Physics 10
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
What is physics?
Is the study of everything. from how atoms work to how the universe works and everything in between. It studies why things move, how energy flows, how light works, how electricity, magnetism, and gravity work, how particles work at incredibly small scales, and how particles work at incredibly fast speeds.
Uniform Motion
Is when an object is traveling at a constant speed. It is not speeding up or slowing down (not accelerating).
In reality, uniform motion is nearly impossible why?
An object is always speeding up or slowing down (accelerating) due to things like friction or the wind.
What formula can be used to find the average speed of something?
d = vt
A person walks 10.0m away from a stop sign in 5.00 seconds. What is the average speed of the person?
v = 2.00 m/s
On a graph, what is gonna represent a higher speed?
Steeper line
The steepness of a line is called?
Slope
How do you calculate the speed from a distance vs. time graph? What is the formula?
Using a slope measurement, using the formula rise/run or change in distance/change in time.
When plotting speed against time for uniform motion on a graph, what will be produced? What does it indicate?
A straight line which indicates a linear relationship between the speed of the object and time elapsed.
In non-uniform motion, what is the slope of the line also known as?
Acceleration (m/s squared)
What is the formula for calculating distance?
d = vt
Scalar quantity, provide examples.
Anything that we measure with just a number (magnitude).
Time, mass, temperature, distance
Vector quantity, give examples
Anything that we measure that has both a magnitude and a direction.
Velocity, acceleration, displacement
What do we put above vector quantities?
An arrow
When indicating direction, what directions are considered positive or negative?
North, East, Up, and Right = Positive
South, West, Down, Left = Negative
What are 2 important paris of vector and scalar quantities?
Speed and Velocity (Speed is Scalar, Velocity is Vector)
Distance and displacement (Distance is scalar, Displacement is vector)
Distance
Is the total distance you have traveled.
Displacement
Is how far you are away from your starting point.
Both distance and displacement are typically measured in?
Meters (m)
A car travels around a circular 100m track…
If the car travels once around the racetrack, what d does it travel?
If the car travels twice around the racetrack, what d does it travel?
If the care travels once around the racetrack, what is its displacement?
100m
200m
0m
A person walks North 10 km to grab some pizza, then goes to their friend's house which is 4 km south of the pizza place.
a) How much distance have they traveled?
b) What is their displacement from where they started?
a) 14 km
b) 6 km [North]
Your dog runs away from you to fetch a stick that is 250 M to your right. because she was so excited, she overran the stick by an additional 50m. She runs back to grab the stick, and returns it to you.
a) What distance did your dog travel?
b) What is the displacement of your dog when she returns to you with her stick?
a) 6.0 × 10 to the power of 2 m
b) 0.0 m
What are the two options you have when the direction does not lie exactly in the left/right/up/down direction, or exactly in the north/east/south/west direction?
X-axis method
Navigator method
X-axis method, what units are attached to the answers? What happens if the direction is between the axis lines?
Uses a coordinate grid and angles are measured counterclockwise from the positive (right) x-axis.
Give answers with a magnitude and direction.
Degrees are given and there is no positive or negative values.
Navigator Method
This method describes the direction as an angle between 2 of the compass directions (north, east, south, or west).
Directions not on an axis are reported as degrees clockwise from North.
Velocity
Represents the rate of motion AND direction of an object.
Speed
Only represents the rate of motion.
What is the formula for velocity?
velocity = displacement / time
Displacement can also be referred to as?
Change in postion or position.
Usha and Melissa travel from Kathy Creek Crossing South to Nick Brook crossing, and the 30 km takes 2.25 hours. They stay at Nick Brooke Crossing for 1.75 hours, and then head north 45 km to Michael Creek crossing, which takes 3.00 hours.
a)What is their average speed for the entire trip?
b)What is their average velocity for the entire trip?
a) 11 km/h
b) 2.1 km/h [North]
Displacement-time graph
Shows an object's position relative to some point over a given amount of time. It is sometimes called a position-time graph.
Velocity-time graph. What does a horizontal line indicate? Sloped line?
Shows an objects velocity over a given amount of time.
Horizontal line indicates that velocity remained constant.
Sloped lines indicate an object is accelerating or decelerating.
Acceleration, formula?
A change in velocity during a specific time interval.
acceleration = change in velocity / time or acceleration = final velocity - initial velocity / time
A car accelerates from rest to 30 m/s in 5.2 seconds in the East direction. What is its acceleration?
5.8 m/s squared [East]
A car traveling 19.4 m/s East changes its velocity to 25 m/s in 4.5 seconds. Determine the average acceleration of the car in meters per second squared.
1.2 m/s squared [East]
The magnitude of acceleration refers to the change in?
Velocity
A larger magnitude in acceleration indicates that? Smaller?
The velocity of the object is getting FASTER.
The velocity of the object is getting SLOWER.
What are the 2 types of Positive Acceleration?
Both the change in magnitude and the direction of the velocity are POSITIVE.
Both the change in magnitude and the direction of the velocity are NEGATIVE.
A car changes velocities from 2 m/s East to 10 m/s East and 5 seconds (solve). What type of acceleration is this?
2 m/s squared [E]
Positive acceleration
A car changes velocities from 15 m per second West to 5 m per second West in 5 seconds (solve). What type of acceleration is this?
2 m/s squared [E]
Positive acceleration
What are the 2 types of Negative Acceleration?
The change in magnitude of the velocity is NEGATIVE while the direction is POSITIVE.
The change in magnitude of the velocity is POSITIVE while the direction is NEGATIVE.
A car changes velocities from 12 m per second East to 4 m per second East in 4 seconds (solve). What type of acceleration is this?
2 m/s squared [W]
Negative acceleration
A car changes velocities from 2 m per second West to 10 m per second West in 2 seconds (solve). What type of acceleration is this?
4 m/s squared [W]
Negative acceleration
A car traveling 25 m/s accelerates at 0.50 m/s squared while passing another vehicle. If it takes 5.0 seconds to pass the vehicle, determine the final velocity traveled by the vehicle during this time.
28 m/s [East]
On a position-time graph with acceleration (non-uniform motion), does the slope change?
It changes depending on the acceleration.
A passenger car can be moving in the following ways:
A car is moving forward while the brake is applied.
A car is moving backwards while the brake is applied.
A car in reverse ® and moving backwards while the gas pedal is pressed down.
A car is in drive (D) and moving forward while the gas pedal is pressed down.
In which of these ways would the car be moving with positive acceleration?
2 and 4 only
What type of quantities are weight and work?
Weight = vector
Work = scalar
On his way to school, a student walks 50.0 m north, 35.0 M east, 25.0 M north, then walks West for 65.0 m.
a) Calculate the distance that the student traveled. you may find it useful to draw a diagram.
b) Calculate the students displacement. (Note: this is a challenge problem).
c) If the trip took 1.20 minutes, what was the student speed in meters per second? What was the student's velocity in kilometers per hour?
a) 175m
b) 80.8m [68.2 degrees N of W]
c) v = 2.43 m/s, velocity = 4.03 km/h [68.2 degrees N of W]
Provide a summary of how ticker tape works.
This is where a long tape is attached to an object that's moving. That tape is threaded through a device that puts a 'tick,' or impression, on the tape at regular time intervals (for example, every 0.1 or 0.2 seconds). This leaves a line of dots on the tape, recording the object's motion.
The distance between dots on a ticker tape represents the object's position change during that time interval.
The farther the dots the faster the velocity, the closer the dots the slower the velocity.
Use vector components to determine the displacement of a cross country skier who travelled 15.0m [220 degrees] and then 25m [335 degrees].
23m [299 degrees] (Navigator method)
Determine the distance travelled and the displacement: Blading through Fish Creek Park in Calgary takes you 5.0km [W]. 3.0km [N], 2.0km [E], and 1.5 km [S]
d = 11.5 km
displacement = 3.4 km [27 degrees N of W].
Determine the resultant displacement of a skateboarder who rolls 45.0m [310 degrees] and 35.0m [135 degrees].
10.6m [293 degrees]
Tourists on a jet ski move 1.20 km [55 degrees N of E] and then 3.15 km [70 degrees S of E]. Determine the jet ski’s displacement.
2.7 km [48 degrees S of E]
While tracking a polar bear wildlife biologist travels 300m [S] and then 550m [75 degrees N of E]. What is her displacement?
272m [58 degrees N of E]
A 100 m track is marked off in meters. When a sprinter leaves the starting line, timers are started. The sprinter passes a 12m East mark at 1.8 seconds and passes the 56m East mark at 6.7 seconds. What was the sprinter’s velocity between those two positions?
9.0 m/s [E] or +9.0 m/s
The fence posts around a large pasture are 2.5 m apart. A horse starts running West beside the fence. When the horse passes the fifth fence post, your second hand is on the 9.0s mark. When the horse passes the 14 fence post, the second hand is at 11.5 seconds. What is the horse's velocity?
9.0 m/s [W] or -9.0 m/s
Imagine that your house is 0.75 km North from school. Your friend's house is 1.6 km South from school. If it takes you 6.5 minutes to bike to your friend's house, what is your velocity?
-22 km/h or 22 km/h [S]
Quinn is driving down the street in a car at 42 km per hour. Suddenly, a child runs into the street to pick up a ball. If it takes Quinn 0.675 seconds to react and apply the brakes, what was Quinn's acceleration?
-17 m/s squared
Force
A push or pull on an object.
What is force commonly measured in?
Newtons (N)
What are the multiple types pf forces that may exist on an object?
Force of gravity (Fg)
Centripetal force (Fc)
Force of friction (Ff)
Objects at rest do not move because?
All forces acting on it are in BALANCE
Objects will only move when?
An UNBALANCED force is applied to an object over a distance.
A force in one direction needs to be greater than a force in the opposite direction in order to cause movement.
An object in motion will stay in motion unless?
An unbalanced force operates on that object.
Work
When a force is applied to an object against another force, it can result in a transfer of energy.
The transfer (change) of energy results in WORK being done.
In simpler words: Work = A force moving an object through a distance.
What if there is no movement when a force is applied to an object?
No work is done as the object gains no energy.
Work is measured in?
Joules (J)
What is the formula for work?
Force x distance the object travels (F x d)
For work to be done, what are all the three requirements that have to be satisfied.
There must be movement: Pushing an object into a wall has no movement, so no work.
There must be a force being applied:There is no work done by a person when they are coasting on a bike. (Gravity = work)
The force and the distance the object travels must be in the same direction:When someone is pushing uphill against a box sliding downhill, no work is being done.
A weightlifter lifts a barbell a vertical distance to 2.40m. If the average force required to lift the barbell is 2.00 x 10 ^ 3 how much work is done by the weight lifter in the barbell?
4.80 × 10 to the power of 3 J
When work is done to an object, the object gains energy. How does the concept of Work Input and Work Output apply to this?
In a system where the outside forces (friction etc.) are negligible, the total work input equals the total work output.
What is the equation relating work input and work output?
Ein = Eout
WInput = W output
Energy
The ability to do work
In relation to energy, when objects do work they?
LOSE energy
In relation to energy, when objects have work done to them they?
GAIN energy
Work and Energy are what type of quantities?
Scalar (magnitude ONLY)
Work Done = ?
Change in Energy (W = △E)
A change energy can be both?
Decreased or increased (+△E or -△E)
A student applies a force of 100 Newtons to push a heavy wagon a horizontal distance of 35.0 m. How much work is done?
3.50 × 10 to the power of 3 J
A block of cement is lifted 50 m with 2.5 * 10 ^ 4 joules of energy. How much work is being done?
2.5 × 10 to the power of 4 J
A weightlifter does 4.80 * 10 ^ 3 joules of work in lifting a barbell. How much energy is gained by the barbell?
4.80 * 10 ^ 3 J
Force-Distance Graphs
These graphs show the relationship of force being applied to an object over a given distance.
The area underneath a force-distance graph represents?
The WORK done.
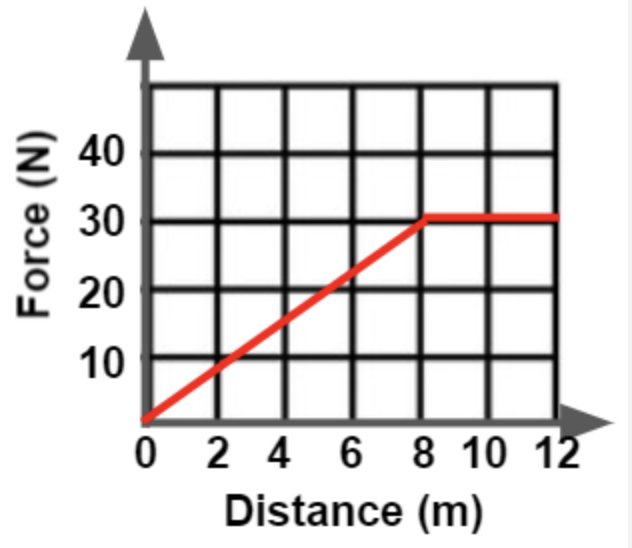
Determine the amount of work done by the force represented on the force-distance graph.
240 J
Potential Energy
The energy stored in an object due to its position relative to some other object.
An object with potential energy has the potential to do what?
WORK
What is the potential energy also equivalent to?
The work done to move that object to its height.
There are multiple types of potential energy. Why?
It depends on how the energy is being stored. (W△E)
eg. Bonds in our food, springs compressed or stretched.
Gravitational potential energy. Does this only happen on Earth?
The energy stored in an object at any position above the Earth.
Could also be on the Moon/Mars/Sun)
What is gravitational potential energy commonly denoted by?
Ep (grav)
In physics, Mass (m) is measured in?
Kilograms (kg)
What type of quantity is Mass?
Scalar
The mass of an object never chnages because?
The amount of matter the object posses is constant.
In physics, Weight (W with an arrow over) is measured in?
Newtons (N)
Weight is what type of quantity?
Vector
The weight of an object depends on its?
Mass (scalar) and acceleration due to gravity (vector).
Weight is a?
Force
What is the equation for weight?
W (with an arrow over) = m x g (with an arrow over)
What is g (with an arrow over)?
The acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s squared.
Calculate the weight of a person with a mass of 50.0kg on the surface of the Earth where the value of acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m per second squared.
Calculate the weight of that same person on the moon where the acceleration due to gravity is 1.62 m/s^2.
What about on Jupiter with acceleration due to gravity is 24.91 m/s^2?.
a) 491N [down]
b) 81.0N [down]
c) 1.25 × 10 to the power of 3 N [down]