Earth Science Unit Review
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Continental Drift Theory
the idea that continents slowly shift their positions due to movement of the tectonic plates on which they ride
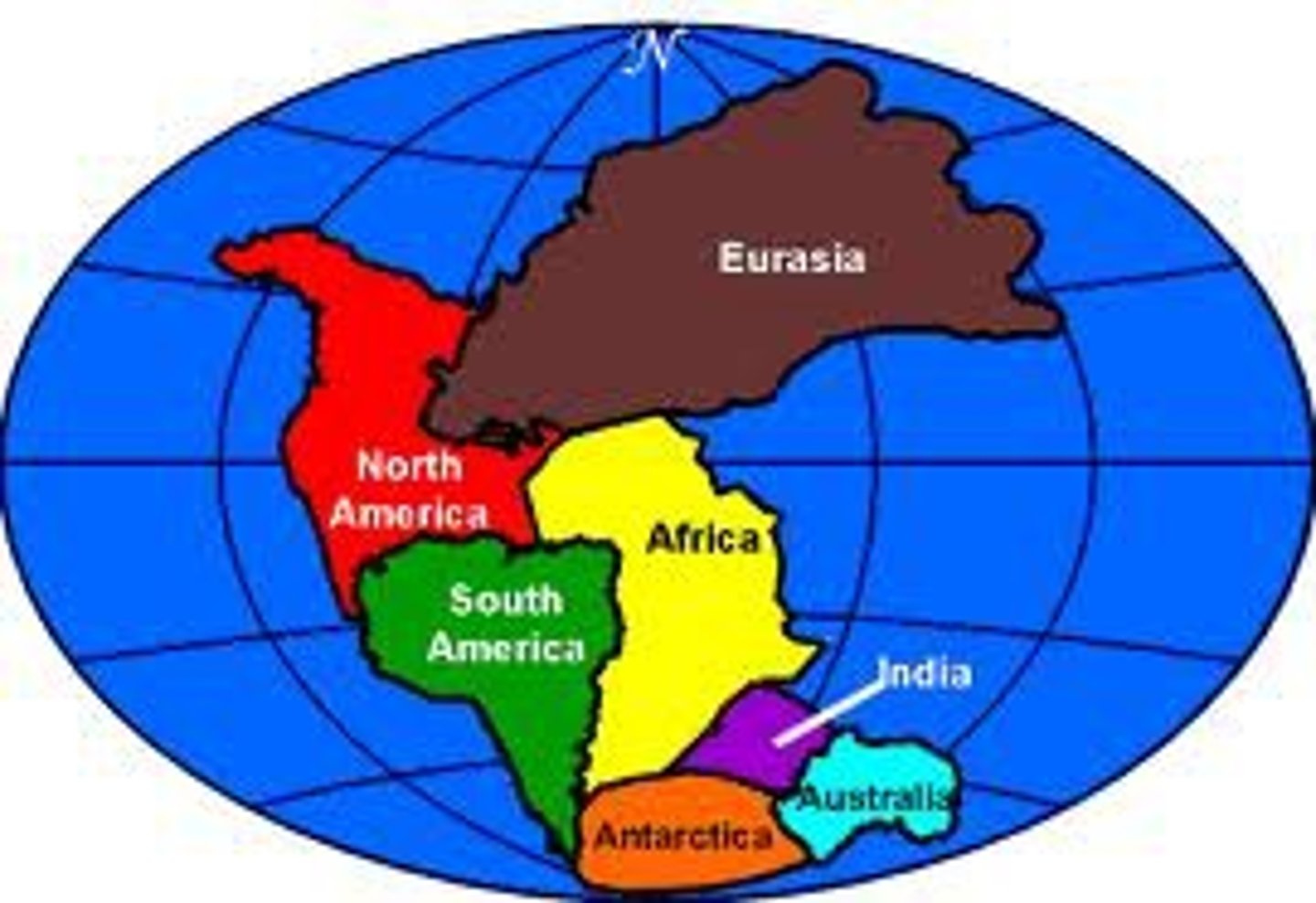
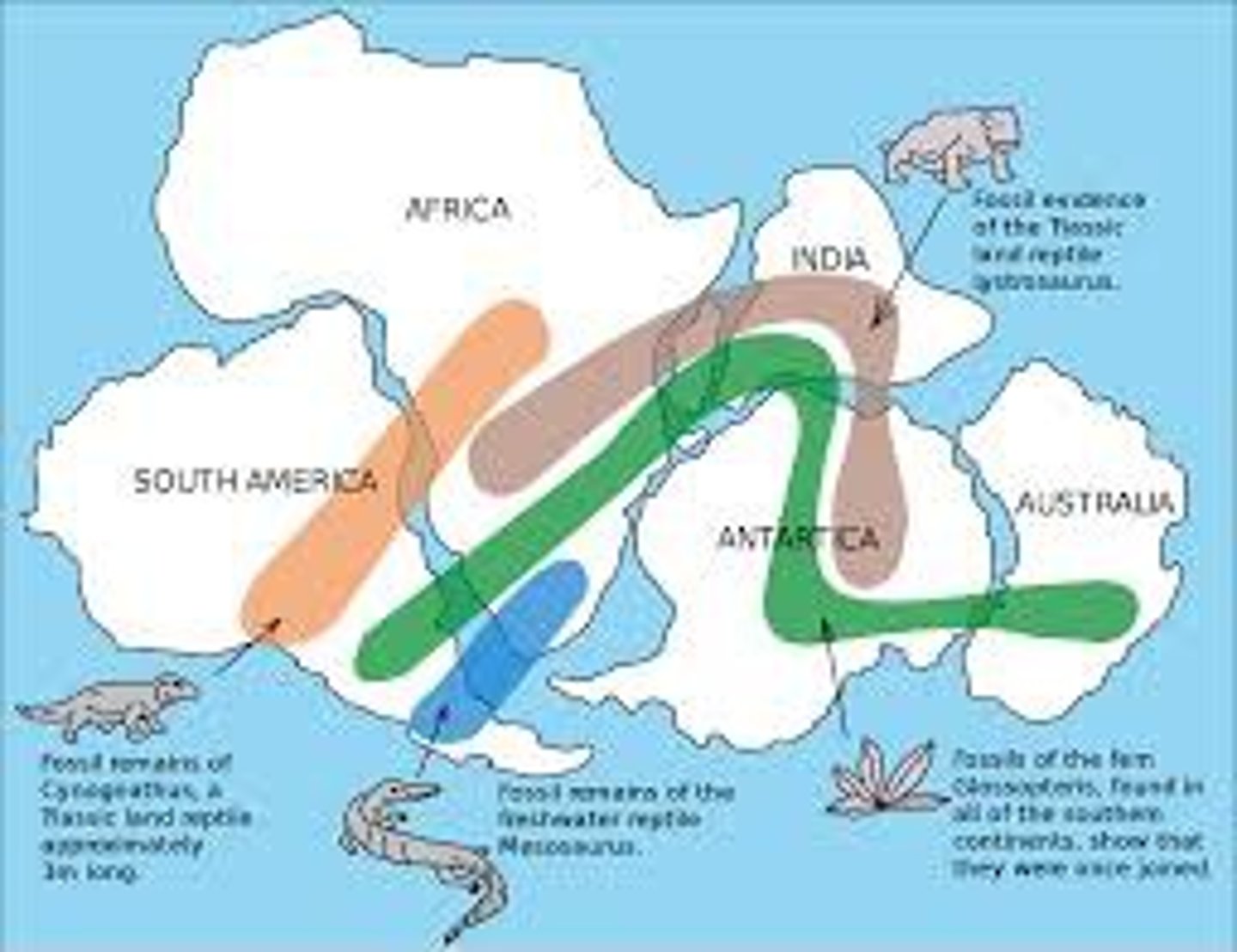
Evidence of Continental Drift
Fossils, climate, rocks, glacial deposits
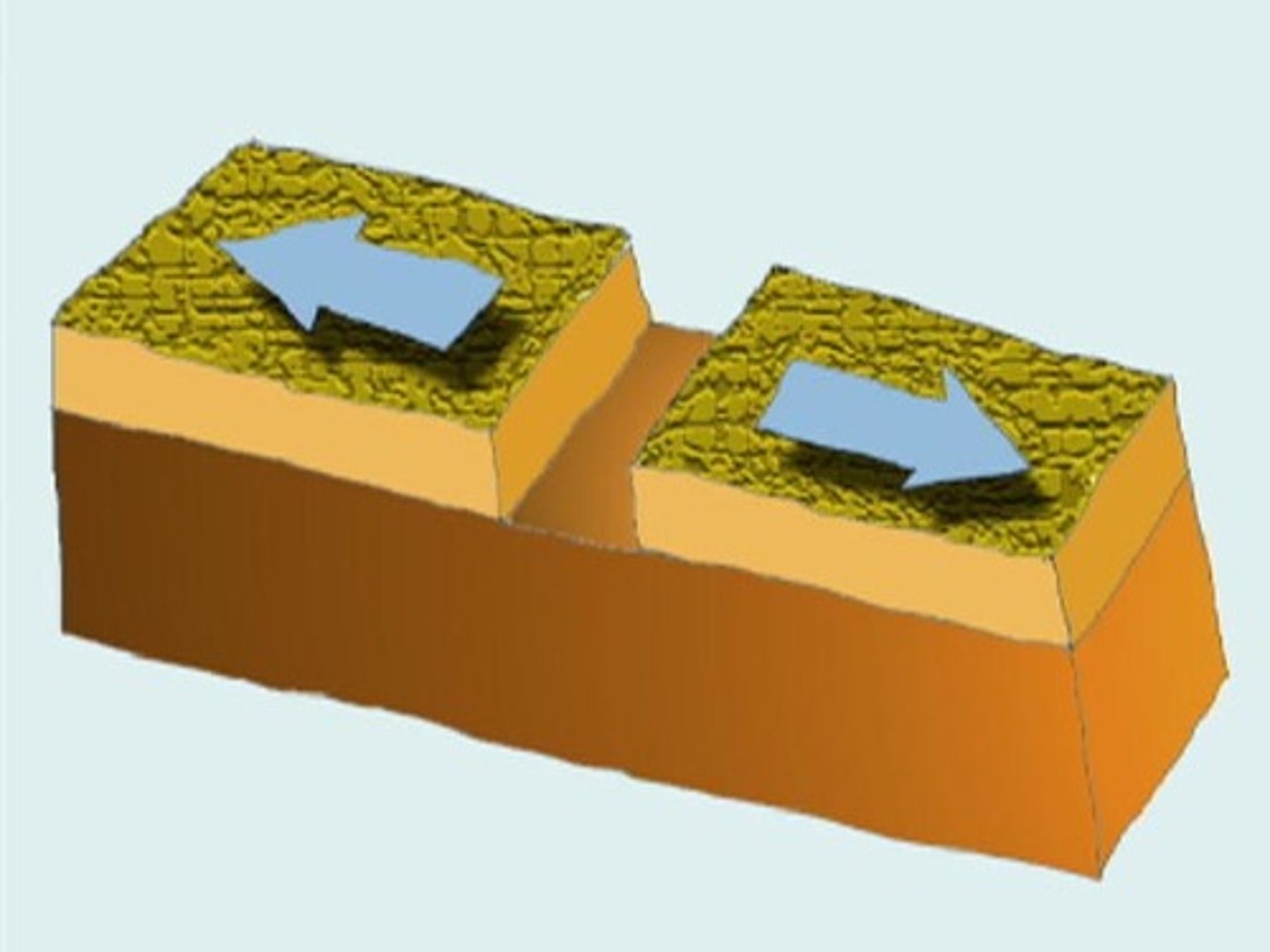
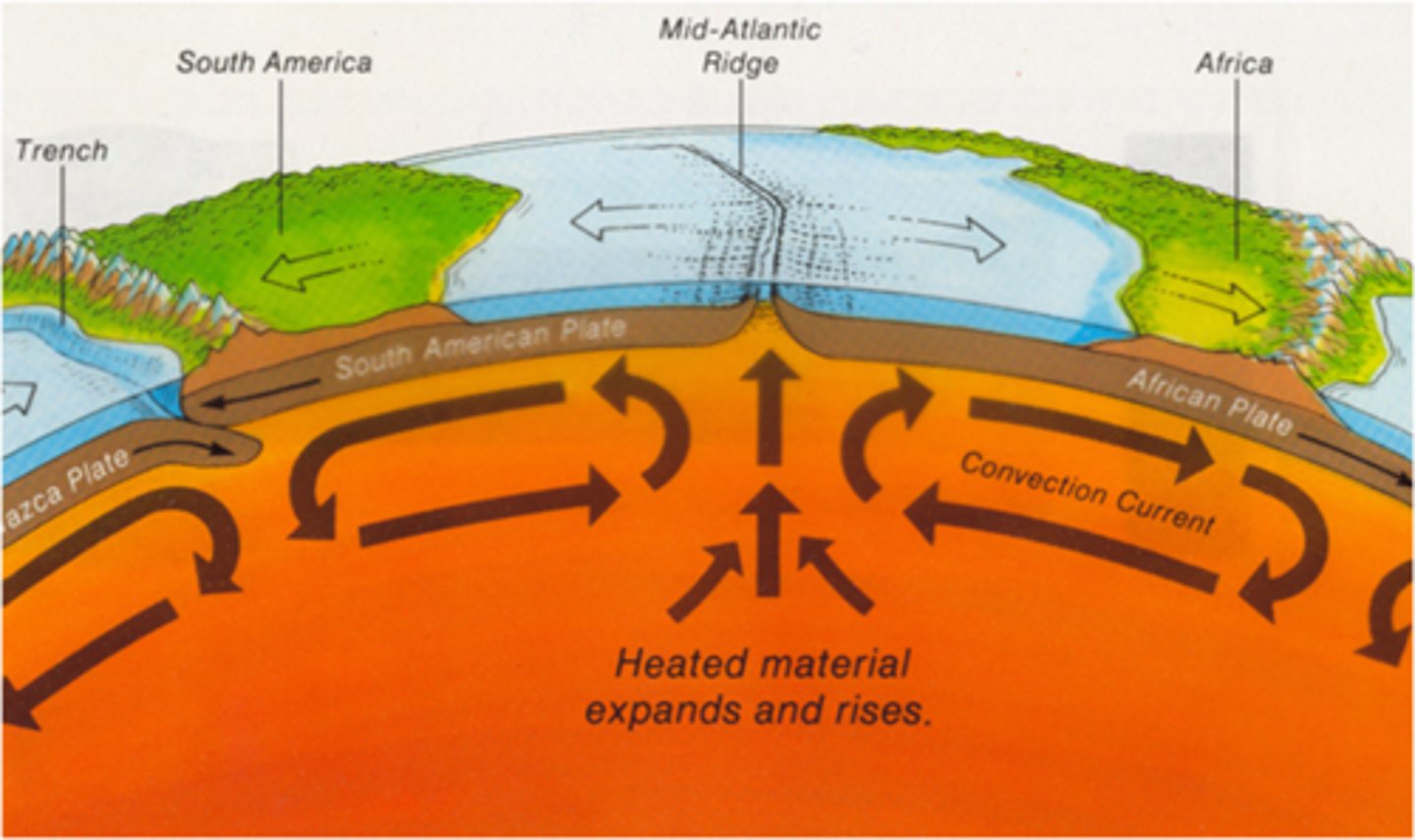
divergent boundary
The boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other
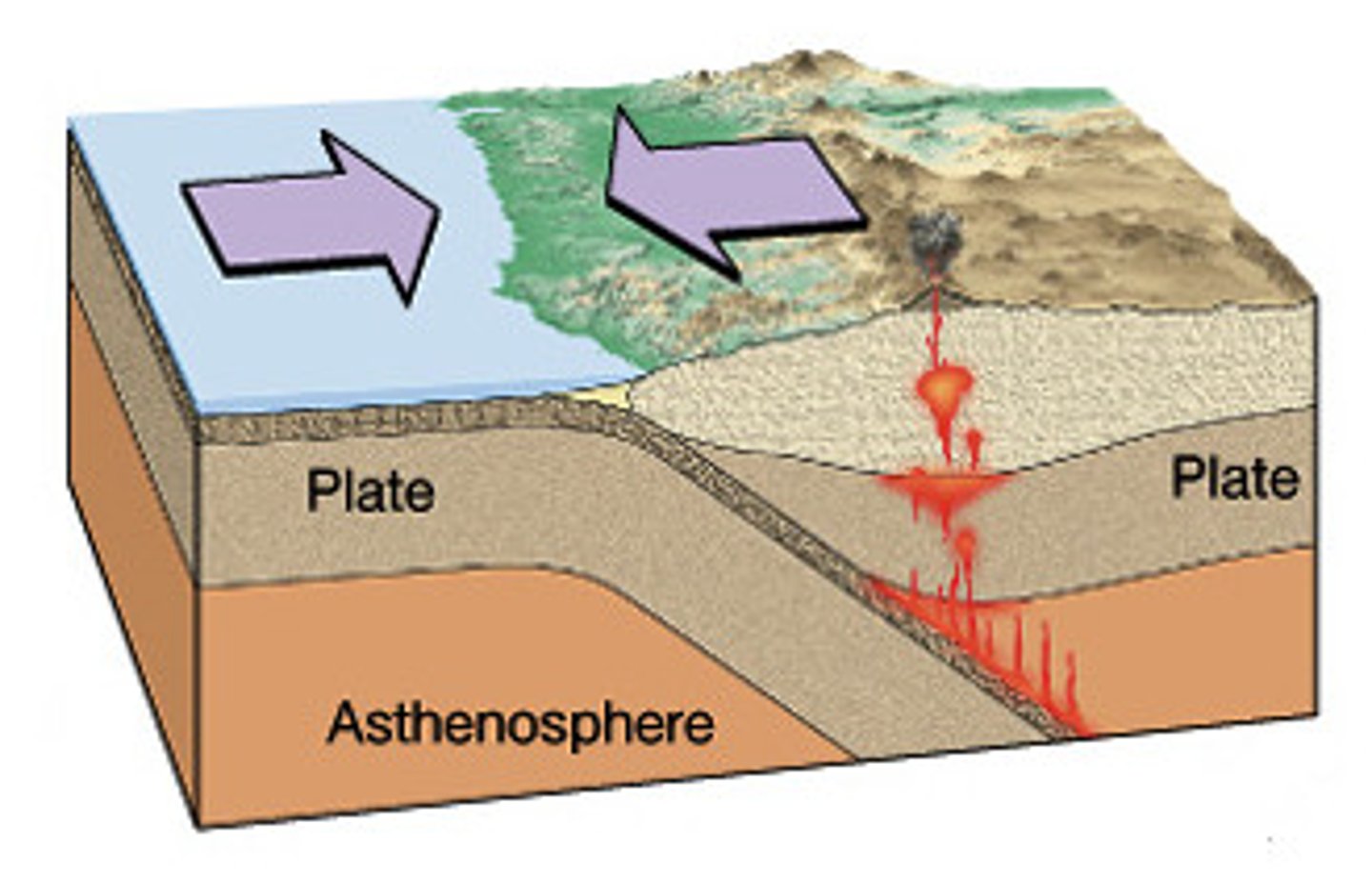
convergent boundary
A tectonic plate boundary where two plates collide, come together, or crash into each other.
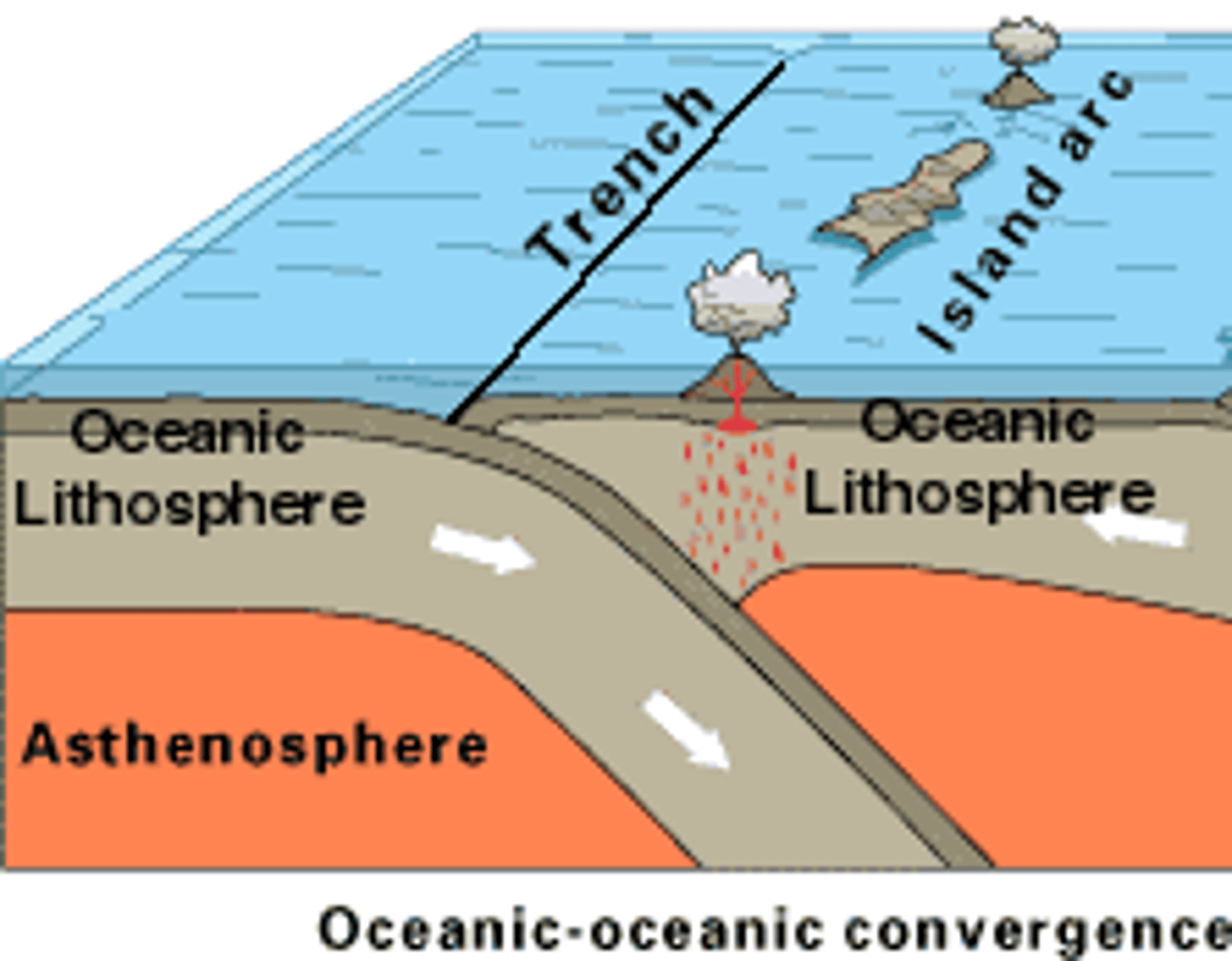
Ocean trenches are associated with
plate subduction
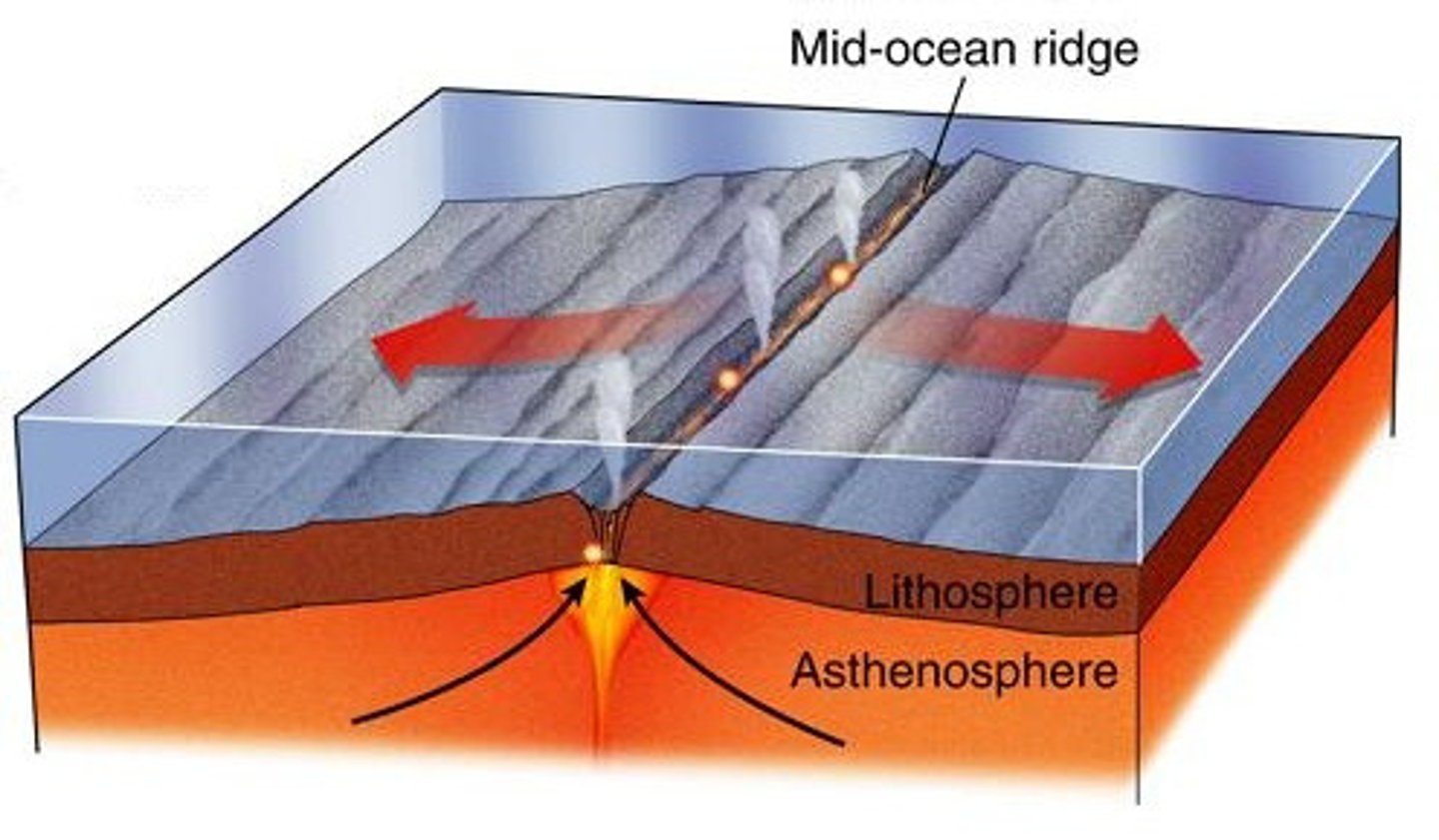
Mid-ocean ridges are
divergent plate boundaries
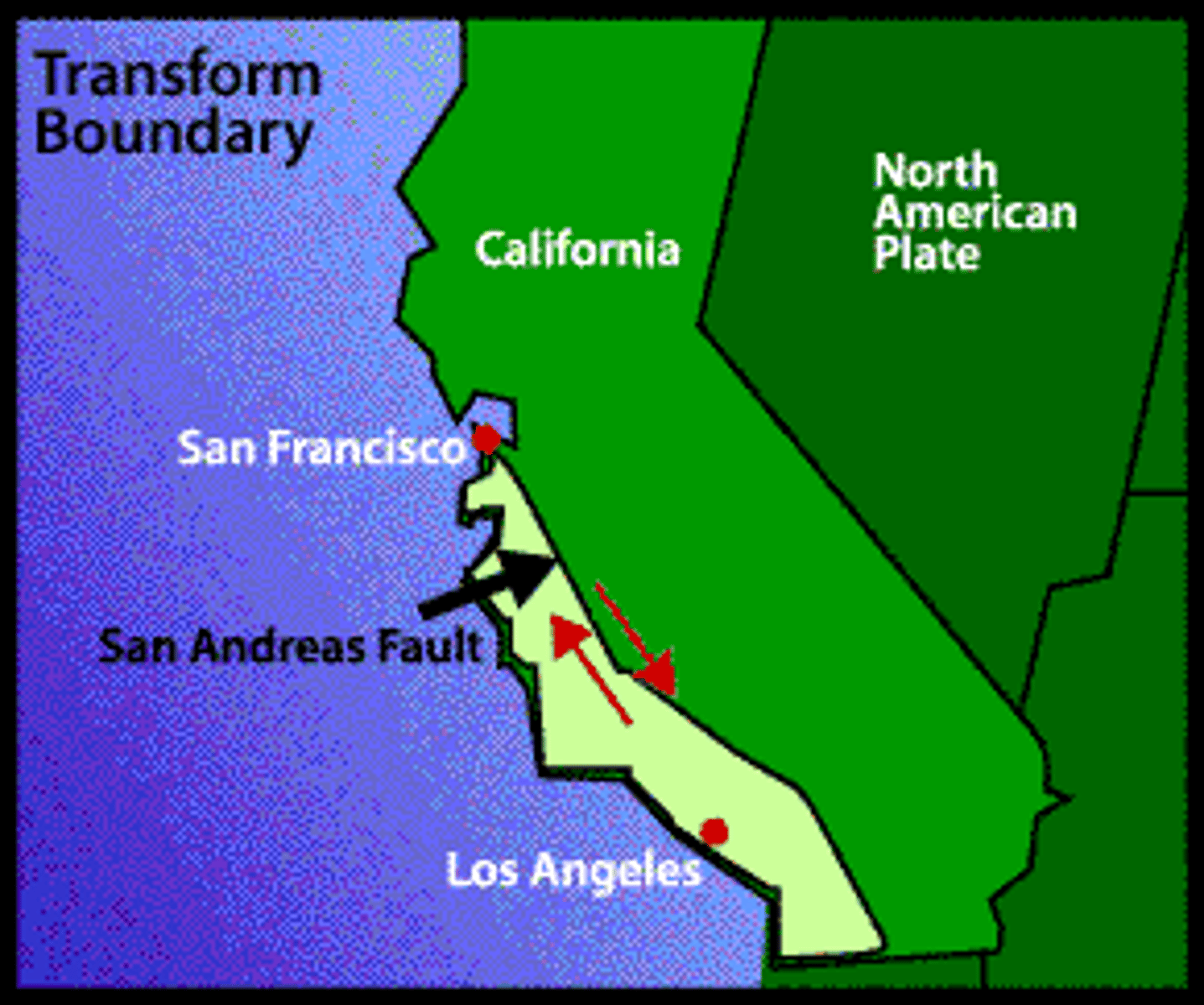
San Andreas Fault
A major geological fault in California formed by a sliding transform boundary.
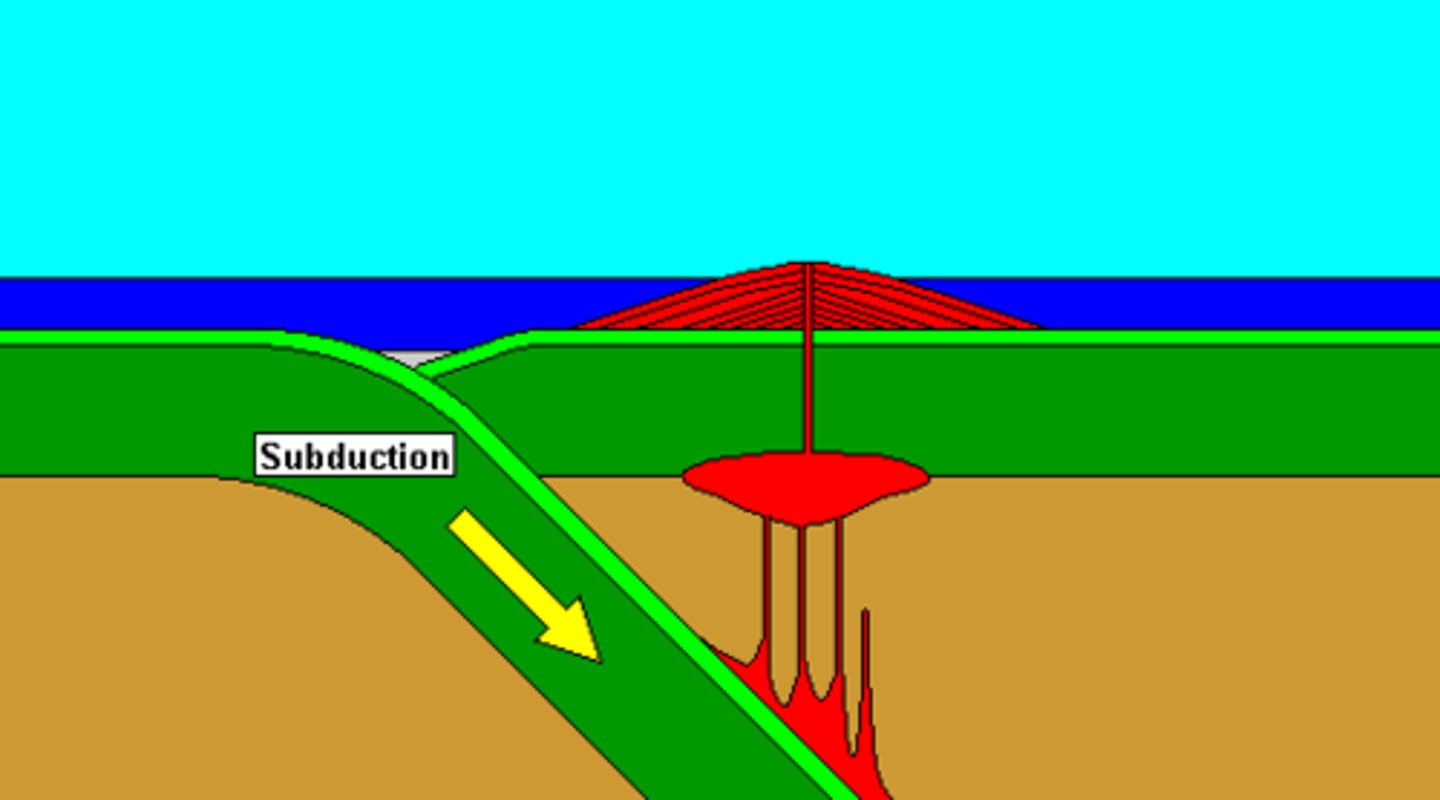
subduction zone
in tectonic plates, the site at which an oceanic plate is sliding under a continental plate.
radiometric dating
method used to determine the age of rocks using the rate of decay of radioactive isotopes
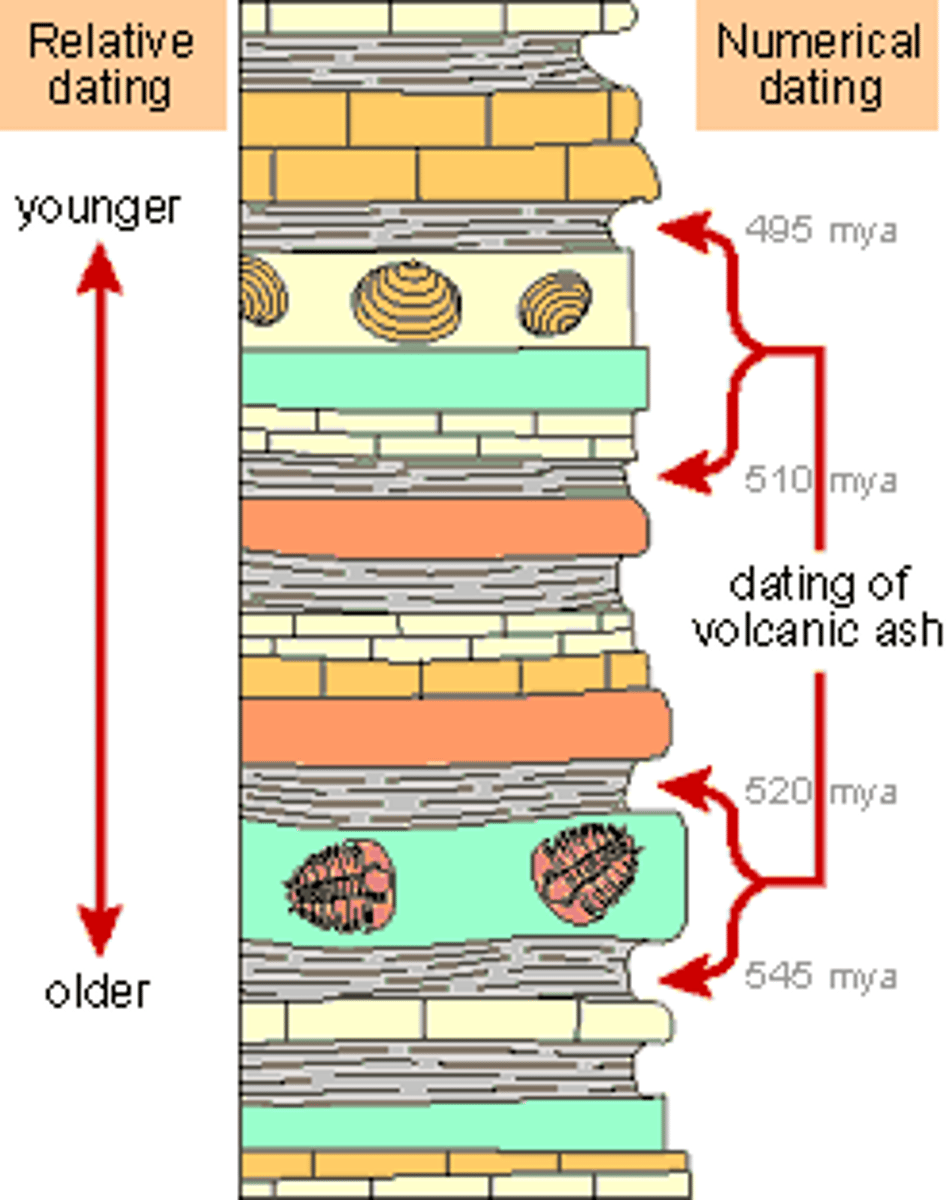
Law of Uniformitarianism
the idea that the same processes we see occurring now also occurred in the past

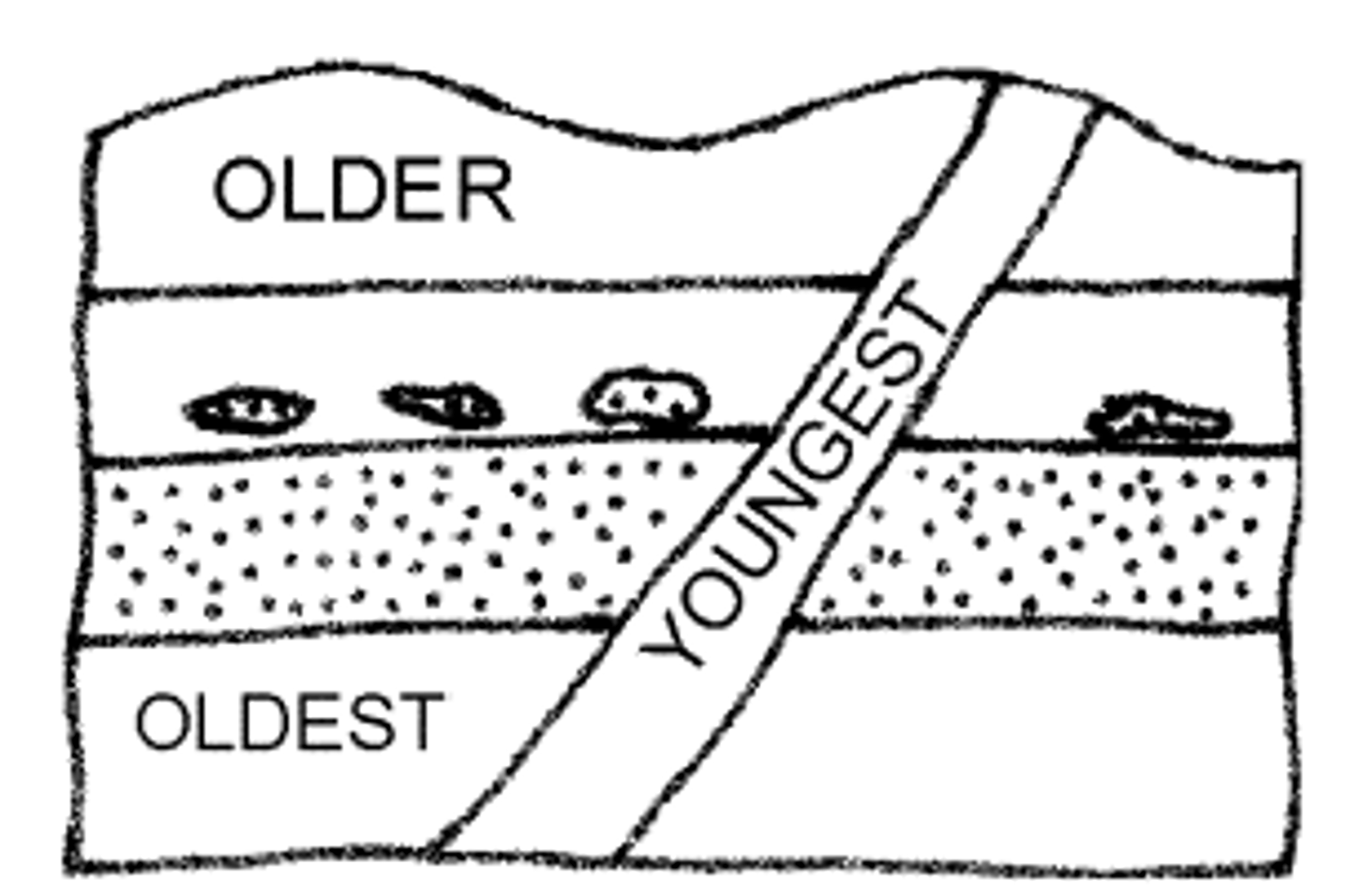
Law of Superposition
The top rock layer and its fossils is the youngest and the bottom is the oldest.

convection currents in the mantle
Most geologists think that the movement of Earth's plates is caused by
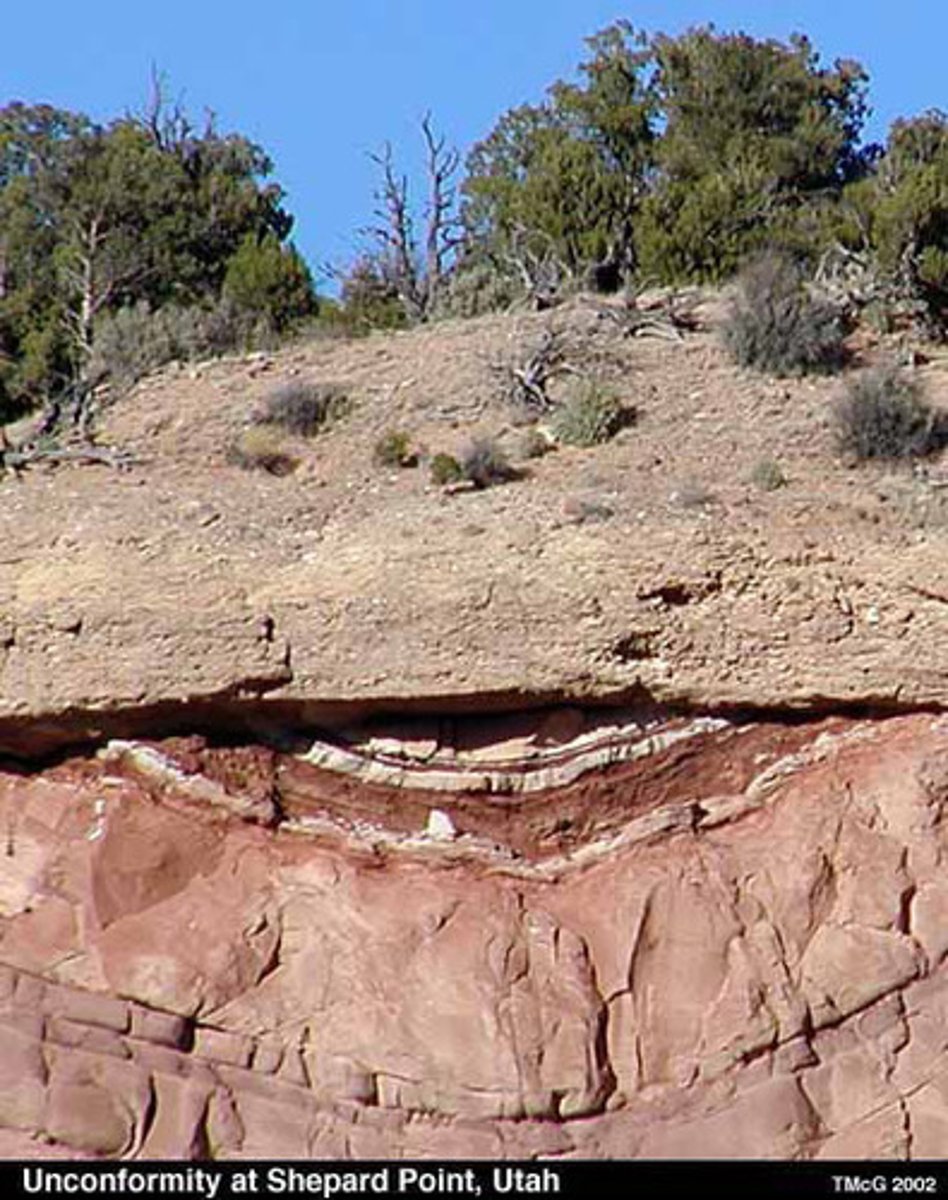
Law of Unconformity
break in the geologic record that is made when rock layers eroded or when sediment is not deposited for a long period of time. often due to erosion

Law of Cross-Cutting Relationships
the principle that a fault or body of rock is younger than any other body of rock that it cuts through
absolute dating
A technique used to determine the actual age of a fossil
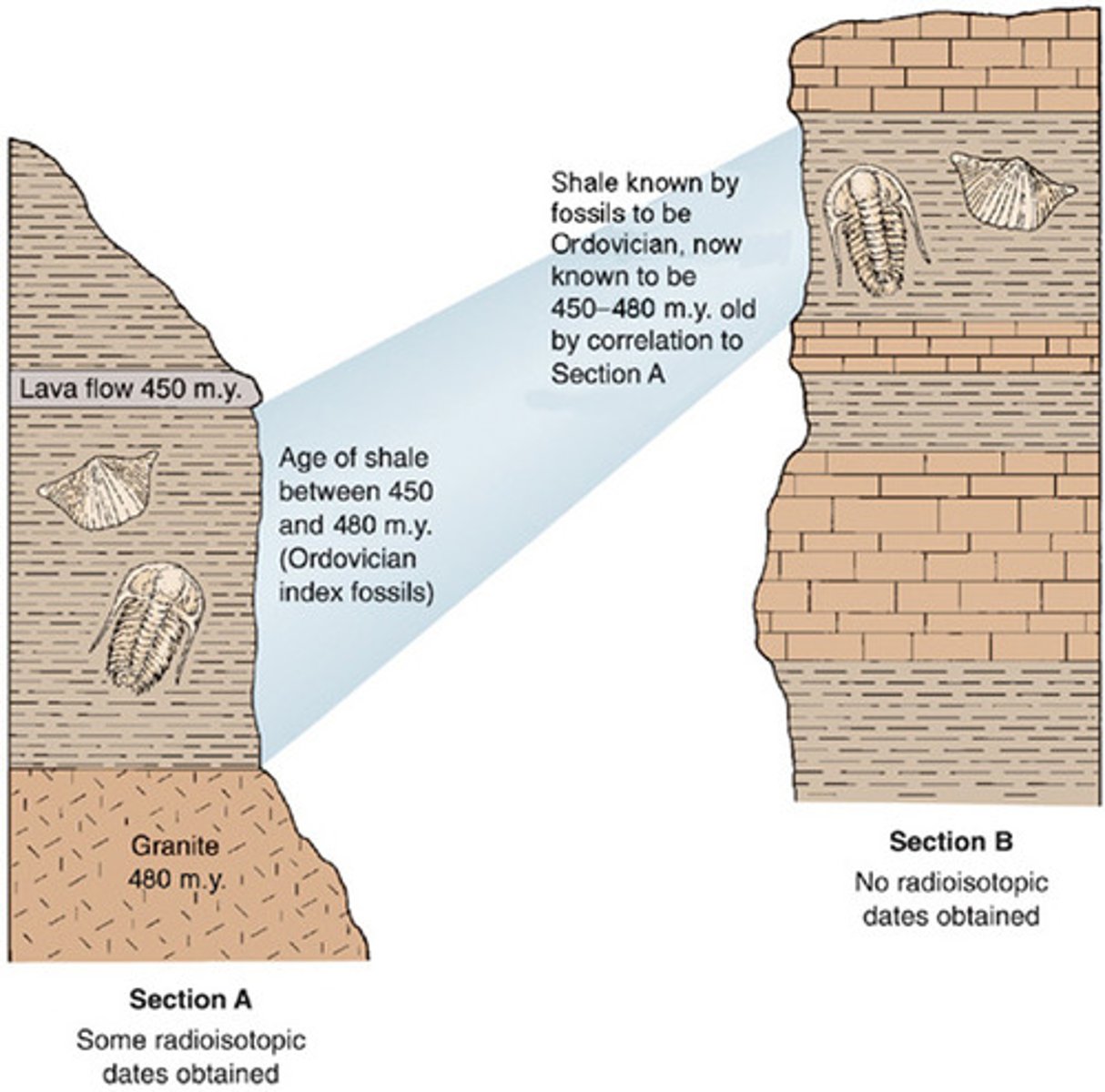
relative dating
Method of determining the age of a fossil by comparing its placement with that of fossils in other layers of rock

index fossil
a fossil known to have lived in a particular geologic age that can be used to date the rock layer in which it is found
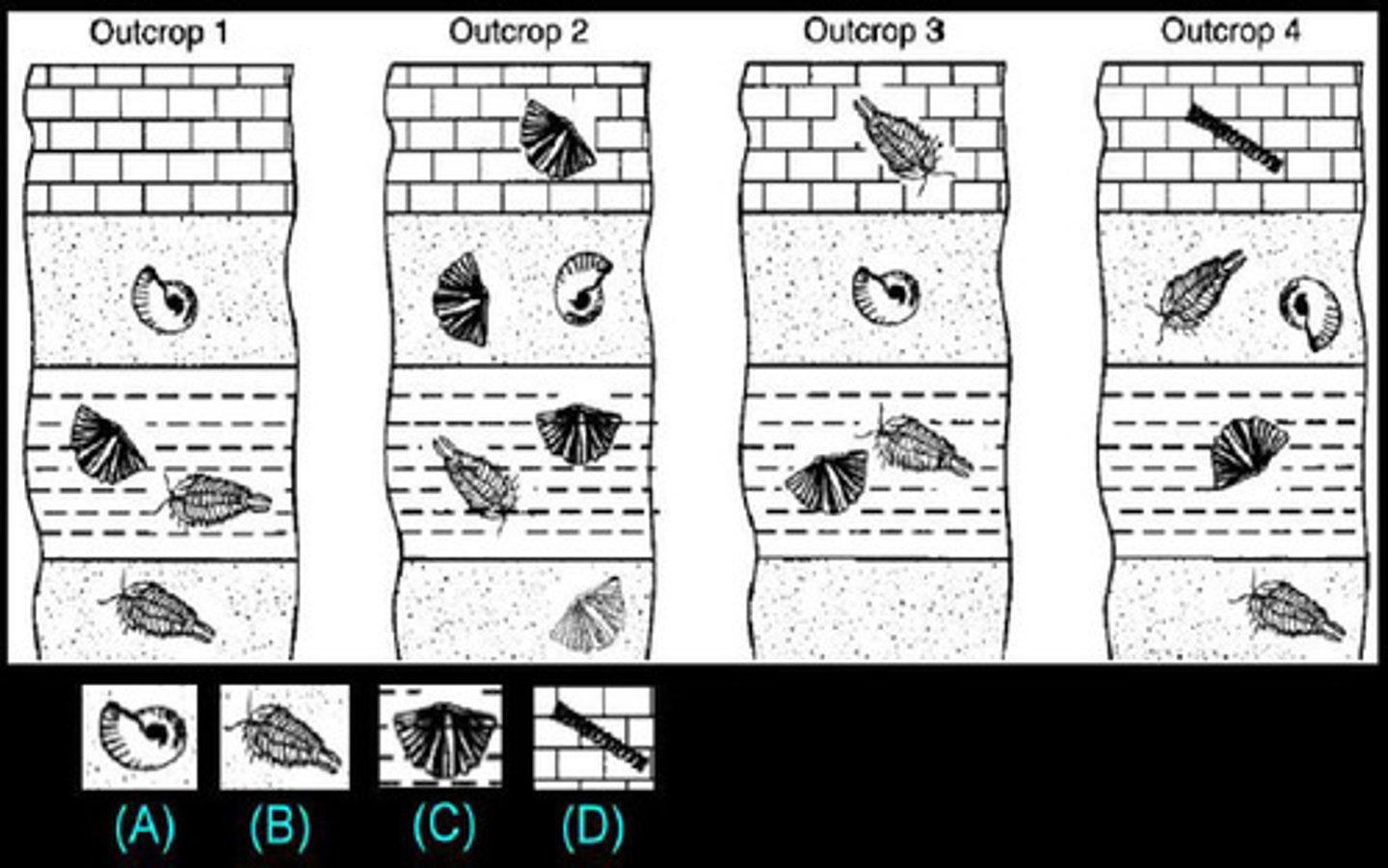
Strata
layers of rock, representing various periods of deposition

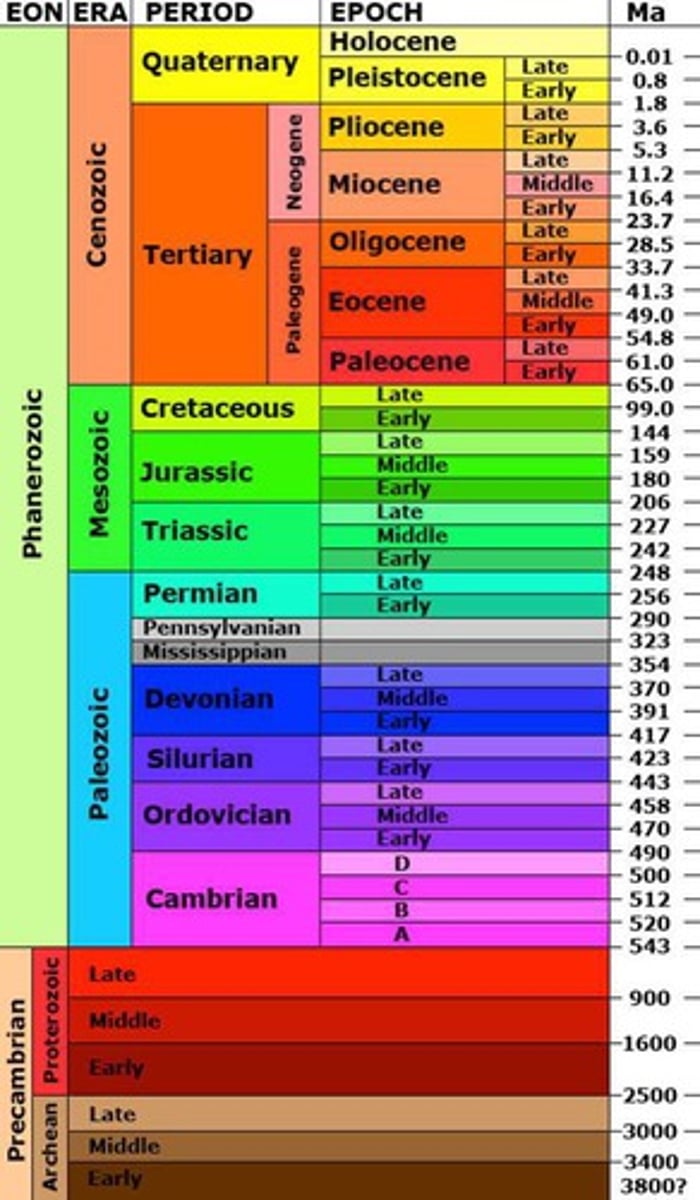
Geologic Timeline
The summary of Earth's history, divided into intervals of time defined by major events or changes on Earth.

Era
the largest division of geologic time
igneous rock
a type of rock that forms from the cooling of molten rock at or below the surface
Metamorphic Rock
A type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
sedimentary rock
A type of rock that forms when particles from other rocks or the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together
The law of original horizontality states that:
sedimentary rocks are originally deposited as horizontal bodies
inclusions
Any part of a previous rock layer, like a piece of stone, is older than the layer containing it.
Lateral Continuity
Sedimentary layers or lava flows extend sideways in all directions until they thin out or reach a barrier