1.1 - 1.3, 1.8-1.11, 4.5, 4.6, 4.8 AP ES Unit 1A & 4 (Species Interactions, Biomes, Nutrient Cycling, Ecosystem Productivity, Trophic Levels, Energy Flow, Food Webs & Food Chains)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Trophic levels
The hierarchical levels of the food chain through which energy flows from primary producers to primary consumers, secondary consumers and so on.
Omnivore
A consumer that eats both plants and animals
Carnivore
A consumer that eats only animals.
Herbivore
A consumer that eats only plants.
First law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
second law of thermodynamics
when energy is changed from one form to another, some useful energy is always degraded into lower quality energy (usually heat)
Energy pyramid
Shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another in a food web
10% rule
Only 10% of the total energy produced at each trophic level is available to the next level. The amount of energy passed up to the levels of the food pyramid reduces as you go up.
Food chain
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
Food web
a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
producers (autotrophs)
Organisms that make their own food
Ecological pyramids
illustration of the relative amounts of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a given food chain or food web
Primary consumers
animals that feed on producers; ex. herbivores
secondary consumers
carnivores that eat herbivores
tertiary consumers
carnivores that eat secondary consumers
heterotrophs
An organism that obtains organic food molecules by eating other organisms or their by-products.
Competition
A common demand by two or more organisms upon a limited supply of a resource; for example, food, water, light, space, mates, nesting sites. It may be intraspecific or interspecific.
Resource partitioning
The division of environmental resources by coexisting species such that the niche of each species differs by one or more significant factors from the niches of all coexisting species
Ecological niches
the role an organism plays in its environment
Fundamental niche
The niche species could potentially occupy.
Realized niche
The niche species actually occupies.
Competitive exclusion
Strong competition can lead to local elimination of one of the species.
predator-prey relationship
Interaction between two organisms of different species in which one organism, called the predator, captures and feeds on parts or all of another organism, called the prey.
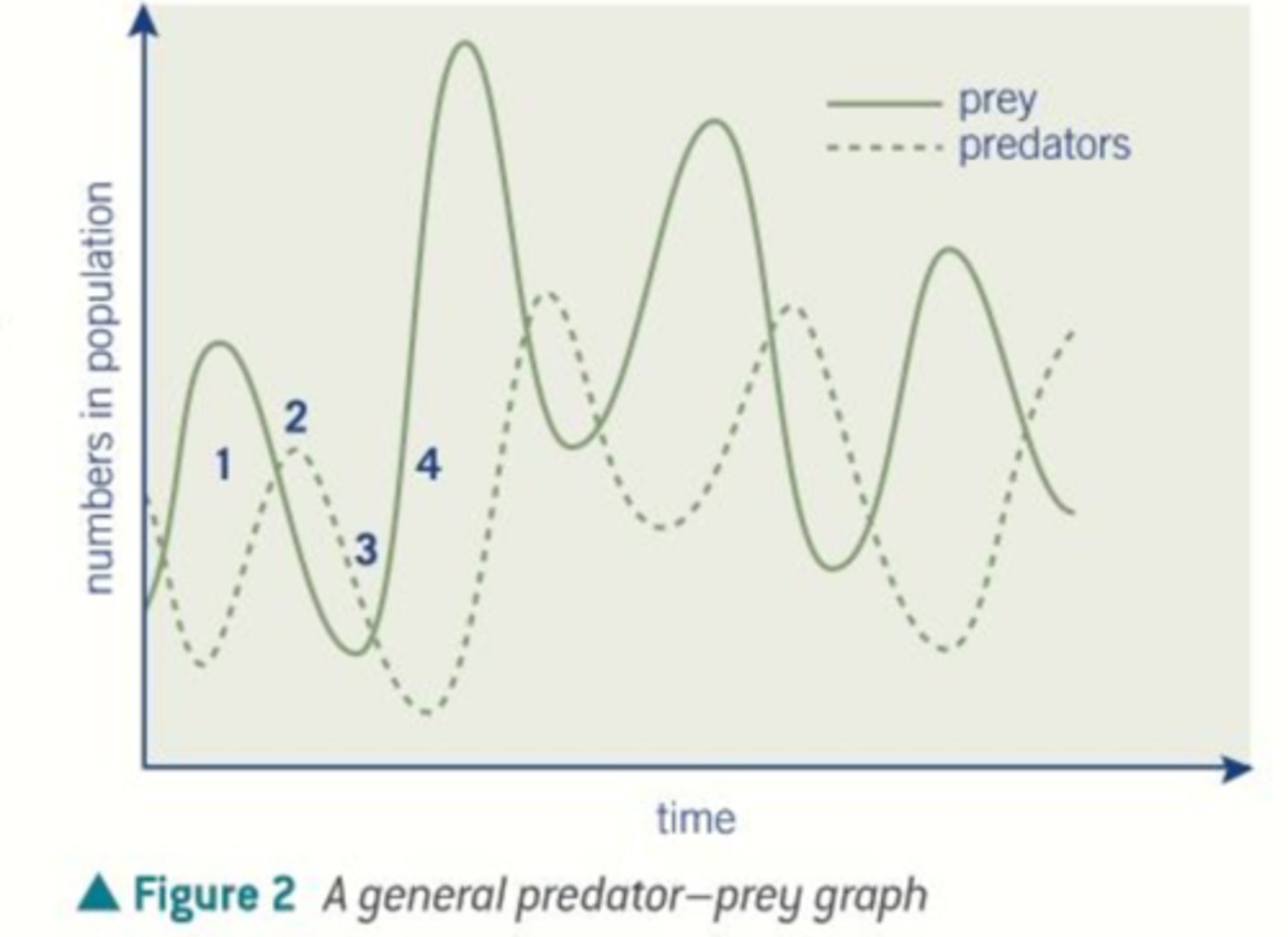
predator-prey graph
This is a graph that has peaks and valleys for two different species with the prey population greater than the predator graph. The predator graph lags behind the prey graph.
Symbiosis
A relationship in which two different organisms live in close association with each other
Mutualism
symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit from the relationship
Mutualism example
A clown fish lives with a sea anemone
Commensalism
A symbiotic relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
Commensalism example
barnacles live on whales. Whales are not affected, and barnacles feed on water that passes over them
Parasitism
A symbiotic relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed
Parasitism example
A Tick feeds on the blood of a human, negatively impacting the health of the human
Latitude
distance north or south of the Equator, measured in degrees
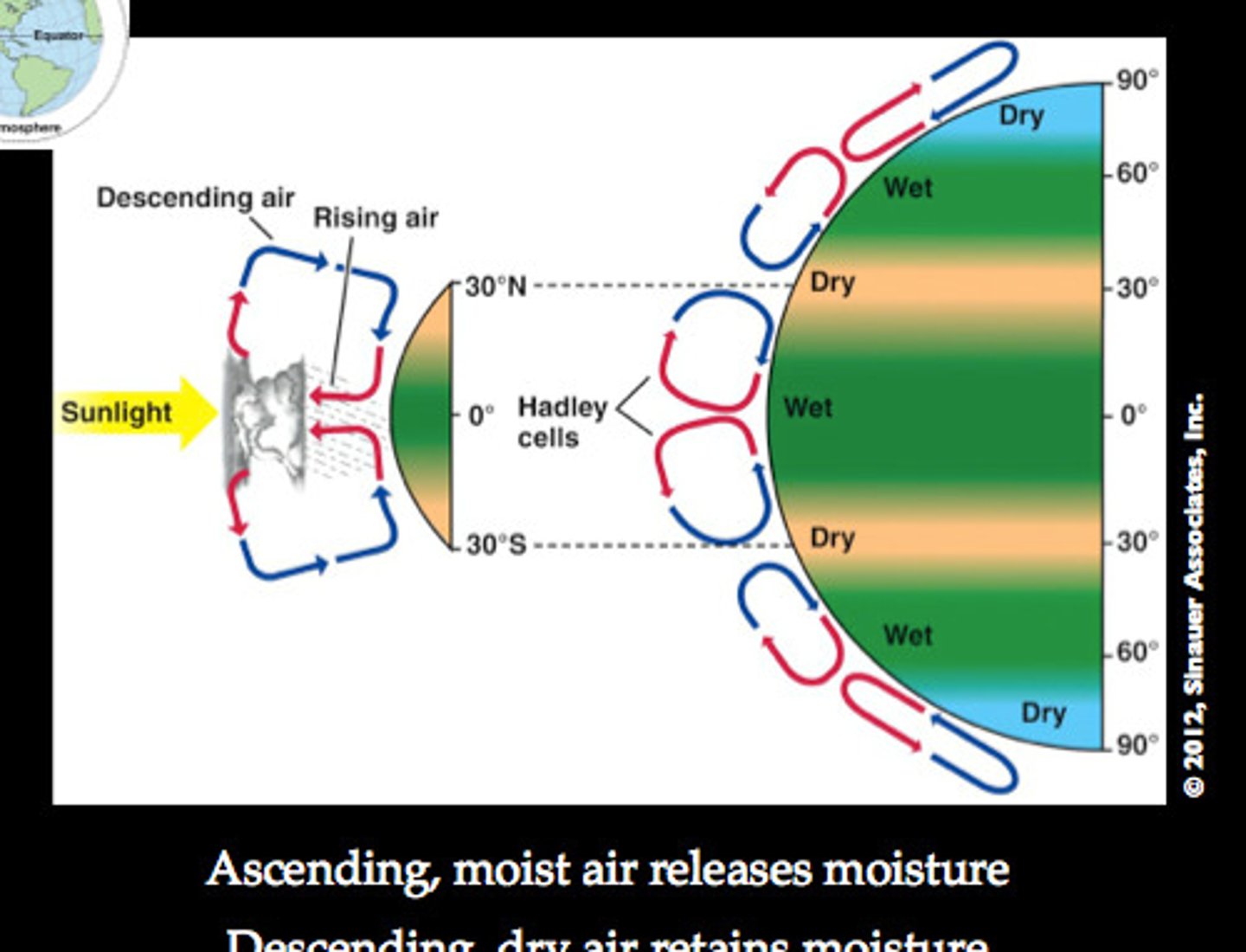
Hadley Cell
a large-scale atmospheric convection cell in which air rises at the equator and sinks at medium latitudes, typically about 30° north or south.
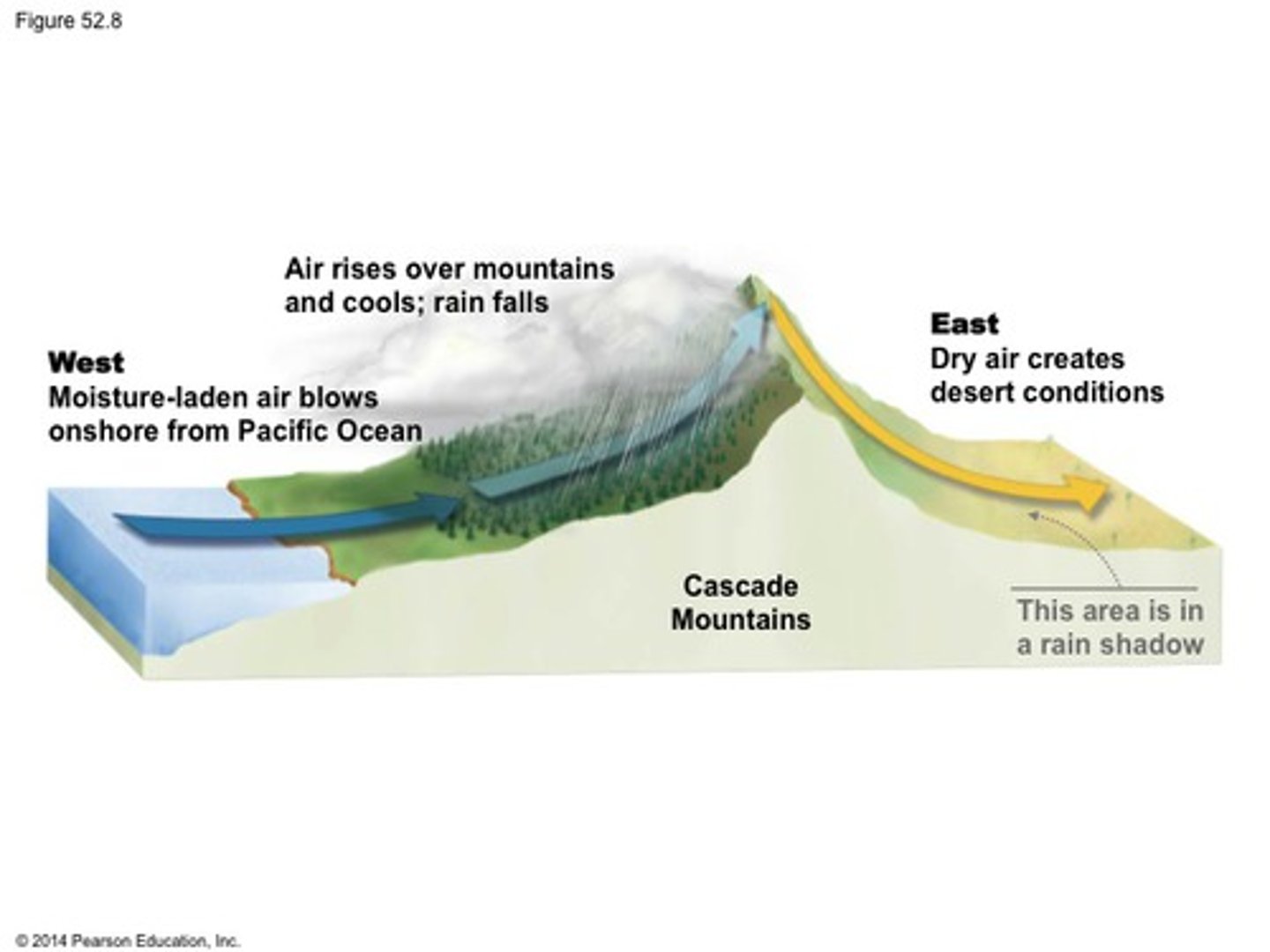
rain shadow
a region with dry conditions found on the leeward side of a mountain range as a result of humid winds from the ocean causing precipitation on the windward side
Primary productivity
rate at which solar energy (sunlight) is converted into organic compounds (glucose, cellulose, etc.) via photosynthesis over a unit of time.
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
total rate of photosynthesis in a given area
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The rate of energy storage by photosynthesizers in a given area, after subtracting the energy lost to respiration.
Net Primary Productivity Equation
NPP = GPP - respiration