Natural Clones in Animals
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
How can natural cloning occur?
- Embryo splitting
- Fragmentation
- Budding
- Parthenogenesis
What is budding?
The growth of a new animal out of the side of the original animal by mitosis
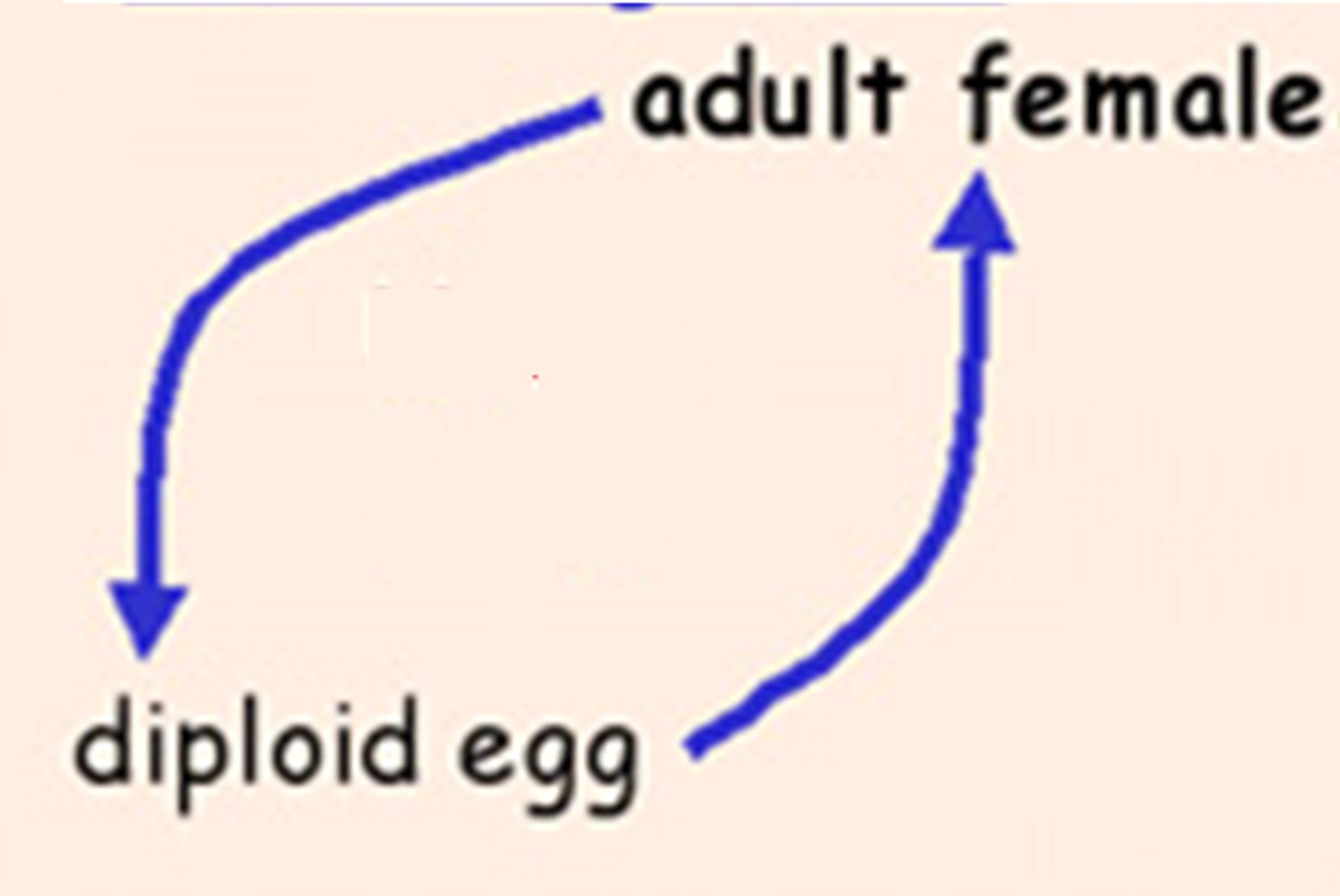
What is parthenogenesis?
A natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and development of embryo clones occur without fertilisation by a male gamete
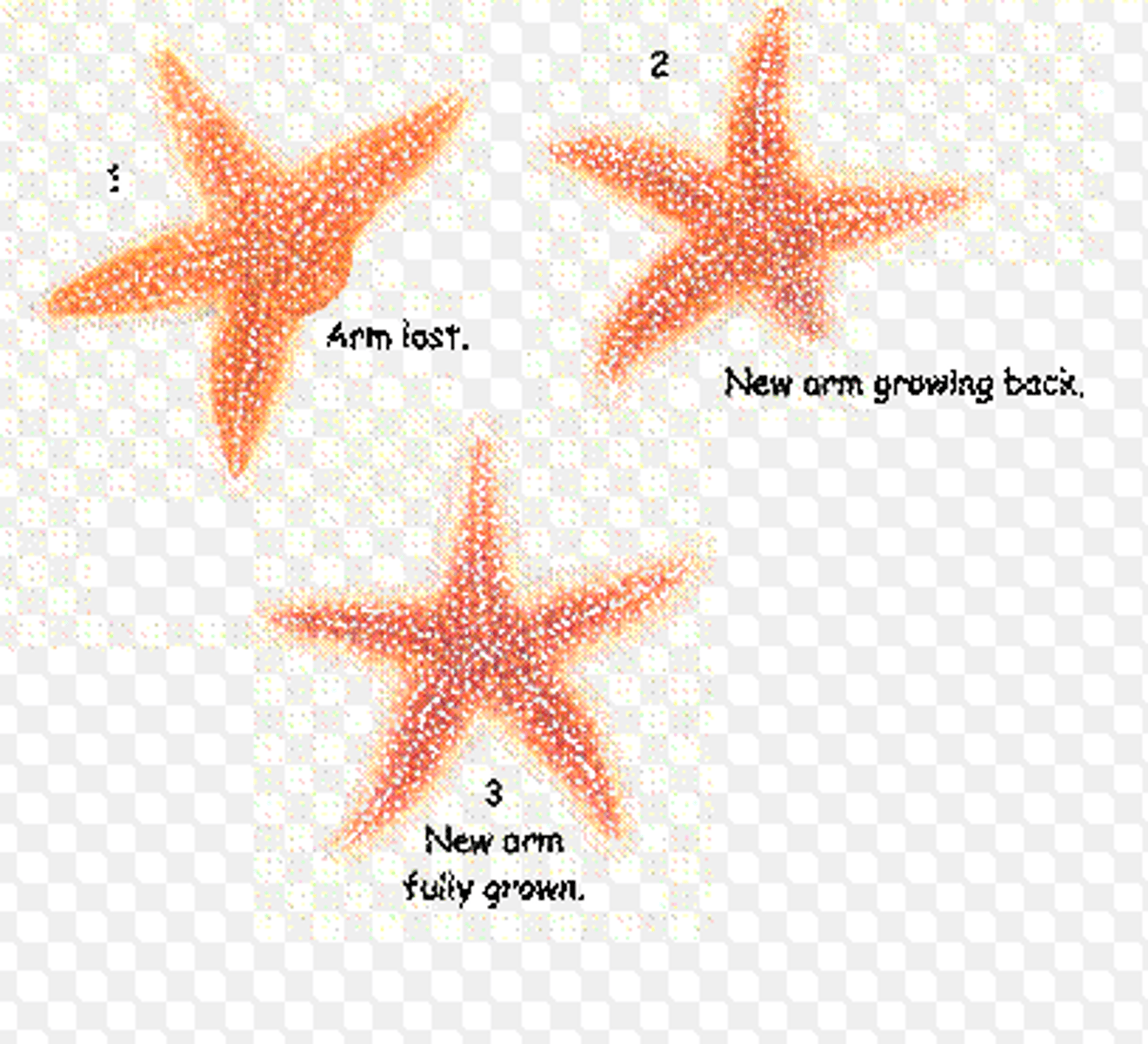
What is fragmentation?
It involves the breaking up of the original animal into small parts, each of which can then grow into a whole animal as seen in some corals, sea anemones and starfish.
Monozygotic Twins Process
An egg is fertilised by a sperm as in a singleton birth
This forms a zygote
The single zygote undergoes a few cell cycles (mitotic divisions) to become an embryo. This is why identical twins are referred to as monozygotic
At the embryo stage, the embryo splitting occurs.
Two embryos that form are identical, with the same genotype and develop in utero together
The result is the birth of identical offspring, always of the same gender, with identical phenotype
Why are non identical twins not considered twins?
Because non-identical twins are formed from separate eggs and sperm, they are not considered clones
Arguments for Artificial Plant Cloning
Desirable genetic characteristics always pass on to clones (doesn't always happen when plants reproduce sexually)
It produces lots of plants quickly, compared to the time it would take to grow them from seeds
Used to reproduce seedless fruit/plants
Propagation can be done at any time of the year
All the plants produced will be uniform
Arguments against Artificial Plant Cloning
Undesirable characteristics passed on
Low genetic diversity, so disease can easily wipe them out
Contamination by microorganisms during tissue culture can be disastrous and result in complete loss of the plants being cultured