CH 13 Viruses and Prions
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Why are viruses considered intracellular parasites?
Multiply inside of a host using the host’s machinery
Viruses can contain what type of nucleic acid?
They can either have RNA or DNA but not both.
What is a host range?
Where viruses can infect only specific types of cells of only 1 host specie.
How can we see a viral’s size?
We observe using an electron microscope. They are smaller than bacteria.
What is usually the range of size for a virus?
Most range from 20 to 1000 nm.
What is the viral’s structure? Be really specific with Nucleic Acid (if they do contain it..)
What is typically the primary genetic material for viruses?
They are complete, with a fully developed viral particle made of nucleic acid and a protein coat.
Nucleic Acid
Either RNA or DNA but never both
Can be single or double stranded
Linear or Circular
DNA is typically the primary genetic material in viruses.
What is the nucleic acid for viruses protected by>?
They are protected by a protein coat called a capsid.
What does a capsid consists of?
Each consists of a protein subunit called capsomere
Can be covered by an envelope.
What can an enveloped virus have?
They can have lipids, carbohydrates and/or proteins on its surface.
What is a non-enveloped virus?
It’s capsids are not covered by an envelope.
The capsid of nonenveloped virus protects the nucleic acid from nuclease enzymes.
What is nuclease enzyme?
Degrades nucleic acids from a host.
Animal viruses are released from the host’s cell. What do they need to be coated with?
They need to be coated with the host cell’s plasma membrane.
Some viruses can have what?
Some viruses can have spikes..
They project from the surface of the envelope
Spikes are used as means of identification
Why can the influenza virus escape the host’s immune system?
Viruses can escape antibodies because of mutations on the surface
Influenza virus constantly undergoes changes in spikes.
Can viruses have extra structures? If so what?
Some bacterial viruses can have complicated structures. They can have a protein tail and a complex outer wall.
What do bacteriophages have?
They have capsids which have an additional structure attached.
A Capsid contains the nucleic acid.
Is influenza A a cross species barrier?
Yes, It is.
Prior to 1998, H1N1I was only pigs
In 1998, H3N2 spread from humans to pigs.
Where is H5 and H7 mostly found? Can it infect us?
They are mostly found in birds. Bird viruses typically don’t infect human
How can we grow animal viruses in living animals in a lab?
Virus is inoculated into an animal
Then the animal is observed for signs of disease or euthanized to study infected tissues.
How can we grow animal viruses in a embryonated egg and cell cultures?
Embryonated egg is used to grow viruses for vaccines.
In cell cultures, cells are isolated from the infected animal tissue and grown in culture media. (We have a solution that mimics the human body)
How can viruses multiply?
They need nucleic acid in a virion. It contains a few of the genes needed to make new viruses.
Their main goal is to replicate and process viral nucleic acid.
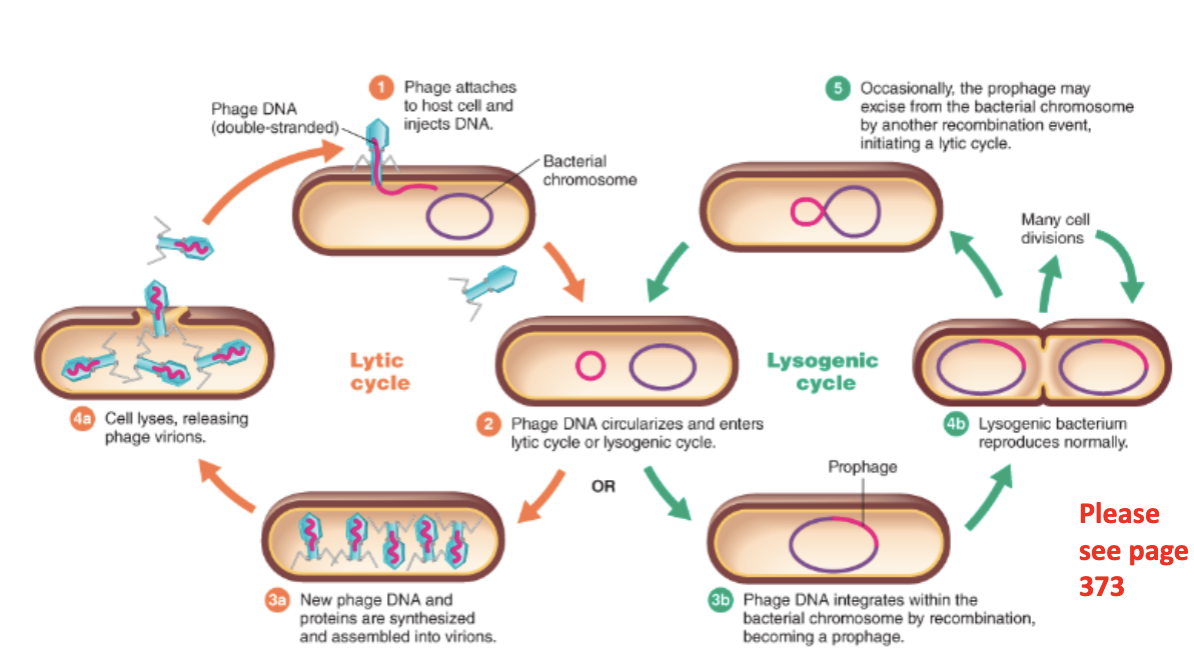
Explain the Lytic Cycle. How do bacteriophages multiply.
In the Lytic Cycle
Bacteriophage attaches to host cells and injects DNA.
Phage DNA circularizes and enters the lytic cycle.
New bacteriophage DNA and proteins are synthesized and assmebled into virions.
Cell lysis, releasing phage virions
Explain the Lysogenic cycle. How do bacteriophages multiply?
Phages attaches to host cell and injects DNA
Phage DNA circularizes and enters the lysogenic cycle
Bacteriophages DNA integrates within the bacterial chromosome by recombintion becoming a prophage
Lysogenic bacterium reproduces normally
Prophage may excise from the bacterial chromosome by another recombination event, initiating a lytic cycle
Which cells are immune to reinfection by the same phage?
Lysogenic Cells
What is Phage Conversion? Be specific.
They can cause the host cell to exhibit new properties
Only streptococci carrying a lysogenic phage can cause toxic shock syndrome
It’s encoded by a prophage gene.
What is specialized transduction?
Bacterial genes are transferred to another m-o
Bacteria DNA is packaged along with phage DNA.
How d animal viruses multiply?
Attachment → Animal viruses attach to the plasma membrane of host cell
Entry → Occurs by receptor-mediated endocytosis or fusion
Uncoating → Animal viruses are uncoated by viral or host cell enzyme
What virus is able to do maturation and release? Explain it!
Animal Viruses are able to do maturation and release.
Animal Virus put together into a protein capsid.
Envelope proteins are incorporated into the host’s plasma membrane.
Budding doesn’t always kill the host.
Non-enveloped viruses are released through breaks in the plasma membrane/they leave by breaking the plasma membrane open
How do Normal Cells turn into Tumor Cells?
Oncogenes cause malignant transformation in cells.
10% of cancers are virus induced
Tumor cells undergo transformation.
Various agents can cause oncogenes to abnormally function
What are latent viral infections?
It can inhibit a host’s cells but not cause damage until it’s activated by a stimulus.
An example is Varicellovirus (chickenpox)
What is Varicellovirus?
(chicken pox)
It’s a childhood skin disease that can exist in a latent state
The virus gains access to the skin via the blood, then enter the nerve cells, where remains latent.
Later changes in the immune response can activate the latent viruses causing shingles.
Read the AIDS and HIV on slide..
Whos more susceptible to HIV infection?
Older adults and young children do not have a fully developed immune system which makes them more in risk.
What are prions?
They are infectious material due to misfolded proteins.
What causes misfolded proteins?
It’s caused by conversion of normal host glycoprotein PrPc into → PrP Sc
What is a Mad Cow Disease?
It’s an infected prion.
Prions cannot be destroyed by heating or cooking infected beef.
What is the source of Mad Cow Disease?
Usually a disease source. It jumped species from infected sheep with scrapie.
What is Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease?
It’s caused by prion infection
Extremely rare, but it’s a terminal brain disease.
They can be sporadic, hereditary, or acquired.
What are the early symptoms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease?
Memory Loss
Loss of coordination
Behavioral Changes
In 1981, clusters of Pneumocystis pneumonia, Kaposi’s sarcoma, and loss of immune function were first discovered in which population group in the United States?
Young homosexual men.
The virus that is responsible for causing loss of immune function, later known as HIV was discovered in what year?
Was discovered in 1983
Where and how did HIV cross over into the human population??
HIV crossed over into the human population in the west and central Africa from chimpanzees around 1908 from bushmeat.
Did urbanization and increased sexual encounters played a role in the spread of HIV throughout Africa? Yes or No?
Yes it did.
When was the earliest known cases of HIV in the Western World?
The earliest known was from a 1969 sample from a patient in Missouri who was confirmed for the HIV infection & Norwegian sailor who died in 1974 is one of the earliest cases in the Western World.
What is HIV? What is the structure that allows it to attach to CD4+ receptors on T helper cells, dendritic cells and macrophages?
HIV is a retrovirus and a Reverse Transcriptase Enzyme.
It has a phospholipid bilayer envelope.
→ Gp120 glycoprotein spikes is the structure that allows attachment.
Explain the body’s initial response to HIV and why the infection cannot be completely cleared. What phase does it occur in?
Once it hits Phase 3, immune system can no longer protect the body effectively. CTLs suppress viral numbers.
HIV later establishes a pool of latently infected CD4+ T cells. Because of this hidden reservoir, infection cannot be eliminated which makes developing a vaccine challenging.
What groups are more susceptible to HIV infection because of weaker immune systems?
Older adults and young children because they have weak immune systems.
Some people can be exposed to HIV but do not become infected because they carry what genetic mutation?
They carry CCR5 mutation.
Long term HIV survivors are often characterized by what?
They have a low viral load and effective CTLs.