Prevention and Care Exam 3
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
absorption
the ability of the body's tissues to deform
propulsion
the ability to generate enough force to overcome external resistance from the environment
- action of moving forward/accelerate
stability
the ability of a muscle to rapidly switch between concentric
and eccentric contractions to maintain a target position
injury prevention
physical conditioning, footwear, and protective equipment (ex: orthotics) can be effective in preventing injuries
physical conditioning injury prevention
strengthening both intrinsic and extrinsic muscles & promotes flexibility (achilles tendon)
resistive range of motion RROM
apply resistance while the athlete moves the joint - used to test muscles to see how well they're working
stress tests
stressing ligaments to see how strong they are/laxity
- anterior drawer test, talar tilt, dorsiflexion & external rotation test
Thompson Test (Ankle)
testing for Achilles tendon rupture by squeezing calf
- should produce plantar flexion when intact: If NO motion = injury
neurological dysfunction
tapping on nerves located @ the joint to see reaction
- Tinel sign
pes cavus (foot deformity)
high arch and rigid foot deformity
pes planus (foot deformity)
characterized as flatfoot
hammer toe
extension of the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint, flexion at the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP) joint, and hyperextended at the distal interphalangeal joint (DIP) joint
- toe deformity
claw toe
hyperextension of the MTP joint and flexion of the DIP and PIP joints
mallet toe
Neutral position at MTP and PIP joints, flexion at DIP joint
turf toe
sprain of the plantar capsular ligament of first MTP joint caused by forced hyperflexion or hyperextension of great toe\
- potential tear in flexor tendons or fracture of sesamoid bones
management: standard acute; rest; protection from excessive motion
hallyux valgus (bunion)
thickening of capsule and bursa of medial (inside) aspect of MTP joint of great toe; lateral aspect of the fifth toe caused by rubbing against inside of shoe
- surgery is needed to correct
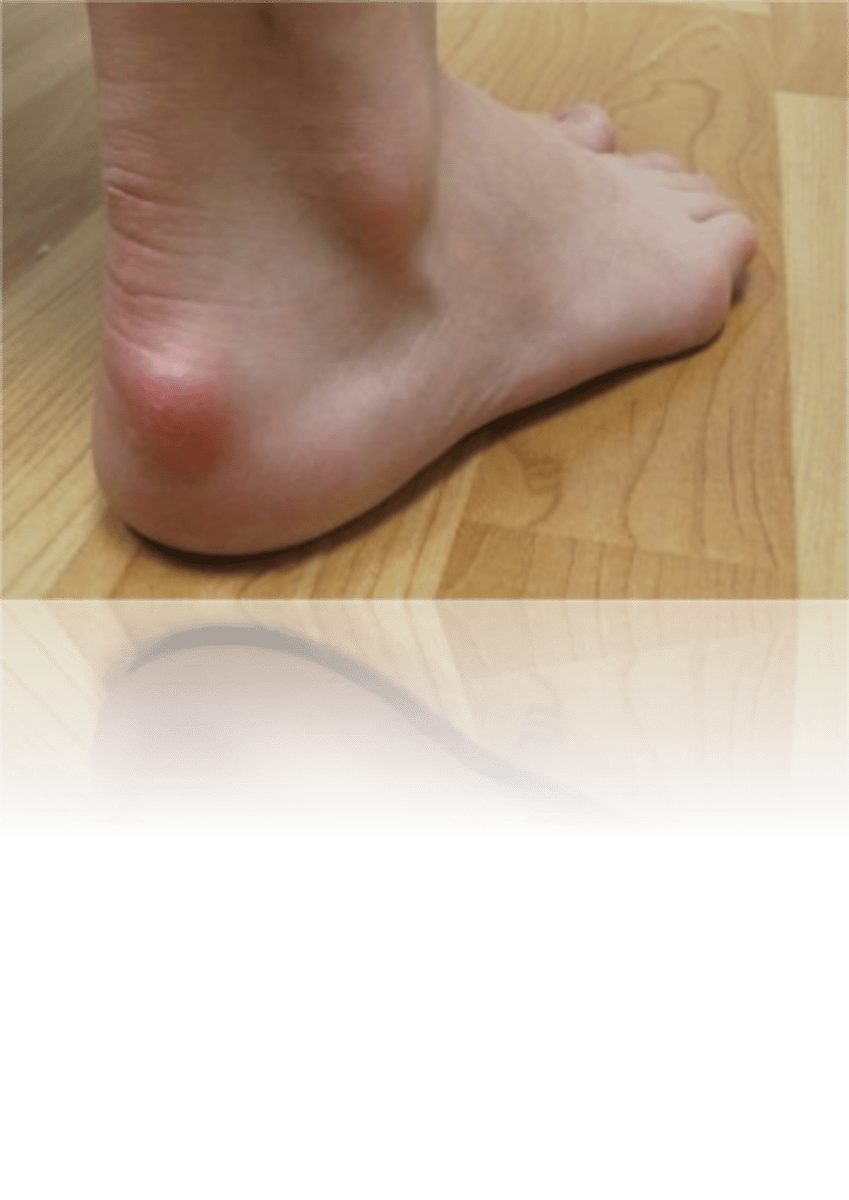
Retrocalcaneal Bursitis (pump bump)
caused by external pressure- constrictive heel cup, coupled with excessive pronation or varus hindfoot
Management: standard acute; shoe modification; AT stretching
acute compartment syndrome
direct blow to anterolateral aspect of the tibia causing rapid increase in tissue pressure causing neurovascular compromise
- irreversible damage can occur within 12 to 24 hrs
Management: cold; no compression or elevation; immediate physician referral
Ottawa Ankle Rules
Inversion ankle sprain
caused by plantar flexion and inversion
first degree ankle sprain
pain and swelling on anterolateral aspect of lateral malleolys
what kind of pain is burning pain?
nerve pain
chronic condition: tight lateral retinaculum or weak vastus medialis, leading to patella tracking causing lateral pain
patellafemoral stress syndome
A positive Thomas test indicates the presence of ____ contractures in the right iliopsoas muscle
flexion
In a posterior and superior hip dislocation, the leg typically rests in what position?
hip flex and interiorly rotated
Avascular necrosis of the hip usually occurs at the?
head of the femur : Legg- Calves- pertheses
Which special test is positive when diagnosing a PCL sprain?
Posterior Stag Test
Which special test is positive when diagnosing a LCL sprain?
Varus
Which is known as the true ankle joint that performs dosiflexion and plantarflexion
talocrural joint
What structure is damaged during a lateral ankle sprain?
calcaneofibular ligament
which structure is damaged during a syndesmosis ankle sprain?
interosseus membrane
the structure that is involved with sever's disease is?
calcaneus
the structure involved in Sinding-Larsen-Johansen disease is?
apex of patella
What toe involves hyperextension of the MTP joint and flexion of the DIP and PIP joints?
Claw
a nondisplaced fracture of the pars interarticularis is termed?
spondylolysis
Which one of these spinal alignments is often associated with increased lordotic curve and kyphosis?
Sway back
Which type of swelling would we most likely see for an ACL sprain?
effusion (inside the joint)
which of the following injuries will have no radiating pain or neural involvement?
lumbar strain
2 multiple choice options
eversion ankle sprain
caused by excessive dorsiflexion and eversion effecting the deltoid ligament
syndesmosis sprain (high ankle sprain)
spreading of space at distal tibiofibular joint caused by dosriflexion and external rotation
lumbar spine
The lower part of the back, formed by five lumbar, five fused sacral, and four small coccygeal vertebrae
- forms convex curve anteriorly
sacroiliac joint
sacrum articulates with the ilium
primary movers for back extension
erector spinae muscles
kinematics
study of motion- movements are a result of additive motion from muscle segmental levels
- flexion, extension, hyperextension, lateral flexion, rotation
prevention of spinal injuries
- protective equipment
- proper technique
- physical conditioning
lordosis
abnormal anterior curvature of the lumbar spine
caused by: congenital deformities, weak abdominal musculature, poor posture, activity with excessive hyperextension
sway back
increased lordotic curve and kyphosis caused by muscle weakness & compensatory muscle tightness
- entire pelvis shifts anteriorly causing the hips to move into extension
- impacts the center of gravity
flat back
decreased anterior lumbar curve/lordosis causing spine to appear flat
- impacts center of gravity
kyphosis and scoliosis
curvature of the spine
palpation
an examination technique in which the examiner's hands are used to feel the texture, size, consistency, and location of certain body parts
slump test