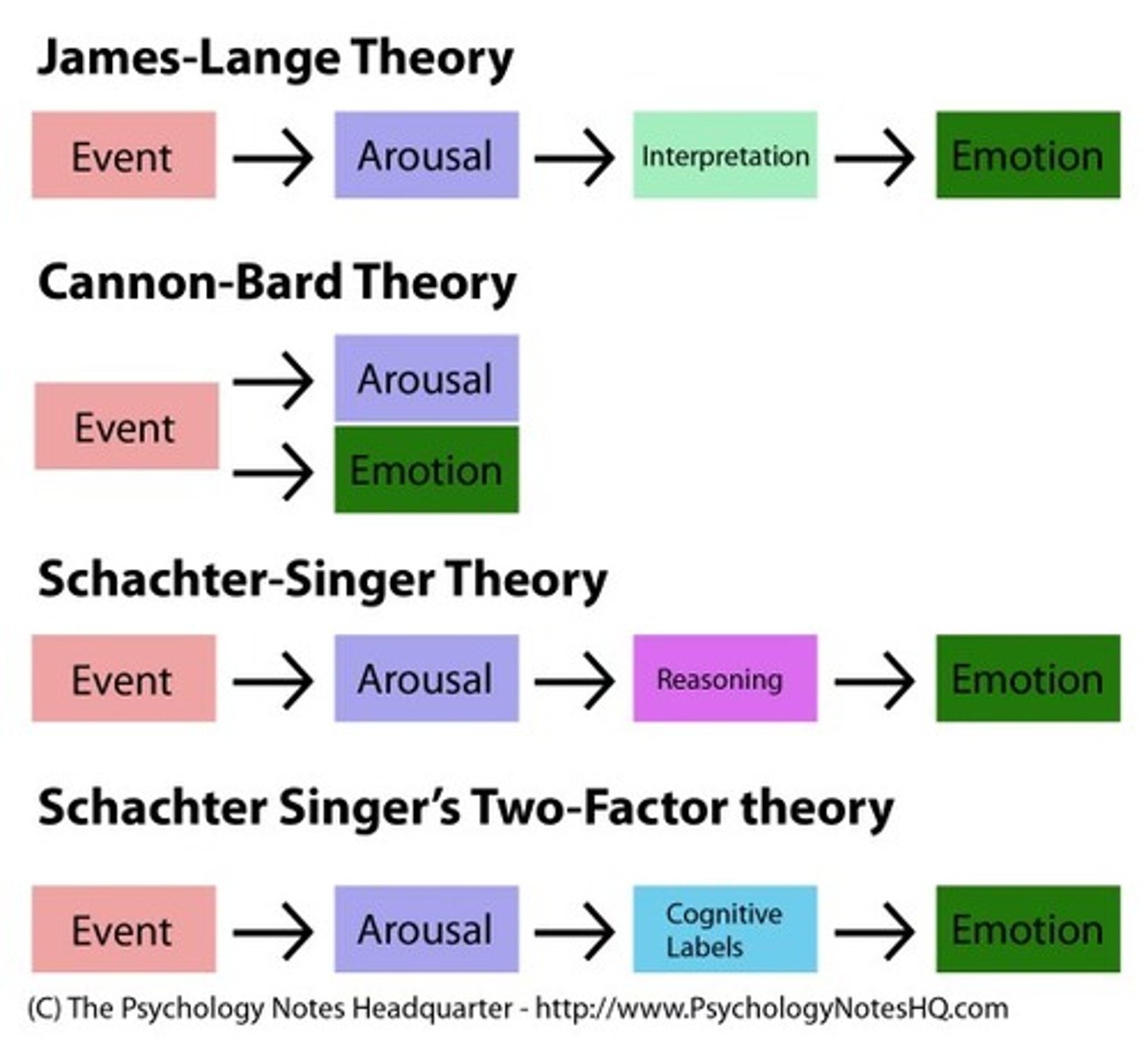
Cannon-Bard Theory
Theory that stimulus triggers physiological responses and emotions at the same time
James-Lange Theory
emotions result from our awareness of our physiological responses to emotion
Schachter-Singer Theory
To experience emotion one must be physically aroused, and cognitively label the arousal
Lazarus Theory
Cognitive appraisal, sometimes without our awareness defines emotions

Framing
How an issue is posed; can change decisions and judgement
Ostracism
Social exclusion
Narcissism
Extreme obsession with oneself
Narcissism and Social Networking
Often very active on social networks.
Hypothalamus
Keeps your body at homeostasis.
Hippocampus
"Save button"; neutral center in the limbic system.
Type A Personality
Competitive, hard-working, impatient, stressed, and anger-prone.
Facial Feedback Effect
Facial muscles triggering to corresponding feelings
3 Parts of Memory
1. Encoding
2. Storage
3. Retrieval
Chunking
Natural organization of something with familiar things.
Memory Pegs
Mnemonic device to memorize lists
Hiearchies
System where people/things are ranked according to status
Distributed Practice
Working with information over time
3 Major Areas of Developmental Psychology
1. Physical development
2. Cognitive development
3. Psychosocial development.
Recall
Retrieval of previously learned information; fill in the blank
Recognition
Identification of previously learned information; multiple choice
Implicit Memory
Automatic remembrance
Explicit Memory
Memory you have to work for
Piaget's 4 Stages of Child Development
1. Sensorimotor (0-2)
2. Preoperational (2-7)
3. Concrete Operational (7-11)
4. Formal Operational (12-death)
Accommodation in Child Development
Learning what family is based on personal experience
Assimilation in Child Development
How a child might learn about different types of animals
4 Types of Parenting Styles
1. Authoritarian
2. Permissive
3. Negligent
4. Authoritative
Maslow's Pyramid of Needs
Hierarchy of needs theory
1. Physiological Needs
2. Safety Needs
3. Love and Belonging
4. Esteem
5. Self-Actualization
Working Memory
Transferring short-term memory into long-term
Sensory Memory
Immediate, quick memory of the senses
Context Dependent Cue
Environmental changes may lead you to recall a time that the environment was the same
Mood Dependent Cue
When you're in a mood, your brain pushes similar memories
Inference
Disruption when trying to recall new or old information.
Maturation
Biological growth changes allowing orderly changes.
Kohlberg's Morality Development Stages
1. Preconventional
2. Conventional
3. Postconventional
Imprinting
Forming strong attachments in the critical period.
Cross Sectional Studies
Data collection from different groups at the same point in time.
Longitude Studies
Data collection from the same group over a longer span of time.
Optimum Arousal Theory
Claims some behavior increases arousal
Erikson Stages of Development
1. Trust vs. Mistrust (0-18 months)
2. Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt (18 months-3)
3. Initiative vs. Guilt (3-5)
4. Industry vs. Inferiority (6-11)
5. Identity vs. Confusion (12-18)
6. Intimacy vs. Isolation (18-40)
7. Generativity vs. Stagnation (40-65)
8. Integrity vs. Despair (65-death)
Retrograde Amnesia
Can't remember old memories
Anterograde Amnesia
Can't form new memories
Prototypes
Mental image of something
Authoritarian Parenting
Strict, care
Permissive Parenting
Not strict, care
Negligent Parenting
Not strict, don't care
Authoritative Parenting
Happy medium of strictness, care
Concept
Mental grouping of similar things to remember what they are and mean and where they belong
Motivated Forgetting
Repression; defense mechanism to push away bad feelings/memories.
Type B Personality
Easy-going and relaxed.
Trust vs. Mistrust
Erikson; 0-2; Trust/Mistrust that basic needs will be met
Autonomy vs. Shame/Doubt
Erikson; 2-3; Develop independence in tasks
Initiative vs. Guilt
Erikson; 3-6; Taking initiative in some tasks, guilt when unsuccessful or overstepping
Industry vs. Inferiority
Erikson; 6-13; Developing self-confidence in abilities, feeling inferior when unable
Identity vs. Confusion
Erikson; 13-19; Experiment with and develop identity and roles
Intimacy vs. Isolation
Erikson; 19-40; Establish intimacy and relationships with others
Generativity vs. Stagnation
Erikson; 40-65; Contribute to society and be part of a family
Integrity vs. Despair
Erikson; 65-death; Make sense of life and contributions
Maslow's Physiological Needs
Food, water, etc.
Maslow's Safety Needs
Health, employment, security
Maslow's Love and Belonging
Friendship, family, and intimacy
Maslow's Esteem
Respect, strength, and freedom
Maslow's Self-Actualization
Desire to become the most that one can be
Sensorimotor
0-2; Piaget; Object permanence
Preoperational
2-7; Piaget; Egocentric and struggle with Conservationism
Concrete Operational
7-11; Piaget; Children begin to think logically but struggle with abstract things
Formal Operational
11+; Piaget; Logical reasoning and abstract thinking
Preconventional
Kohlberg; In search of rewards and self-centered; Younger children
Conventional
Kohlberg; Cares about effect of actions on others; Older children and most adults
Post Conventional
Kohlberg; Universal or ethical principles, abstract thinking; some adults