IB DT: Topic 3.5: Rapid prototyping
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://dl.ibdocs.re/IB%20BOOKS/Group%204%20-%20Sciences/Design%20Technology/VARIOUS/Design%20Technology%20-%20Study%20Guide%20-%20Core%20Topics%201-6%20SL.pdf
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
what is rapid prototyping?
the production of a physical model of a design using 3D CAD data. models can be simulated by designers using software, tested and trialled virtually before sending to a variety of peripheral machines for prototype manufacture in a range of materials.
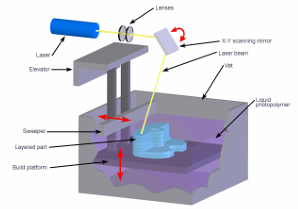
how does stereolithography (sla) work?
uses laser or light to set liquid plastic
uses a liquid bath of resin combined with an ultraviolet laser. the uv light hits the liquid, hardening it to form the structure of the object being printed. the base plate of the bath then moves down, allowing more liquid to flow over the previously hardened liquid so the same process can be repeated until the object being printed has been completed
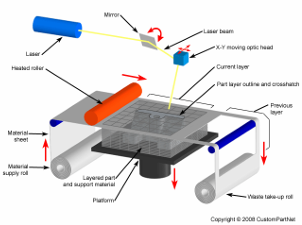
how does laminated object manufacturing (lom) work?
takes the sliced cad data from a 3d model and cuts each layer from a roll of material, using a laser or plotter cutter. these sliced layers are glued together to form the model, which is built on a moveable platform below the machine, or on moving pins (if card)
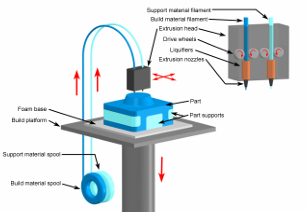
how does fused deposition modelling work?
uses an additive principle by laying down material in layers. plastic/metal is unwound from a coil and sent to an extrusion nozzle that can turn the flow on and off. the nozzle is heated to melt the material, moving in a horizontal and vertical direction by a numerically controlled mechanism (CNC/CAM).
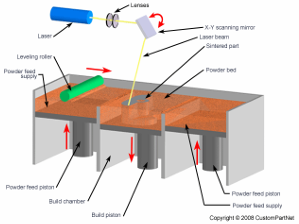
what is selective laser sintering and how does it work?
uses laser to set powder
an additive manufacturing technique that uses a high power laser to fuse small particles of materials (plastic, metal, ceramic, glass) into a mass with a desired 3d shape.
what are the advantages of rapid prototyping?
decrease development time
decrease costly mistake
increase number of variants of product (less time in production therefore more time to develop more ideas)
increased product complexity
increased effective communication (models can easily be made tangible to test and show users - concrete proof to attract funds)
what are the disadvantages of rapid prototyping?
it fails in replicating the physical and mechanical properties of an actual product unless it would be made the same way
problems can be overlooked when designing on CAD
not suitable for large products, or large production runs