APUSH Period 5
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Popular Sovereignty
Notion that the people of a given territory should decide whether to allow slavery.
New York City Draft Riots
Uprising, mostly of working-class Irish-Americans in 1863, in protest of the draft. Rioters were particularly incensed by the ability of the rich to hire substitutes or purchase exemptions.
Sherman's March to the Sea
Destructive march through Georgia from 1864-1865. An early instance of "total war", purposely targeting infrastructure and civilian property to diminish morale and undercut the Confederate War effort.
Freedmans' Bureau
1865-1872. Created to aid newly emancipated slaves by providing food, clothing, medical care, education, and legal support.
Homestead Act of 1862
A federal law that gave settlers 160 acres of land for about $30 if they lived on it for five years and improved it by, for instance, building a house on it. The act helped make land accessible to hundreds of thousands of westward-moving settlers.
Radical Republicans
Congress members that wanted harsh punishment for the South for the Civil War, passed the 13th-15th amendments and impeached Johnson.
Know-Nothing Party
This political party in the 1840s and 1850s carried anti-immigrant sentiments against the Catholic and the Irish and saw some electoral success at the state and local levels.
Free-Soil Party
Political party dedicated to stopping the expansion of slavery. Eventually will merge with other factions to become the Republican party.
Personal Liberty Laws
Laws passed by Northern states in response to the Dred Scott case forbidding the imprisonment of escaped slaves.
Compromise of 1850
California admitted as free state, popular sovereignty in the Mexican Cession to determine if each individual state will be a free or slave state, an end of slave trade in DC, and a fugitive slave law that angered Northerners.
Treaty of Fort Laramie
The first major treaty between the U.S. government and Plains Indians. The United States recognized the Black Hills as part of the Great Sioux Reservation, set aside for exclusive use by the Sioux people. In 1874, however, Gen. George A. Custer led an expedition into the Black Hills accompanied by miners who were seeking gold. Once gold was found in the Black Hills, miners were soon moving into the Sioux hunting grounds and demanding protection from the U.S. Army.
Bleeding Kansas
A sequence of violent events involving abolitionists and pro-Slavery elements that took place in Kansas-Nebraska Territory where popular sovereignty would decide whether a state was to be a slave state or a free state. The dispute further strained the relations of the North and South
Dred Scott v. Sanford
1857 Supreme Court case that decided US Congress did not have the power to prohibit slavery in federal territories and slaves, as private property, could not be taken away without due process. Invalidated the Missouri Compromise as basically the decision allowed for slavery anywhere.
Sand Creek Massacre
1864 incident in which Colorado militia killed a camp of Cheyenne and Arapaho Indians
Fourteenth Amendment
Amendment that made "all persons born or naturalized in the United States" citizens of the country
Fifteenth Amendment
The constitutional amendment adopted in 1870 to extend suffrage to African Americans.
Manifest Destiny
A notion held by a nineteenth-century Americans that the United States was destined to rule the continent, from the Atlantic the Pacific.

Mexican-American War
(1846-1848) The war between the United States and Mexico.
Gadsden Purchase
Purchase of land from Mexico in 1853 that established the present U.S.-Mexico boundary
Secession
Formal withdrawal of states or regions from a nation
Uncle Tom's Cabin
Written by Harriet Beecher Stowe in 1853 that highly influenced England's view on the American Deep South and slavery. A novel promoting abolition. intensified sectional conflict. Believed to be the most popular book (in terms of sales) in the 19th century.
John Brown's Raid
Began when he and his men took over the arsenal in Harpers Ferry, Virginia, in hopes of starting a slave rebellion.

Battle of Vicksburg
Grant besieged the city from May 18 to July 4, 1863, until it surrendered, yielding command of the Mississippi River to the Union.

Ulysses S Grant
An American general and the eighteenth President of the United States (1869-1877). He achieved international fame as the leading Union general in the American Civil War.
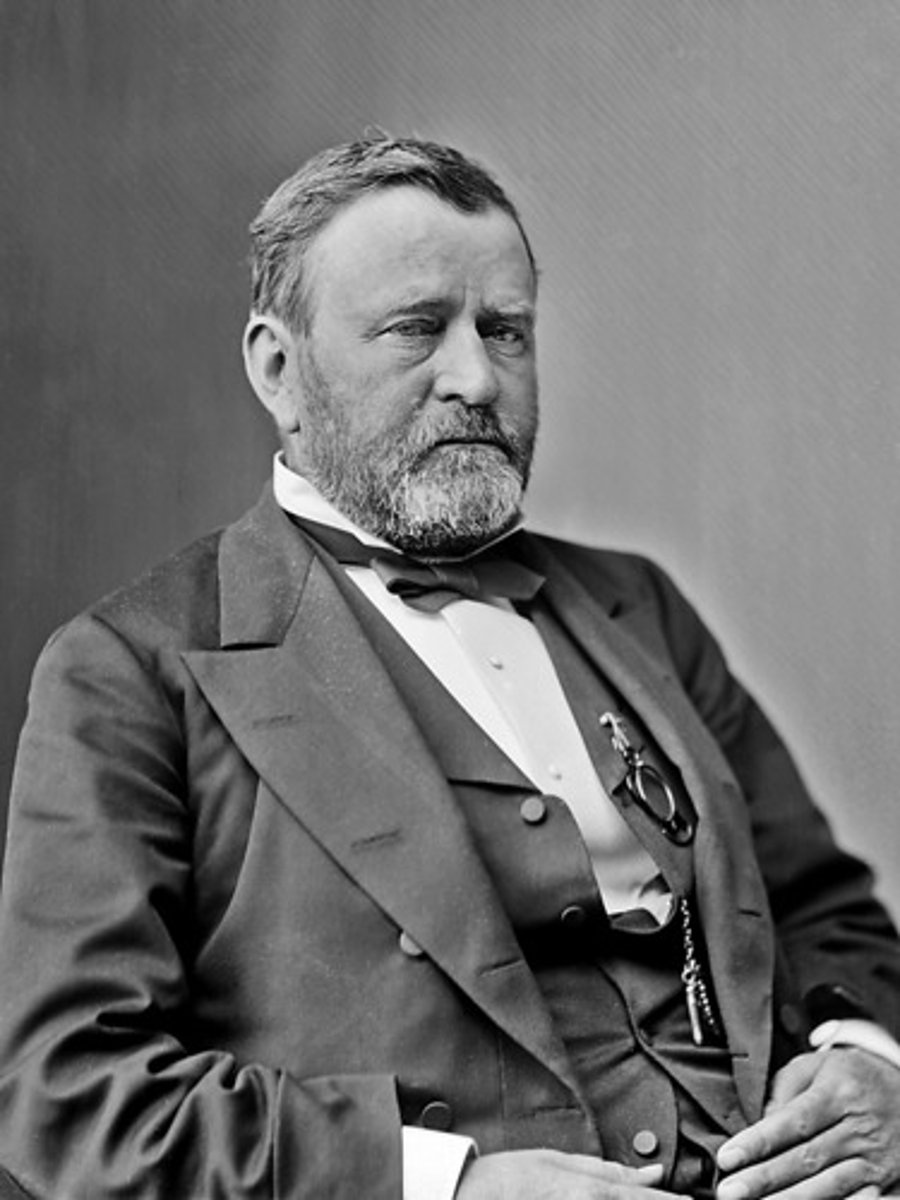

Presidential Reconstruction
President's idea of reconstruction : all states had to end slavery, states had to declare that their secession was illegal, and men had to pledge their loyalty to the U.S.

Radical Reconstruction
Reconstruction strategy that was based on severely punishing South for causing war. Also known as Congressional Reconstruction.

Military Reconstruction Act
1867; divided the South into five districts and placed them under military rule; required Southern States to ratify the 14th amendment
Reconstruction Amendments
13th-15th Amendments are known as the
Carpetbagger
A northerner who went to the South immediately after the Civil War; especially one who tried to gain political advantage or other advantages from the disorganized situation in southern states
Scalawags
White southerners who supported the Republicans during Reconstruction
Harriet Tubman
United States abolitionist born a slave on a plantation in Maryland and became a famous conductor on the Underground Railroad leading other slaves to freedom in the North
Wilmot Proviso
1846 bill that would ban slavery in the territories acquired after the War with Mexico. It failed to become law. The Compromise of 1850 later determined how to deal with admission of states from the Mexican cession.
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
Treaty that ended the Mexican War, granting the U.S. control of Texas, New Mexico, and California in exchange for $15 million
Harriet Beecher Stowe
Wrote Uncle Tom's Cabin
Apologists
Christian thinkers who defended slavery and explained its "positive good" through Christian beliefs
49ers
People who rushed to California in 1849 for gold.
Confederate States of America
a republic formed in February of 1861 and composed of the eleven Southern states that seceded from the United States
Anaconda Plan
Union war plan by Winfield Scott, called for blockade of southern ports to cut off cotton exports and prevent the import of manufactured goods.
Morrill Land Grant of 1862
The act gave federal lands to states for the purpose of building universities that would teach agriculture and technical trades
Pacific Railway Act of 1862
This act approved the building of a transcontinental railroad that would utterly transform the West by linking the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific
Reconstruction
The period after the Civil War in the United States when the southern states were reorganized and reintegrated into the Union
Civil Rights Bill of 1866
first congressional attempt to guarantee black rights in the South, passed over Johnson's veto
Black Codes
Southern laws designed to restrict the rights of the newly freed black slaves
Positive Good
what Proslavery whites said about slavery as a response to the abolitionist outcry. Claimed slavery provided safe housing and meals for African Americans.
Bear Flag Revolt
(1846) a revolt that took place during the Mexican American War when 500 Americans (Anglos) in Mexican California took the city of Sonoma, CA in the spirit of Manifest Destiny and declared California to be an independent nation
Californios
descendants of Spanish and Mexican conquerors; Spanish speaking inhabitants of California, they became Americans after the Mexican-American war but faced discrimination.
Liberty Party
a former political party in the United States; formed in 1839 to oppose the practice of slavery; merged with the Free Soil Party in 1848.
Oregon Fever
Movement where over 5,000 Americans migrated to the Oregon Territory via the Oregon Trail, representing the first mass migration to the West coast.
John C. Calhoun
Senator who argued for states' rights for the South.
Matthew C. Perry
Military leader who convinced the Japanese to sign a treaty in 1853 with the U.S. The treaty allowed for a commercial foot in Japan which was helpful with furthering a relationship with Japan.
Fugitive Slave Law
Law that required Notherners to "round up" runaway slaves and ship them back South.
Underground Railroad
Secret route that led many slaves to freedom in the North and eventually Canada.
Kansas-Nebraska Act
An act proposed by Senator Stephen Douglas that stated that slavery in Kansas and Nebraska would be decided by popular sovereignty, ending the Missouri Compromise exclusion of slavery north of latitude 36°30′.
Charles Sumner
Senator who was publicly beaten by Preston Brooks for speaking out against the violence in Kansas. After the Civil War, he spoke out for black freedom and racial equality.
Roger Taney
Chief justice of the Supreme Court who wrote the opinion in the 1857 Dred Scott case that declared blacks property.
Abraham Lincoln
politician who debtated Stephen Douglas and was nominated for the presidency by the Republican party in 1860. Inaugurated as president on March 4, 1861
Jefferson Davis
President of the Confederate States of America
Panic of 1873
Financial panic in which banks closed and the stock market crashed
Lincoln-Douglas Debates
When Lincoln challenged Stephen Douglas to debates during the senatorial race of 1858 which Lincoln ultimately lost (but helped him become more prominent). Also known as the Great Debates.
Border States
Delaware, Kentucky, Maryland, Missouri, and West Virginia
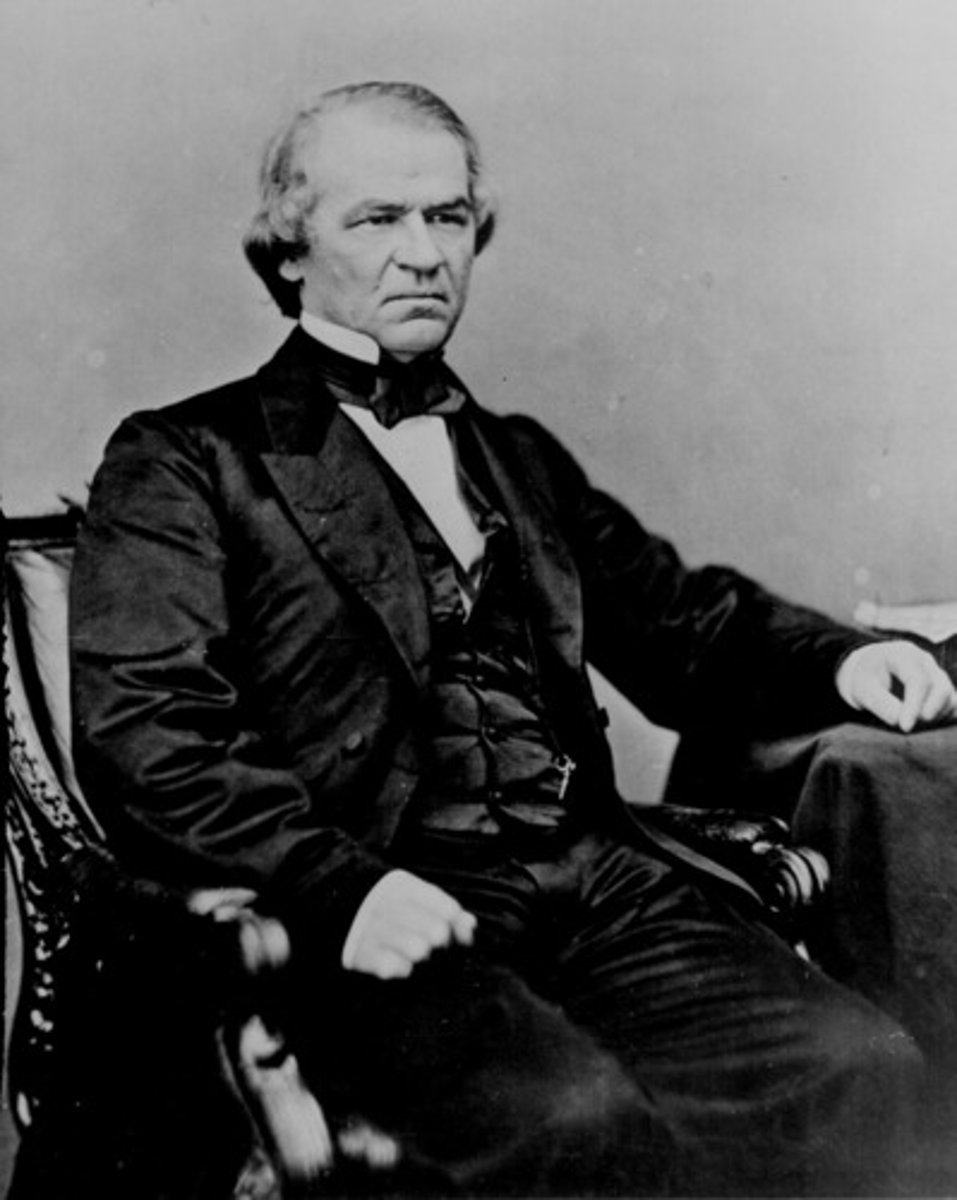
Andrew Johnson
17th President of the United States, A Southerner form Tennessee, as V.P. when Lincoln was killed, he became president. He opposed radical Republicans who passed Reconstruction Acts over his veto. The first U.S. president to be impeached, he survived conviction on impeachment charges by only one vote.
John Wilkes Booth
Southerner who assasinated Abraham Lincoln on April 14, 1865
Robert E. Lee
general of the Confederate Army.
Emancipation Proclamation
(1862) An executive order issued by President Abraham Lincoln freeing the slaves in areas rebelling against the Union; took effect January 1, 1863
Thirteenth Amendment
the constitutional amendment ratified after the Civil War that forbade slavery and involuntary servitude.
First Battle of Bull Run
(July 1861) first major conflict of the Civil War. Southern victory led to overconfidence.
Battle of Antietam
(September 1862) bloodiest day of the Civil War.
Battle of Gettysburg
(1863) this three day battle was the bloodiest battle of the entire Civil War, ended in a Union victory, and is considered the turning point of the war.
Gettysburg Address
(1863) a speech given by Abraham Lincoln after the Battle of Gettysburg, in which he praised the bravery of Union soldiers and renewed his commitment to winning the Civil War; supported the ideals of self-government and human rights
Wade-Davis Bill
bill pushed by Congress in 1864 that required 50 percent of a state's voters take the oath of allegiance and demanded stronger safe-guards for emancipation than proposed in Lincoln's 10 percent plan. Pocket-vetoed by Lincoln.
10 Percent Plan
Lincoln's plan for re-admitting the Southern states into the Union: a state could be reintegrated into the Union when 10 percent of its voters in the presidential election of 1860 had taken an oath of allegiance to the United States and pledged to abide by emancipation.
Sharecropping
A system used on southern farms after the Civil War in which former landowners "rented" plots of land to blacks and poor whites who worked the land owned by someone else in return for a small portion of the crops. Renters did this in such a way that the farmers were always in debt and therefore tied to the land.
Redeemers
largely former slave owners who were the bitterest opponents of the Republican program in the South. Staged a major counterrevolution to "redeem" the south by taking back southern state governments. Their foundation rested on the idea of racism and white supremacy.
Ku Klux Klan
the "Invisible Empire of the South", founded in Tennessee in 1866, made up of embittered white Southerners. They would terrorize, mutilate, and even murder "upstart" blacks to "keep them in their place".
Tenure of Office Act
Law requiring the president to secure the consent of the Senate before he could remove his appointees once they had been approved by that body. Led to Johnson's impeachment when he violated the law, which Johnson felt unconstitutional.
Seward's Folly
refers to the United States' Secretary of State William Seward's decision to purchase the Alaskan territory from Russia in 1867. At the time, Seward's decision to buy the land was regarded as a terrible one by many critics in the United States.
Comstock Lode
First discovered in 1858, some of the most plentiful and valuable silver was found here, causing many Californians to migrate here, and settle Nevada.
Safety Valve Theory
Theory that people from the city could always fall back on the frontier if things didn't work out in the city
Mormons
Church founded by Joseph Smith in 1830 with headquarters in NY. Eventually moved to IL then UT.
Brigham Young
Successor to the Mormons after the death of Joseph Smith; responsible for its establishment in Salt Lake City, Utah (note in 2018 the church signaled it prefers Mormon no longer be used but rather the term Latter Day Saints, however many videos and textbooks created in years prior will still use the old term)
Mexican Cession
Historical name for the region of the present day southwestern United States that was ceded to the U.S. by Mexico in 1848 under the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo following the Mexican-American War.
Clipper ships
Small, swift vessels that gave American shippers an advantage in the carrying trade. Clipper ships were made largely obsolete by the advent of sturdier, roomier iron steamers on the eve of the Civil War.
Nativism
A policy of favoring native-born individuals over foreign-born ones
Battle of Little Bighorn
In 1876, Indian leaders Sitting Bull and Crazy Horse defeated Custer's troops who tried to force them back on to the reservation, Custer and all his men died. Also known as Custer's Last Stand.
Assimilation
the social process of absorbing one cultural group into another
Lone Star Republic
Nation formed in 1835 by Texans who declared independence from Mexico
Sutter's Mill
Where gold was first discovered in 1848; marked the beginning of the California Gold Rush
Joseph Smith
Religious leader who founded the Mormon/Latter Day Saints Church in 1830.
James Polk
11th President of the United States from Tennessee; committed to westward expansion; led the country during the Mexican War; U.S. annexed Texas and took over Oregon during his administration
Spot Resolutions
Measures introduced by Illinois congressman Abraham Lincoln, questioning President James K. Polk's justification for war with Mexico. Lincoln requested that Polk clarify precisely where Mexican forces had attacked American troops. Anti-slavery individuals like Lincoln were afraid of acquiring more territory / spreading slavery.
Abolitonist
A person who wanted to end slavery
German belt
Stretches from Pennsylvania to Oregon, all along the North and Midwest. Many who settled these areas were farmers.
Potato Famine
(1840s) one of the worst famines in modern history; Irish peasants relied on potatoes, but a plant fungus killed most of them → millions starved→ mass immigration to US, Canada, and Australia
Indian Wars
1850 to 1890; series of conflicts between the US Army / settlers and different Native American tribes on the Plains
Great Sioux War
Conflict between Sioux and Cheyenne Indians and federal troops over lands in the Dakotas in the mid-1870s.
Republican Party
Organized in 1854 by antislavery Whigs, Democrats, and Free Soilers in response to the passage of the Kansas-Nebraska Act; nominated John C. Frémont for president in 1856 and Abraham Lincoln in 1860
The Impending Crisis of the South
A book by a southern writer Hinton R. Helper that argued that slavery especially oppressed poor whites
Preston Brooks
Was a Congressman from South Carolina, notorious for brutally assaulting senator Charles Sumner on the floor of the United States Senate.
Crittenden Compromise
A last-ditch effort in 1860 to resolve the secession crisis by compromise. Was rejected.
Crop Lien System
Merchants extended credit to tenants based on their future crops, but high interest rates and the uncertainties of farming often led to inescapable debts.