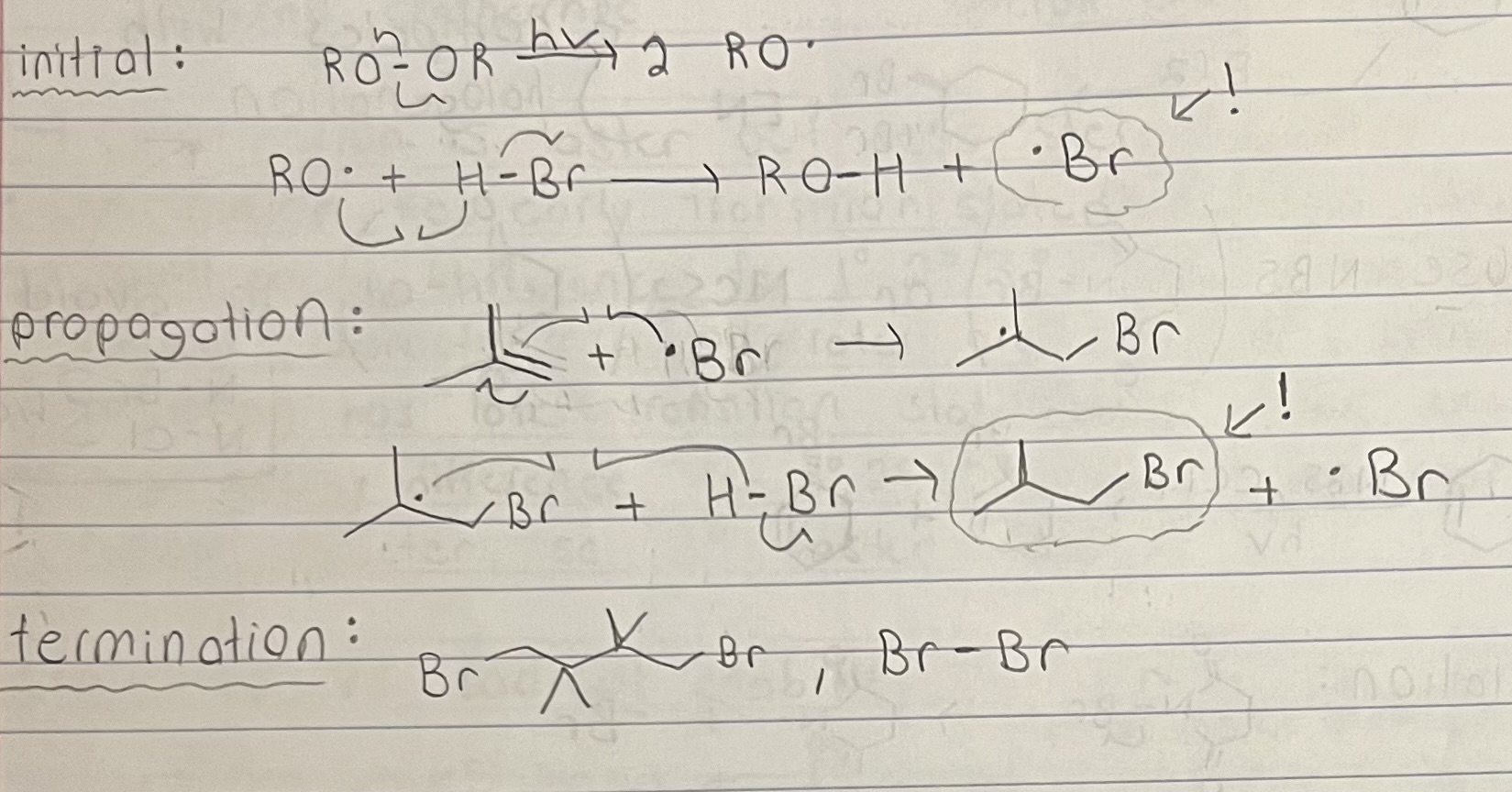ORGO 1 - Chapter 10 - Radical Reactions
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
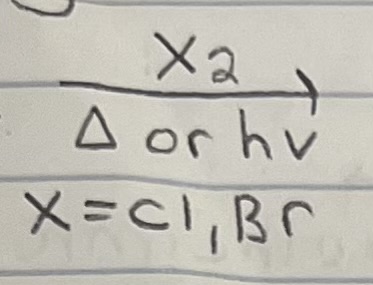
Chlorination on Alkane
Radical mechanism (initiation, propagation, termination).
Chlorination is less stereospecific because of an early transition state (less radical character). There is a small energy difference for each type of radical (1,2,3) since transition state has less radical character, so all rates are relatively similar.
Racemization possible since radical intermediate has rapid inverting or is flat, depending on geometry (trig planar radical (sp2) or shallow pyramidal (sp3)).

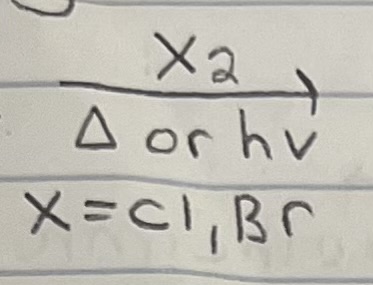
Bromination on Alkane
Radical mechanism (initiation, propagation, termination).
Bromination is more stereospecific because of a late transition state (more radical character). There is a large energy difference for each type of radical (1,2,3) since transition state has more radical character and more stable radical intermediate.
Racemization possible since radical intermediate has rapid inverting or is flat, depending on geometry (trig planar radical (sp2) or shallow pyramidal (sp3)).

Fluoroination/Iodination on Alkane
Fluorination on alkane not done because it is too explosive (delta H too large and negative).
Iodination on alkane not done because it is nonspontaneous. Delta H is positive.
G = H - TS
For these reactions, G only depends on H because change in entropy is too little.
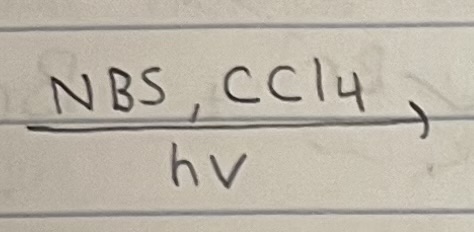
Allyic Bromination (With NBS)
Allylic position C-H bond weakest due to resonance stabilization.
Allylic bromination competes with halogenation when Br2 and hv is used, so NBS or NCS (weak N-Br and weak N-Cl) is used so that only allylic bromination occurs and halogenation doesn’t.
Racemization possible since radical intermediate has rapid inverting or is flat, depending on geometry (trig planar radical (sp2) or shallow pyramidal (sp3)).
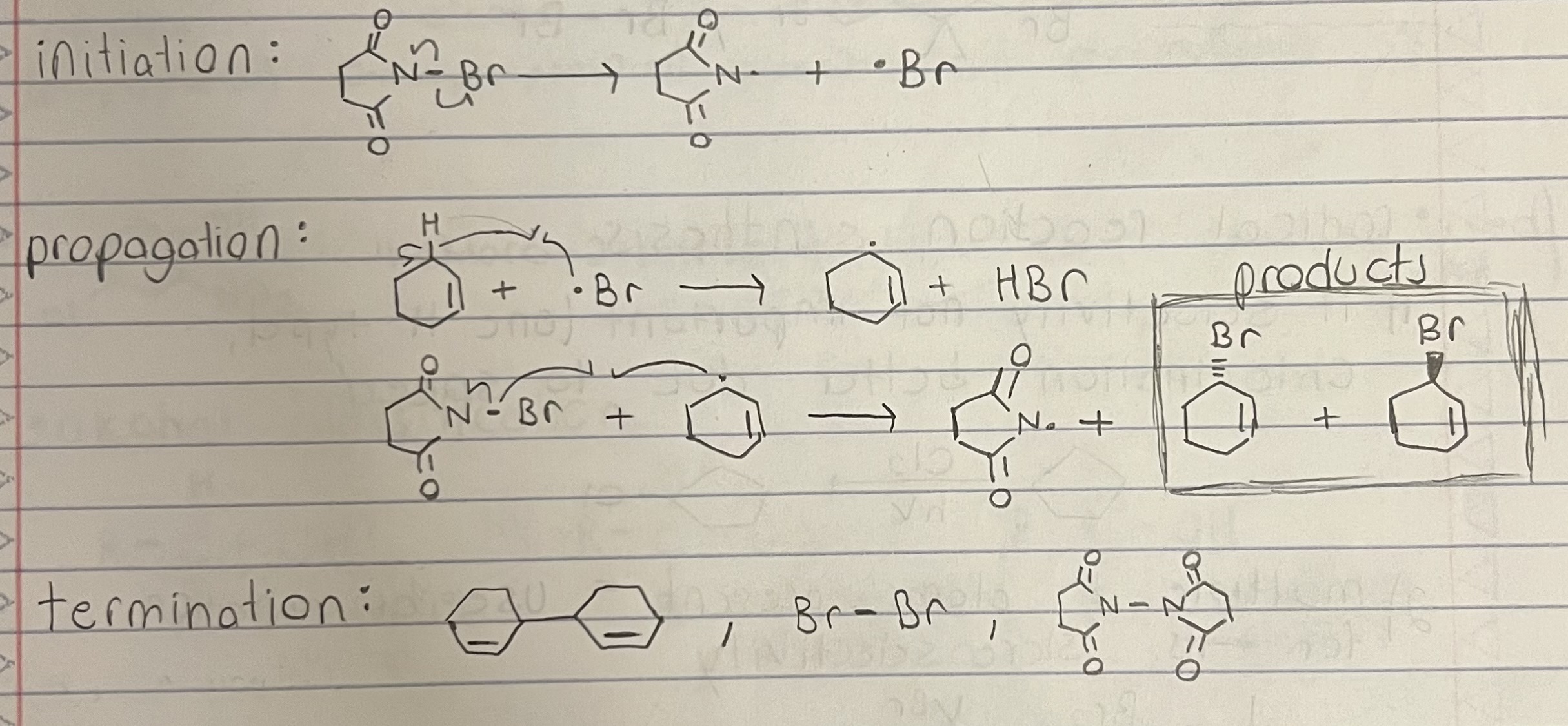
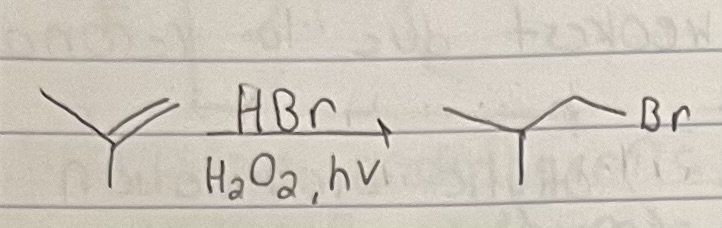
Anti-Markovnikov Addion of HBr on Alkene
Br added to anti-markovnikov position and H added to markovnikov position. Occurs via a radical mechanism.