Nervous System - External & Internal Brain
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain; responsible for voluntary muscular activity, vision, speech, taste, hearing, thought, and memory.
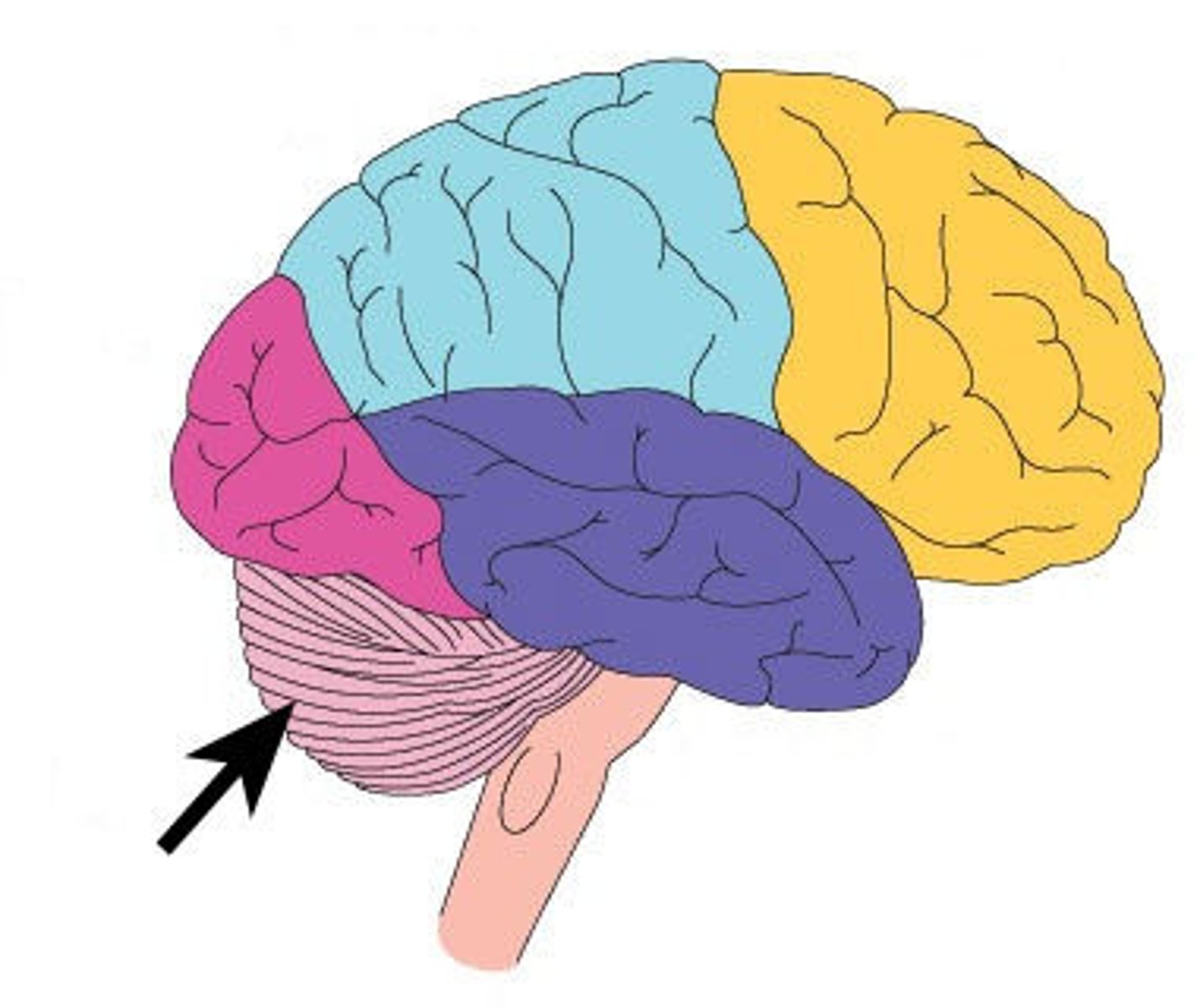
Cerebellum
Balance and coordination
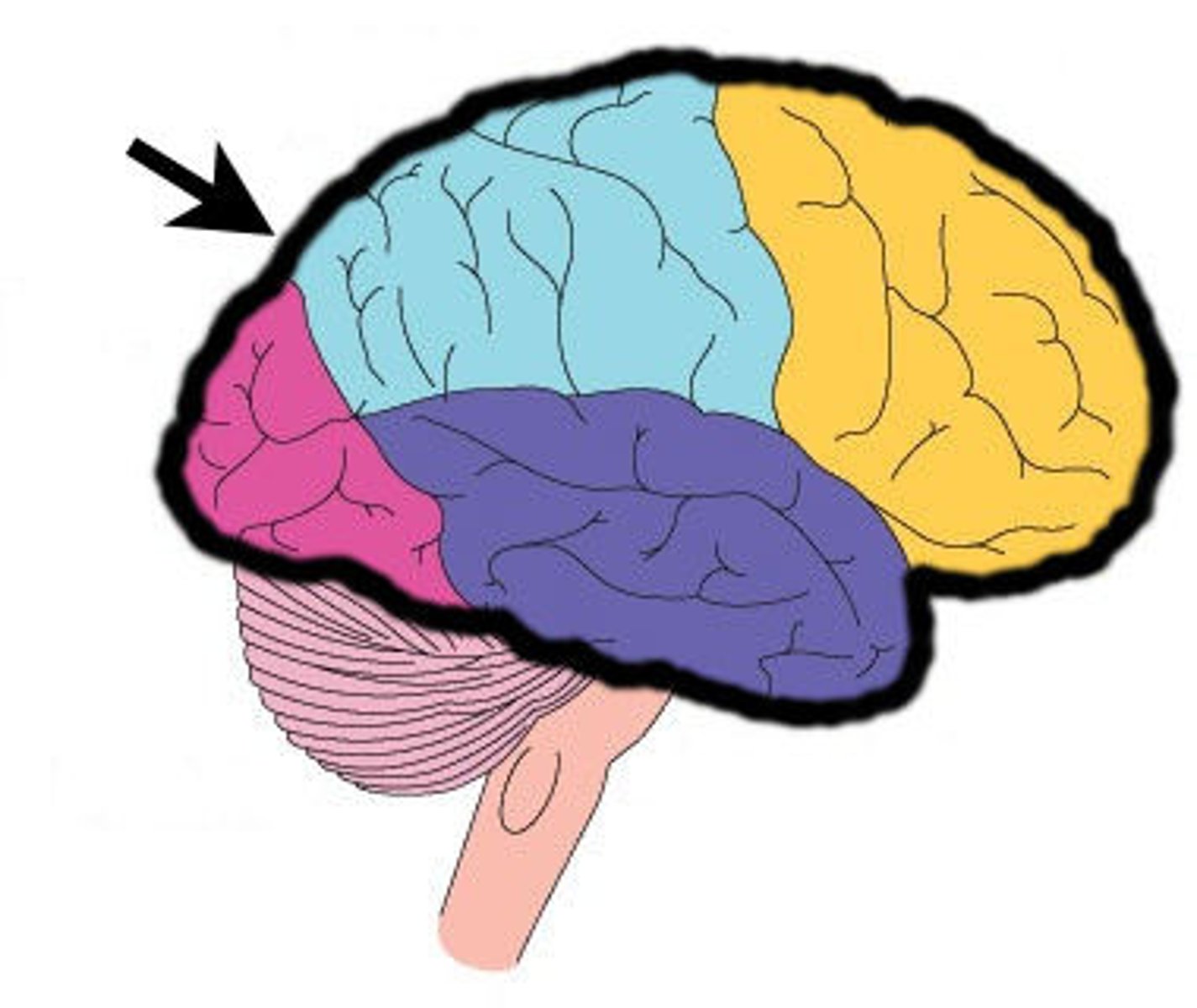
frontal lobe of cerebrum
the top, front regions of each of the cerebral hemispheres. They are used for reasoning, emotions, judgment, and voluntary movement.
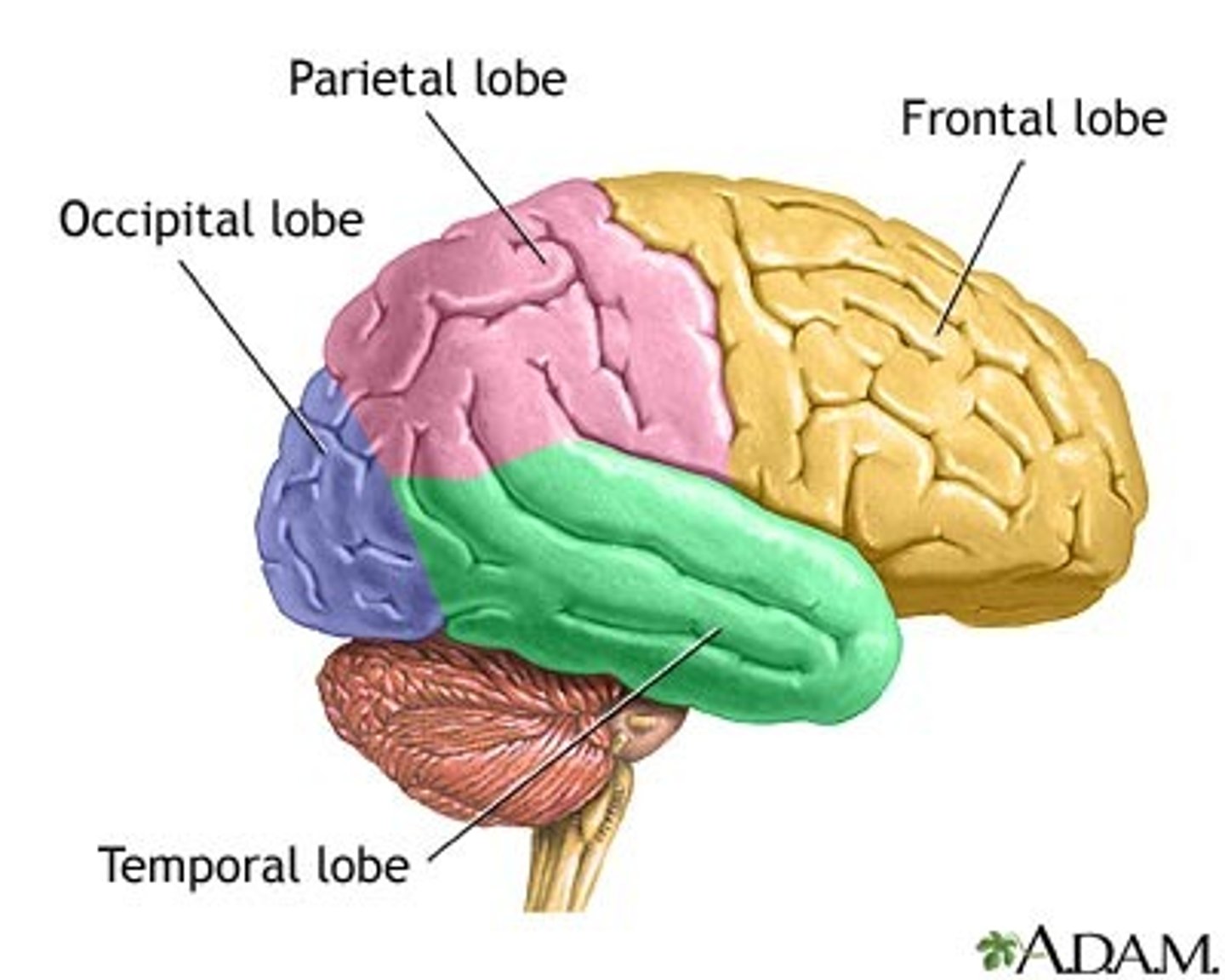
parietal lobe of cerebrum
the middle lobe of each cerebral hemisphere between the frontal and occipital lobes; it contains important sensory centers.
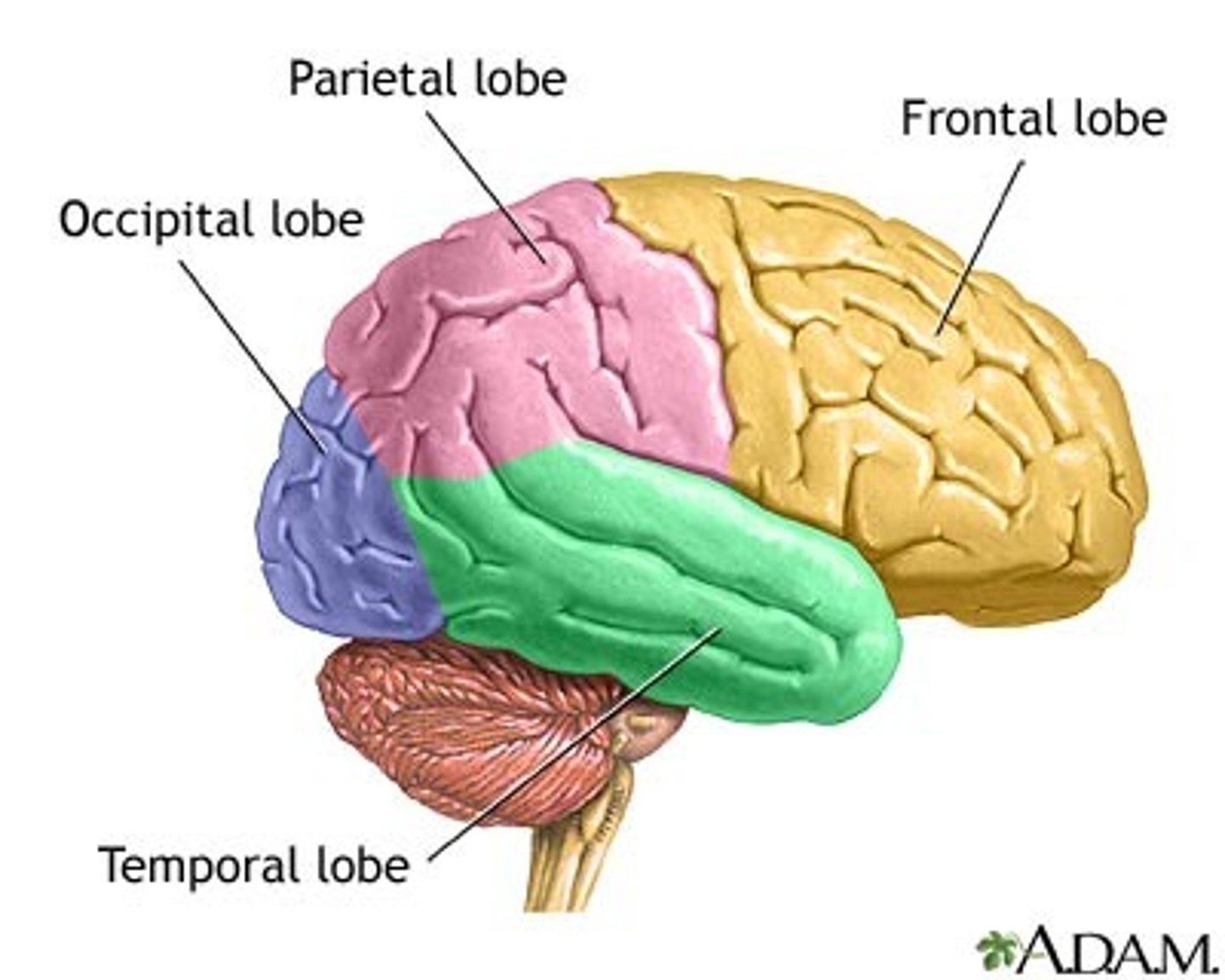
temporal lobe of cerebrum
contains centers of hearing and memory
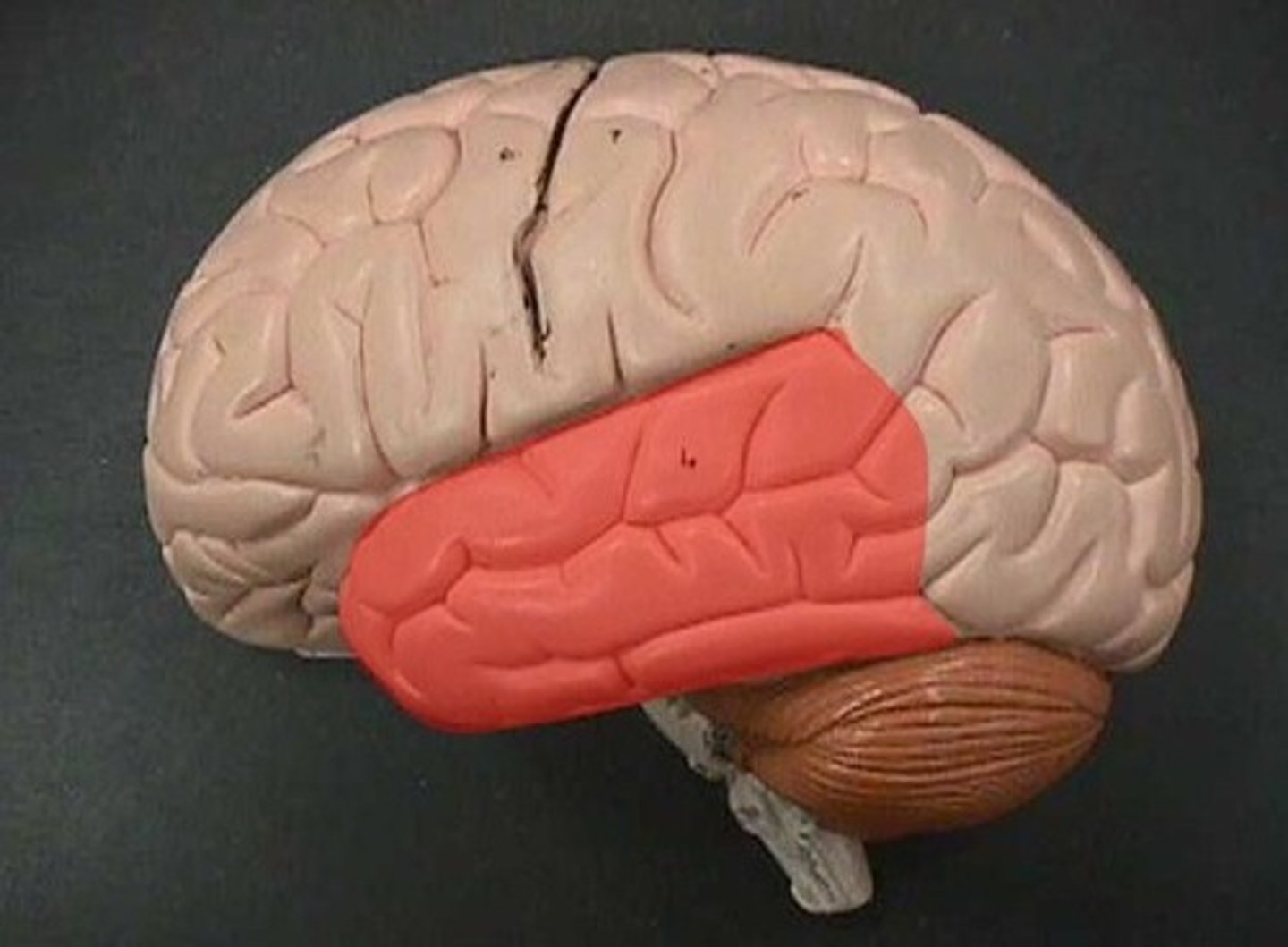
occipital lobe of cerebrum
visual processing
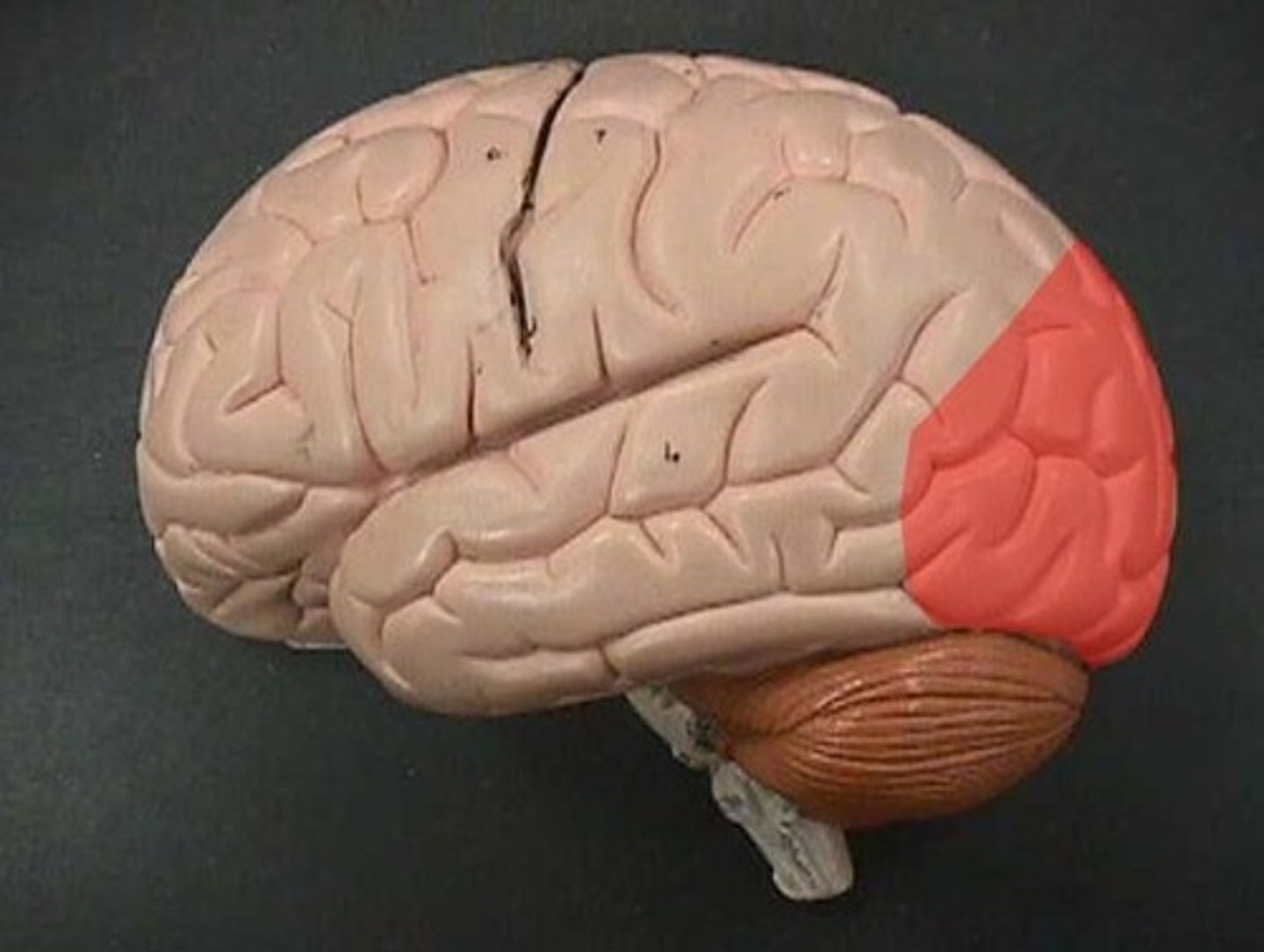
lateral sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
Corpus Collosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
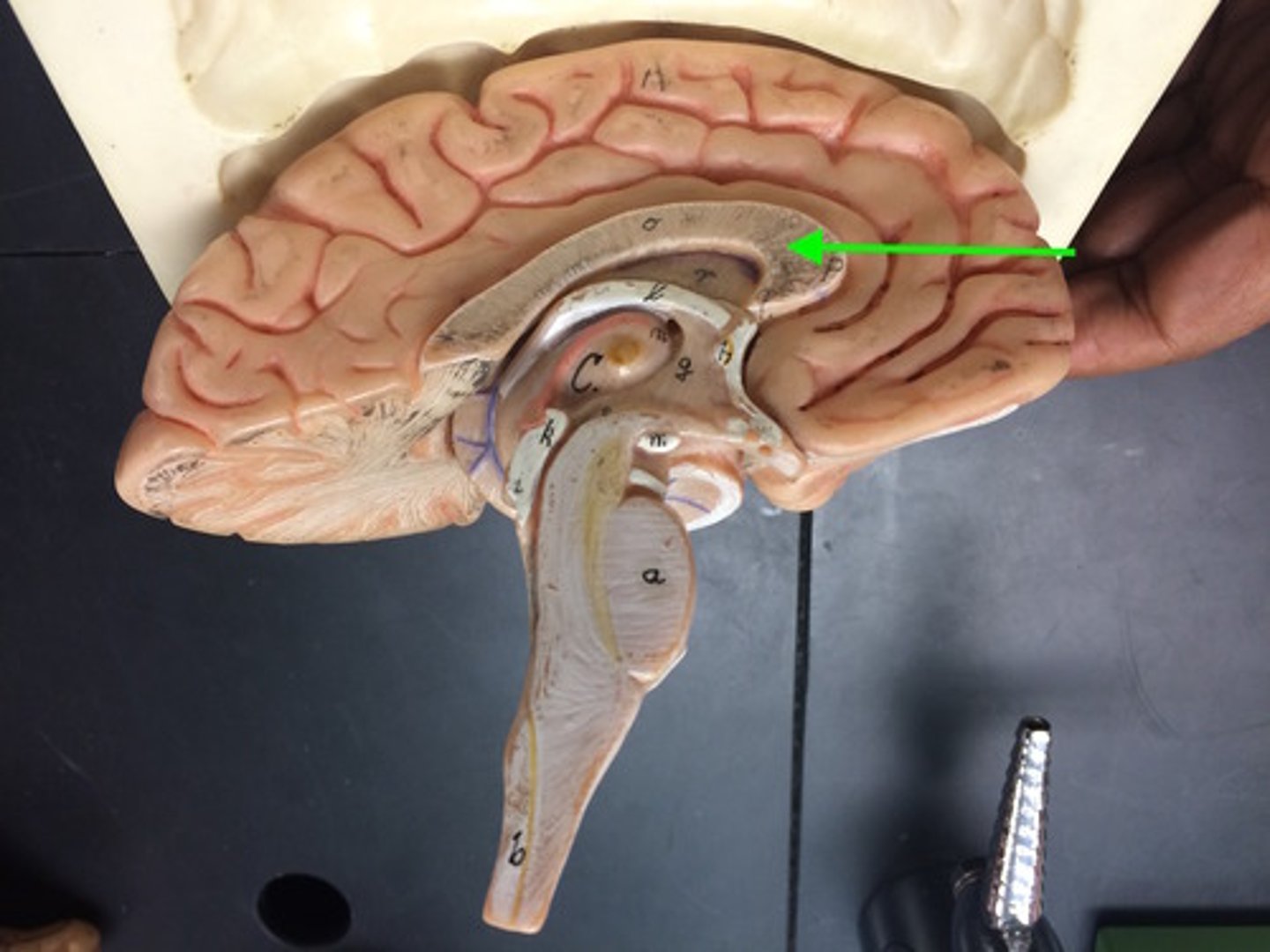
fornix in brain
arched fiber tract connecting hippocampus to mammillary bodies
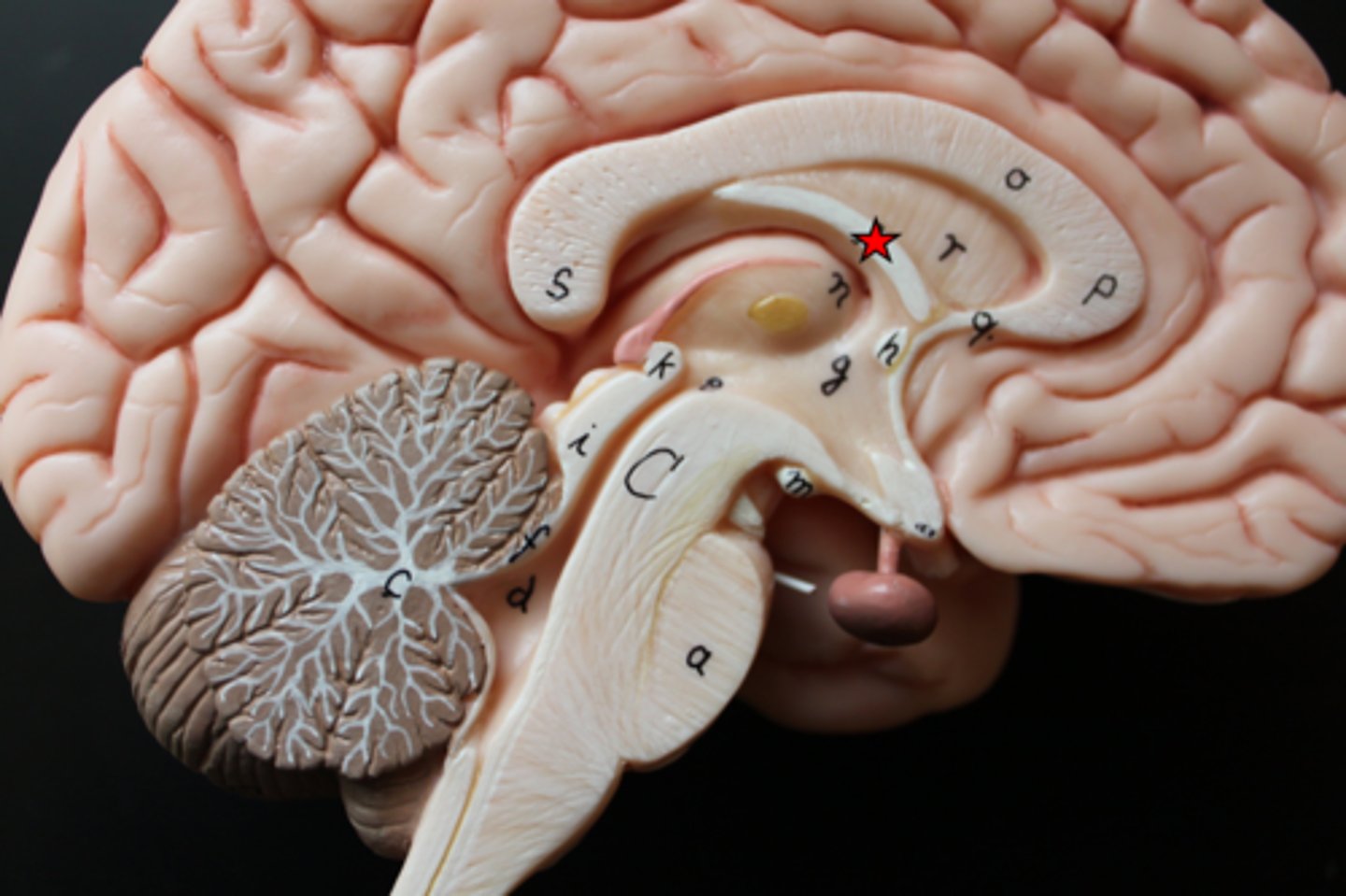
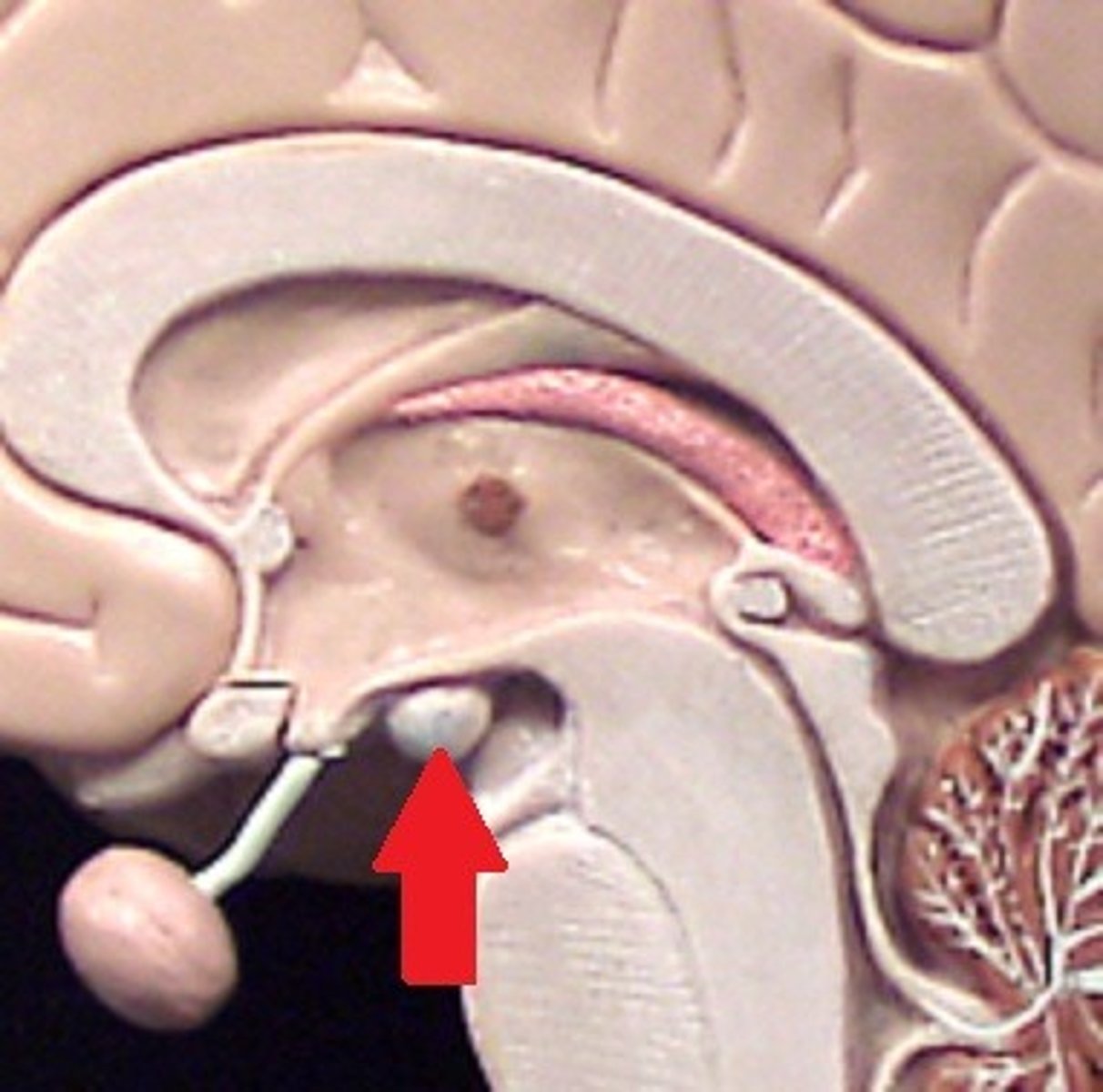
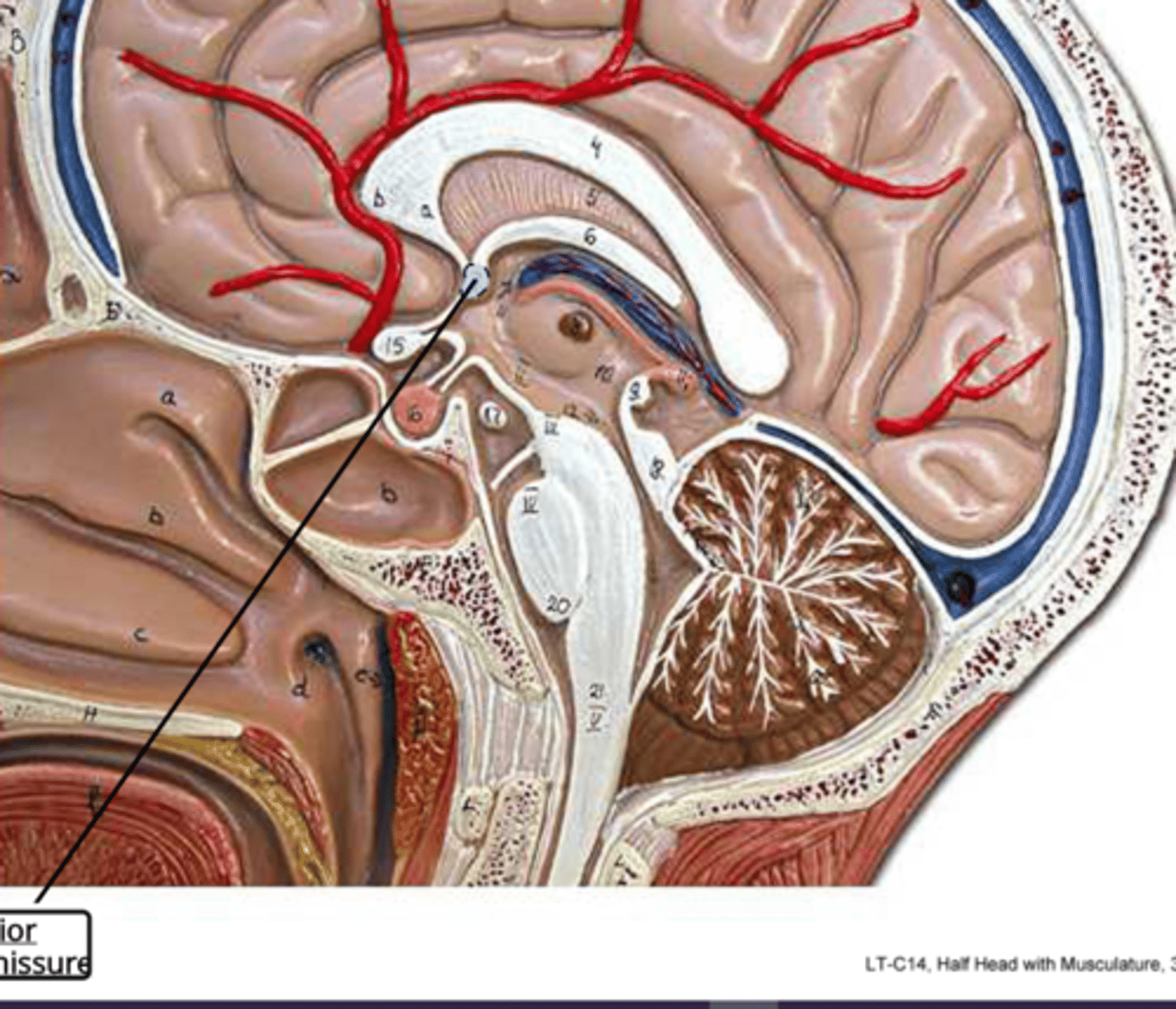
Anterior Commissure of the Cerebrum
small dot on the end of the fornix
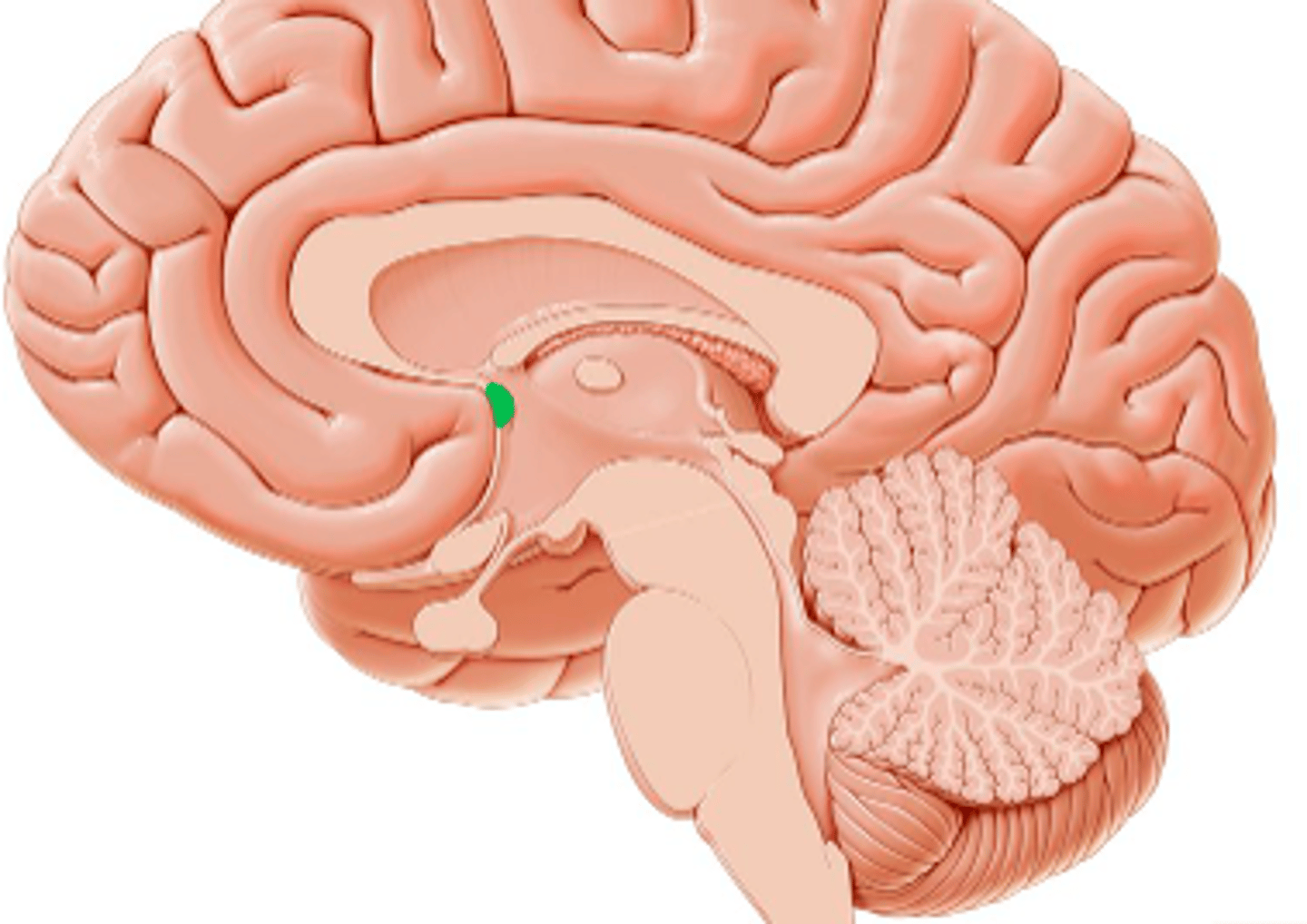
Posterior Commissure of the Cerebrum
above corpora quadrigemina
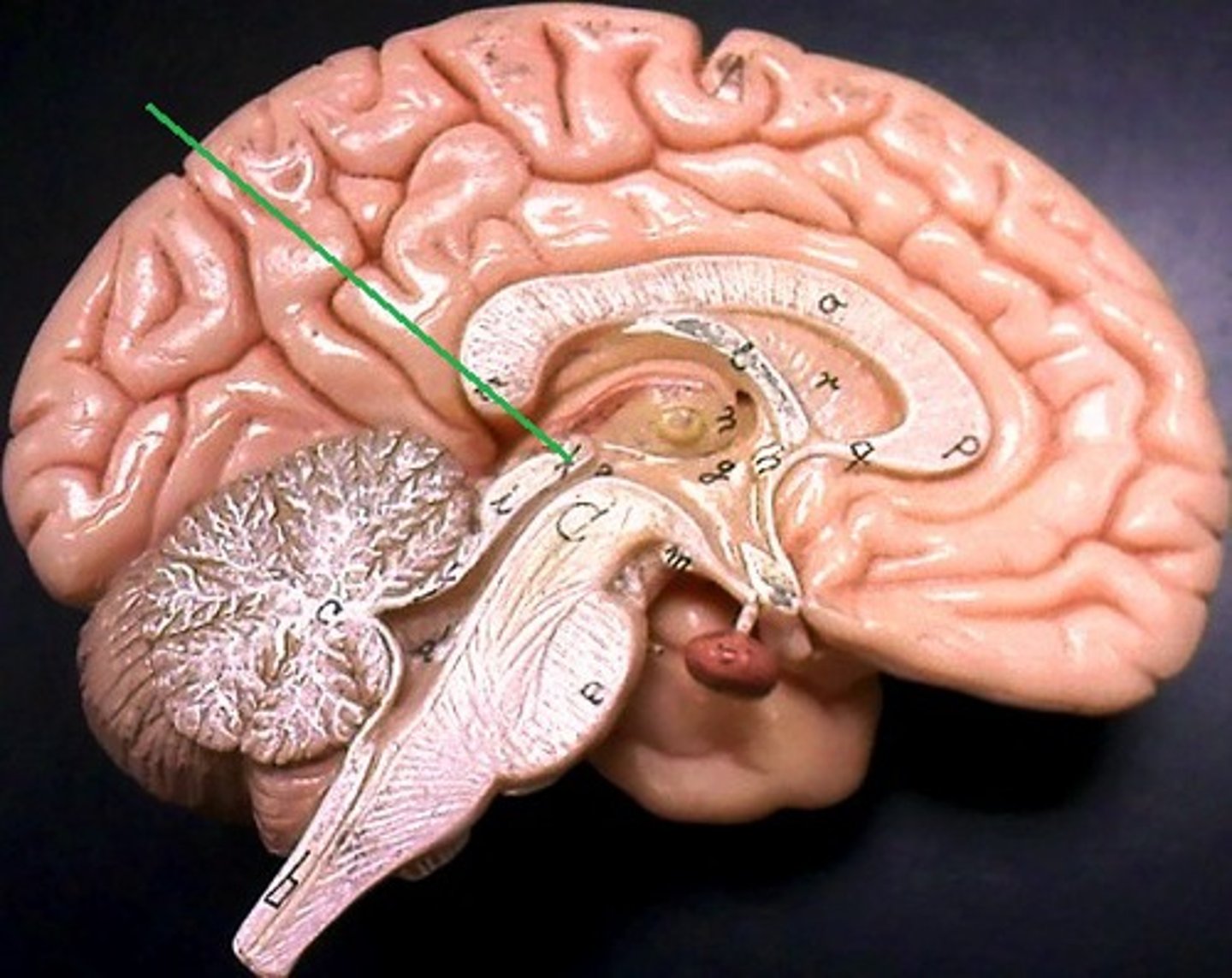
septum lucidum
separates the two lateral ventricles
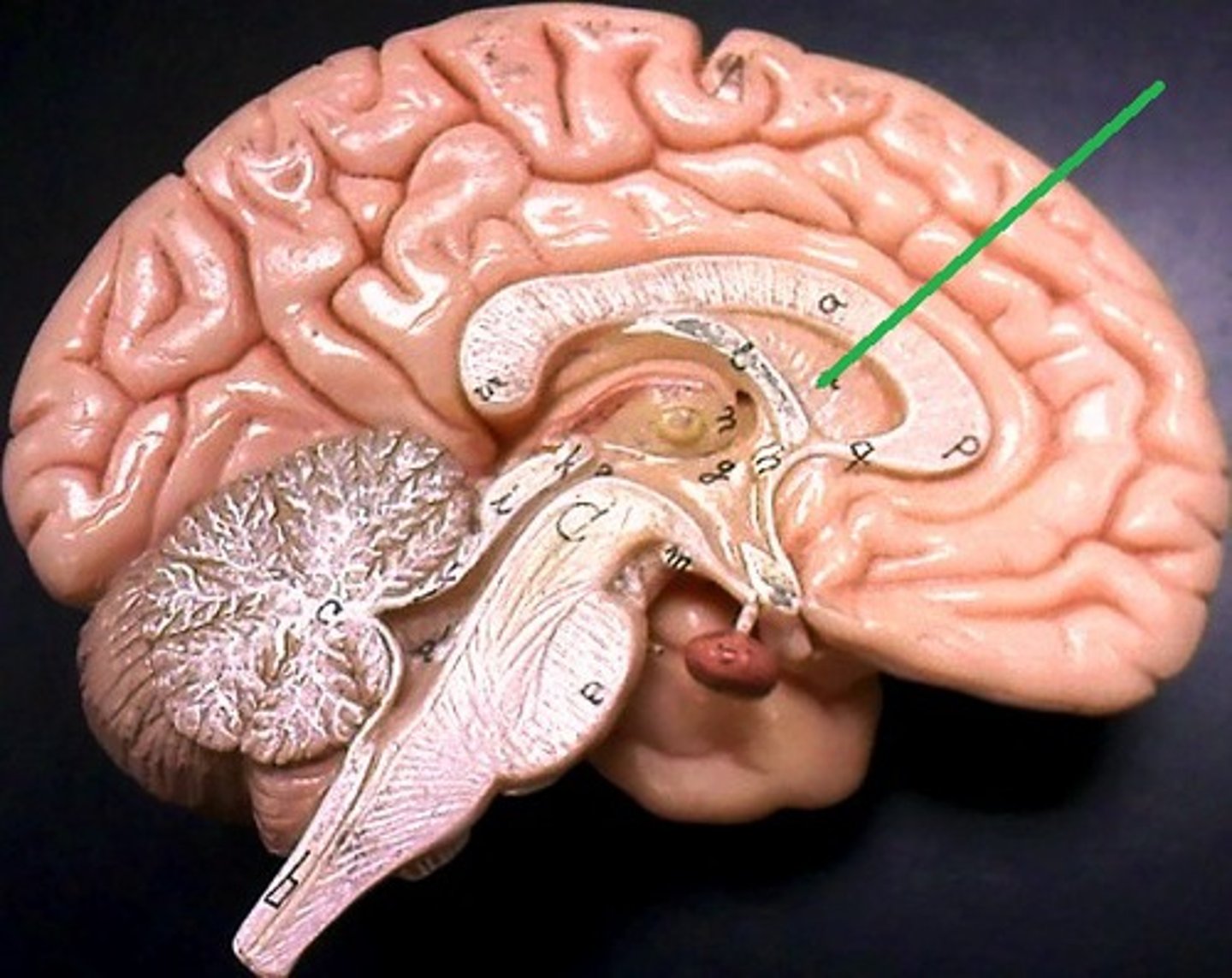
interventricular foramen
present below the lateral ventricles which connects lateral ventricles to third ventricle
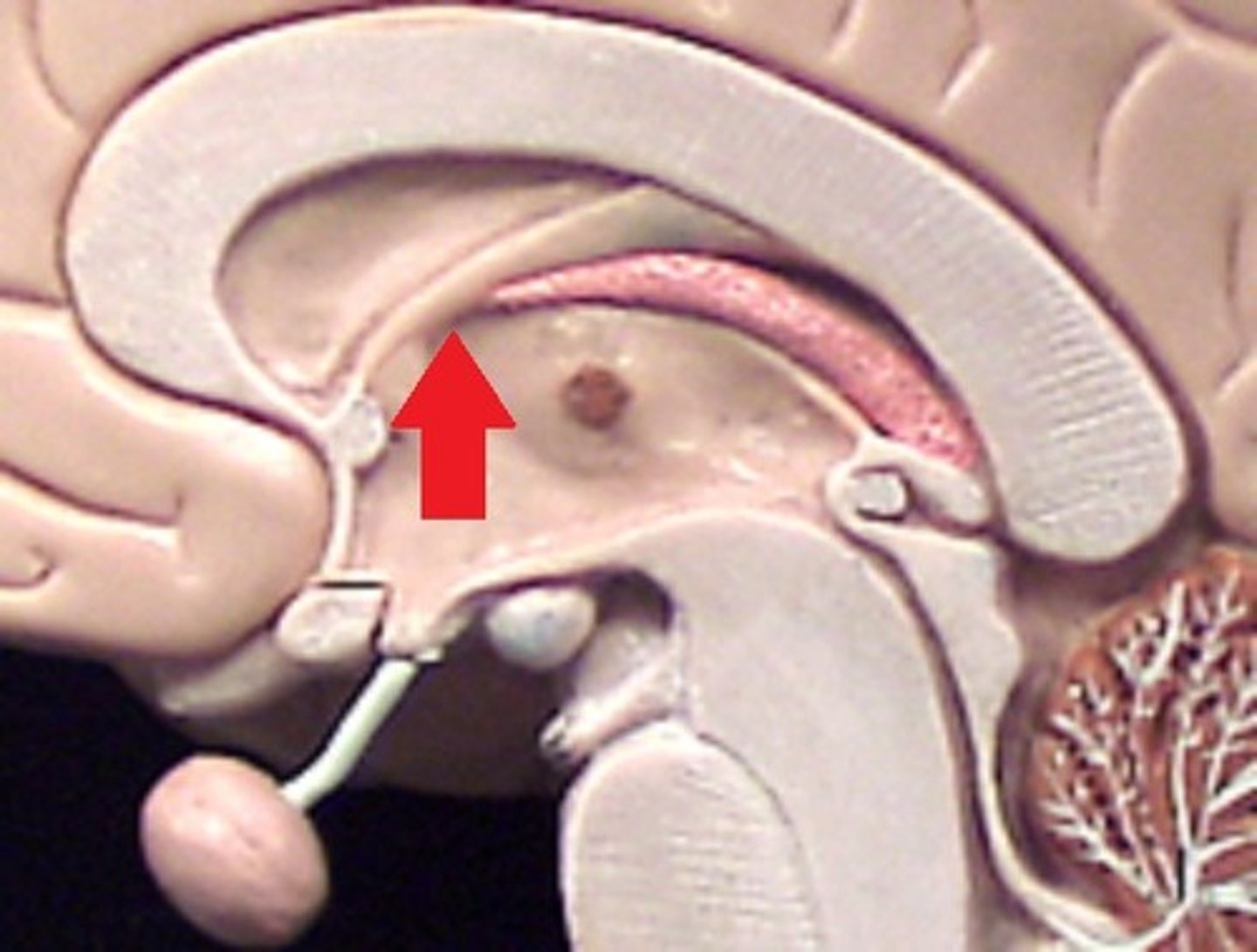
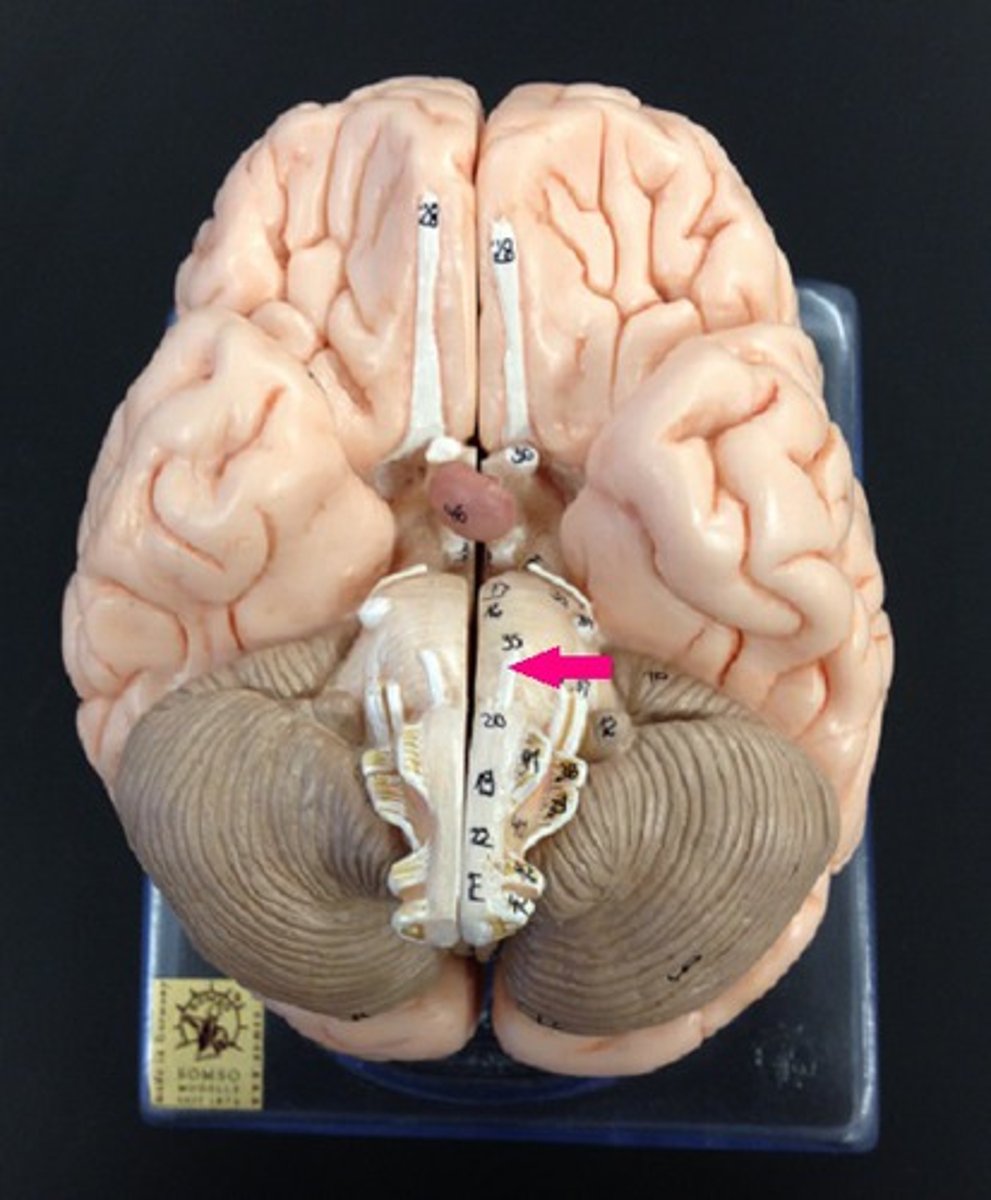
thalamus
the brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem
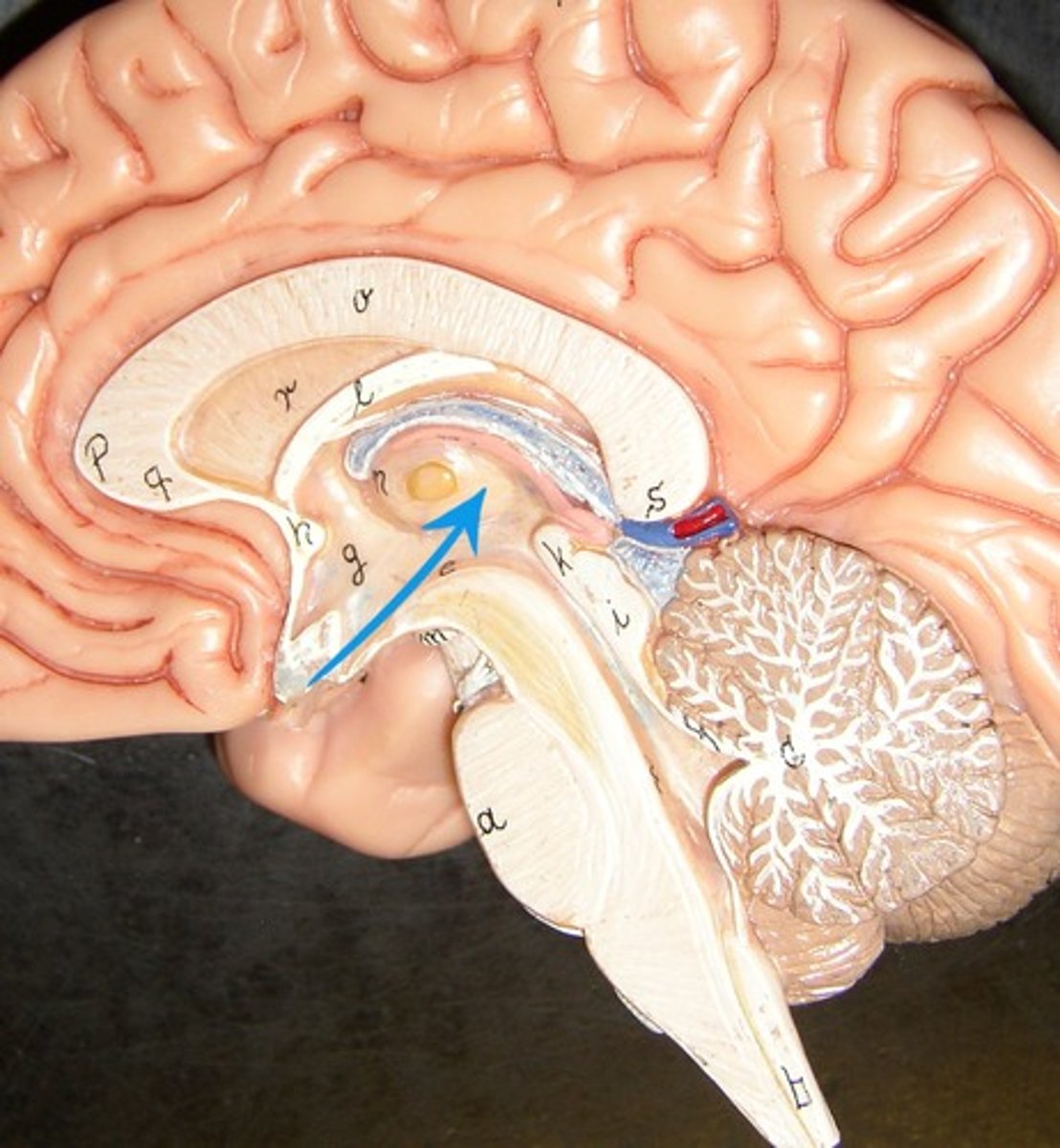
Hypothalamus
brain region controlling the pituitary gland
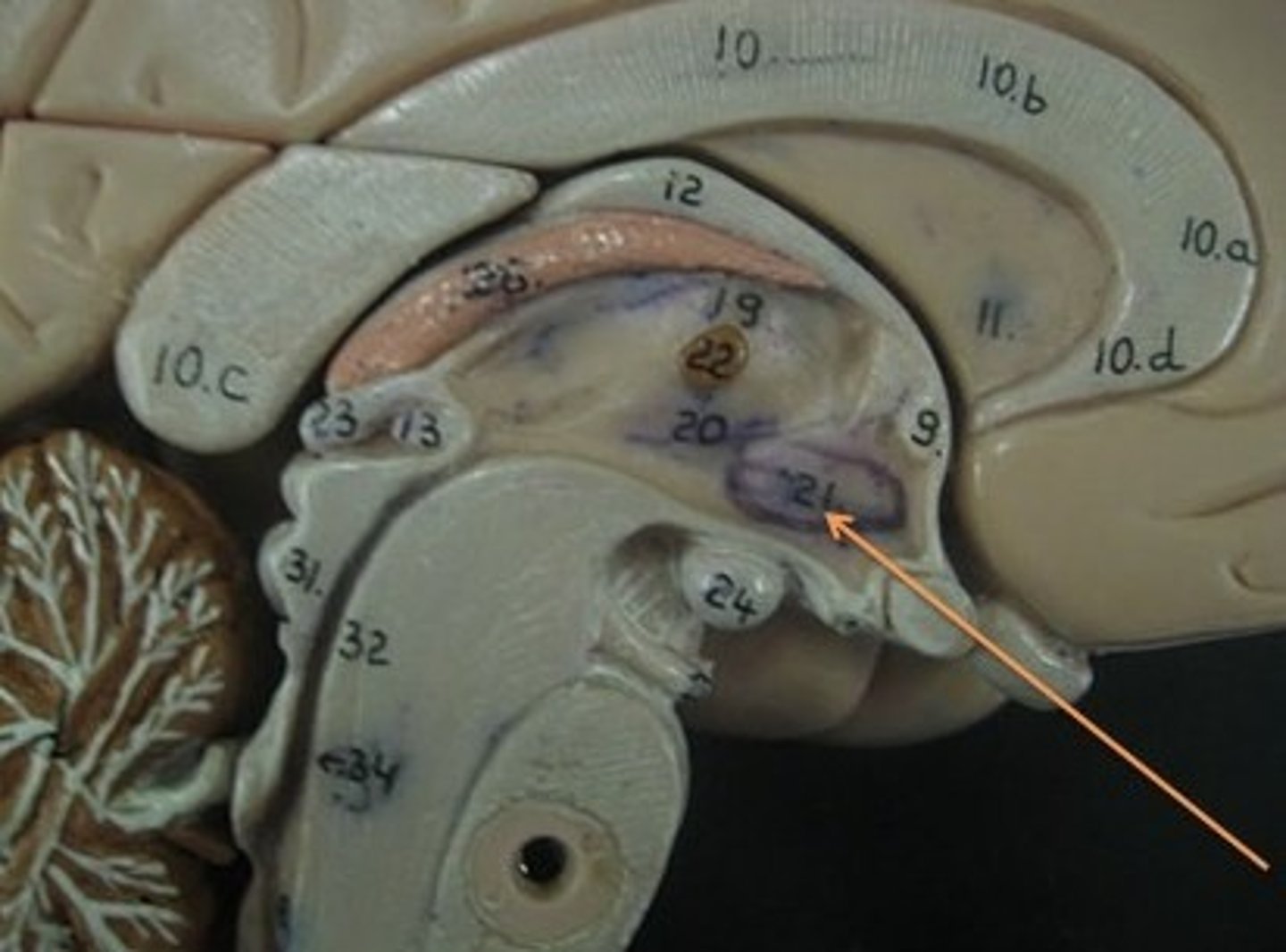
pituitary gland
endocrine gland at the base of the brain
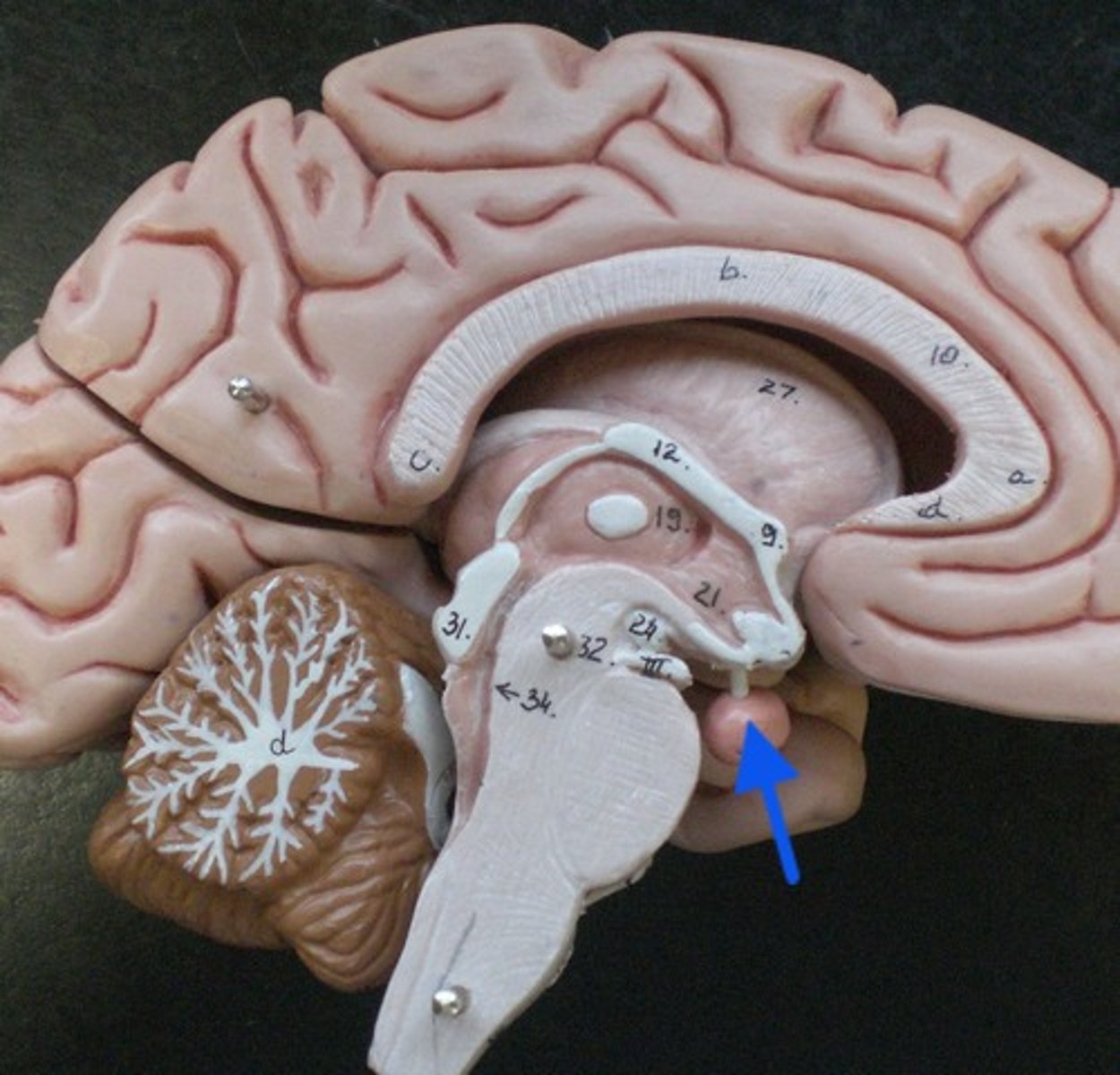
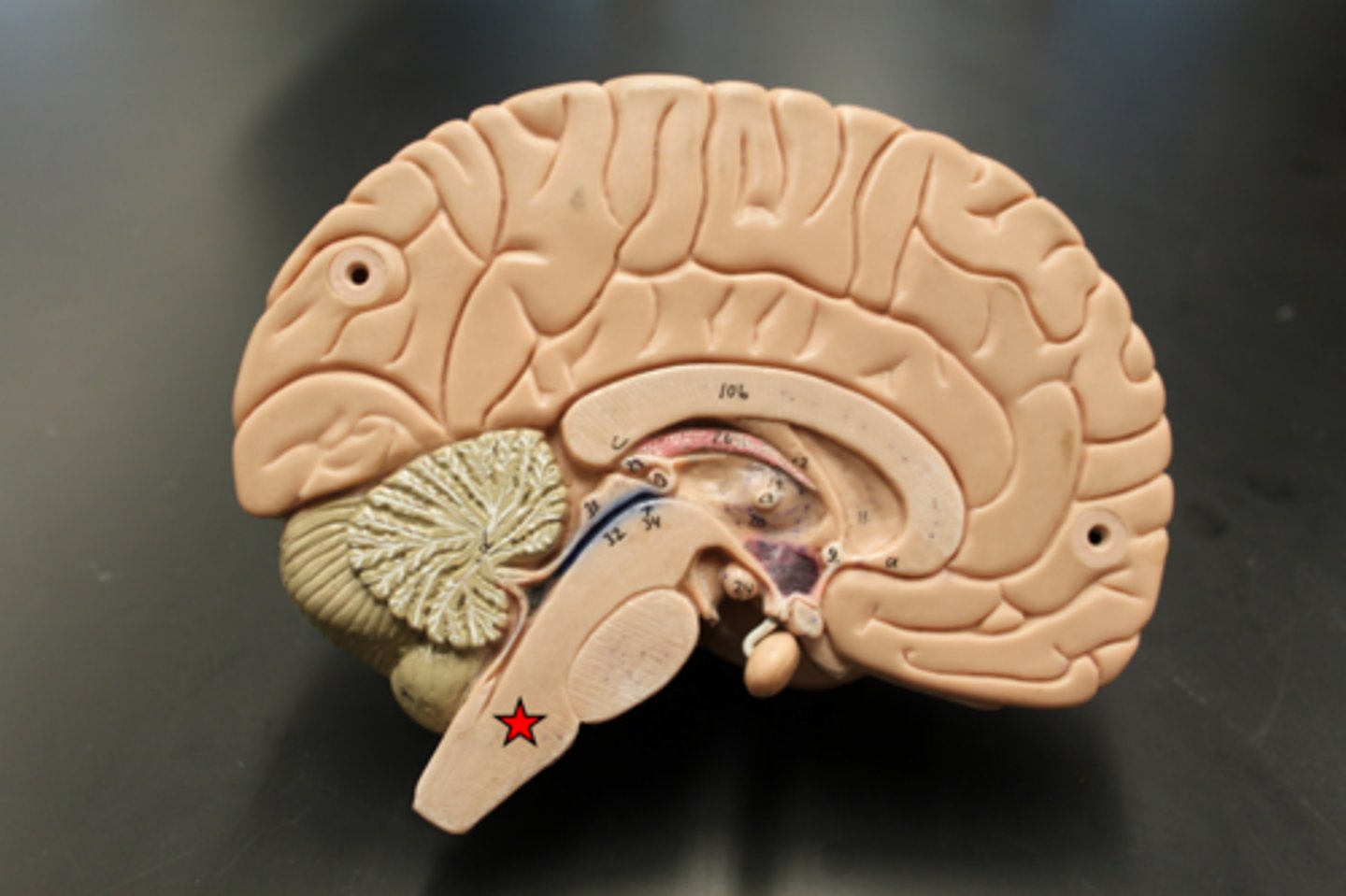
mammillary body of hypothalamus
processes sensations related to smell
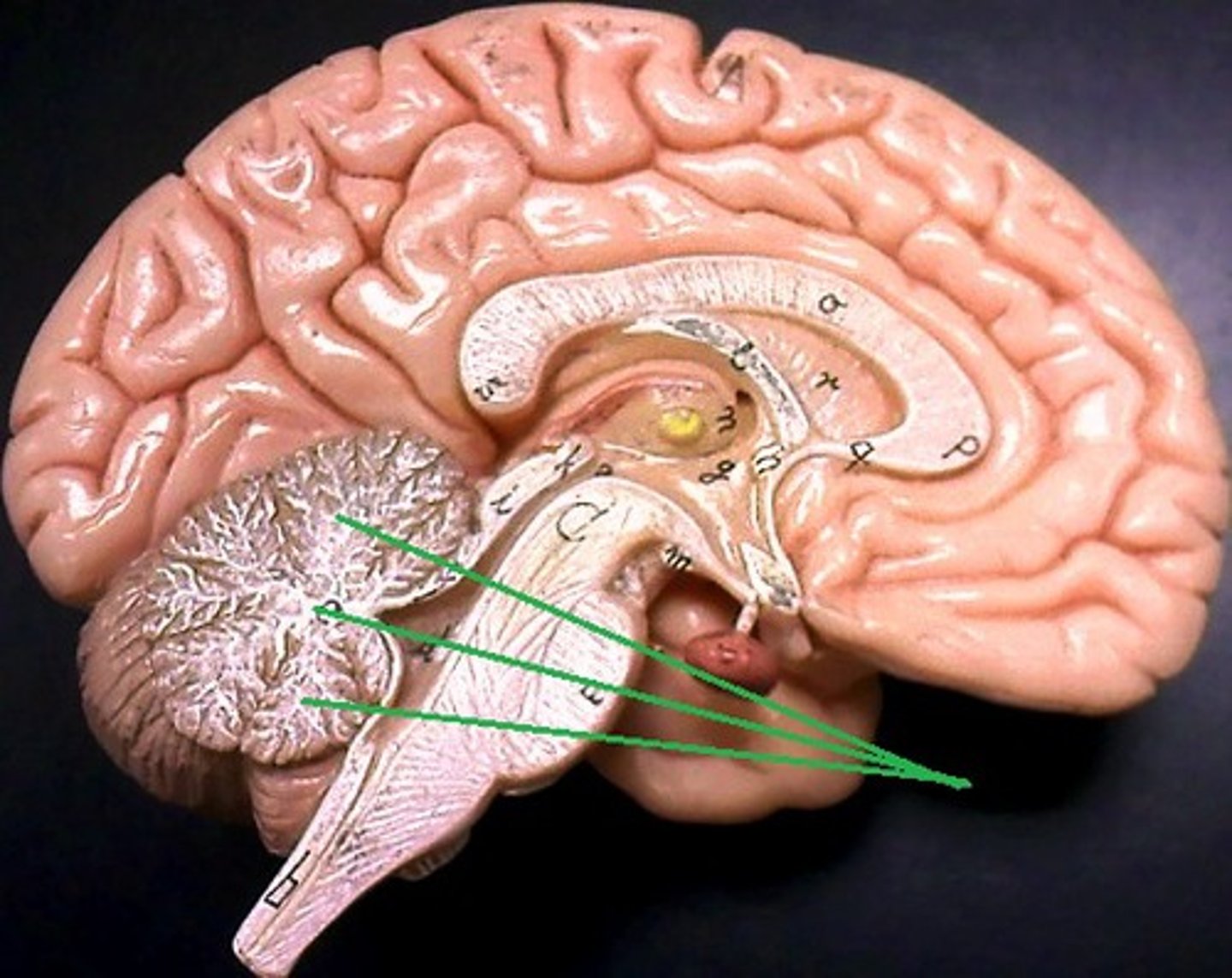
arbor vitae of cerebellum
tree like arrangement of white matter
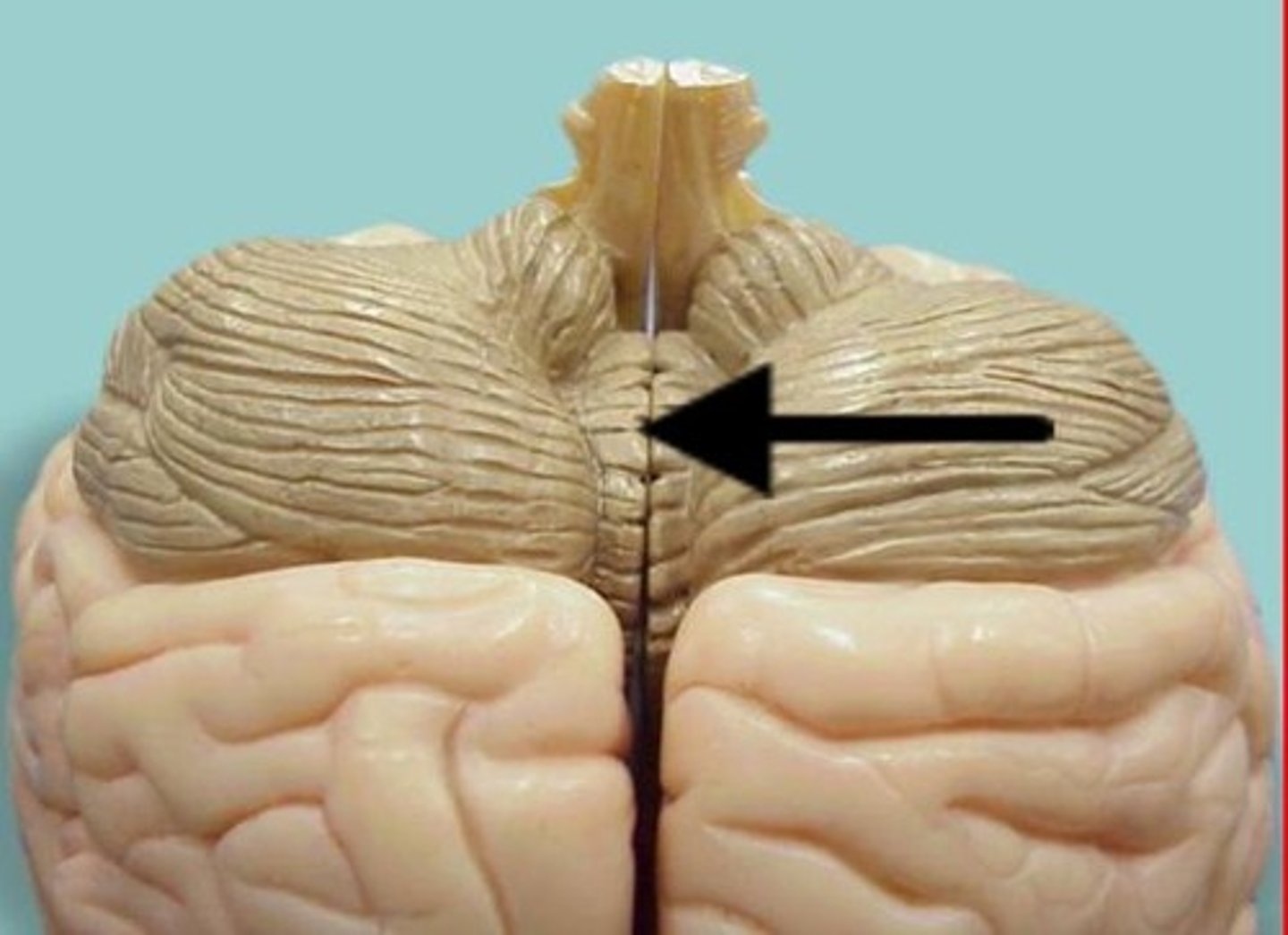
vermis
Connects the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
Brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull
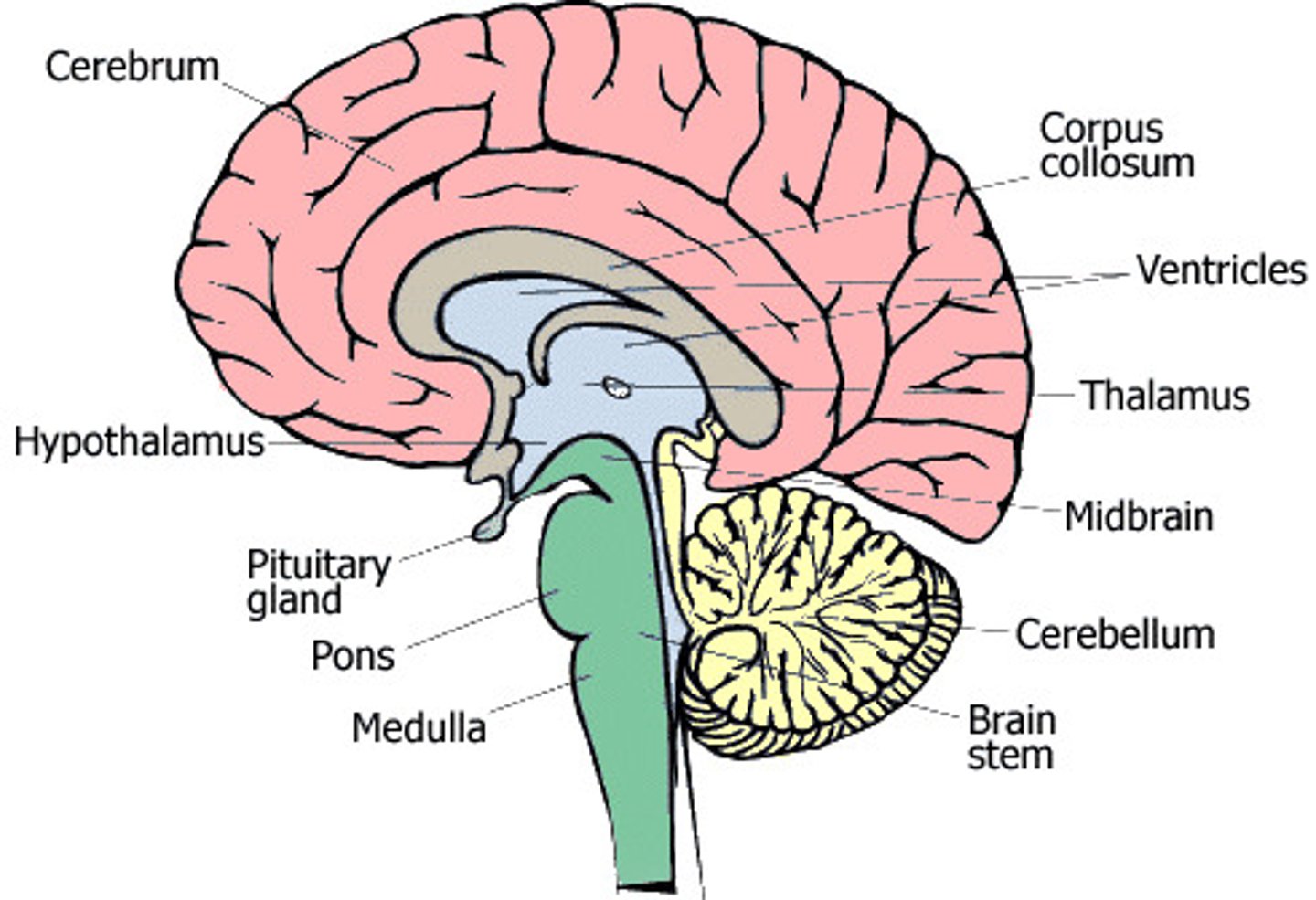
midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
cerebral aqueduct (midbrain)
connects 3rd and 4th ventricles
Pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
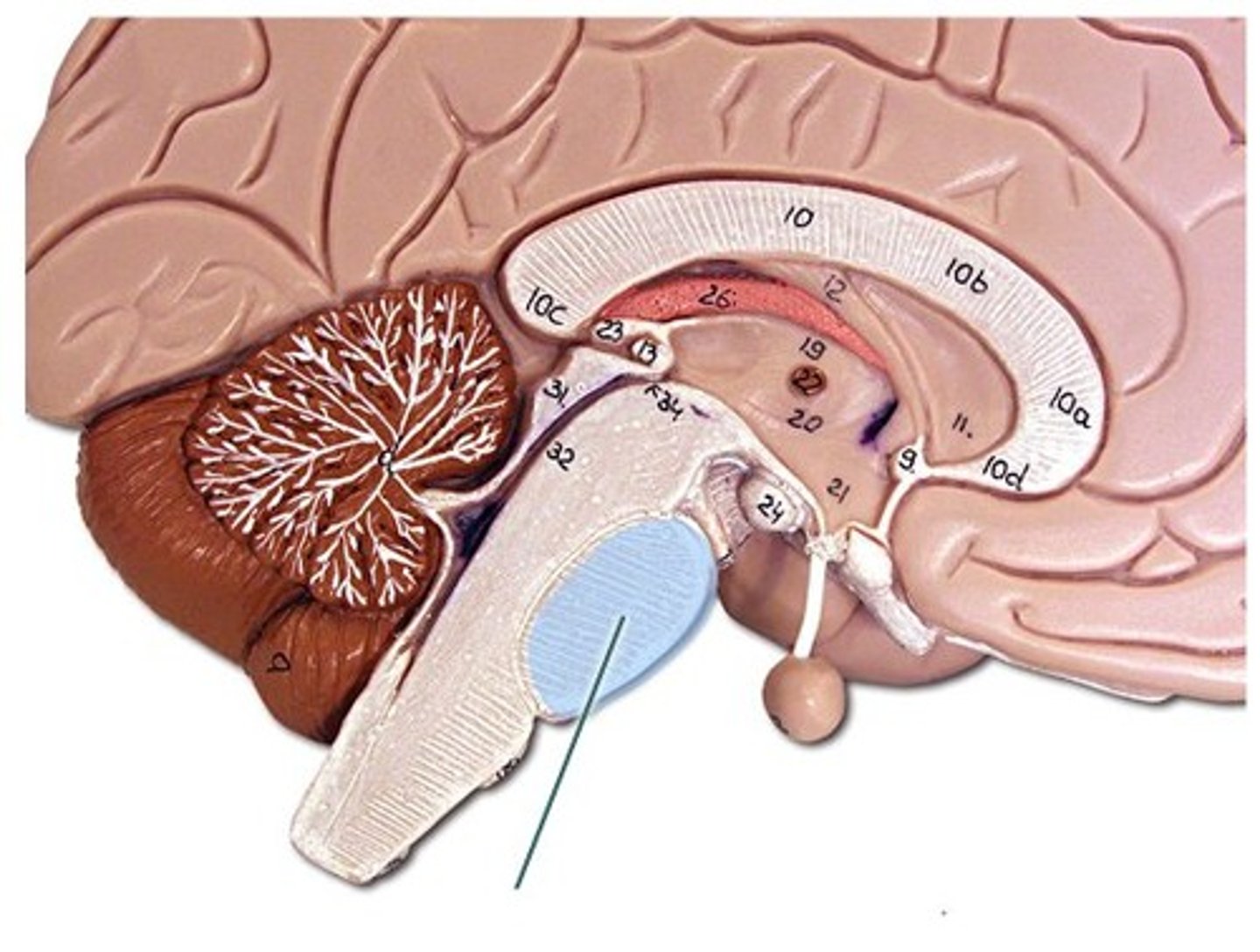
third ventricle location
within diencephalon
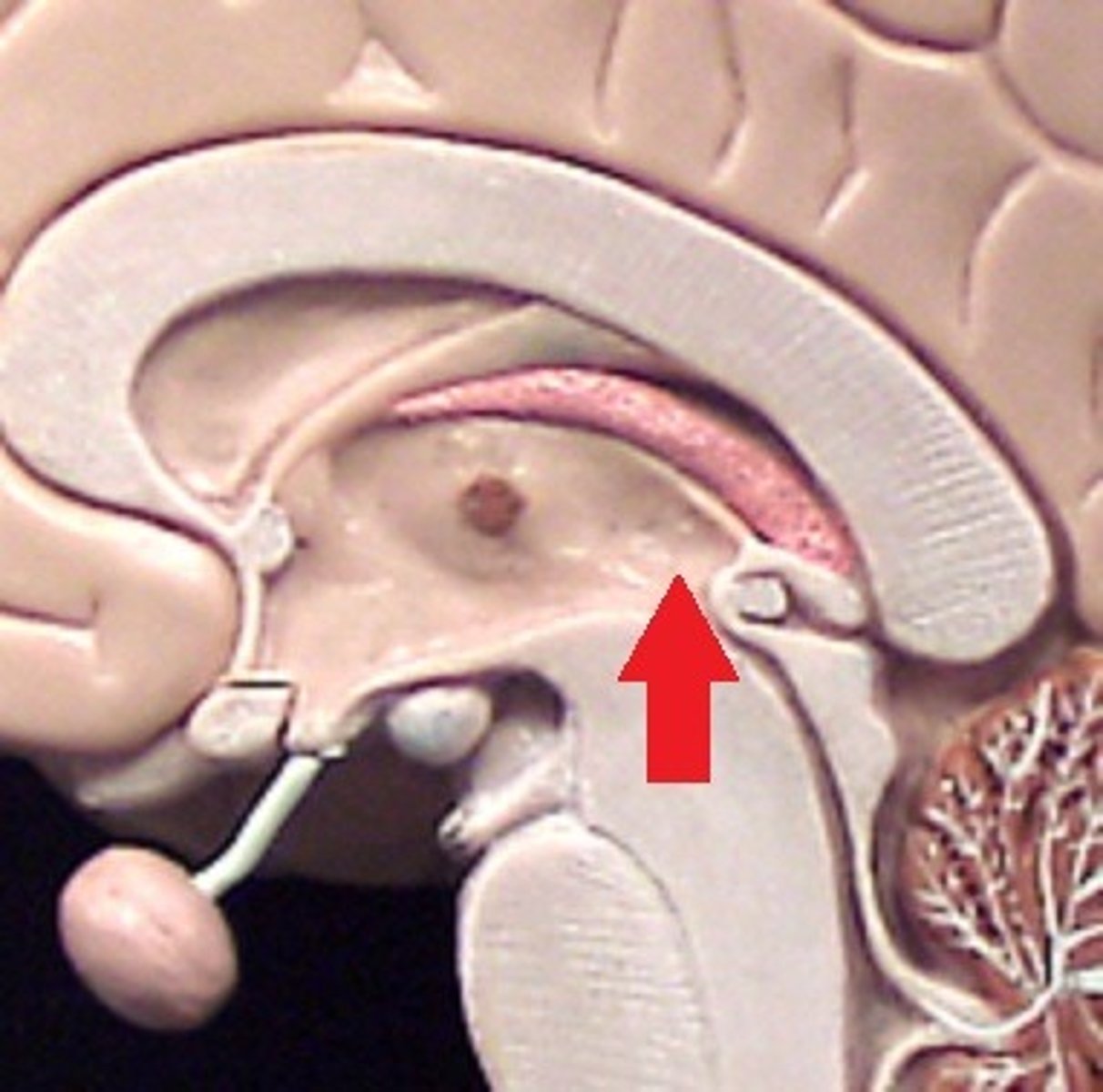
4th ventricle of brain
between brain stem and cerebellum
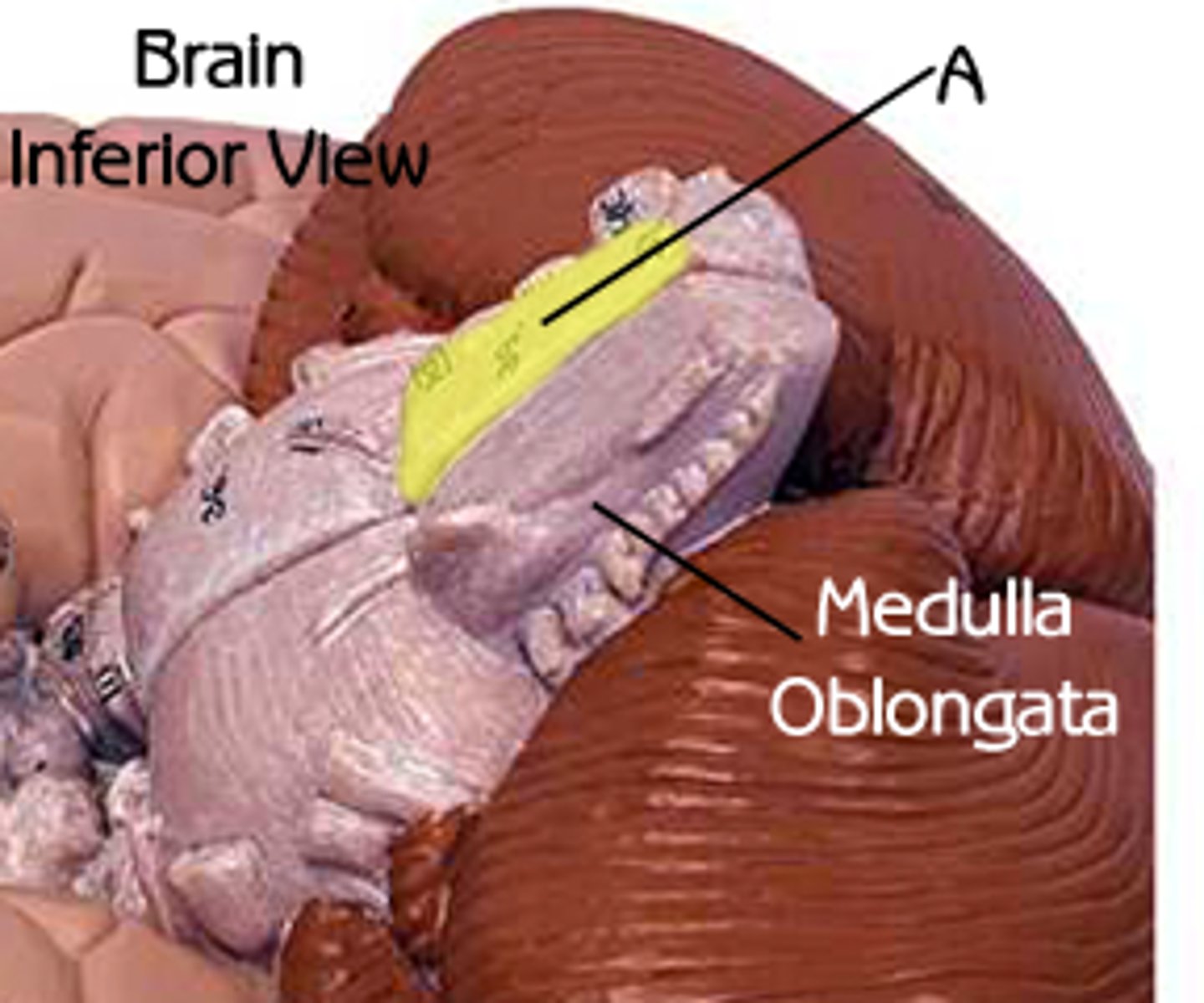
medulla oblongata
the continuation of the spinal cord within the skull, forming the lowest part of the brainstem and containing control centers for the heart and lungs.
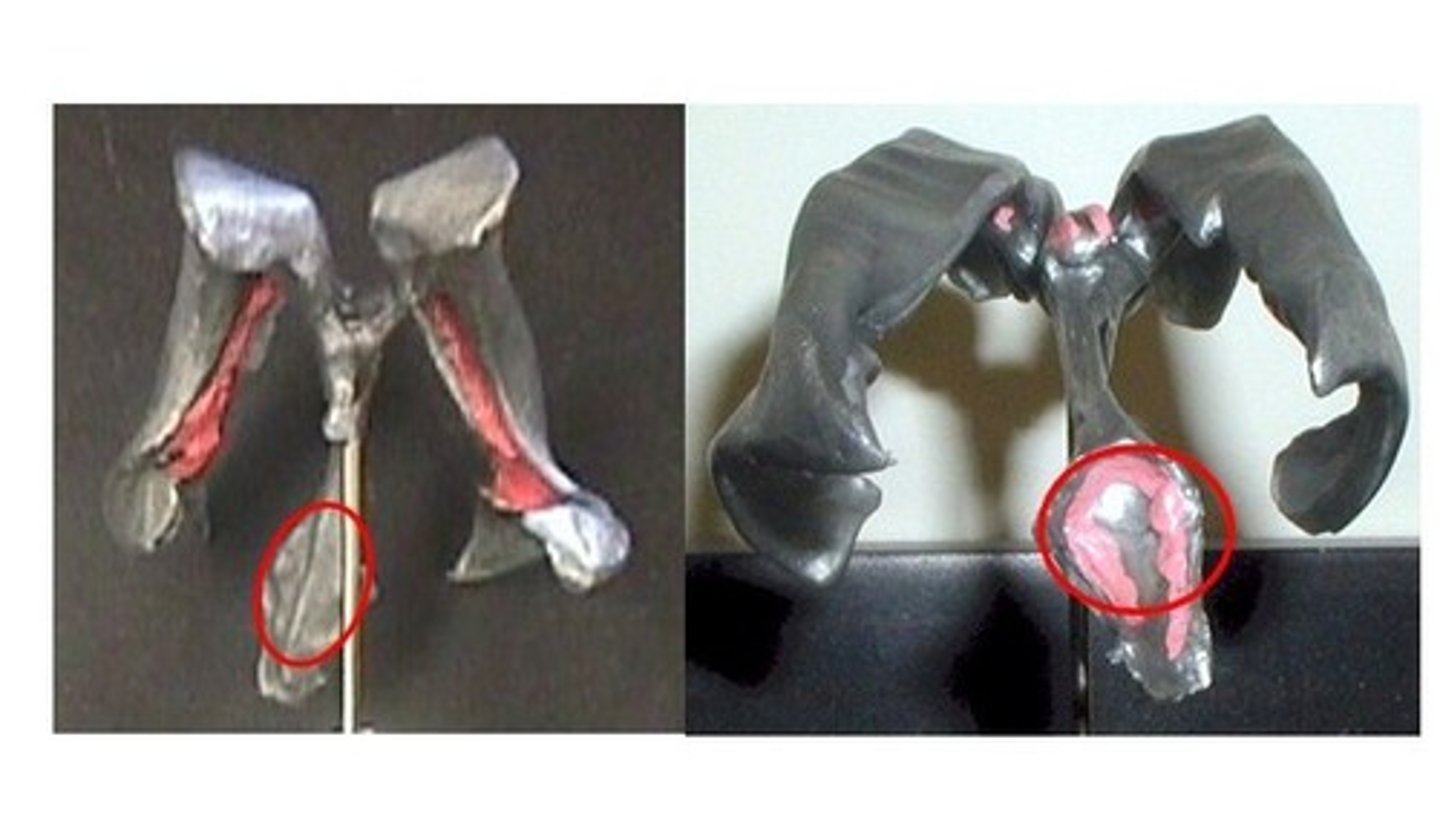
pyramids of medulla
paired white matter structures of the brainstem's medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers
olive of medulla
contains inferior olivary nucleus
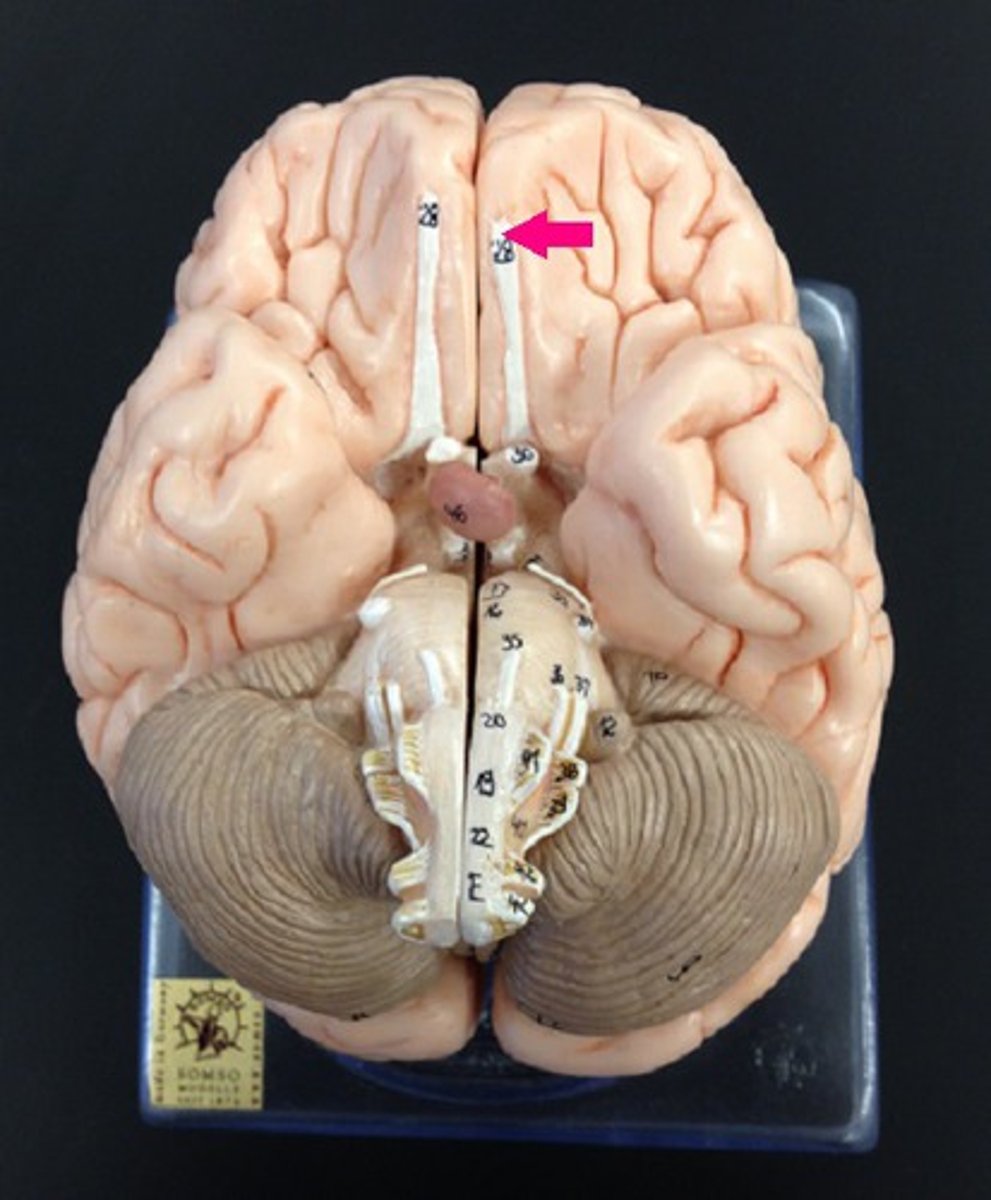
olfactory bulb
the brain center for smell, located below the frontal lobes
optic nerve
carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
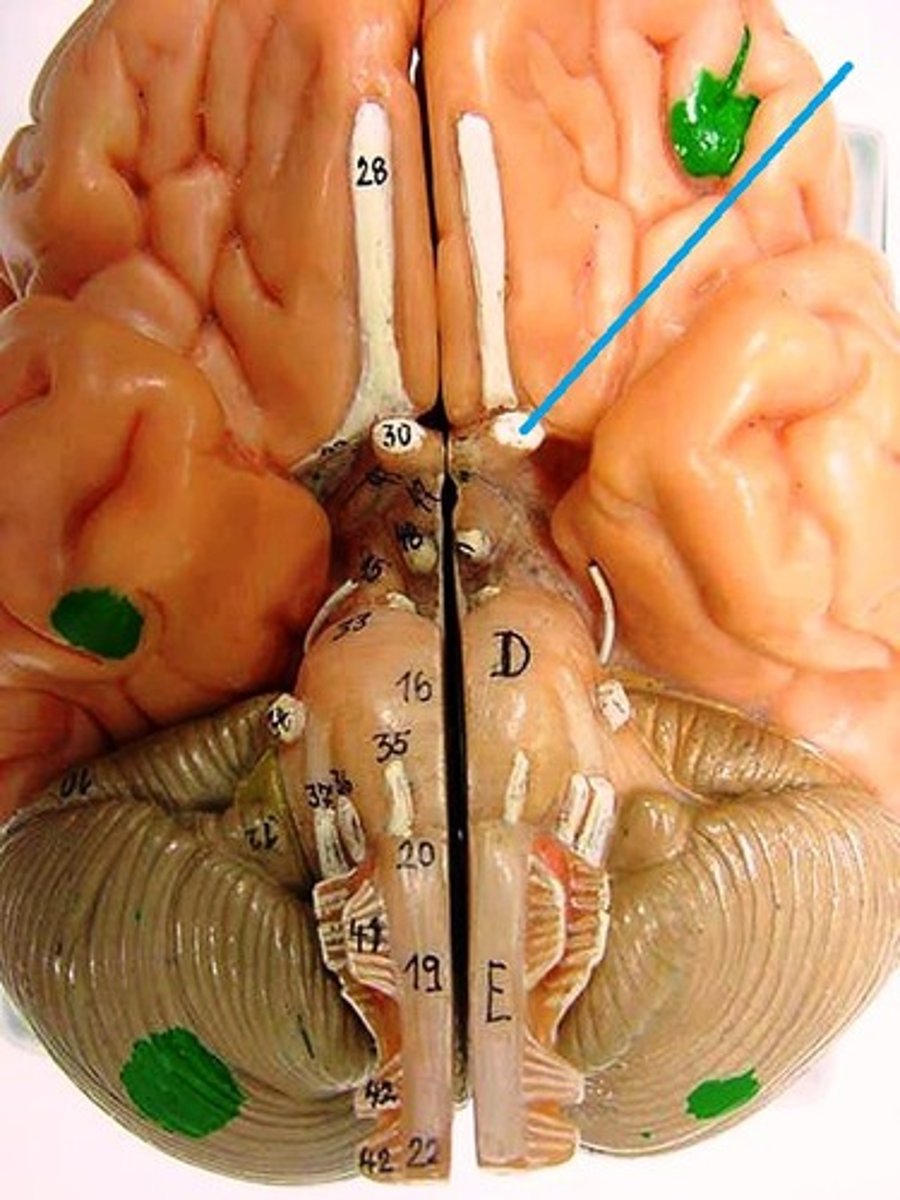
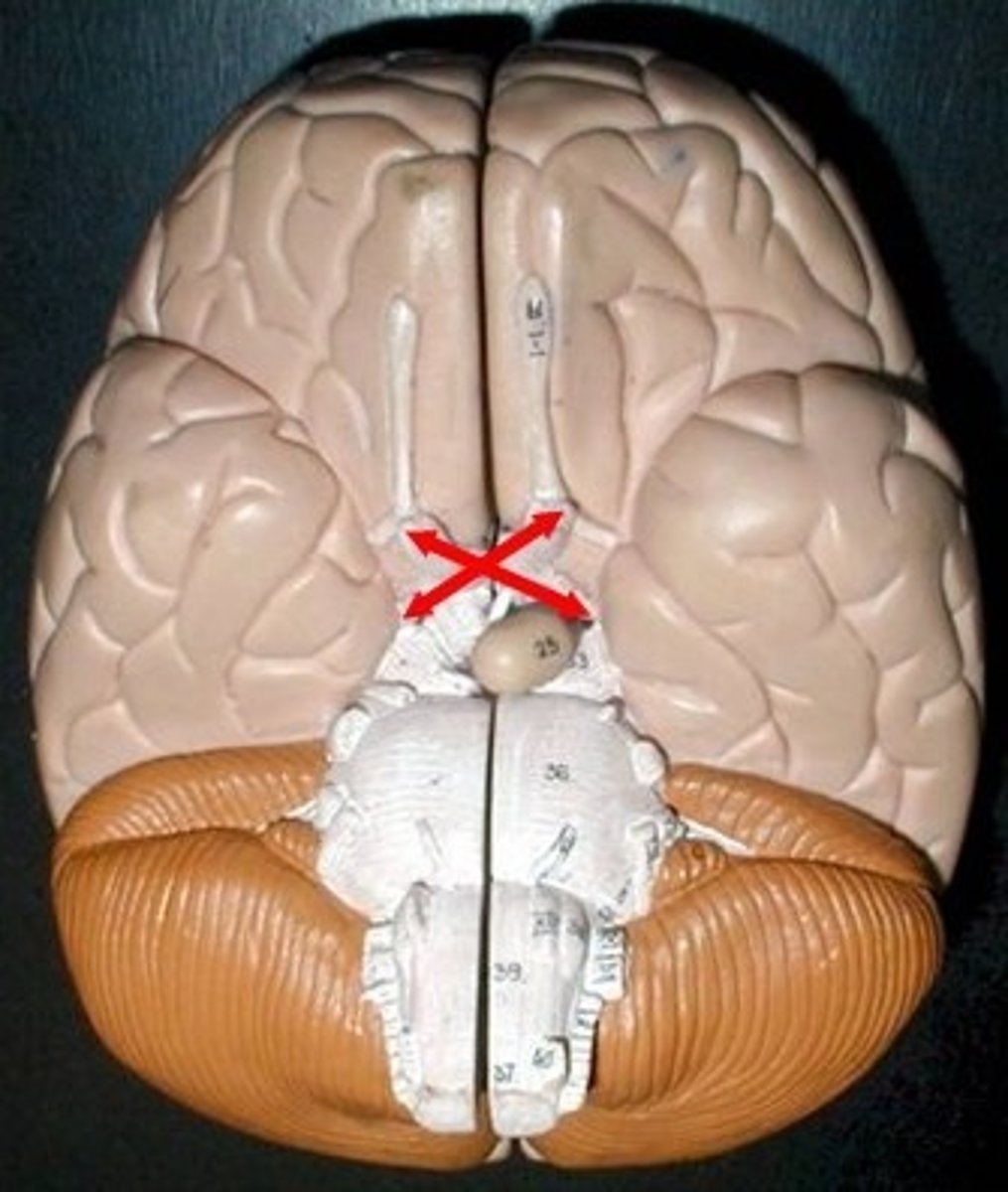
optic chiasma
where optic nerves cross over
oculomotor nerve
eye movement
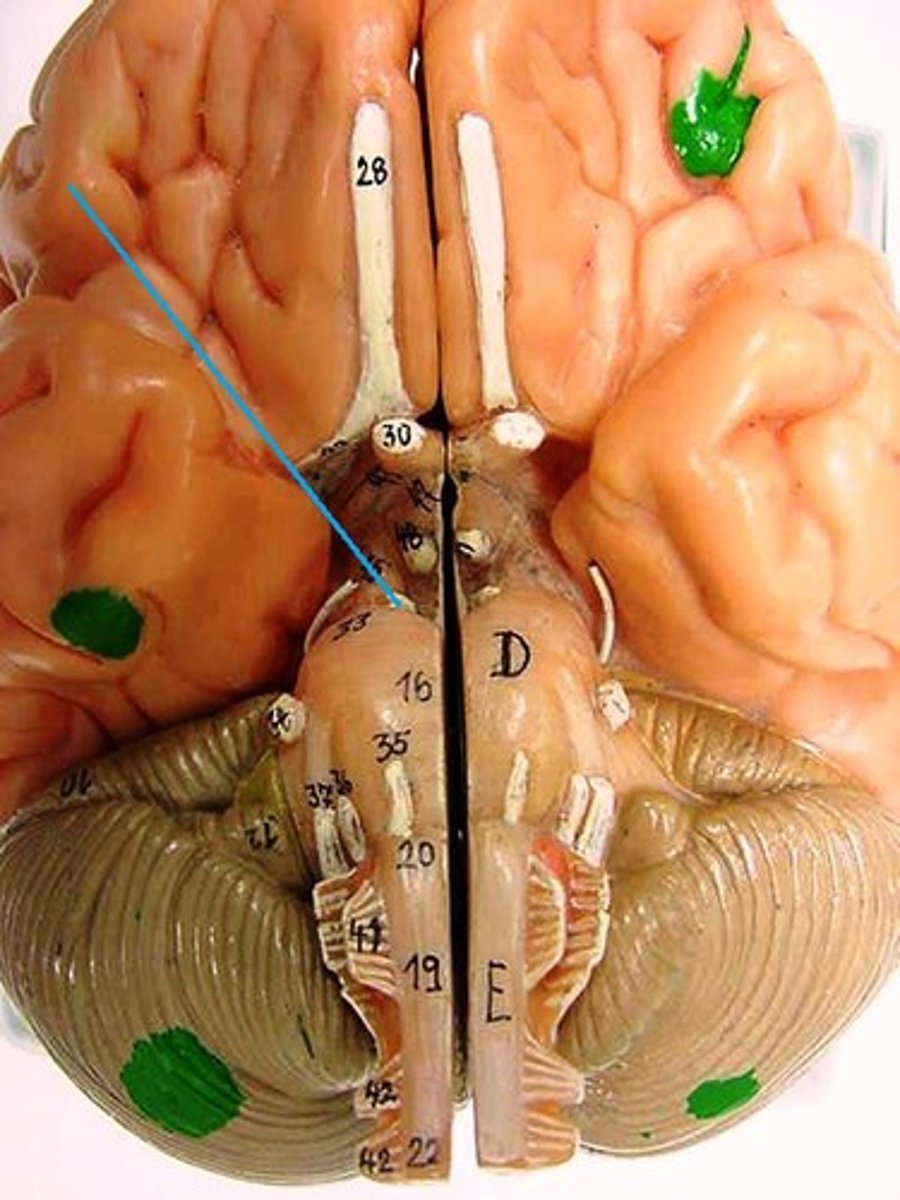
trochlear nerve
eye movement
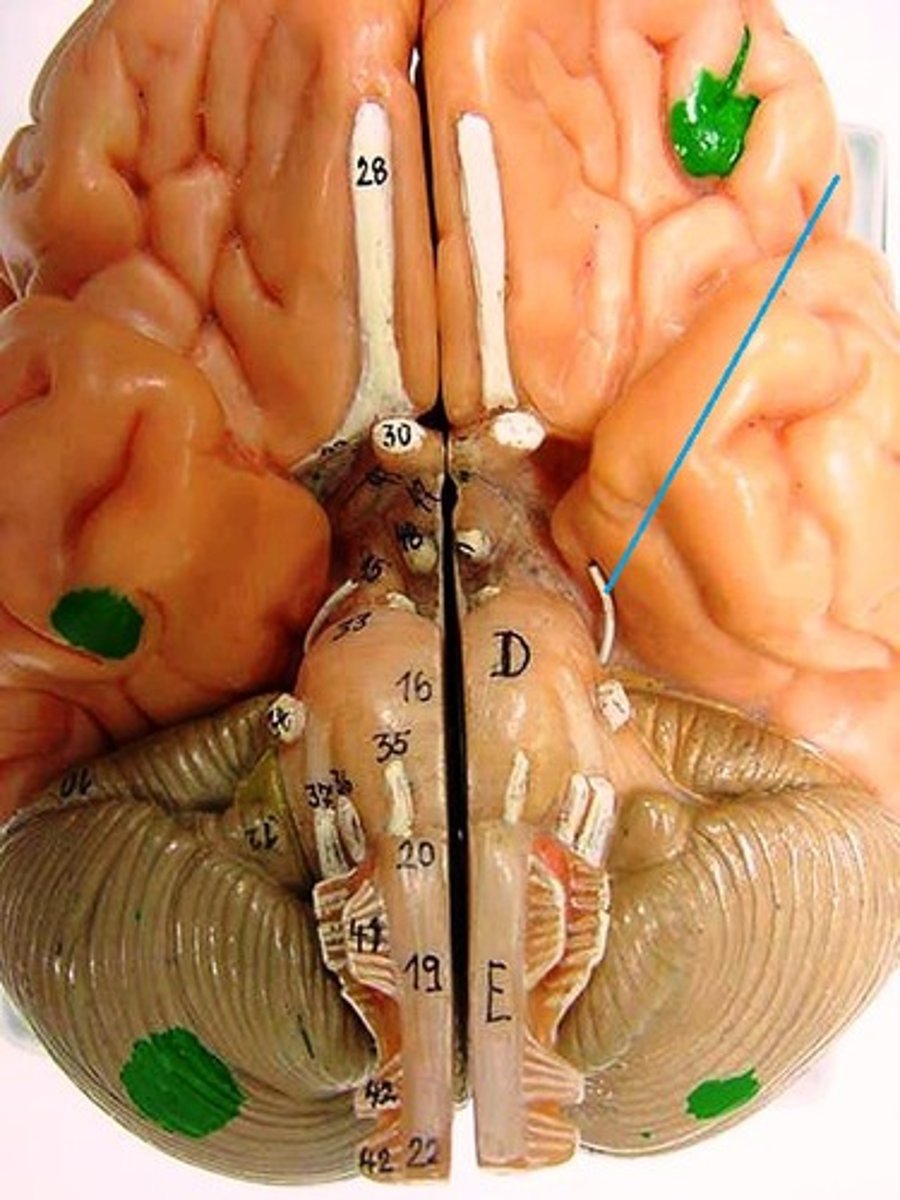
trigeminal nerve
Cranial nerve responsible for chewing and face sensations
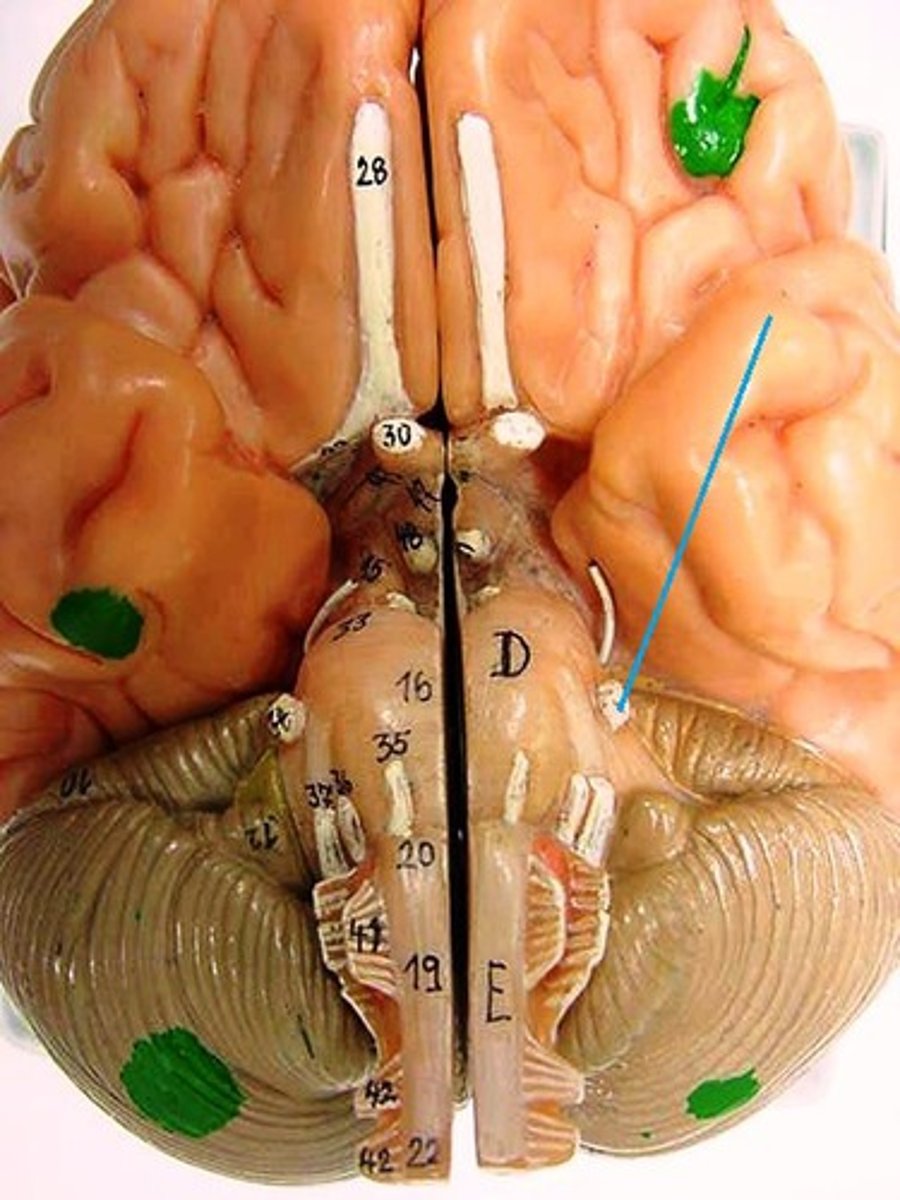
abducens nerve
eye movement
facial nerve
cranial nerve VII
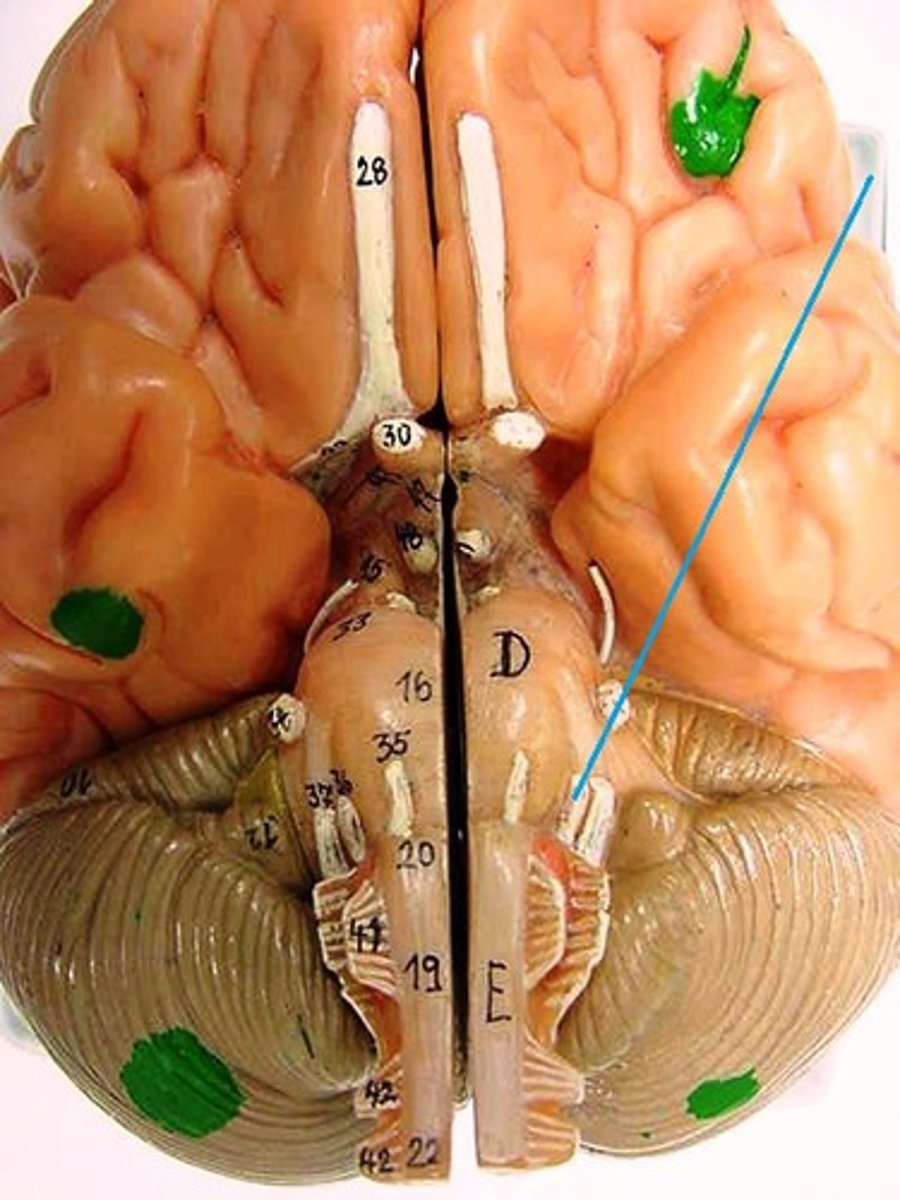
vestibulocochlear nerve
hearing and balance
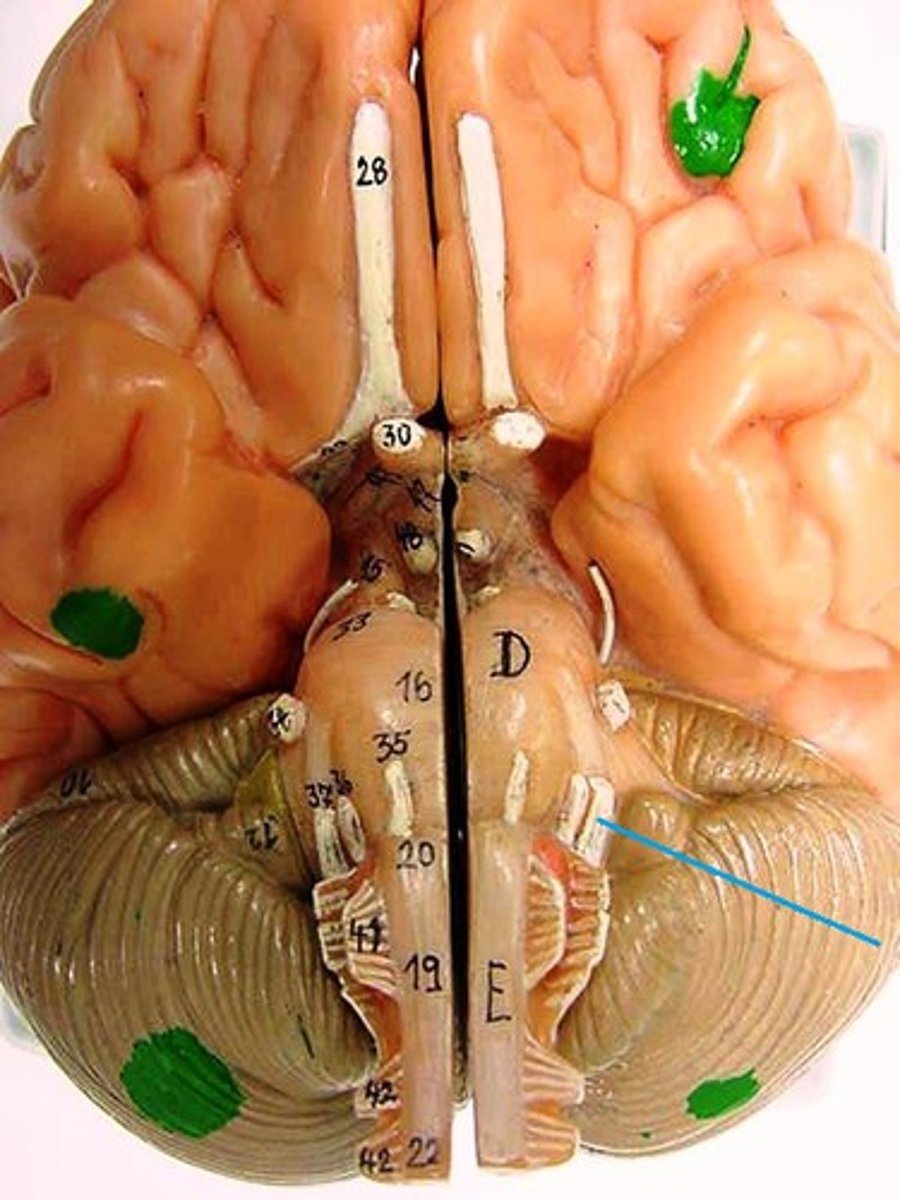
glossopharyngeal nerve
vagus nerve
the tenth cranial nerve that innervates digestive organs, heart and other areas
accessory nerve
CN XI
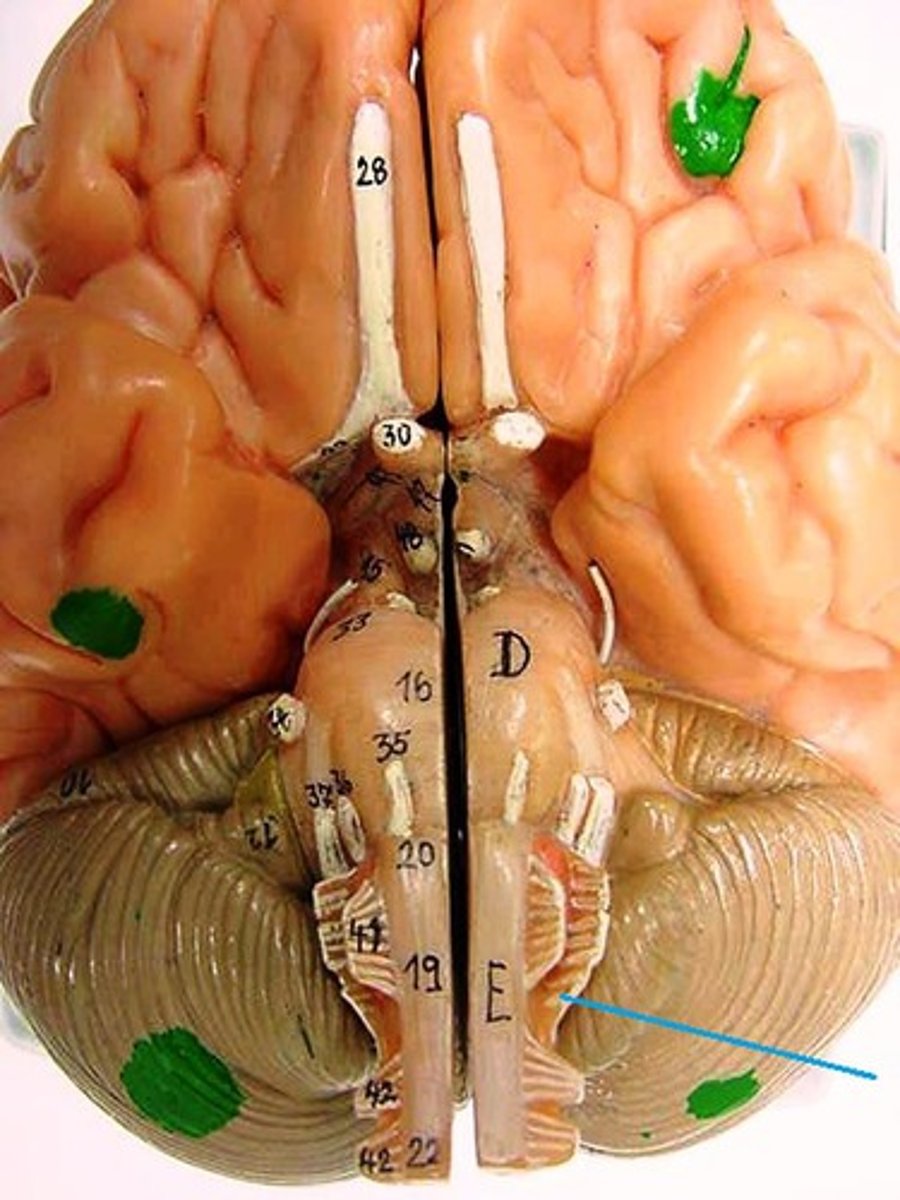
hypoglossal nerve
tongue movement CN XII
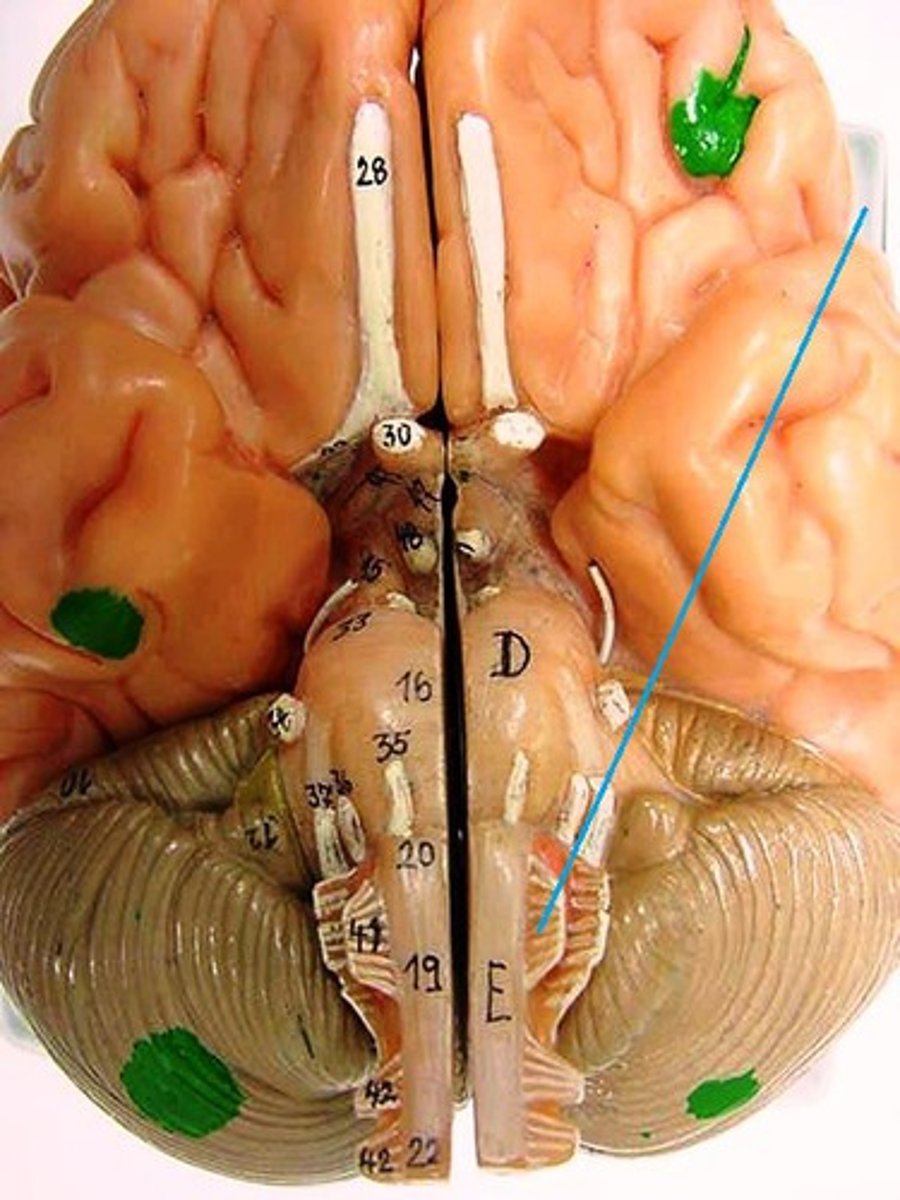
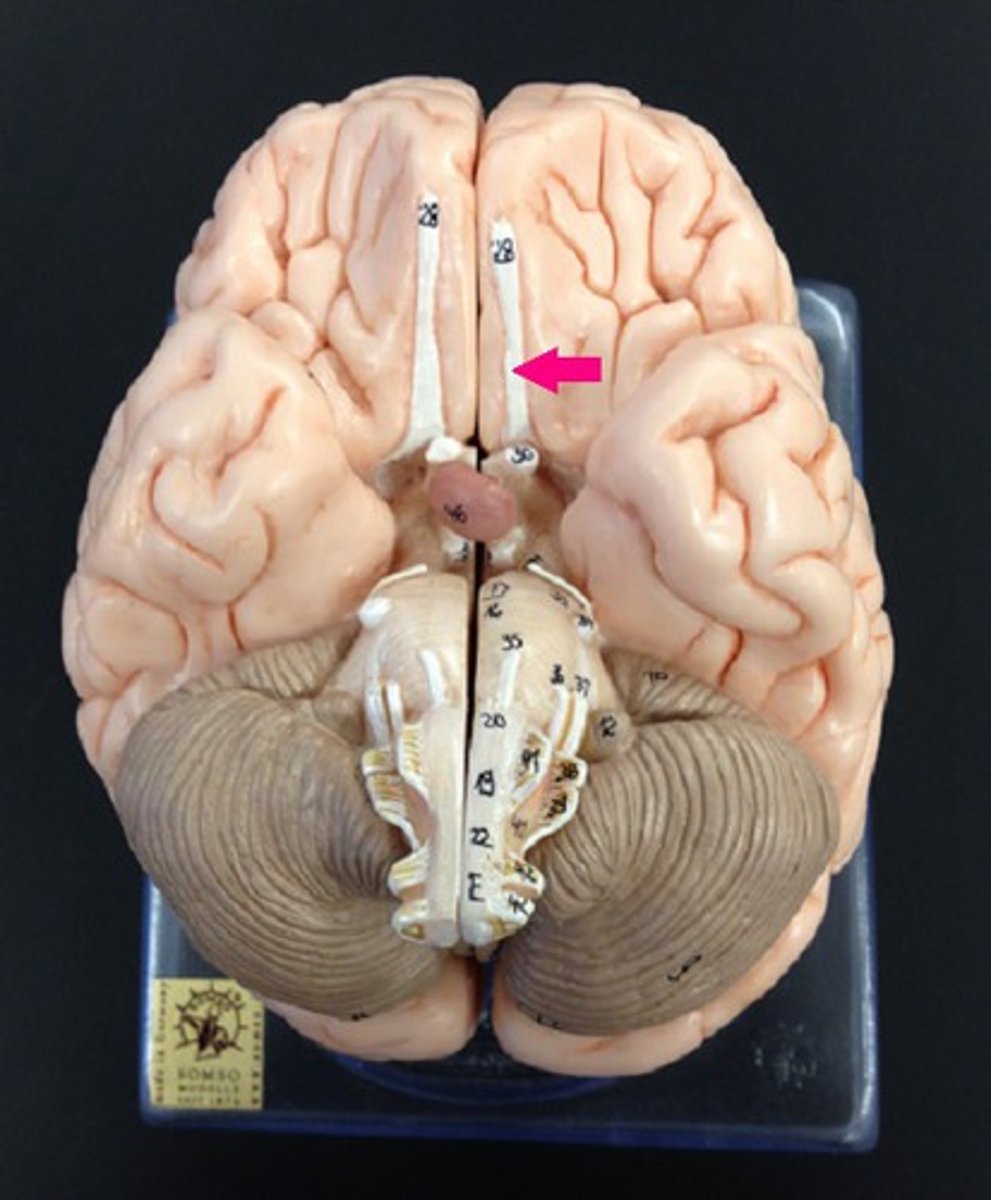
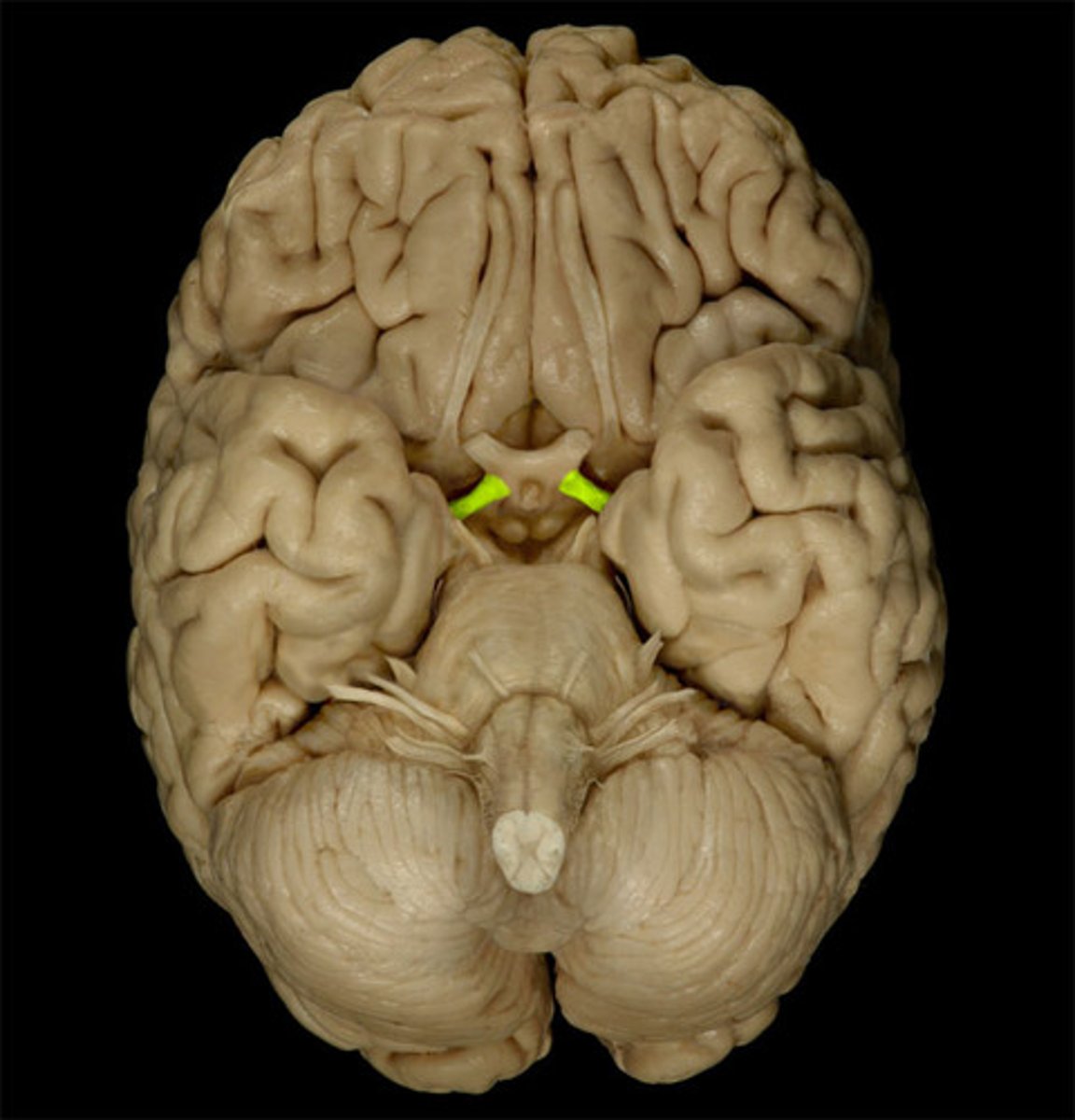
olfactory tract
smell
optic tract
How information from the optic nerve travels to the thalamus.
choroid plexus of third ventricle
produces cerebrospinal fluid
pineal gland
secretes melatonin
transverse fissure
separates cerebrum and cerebellum
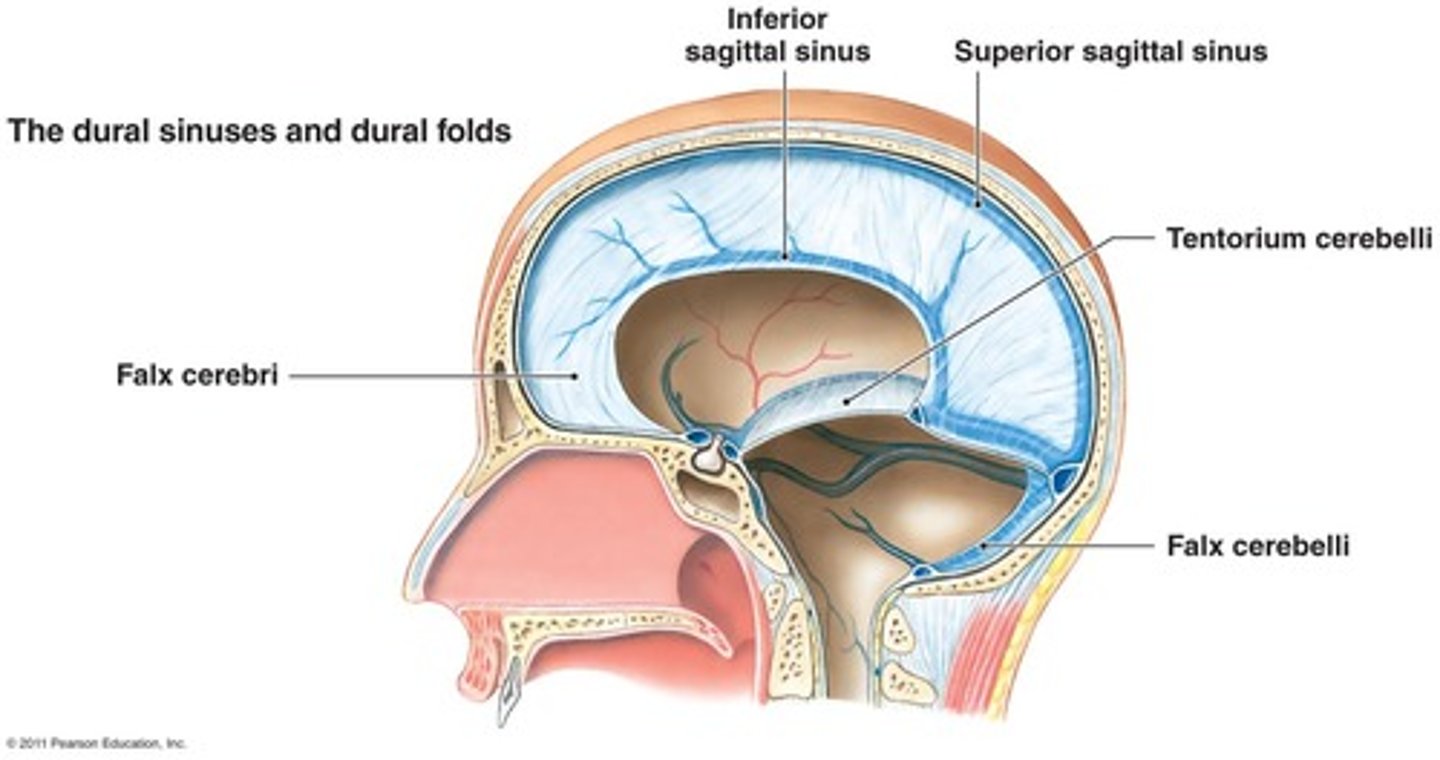
falx cerebri, falx cerebelli, tentorium cerebelli
3 extensions of the dura mater
transverse sinus vein
runs horizontally from the rear of the head toward each ear
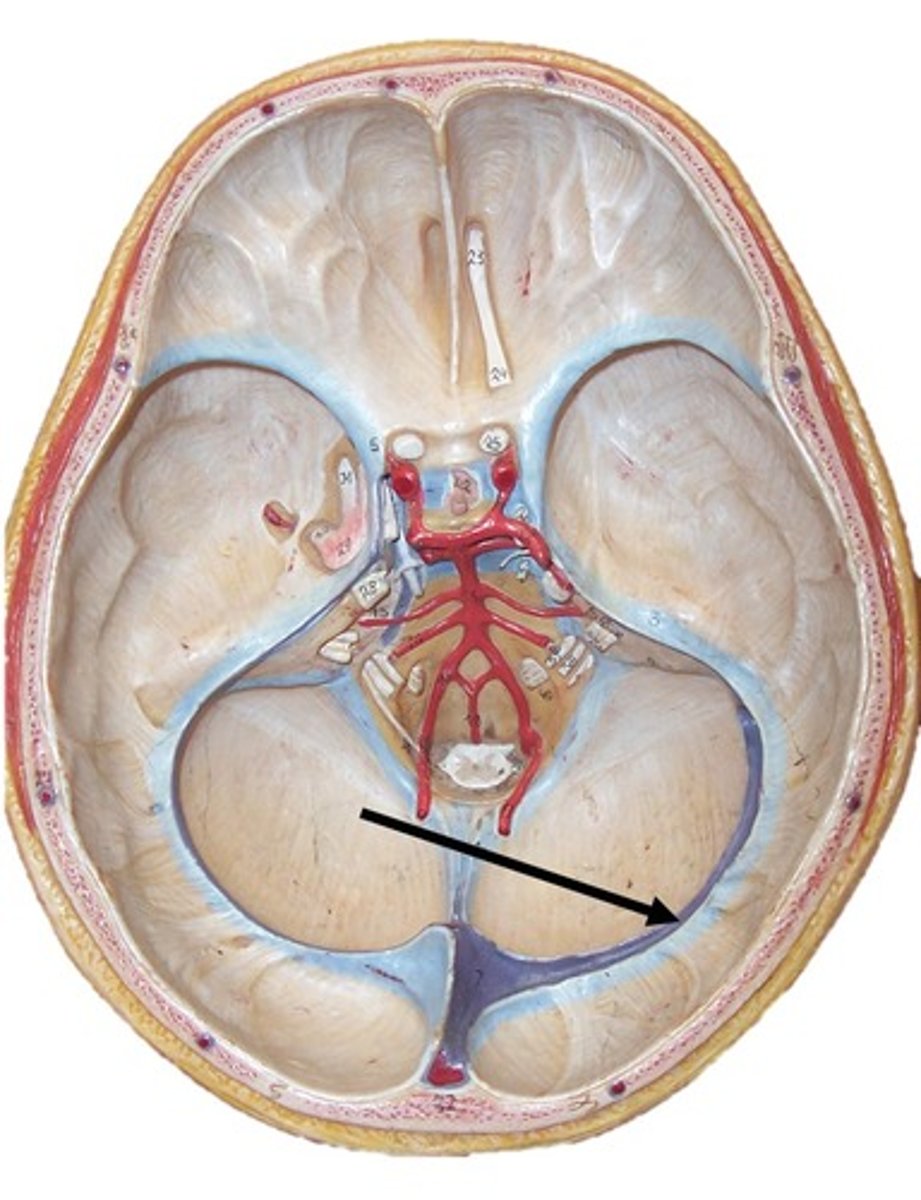
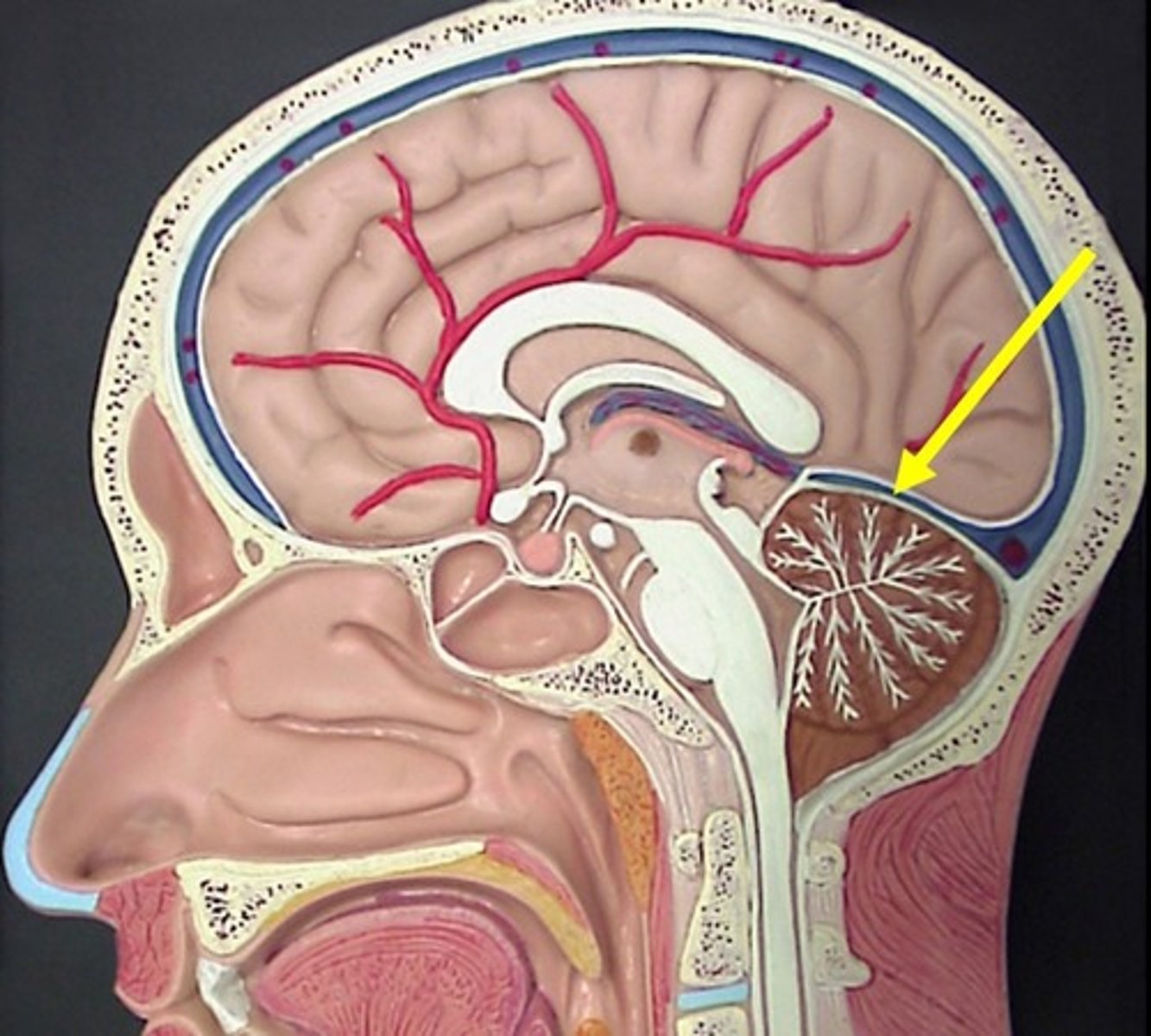
straight sinus vein
between cerebrum and cerebellum
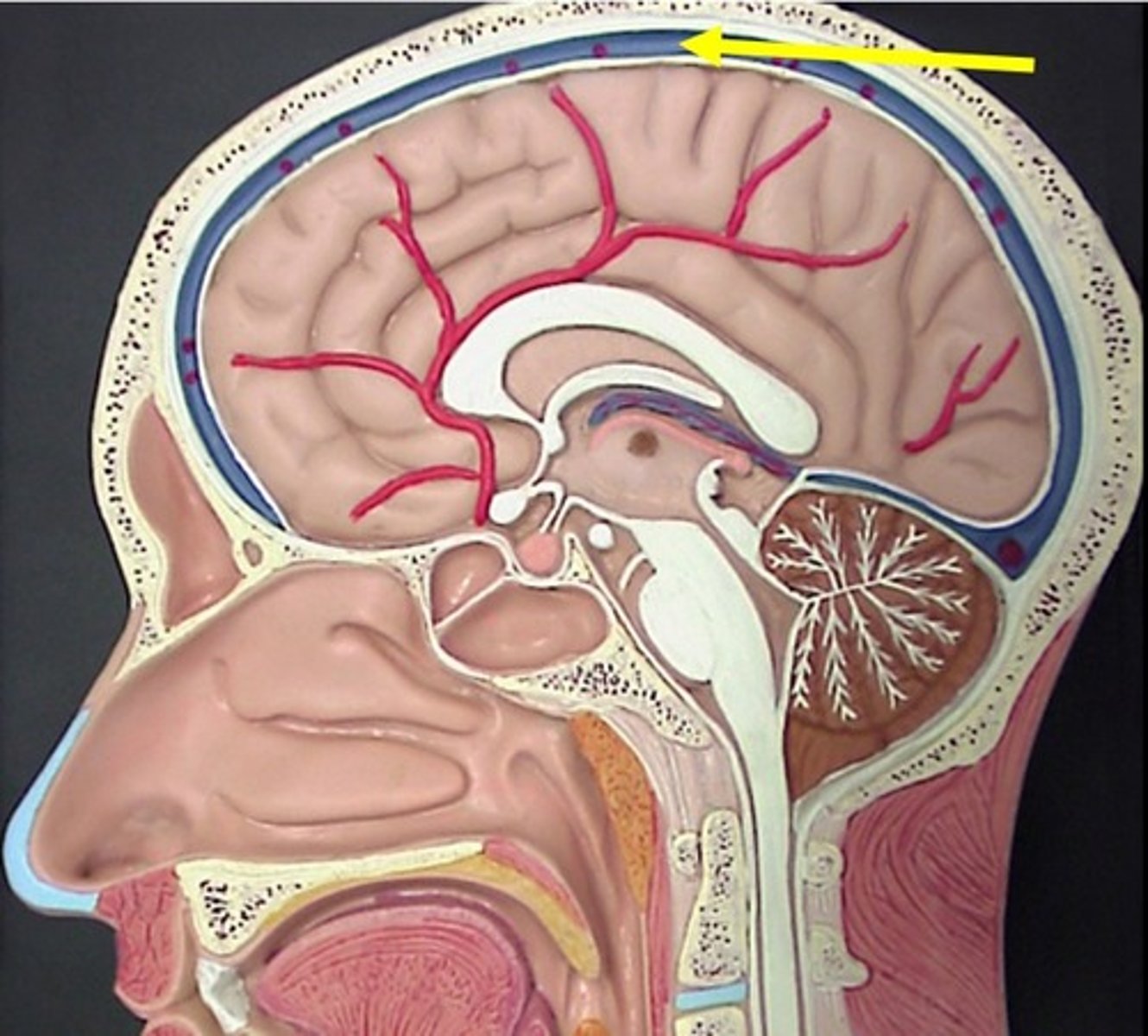
superior sagittal sinus vein
A venous sinus located in the midline just dorsal to the corpus callosum, between the two cerebral hemispheres.
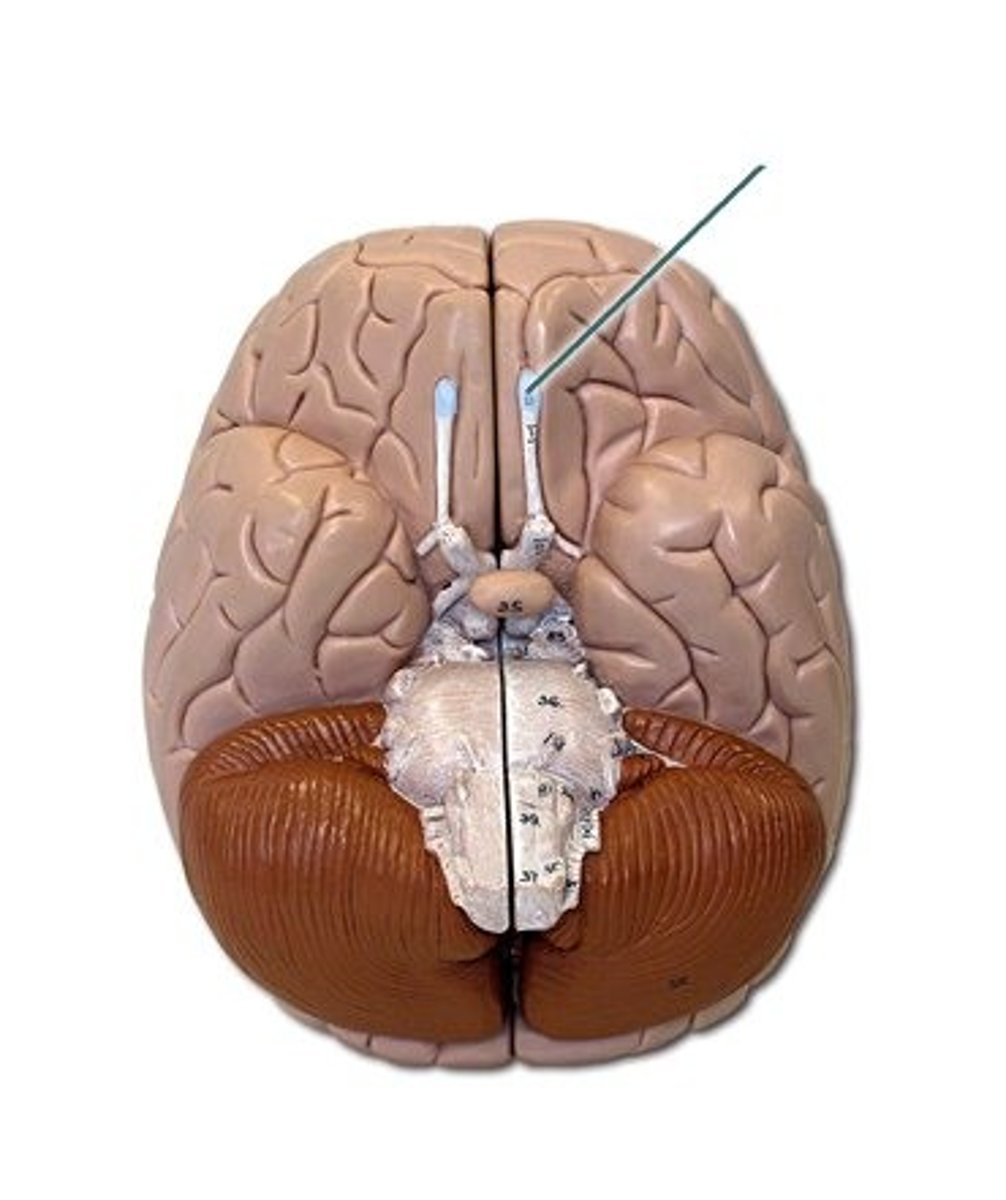
olfactory buld
bulb-like structure at the tip of the frontal lobe, where the olfactory nerves begin
olfactory tract
smell
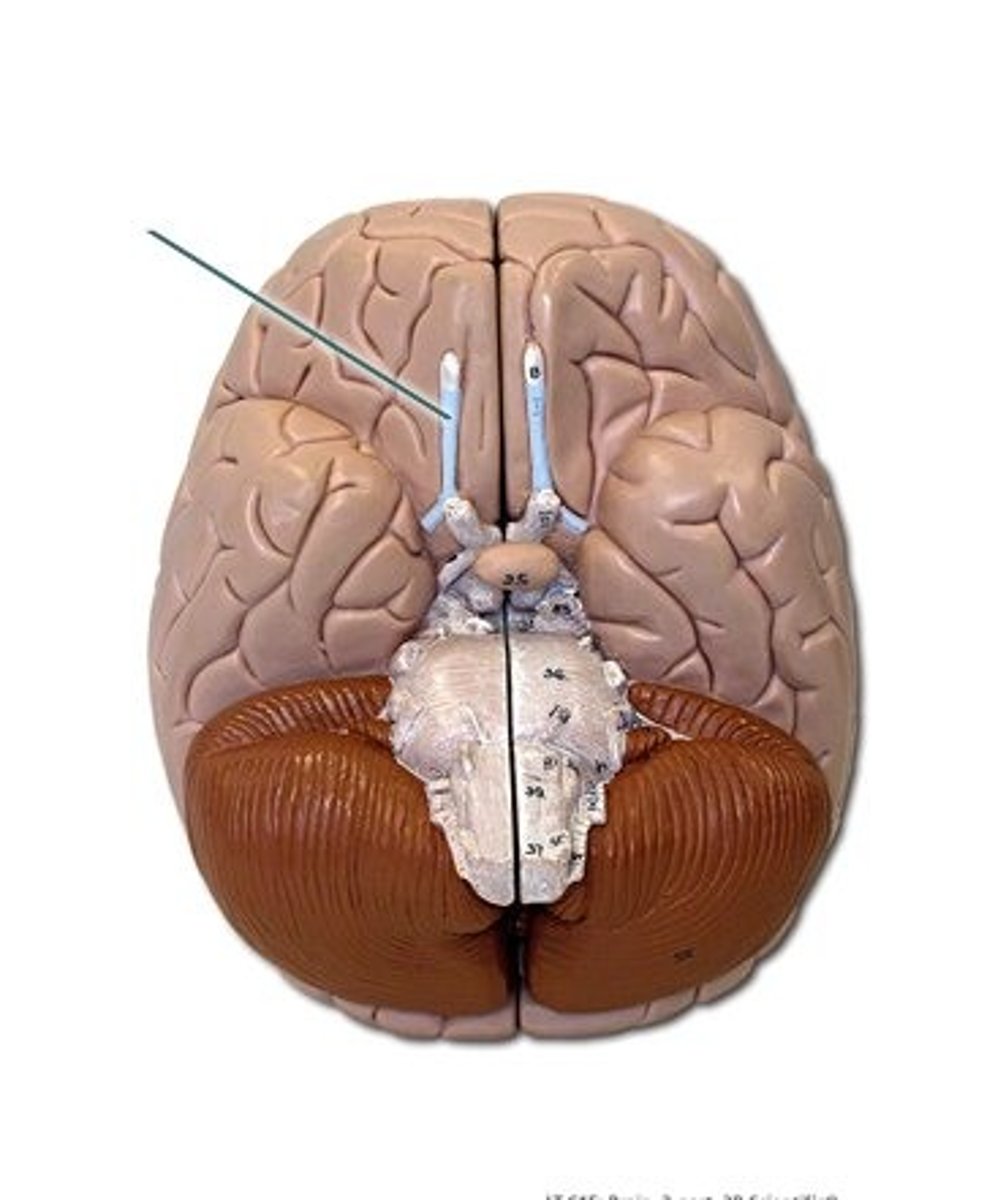
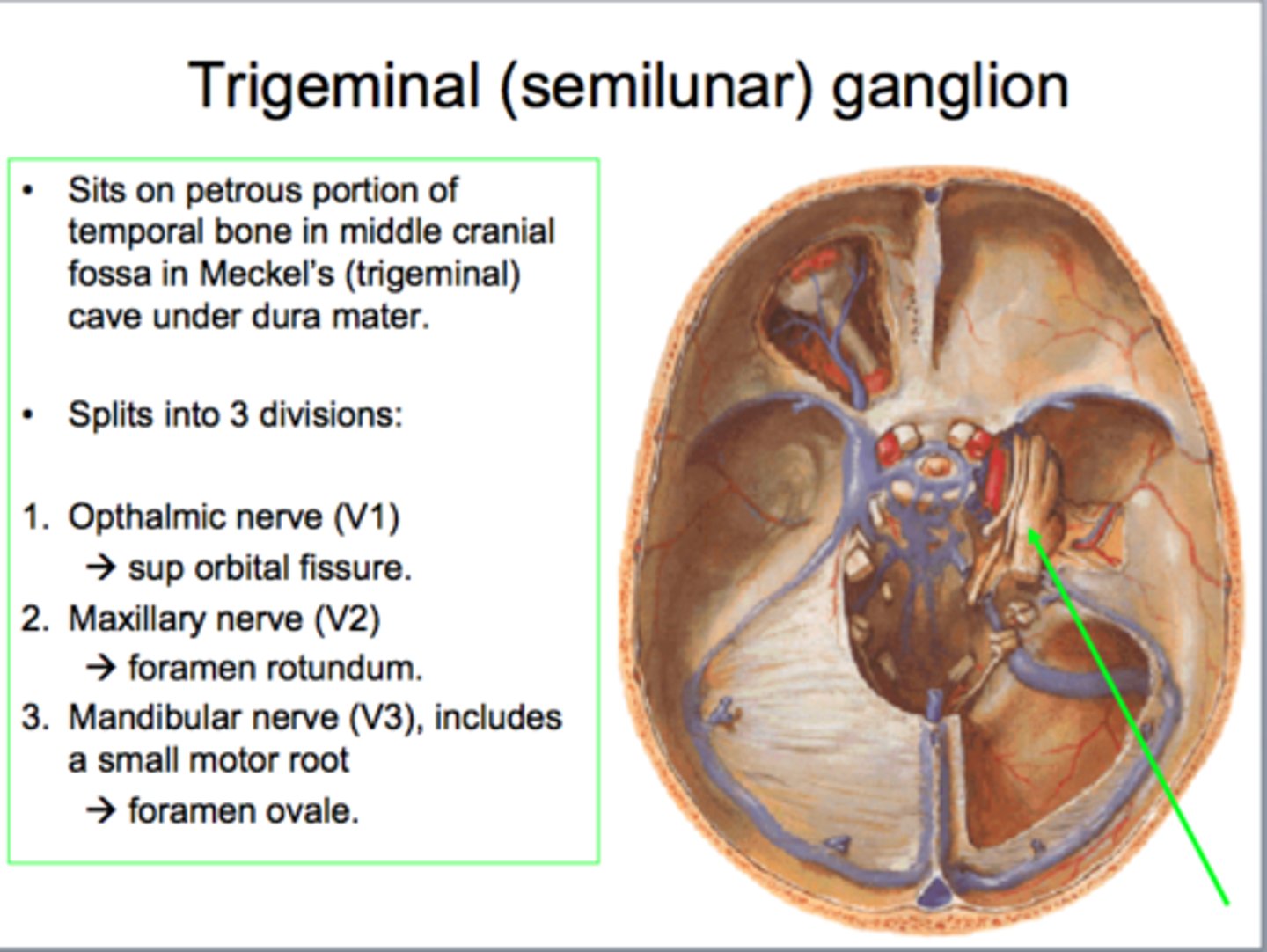
trigeminal ganglion
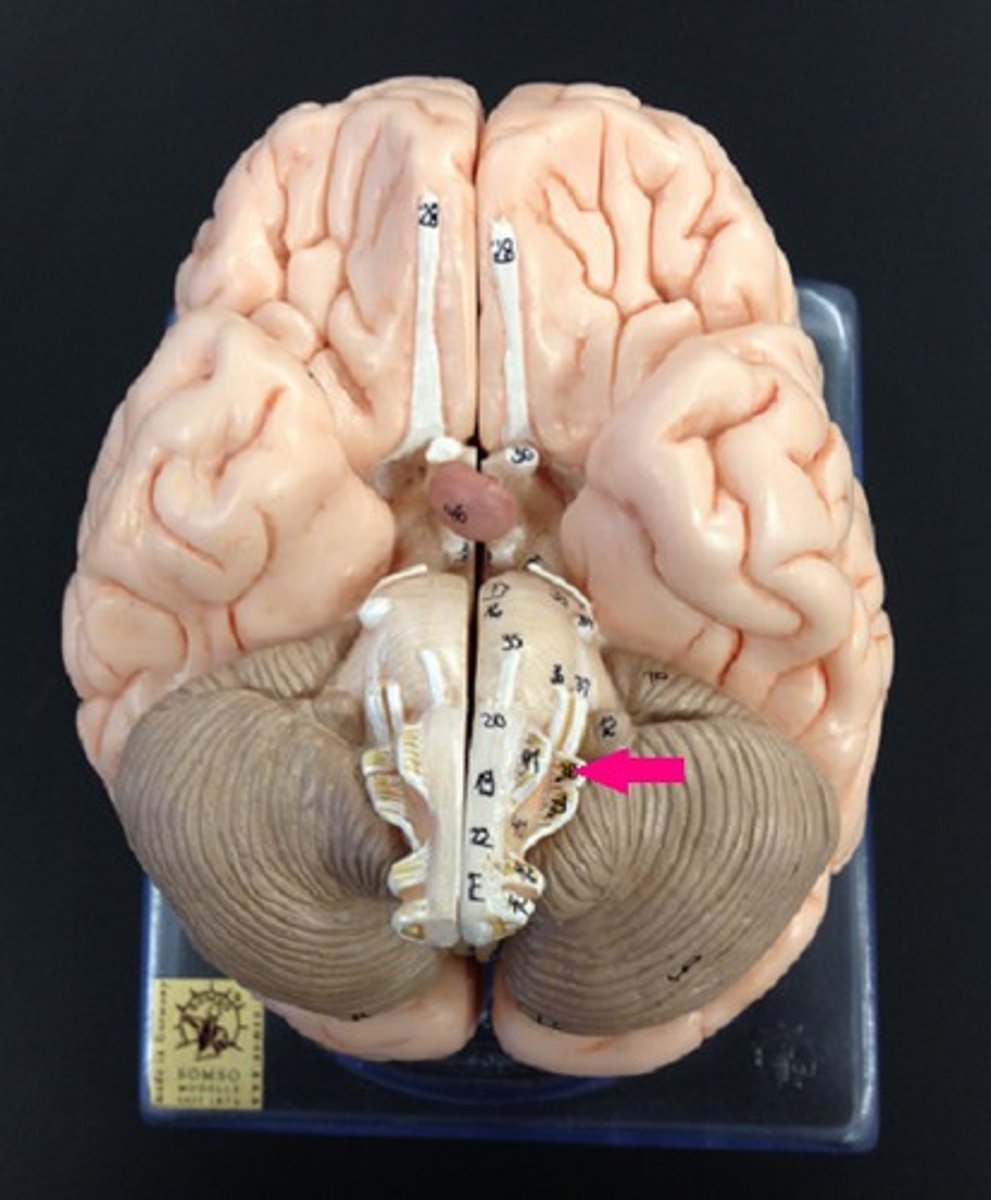
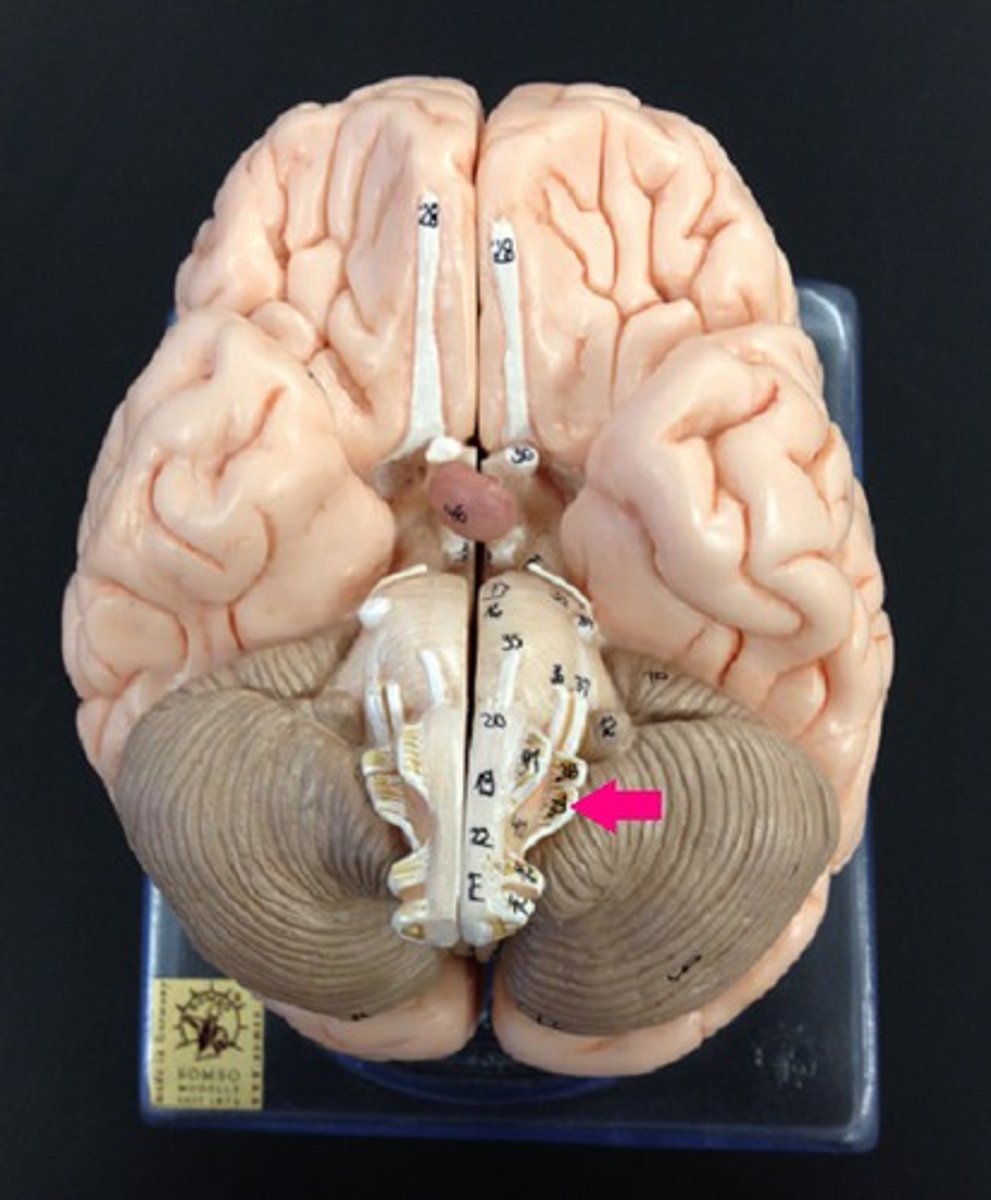
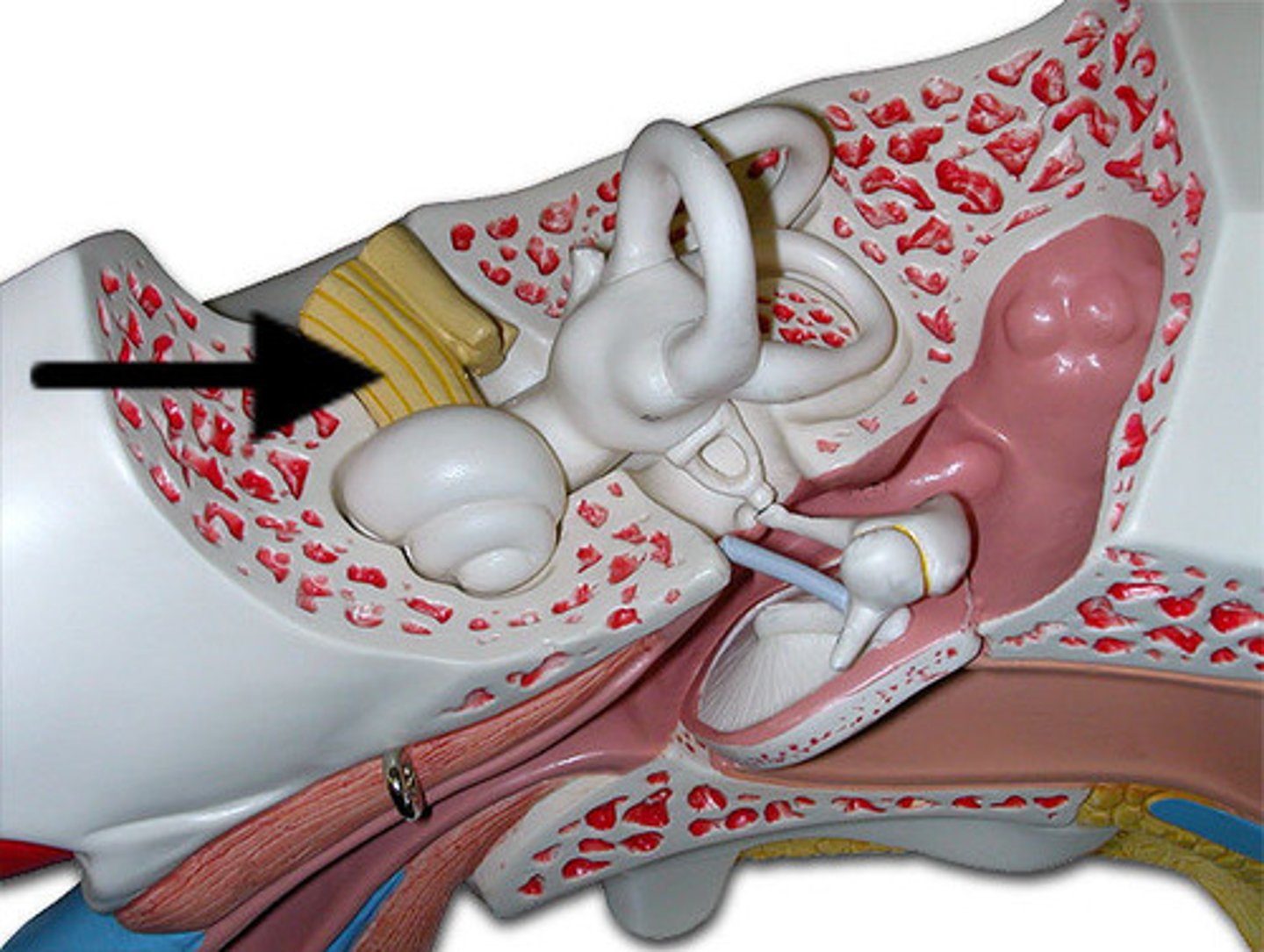
vestibulocochlear nerve
hearing and balance
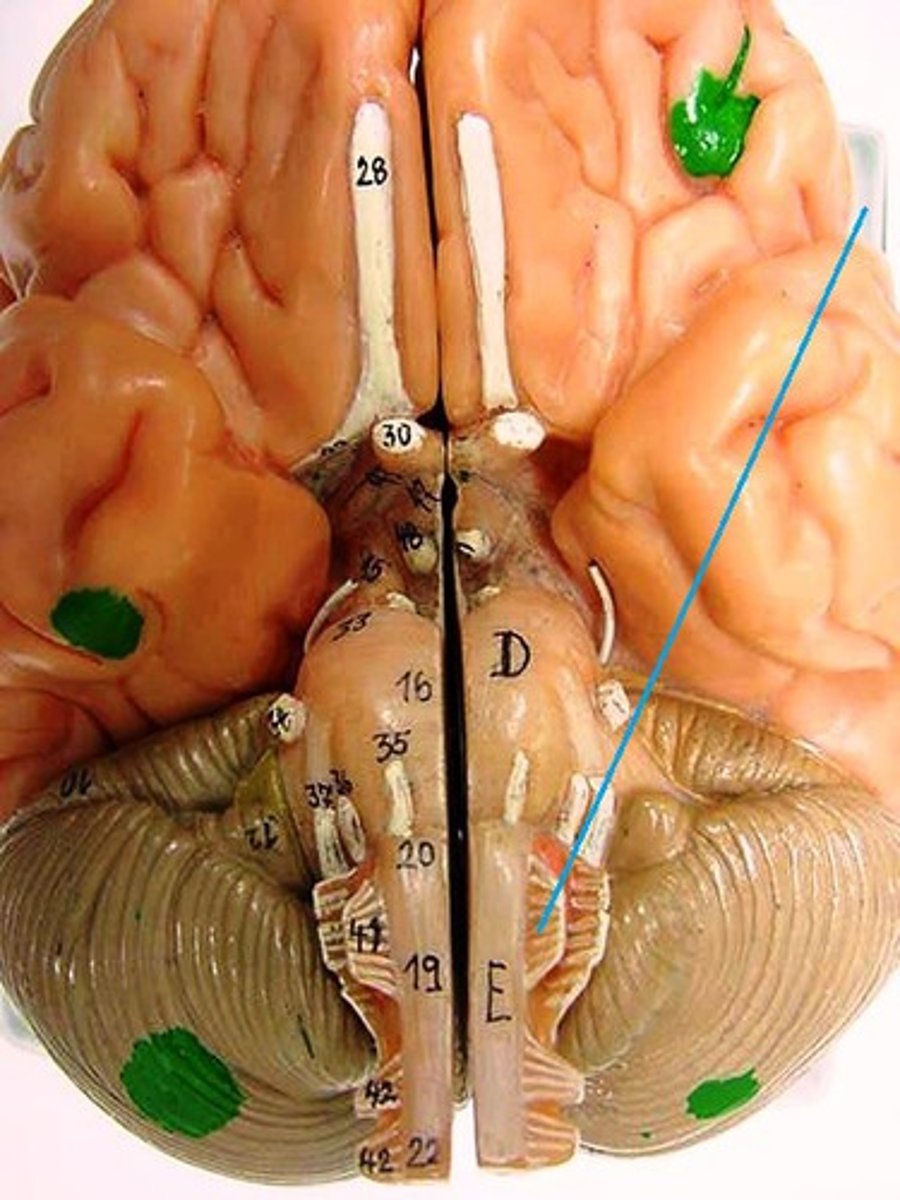
hypoglossal nerve
superior sagittal sinus
blue cavity surrounding the brain which collects blood draining from the brain tissue
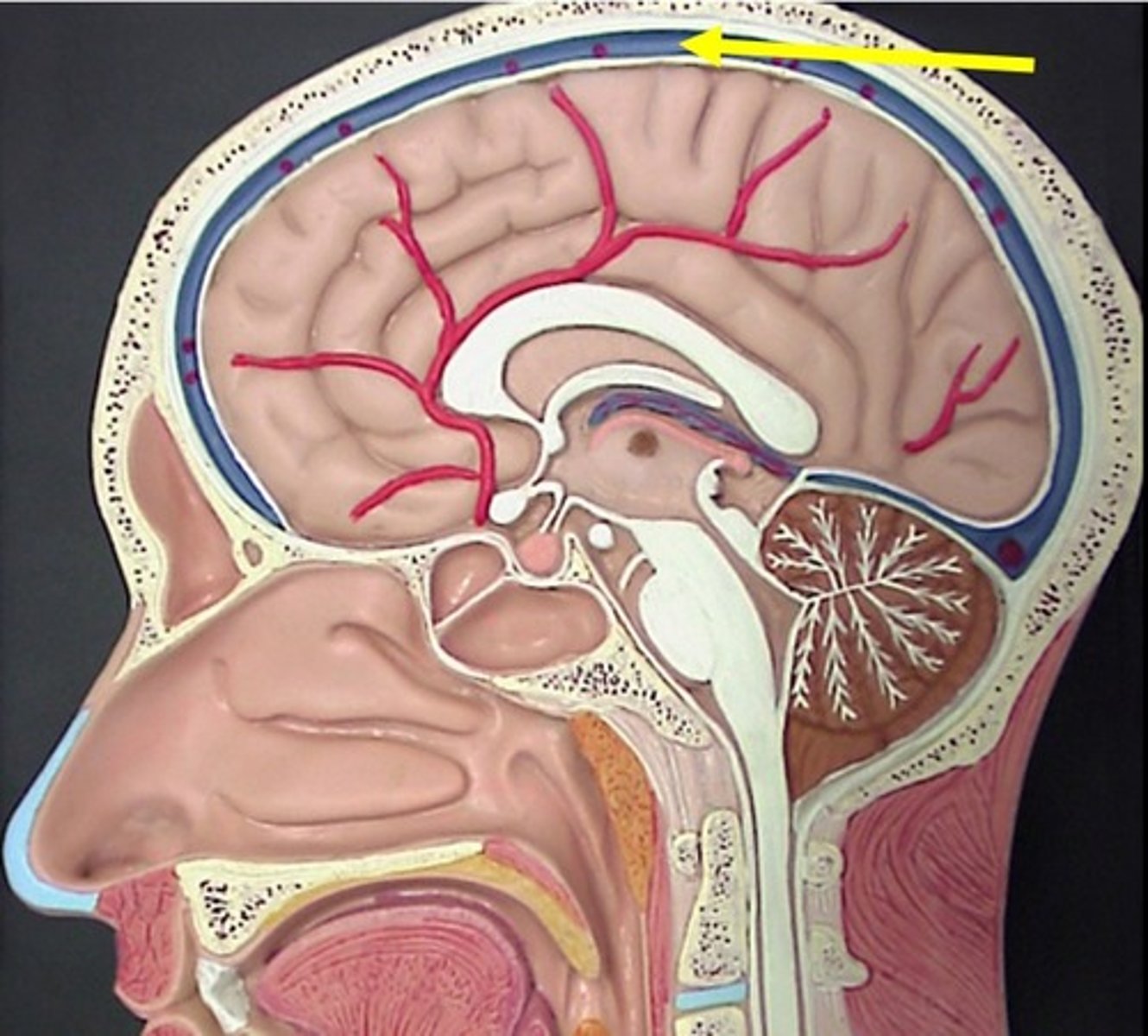
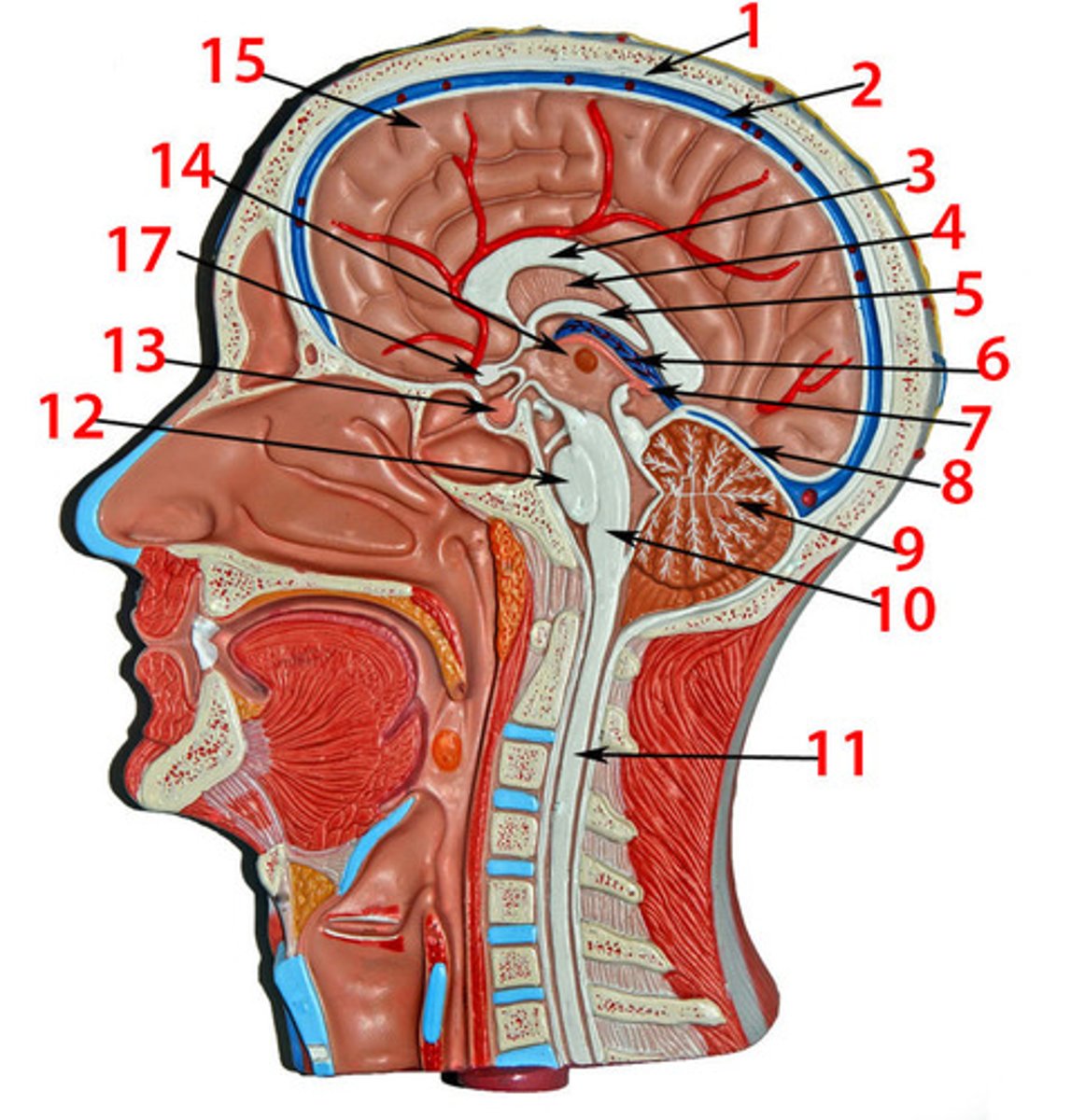
labeled sagittal head
2. superior sagittal sinus
3. corpus callosum
4. septum lucidum
5. fornix
7. pineal gland
14. Intermediate mass of thalamus
13. pituitary gland
12. pons
10. medulla oblongata
11. spinal cord
9. arbor vitae
17. optic chiasma
anterior commissure sagittal head
connects the anterior parts of the cerebral cortex
labeled ventricle model
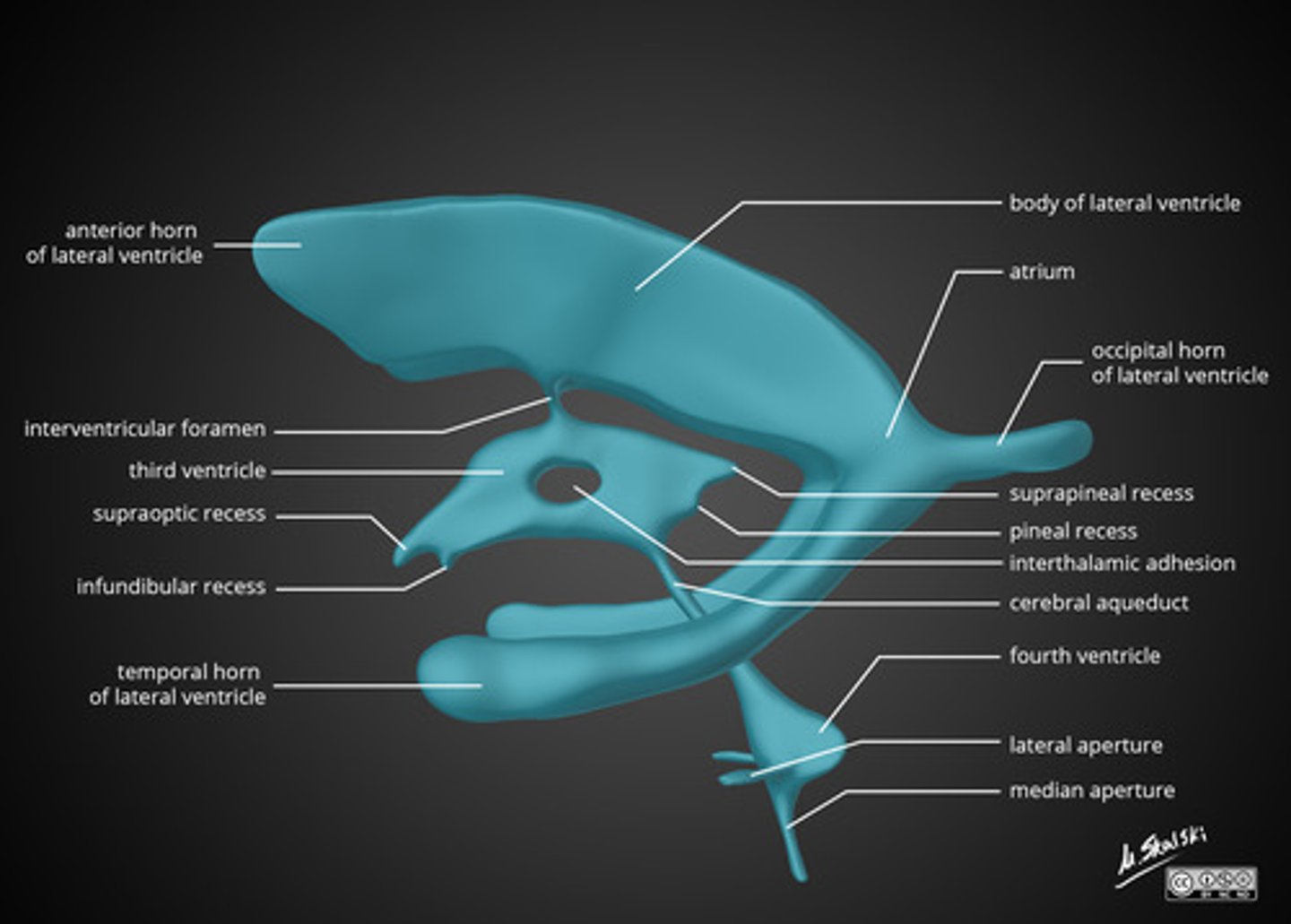
interventricular foramen
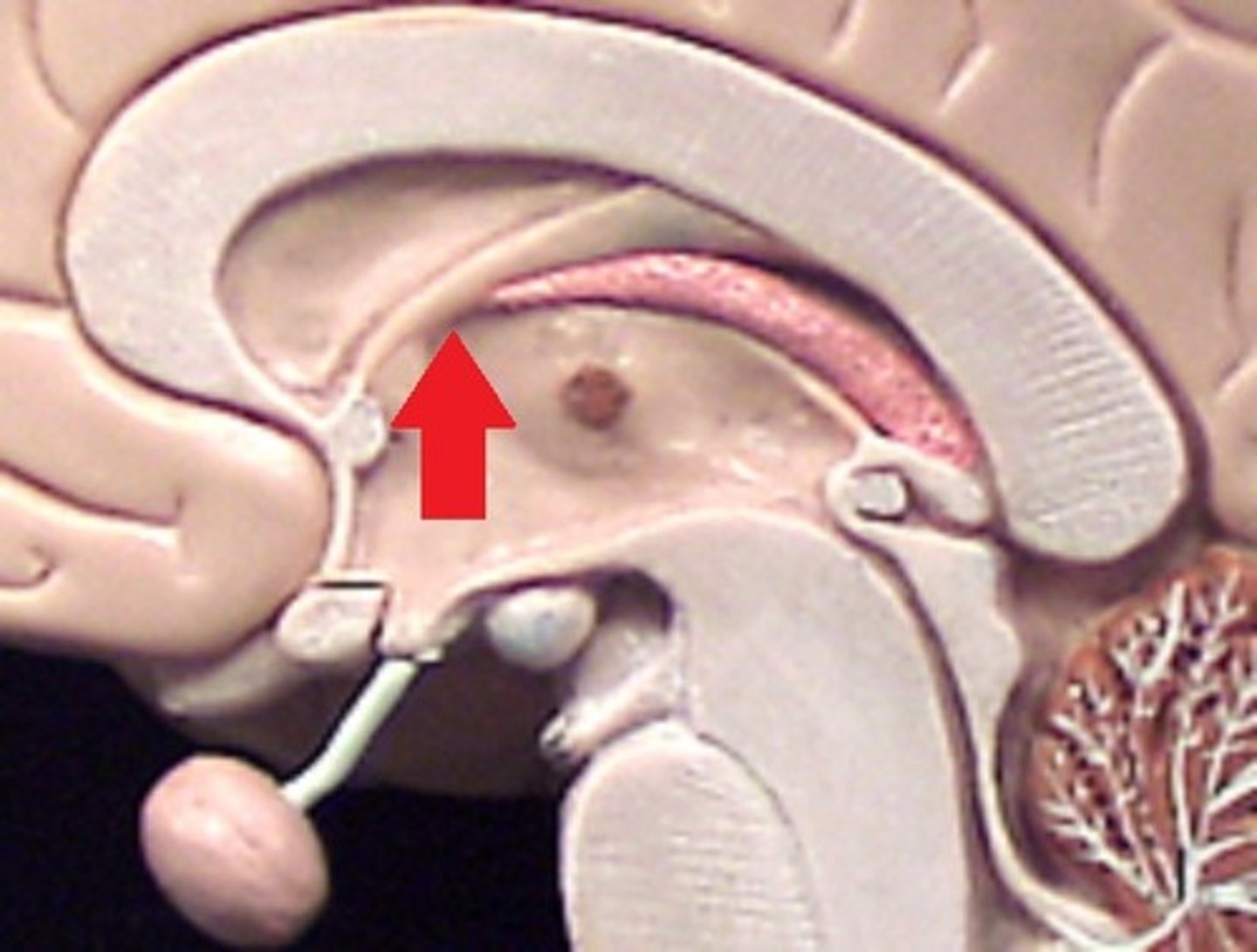
hippocampus
interventricular foramen
connects lateral ventricles to third ventricle
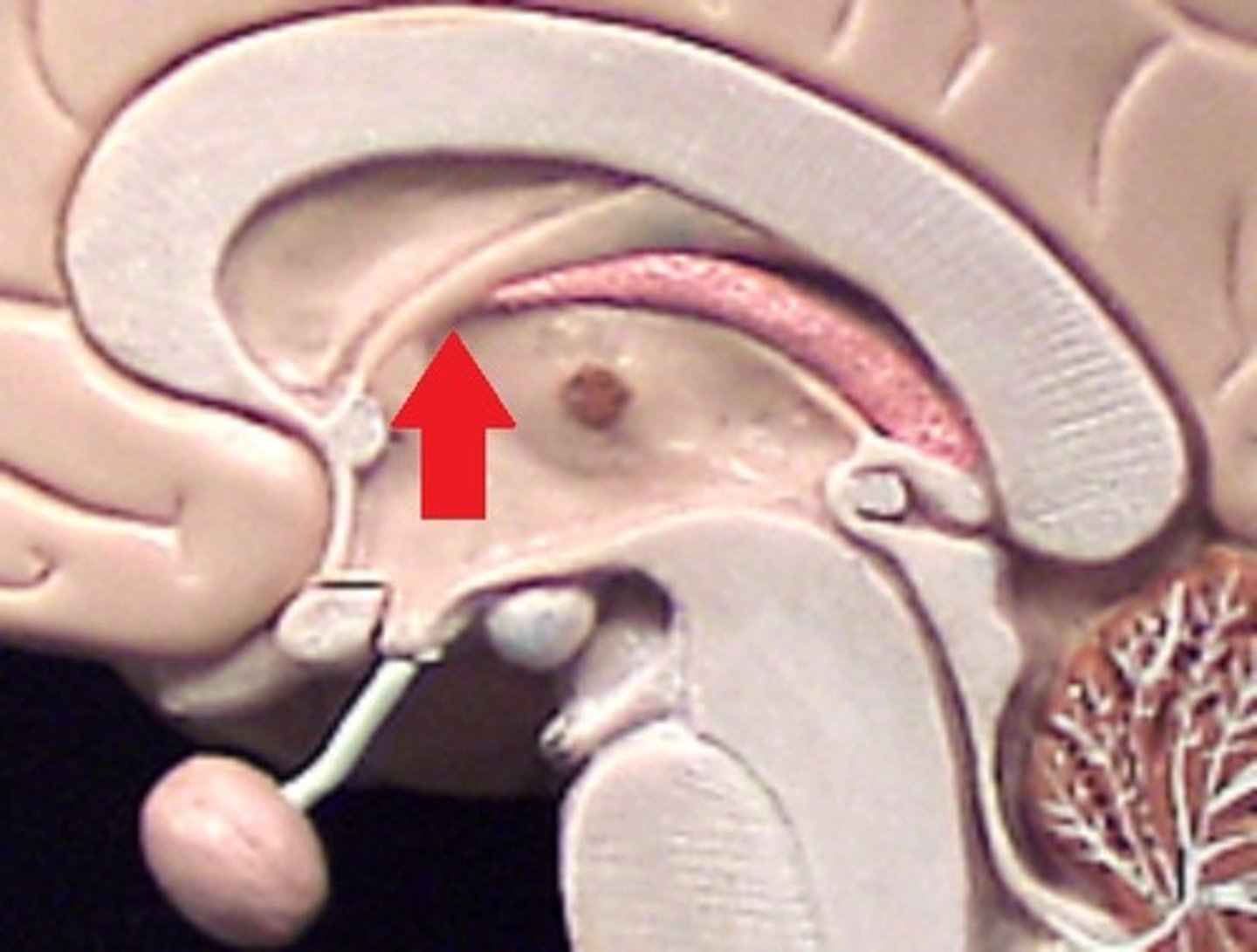
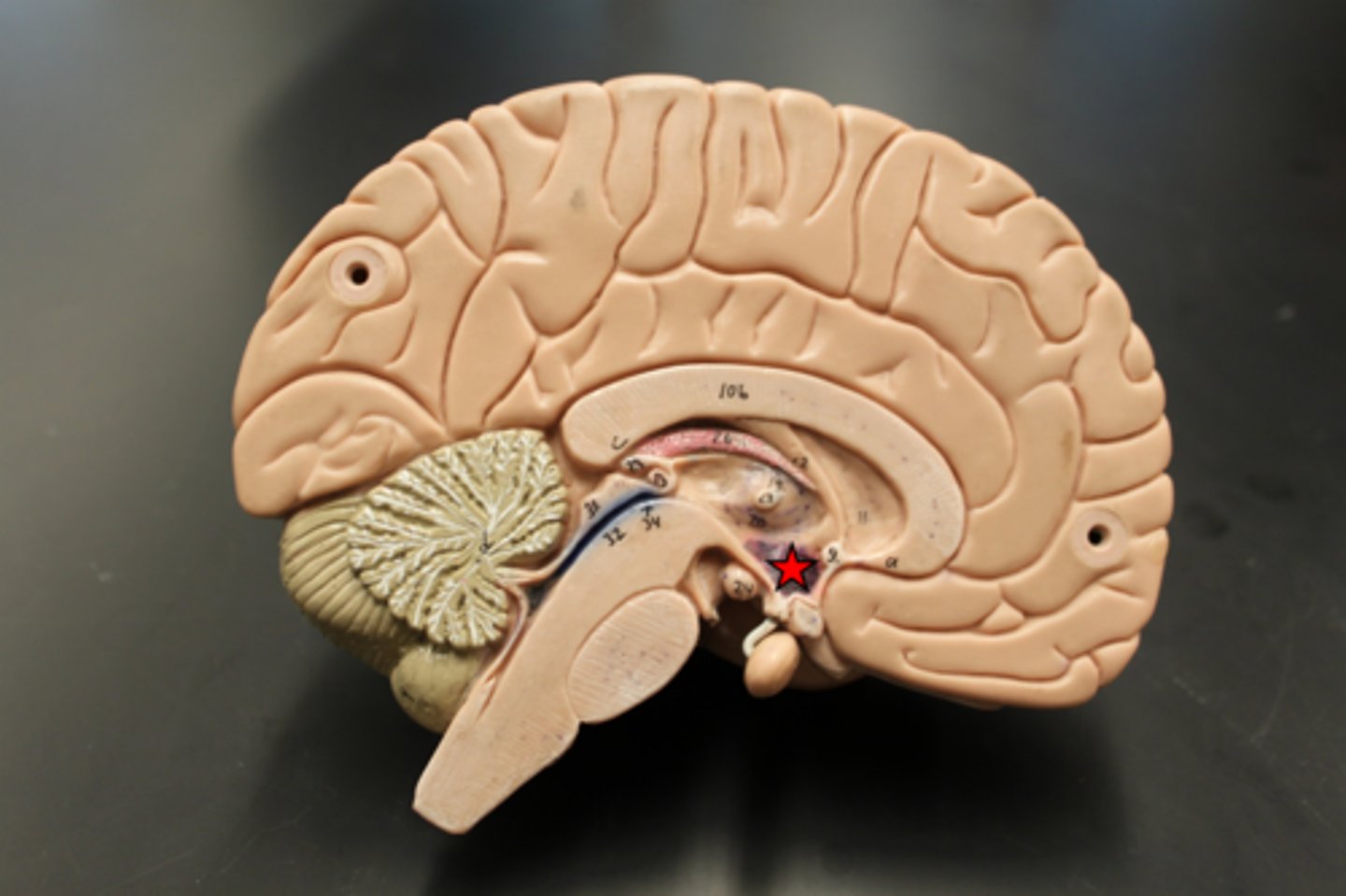
mamillary body
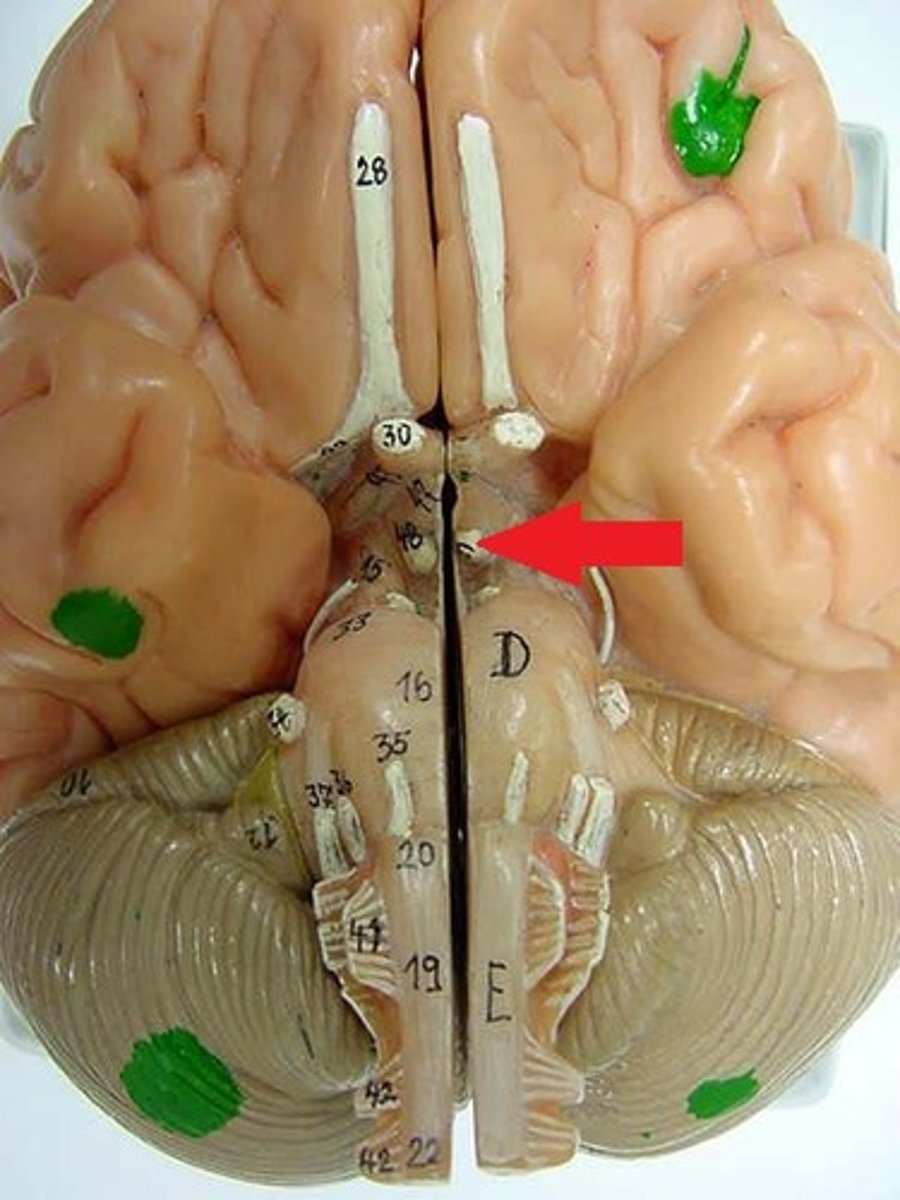
mamillary body