IPC Chapters 1-4
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Generalized Other
Not as important as other, closer, people
Particular Other
Special people in your life
Identity Scripts
Preconceived notions and expectations that guide individuals in social contexts.
I/It Communication
A type of communication characterized by treating others as objects rather than individuals, often lacking personal connection or empathy.
I/You Communication
A type of communication that emphasizes personal connection and acknowledges the other as an individual, fostering empathy and understanding.
I/Thou Communication
A type of communication that emphasizes deep connection and mutual respect between individuals, recognizing each other's humanity. The deepest communication.
Interpersonal Communication
The process of exchanging messages between individuals, which involves both verbal and non-verbal interactions that foster understanding and relationships.
Selective
Who you’re talking to and your relationship to them
Systemic
The system/context which influence interactions
Physical Noise
Interference in our environments, such as sounds made by others, overly dim or bright lights, spam and pop-up ads, extreme temperatures, and crowded conditions.
Physiological noise
Distraction caused by hunger, fatigue, headaches, drugs,
Psychological noise
Thoughts and feelings that affect how we communicate and how we interpret others
Semantic noise
When words themselves are not mutually understood
Linear Model
Who—> Says what—> in what channel—>to who—> with what effect
Had shortcomings.
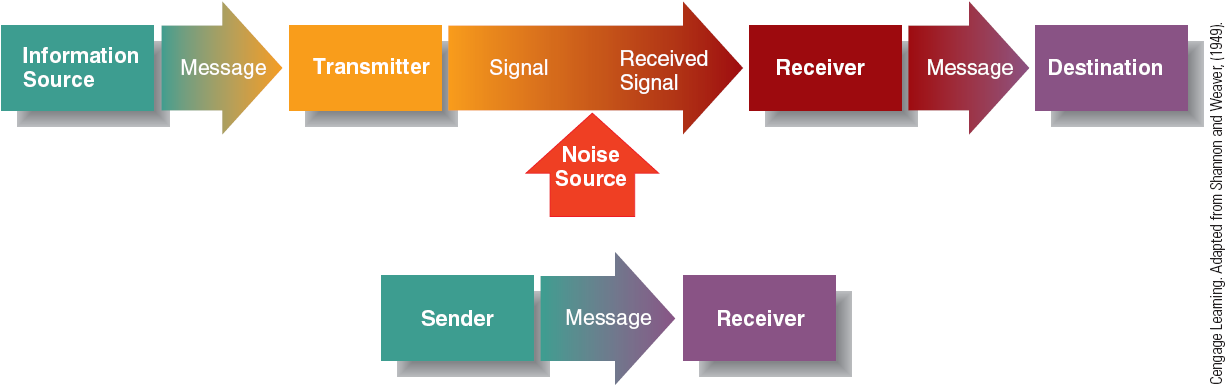
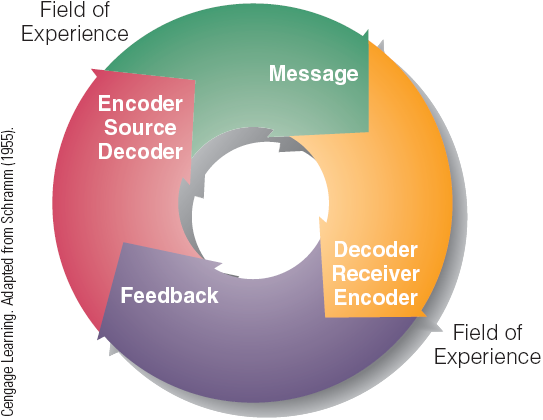
Interactive Model
Listeners give feedback
Still not the best model
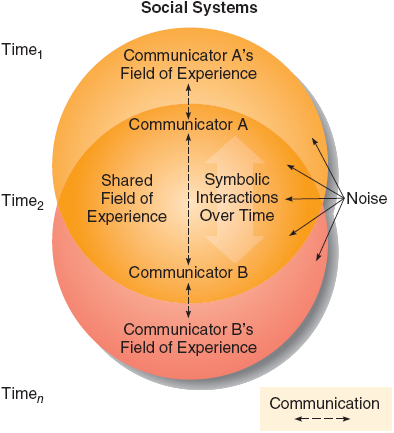
Transactional Models
Show the dynamics of IPC and multiple roles people can take on, while also addressing distractions
The perspectives of the ____ other reflect the views generally held by others in a society.
Generalized
Members of his project group at work consistently comment on Ervin’s excellent
performance as team leader. Ervin begins to view himself as an effective leader and
considers moving into a higher level management position. The process through which Ervin
developed this sense of self at work is called:
reflected appraisal
Reflected appraisal
Our perception of another’s view of us
The views of ____ comprise the generalized other.
a person with whom we have an I–It relationship
Jenna believes that she doesn’t have an aptitude for statistics, so doesn’t put much effort into her statistics class. She performs poorly in the class, supporting her initial belief. This is an example of a(n):
Self-fulfilling prophecy.
Self-fulfilling prophecy
Occur when we internalize others’ expectations or judgments about us and then behave in ways that are consistent with those expectations and judgments
A key foundation for improving your self-concept is:
accepting the self as in process.
Girls and women are expected to be caring, whereas boys and men are expected to be
independent
Secure Attachment style
Facilitated when the caregiver responds in a consistently attentive and loving way to the child. In response, the child develops a positive sense of self-worth (“I am lovable”) and a positive view of others
Fearful Attachment style
Cultivated when the caregiver in the first bond is either unavailable or communicates in negative, rejecting, or even abusive ways to the child. Children who are treated this way often infer that they are unworthy of love and that others are not loving or trustworthy.
Dismissive attachment style
promoted by caregivers who are disinterested in, rejecting of, or unavailable to children.
anxious/ambivalent attachment style
Fostered by inconsistent treatment from the caregiver. Sometimes the caregiver is loving and attentive; at other times, the caregiver is indifferent or rejecting. The caregiver’s communication is not only inconsistent but also unpredictable
Aspects of the Johari Window
Open, blind, hidden, unknown
Prototypes, personal constructs, stereotypes, and scripts are
Cognitive schemata that we use to organize our perceptions of people and phenomena.
Perception
The process of creating meaning by selecting, organizing, and interpreting people. Its an active process that is are not always partial and subjective.
Prototypes
the clearest or most representative example of some category
Scripts
Rules for living and identity, they define our roles, how we are to play them, and the basic elements in the plots of our lives.
Personal constructs
A “mental yardstick” we use to measure a person or situation along a bipolar dimension of judgment
standpoint
A point of view shaped by political awareness of the social location of a group
the fundamental attribution error.
The tendency to overestimate the internal causes and underestimate the external causes of others' undesirable behaviors
Frame of reference
Our beliefs, attitudes, values, and experiences through which we interpret our immediate perceptions
I
The spontaneous, creative self. Acts impulsively in response to inner needs and desires, regardless of social norms.
Me
The socially conscious part of the self that monitors and moderates the I’s impulses. The Me reflects on the I from the social perspectives of others.
Hate speech
language that radically dehumanizes members of a particular group.
In general, masculine-gender speech communities follow this communication rule:
Use talk to accomplish practical goals.
The five symbolic abilities described in your textbook are
definition, evaluation, organization, hypothetical thought, self-reflectionambiguous.
Arbitrary
Words arent connected to what they represent
Ambiguous
What words mean isnt clear cut
Abstract
Not concrete or tangible
The theory of linguistic determinism states that
Language determines what we can perceive and think.
To take responsibility for your own feelings, rely on ________ language.
I
When we respond to a person as if one label totally represents who that person is, we are:
Totalizing
Constitutive rule of communication
How to interpret and preform different types of commuincation
Regulative Rules
When, where, and who we talk to about different things
Communication Rules
Shared understandings of what communication means and whats appropriate in different situations
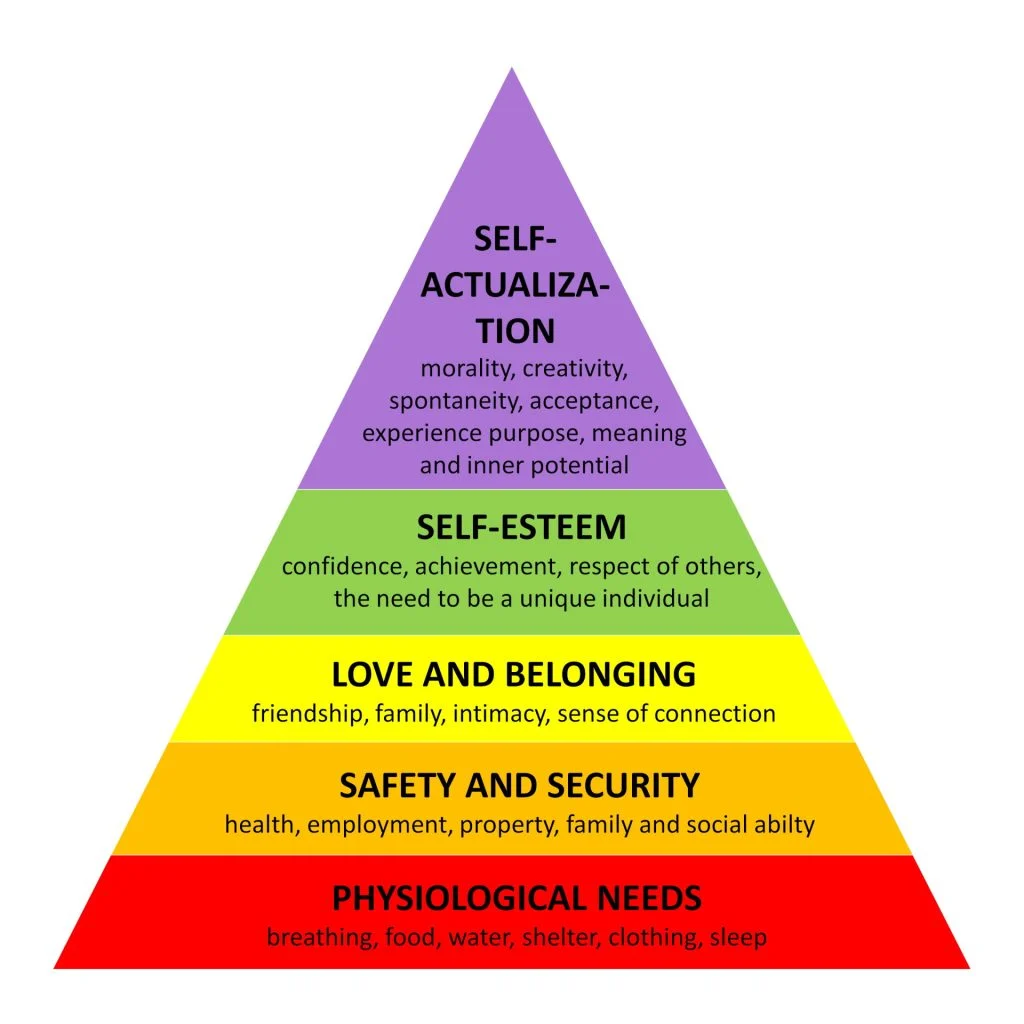
Maslow's hierarchy of needs
Physiological Needs (survival), Safety Needs (security and stability), Love and Belonging Needs (social connections), Esteem Needs (respect and recognition), and Self-Actualization Needs (achieving one's full potential)
Cultures effect on IPC
Can effect how people perceive different types on communication, how they communicate, what they consider rude and not, and overall how they view the world.
Connotative
The emotional and cultural associations a word evokes beyond its literal or dictionary definition
Denotative
The dictionary definition of a word
True or false, people can change attachment styles?
Yes, they can. True