Electrical
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Series Circuits
have only one path electrical current can take. A break anywhere in the circuit stops the whole operation.
Parallel circuits
has multiple paths for electrical current.
Series-parallel circuits
These circuits are more complicated because they include more components, such as on/ off switches and fuses.
most common circuit
Valence Shell
the outer electron shell of an atom
determines whether an element is a conductor, semiconductor, or insulator
Conductors
allow electrons to flow freely between different atoms. These valence shells have more empty spots than they have electrons.
Semiconductors
have half-full valence shells and are neither good conductors nor good insulators.
Insulators
have pretty full valence shells (at least more than half), so electrons can’t move much (or at all) between atoms.
Current
xxx occurs when electrons move from one place to another.
Watt
measures power, the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or transformed into another type of energy, such as light or heat.
Watt-hour
xxx is the amount of energy used in 1 hour at a rate of 1 watt. Most electricity is measured in kilowatt-hours, which is how much energy you’d use if you ran a 1,000-watt (1-kilowatt) device for an hour.
Kilowatt and kilowatt-hours
One kilowatt (kW) equals 1,000 watts,
one kilowatt-hour (kWh) is one hour using electricity at a rate of 1,000 watts.
Megawatt
One xxx is equal to 1,000 kilowatts (and 1,000,000 watts).
Gigawatt
measure the capacity of large power plants (or multiple smaller power plants).
… Volts
measure the difference of potential between two points.
Amperes (amps)
measure the number of electrons that move past a specific point in 1 second.
Ohms
measures resistance, including anything that could limit the flow of electrons.
ohm's law Ω
how the amount of resistance that interferes with the flow is measured
Resistance
can be measured by dividing the voltage measured at any give point by the amount of current at the same point in a circuit.
Voltage
the difference of the potential between two points in circuit
Nucleus
the positively charged central hub of an atom, composed of protons and neutrons
Protons
positively charged subatomic particles
Neutrons
neutrally charge subatomic particles
Electrons
negatively charged, outside of the nucleus
Atomic number
the number of protons
Atomic mass
the sum of protons and neutrons
Fuses
thin wires enclosed in a safe insulating material that are a part of a circuit
Capacitance
xxx is the storage of energy that occurs in a nonconductor. This property resists any change in voltage in a circuit.
Capacitive Reactance (capacitance)
the measure of a capacitor’s opposition to alternating current (measured in Ohms).
Inductive reactance (inductance)
the resistance to a change in the flow of current (measured in ohms).
xxx is the property that causes current to increase or decrease even more based on changes in current induced in a circuit.
This xxx creates an electromotive force and is measured in henrys (H).
Frequency (Hz)
the number of times an alternating current changes direction per second
Chemical effect
Current produces this effect when it passes through a chemical compound and breaks up that compound.
Heat effect
Conducting electricity causes wires to become heated.
Magnetic effect
When a wire is introduced into a magnetic field, electricity flows through the wire and creates a magnetic field that repels a magnet.
Physiological effect
Current produces this effect when it passes through a muscle that causes it to contract.
Current is measured in
amperes (amps)
Voltage is measured in
…. volts
resistance is measured in
ohms
power is measured in…
… watts
the formula for ohms law
current = voltage/resistance
formula for power (watts)
voltage (volts) x current (amperes)
OR
P=VI
current flows from….
… a negative pole to a positive pole
A closed circuit must exist…
… for electricity to flow
AC…
changes direction constantly at a constant rate
Frequency is…
The number of times a current completes two alternations of direction per second
the unit of measurement for frequency is the hertz (Hz).
Electronic devices operate…
at high frequencies…
Electronic devices often require…
a specific capacitive or inductive reactance to work.
Capacitors and inductors are devices used in circuits…
… to provide the type of reactance needed.
Rectifiers
Devices that change alternating current to direct current
a transistor can…
amplify a signal
Load
Any Component that drains power from a circuit. Ex. light bulbs
Rectification
the process in which a current goes from a direct current to an alternating current
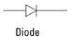
Diodes
conduct electricity in only one direction.
Semiconductor diodes
a component is rectifiers that are made out of a material with conductivity somewhere between that of a conductor and an insulator

Wires
xxx are used to pass current from one part of the component to another. xxx that are connected to each other are indicated by a dark circle and are called joined xxx.
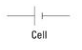
A Cell
… supplies electrical current. Some call this a battery, but technically a battery is more than one cell.
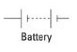
Battery
xxx is two or more cells. The large terminal is positive.

DC power supply
A xxx power supply provides direct current. xxx always flows in one direction.

AC Power Supply
An xxx supply provides alternating current. xxx constantly changes direction at a specific frequency.
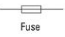
Fuse
A xxx is a safety device that blows (melts) if the current flowing through it exceeds a specified value.
Transformer
A xxx consists of two coils of wire linked by an iron core.

Ground
A xxx is a connection to the Earth.

Transducer
A xxx is a device that converts energy from one form to another

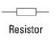
Resistor (nonvariable)
xxx restrict the flow of electric current (and the restriction cannot be changed)
Variable resistor
Restricts the flow of electric current to any value within it’s range.

Capacitor
xxx store electric charge. They’re used with resistors in timing circuits because it takes time for a xxx to fill with charge.
Diode
xxx allow electricity to flow in only one direction. The arrow of the circuit symbol shows the direction in which the current can flow.
Transistor
A xxx can amplify current. xxx is also a semiconductor that controls the flow of electricity in a circuit

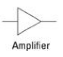
Amplifier
An xxx isn’t actually an electronic component but instead is a complex circuit. The block diagram symbol shows where an xxx circuit would be connected. xxx circuits are used to magnify power, current, or voltage.
Antenna
An xxx is a device designed to receive and/ or transmit radio signals.

brown/black wires
Live current. Transfers power to switches and outlets
Red wires
secondary live wire
blue/yellow wires
carry a current through a conduit
white/gray wires
Neutral wires. Connects a conductive piece of metal that attracts electrical current so it can be distributed everywhere it needs to go.
green wires
Failsafe wire. Gives electricity s place to escape into the ground if it has nowhere else to go.
Rectifiers and commutators
xxx can generate DC to AC
Alternators
xxx produce AC
DC Circuits
what type of circuit have resistance?
AC Circuits
what type of circuit have impedance?