13. Trade offs in Life’s Histories
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Life History
Description of major characteristics of an organism from its birth to its death
Key Traits of Life History (5)
Body size
Fecundity (# offspring per reproductive episode)
Parity (# reproductive episodes over lifetime)
Maturity (age at first reproduction)
Aging/Senescence (lifespan/survival)
Parity in Animals
number of reproductive episodes over lifetime
Semelparity/semelparous: one reproductive event
Iteroparity/iteroparous: multiple reproductive events
Parity in Plants
Monocarpic: flowers and sets seeds only once
Polycarpic: flowers and sets seeds multiple times
NOT the same as annual/perennial plant
Allometry
Study of scaling between body size and various biological traits and functions (shape, anatomy, physiology, behaviour)
Body size influences relationships with temperature, energy, water, nutrient acquisition
Taking into account surface area/volume
Ex: estimating fish biomass in fisheries
Principle of Allocation
Amount of energy and time available to each organism is limited therefore when these factors are allocated to one function, it reduces energy and time available for other functions
Energy Budgets
Need to allocate energy between and within parts of energy budget
Trade offs between reproduction and other activities
Examples of trade offs
Offspring vs. Number
Seed size vs. Dispersal distance
Offspring size vs. Gene flow
Survival vs. Age at maturity
Size vs. Maturity and behaviour (game theory)
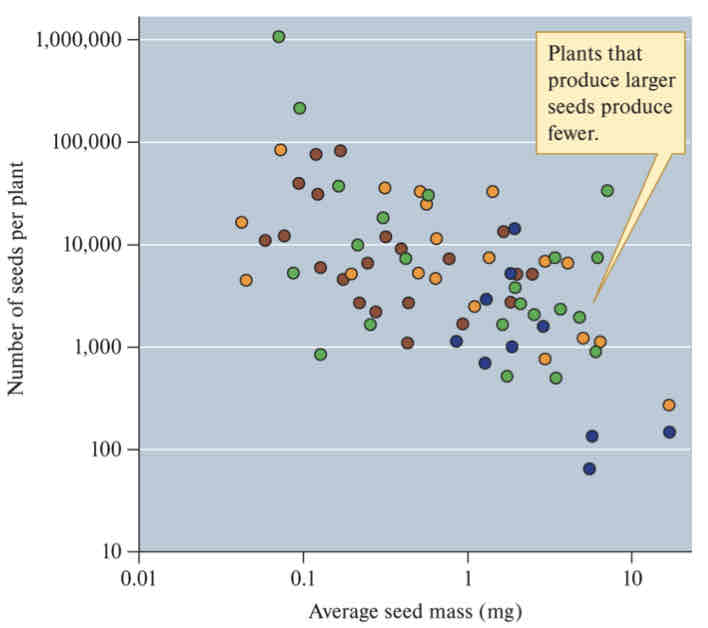
Offspring Size vs. Number of offspring produced
Species with larger females lay larger number of eggs (positive relationship) BUT species producing larger eggs lay fewer eggs (negative relationship)
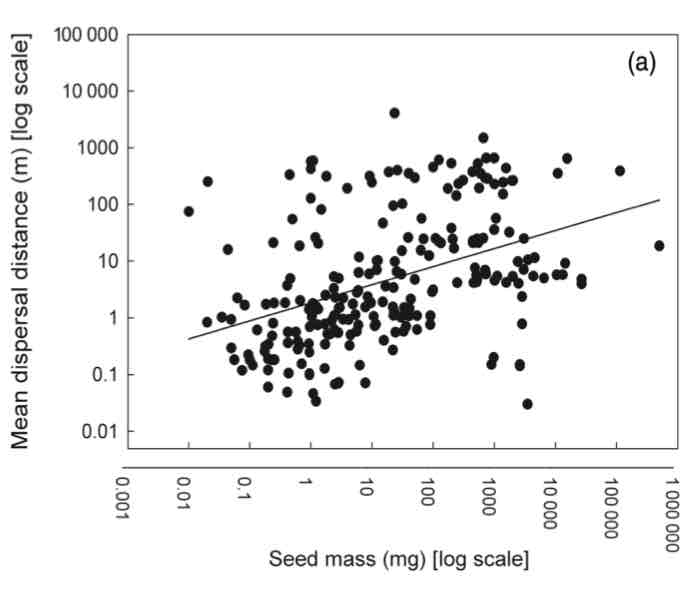
Seed size vs. Dispersal distance
Dispersal: permanent movement of individuals (propagules) from one population to another (NOT MIGRATION)
Seed dispersal: spread of seeds from mother plant across space
larger seed mass, the wider plants can disperse
Only one of many factors influencing how far seeds disperse
Migration
Seasonal movement of individuals from one location to another
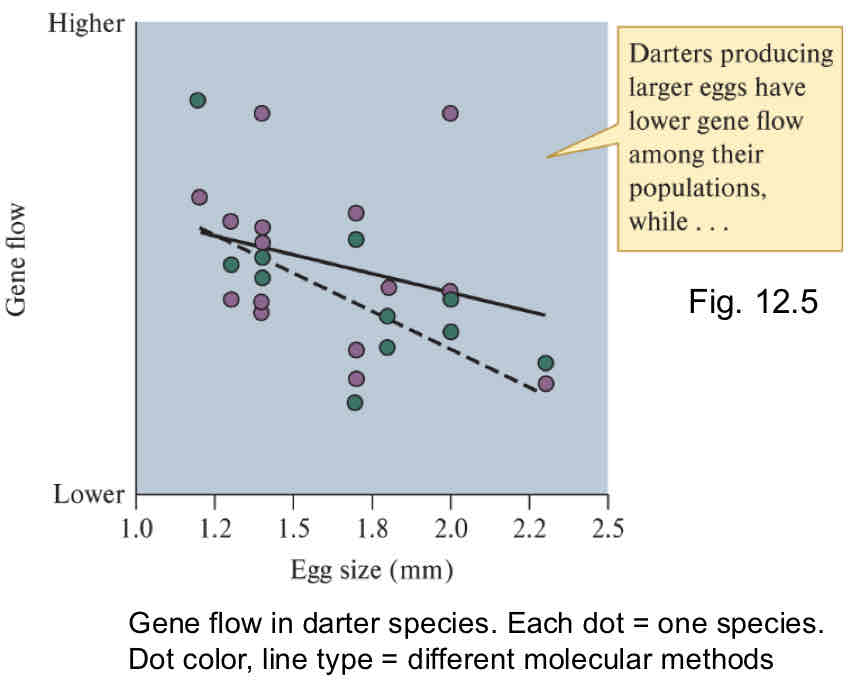
Offspring Size vs. Gene Flow
Gene Flow: transfer of genetic material from one population to another
Smaller offspring have greater dispersal distance (low genetic isolation and high gene flow)
Bigger offspring have shorter dispersal (high genetic isolation and low gene flow)
Ex: fish laying smaller eggs lay more eggs (higher fecundity)
Survival vs. Age at Maturity
Reproductive Effort: allocation of energy, time and other resources to reproduction, including formation of eggs and offspring care
Investing early in reproduction means more energy cannot be allocated to growth and survival
Higher survival rate = reproducing later
Lower survival rate = reproducing early
Size vs. Maturity and Behaviour
Variation within species can be substantial as they represent alternative but successful evolutionary strategies
Game Theory
Disruptive selection
Game Theory**
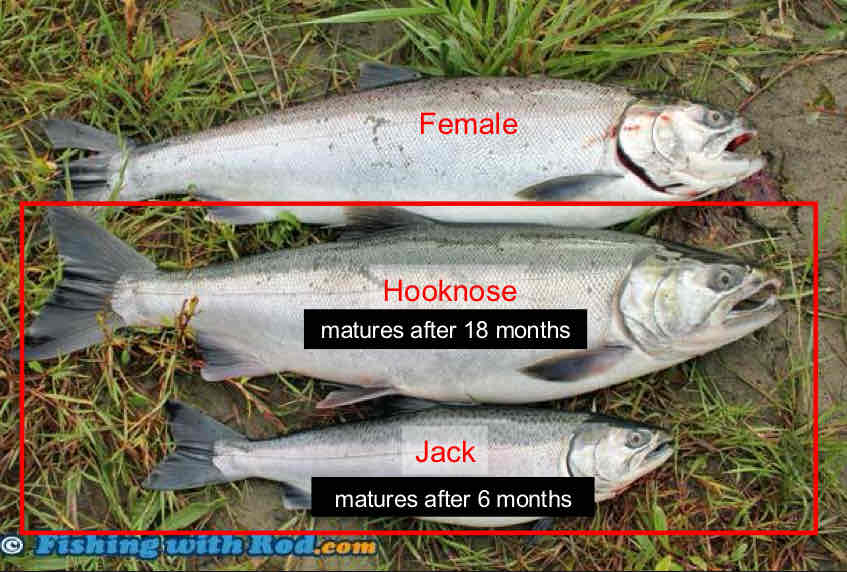
Members of the same species mature at different times
r Selection
Small and fast characteristics
high reproductive output
Put less energy into growth
Dies faster
Not as favoured
K Selection
Large and slow characteristics
lower reproductive output
Put more energy into growth
Longer growth
Better in more stable, less disturbed environments
Types of Life History Classifications
r and K selected species
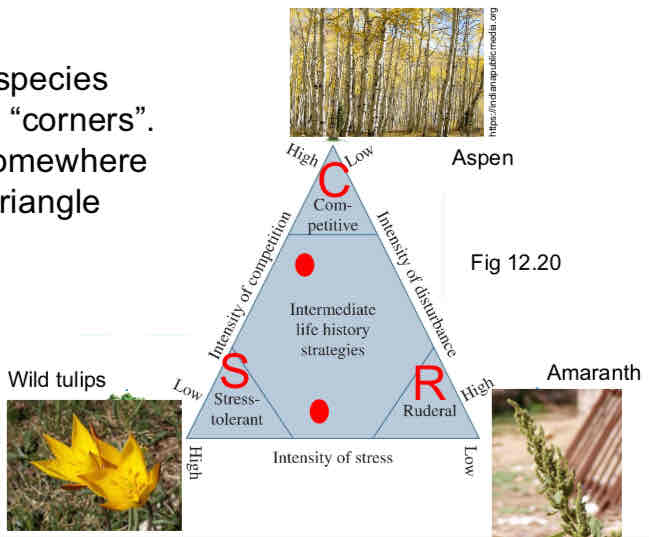
Grime’s Triangle
E-P-O
Life History Classifications - Grime’s Triangle
CSR triangle → Competitive, Stress tolerant, Ruderal
Few plants fall into the “corners“
Most species fall within the triangle
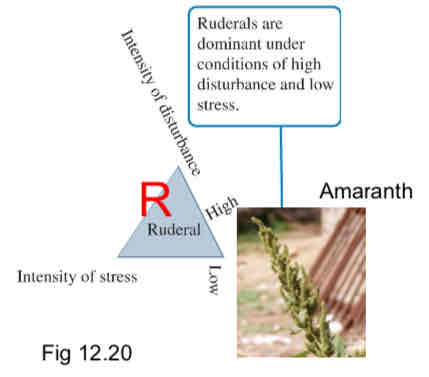
Grime’s Triangle: Ruderal
Thrives best under high disturbance and low stress (many weeds)
Rapid growth
Produces many tiny seeds
Short life (often annuals)
Little maintenance and growth investment of large structure
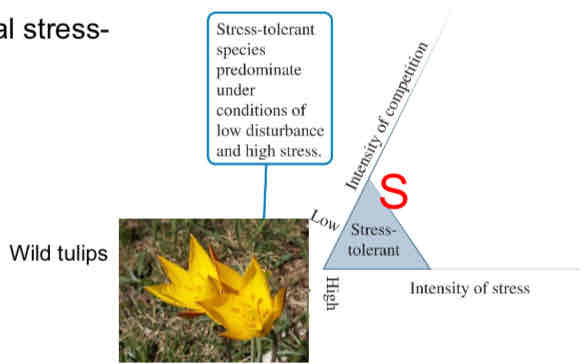
Grime’s Triangle: Stress-Tolerant Plants
Occupy environments of high stress and low competition
Invest in physiological stress-tolerance instead of growth
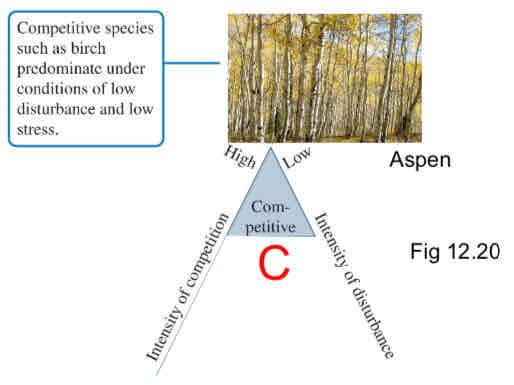
Grime’s Triangle: Competitive Plants
Occupy environments of low disturbance and high productivity
FAST growth
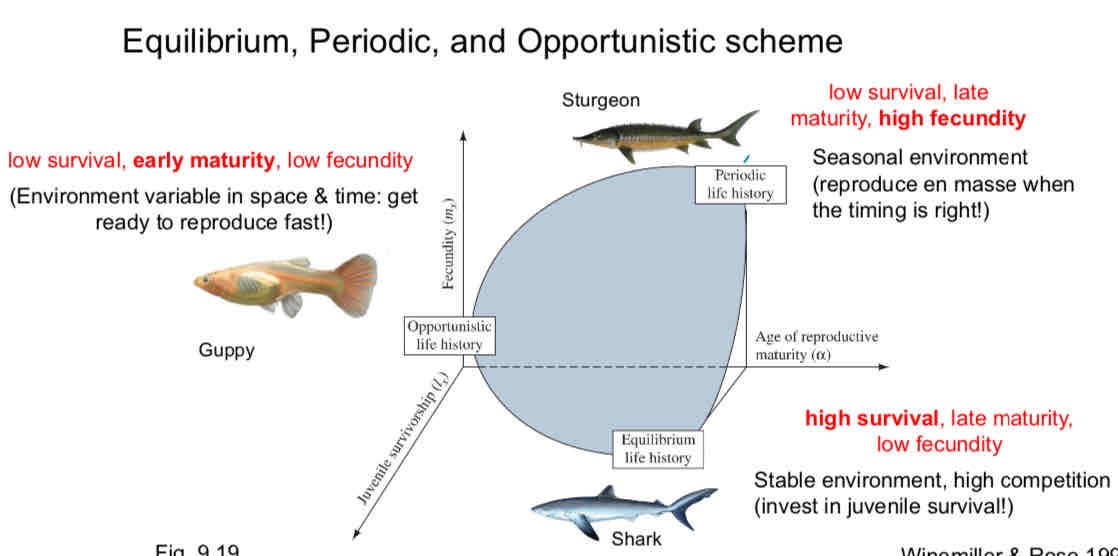
Life History Classification: E-P-O Approach
Equilibrium, Periodic, Opportunistic Scheme