Refraction and Total Internal Reflection
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
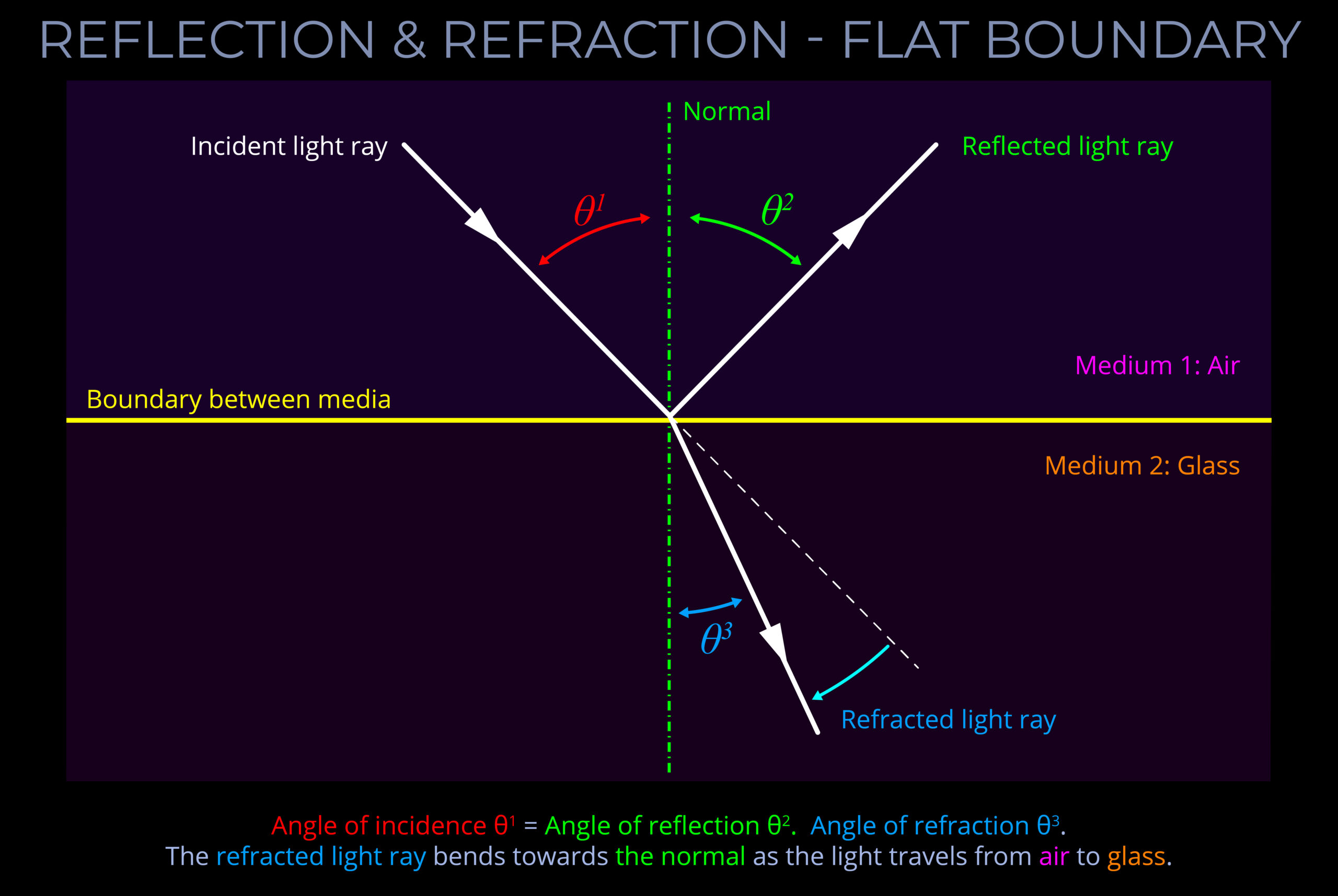
Refraction
Refraction is the bending of a wave, like light, as it passes from one medium to another where the speed of the wave changes
Draw a diagram for refraction and reflection
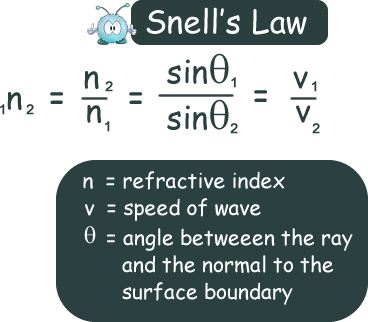
What is the refractive index of a material
The ratio of sini/sinr
Snell’s Law
What is the refractive index of light in space and air?
1
What happens to the velocity, frequency and wavelength of an EM wave as it travels from an optically less dense to an optically more dense medium?
Velocity: decreases
Frequency: unchanged
Wavelength: decreases
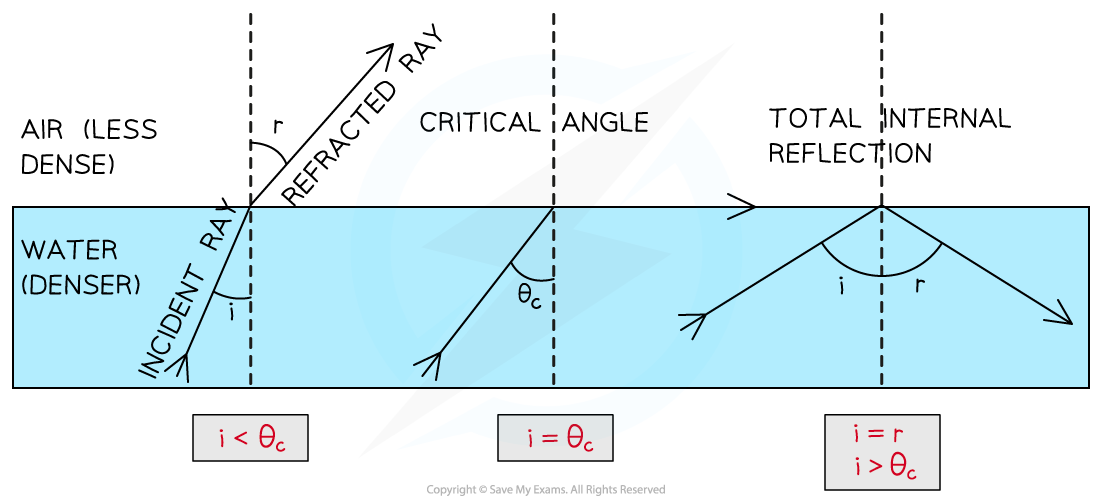
Total internal reflection
Total internal reflection (TIR) is a phenomenon where light traveling from a denser medium (like glass or water) to a less dense medium (like air) is completely reflected back into the denser medium instead of being refracted.
What conditions are required for total internal reflection to take place?
The incident substance has a larger refractive index than the other substance
The angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle
What happens when the critical angle = the angle of incidence?
A refracted ray at 90°
Total internal reflection diagram
Fibre optics diagram
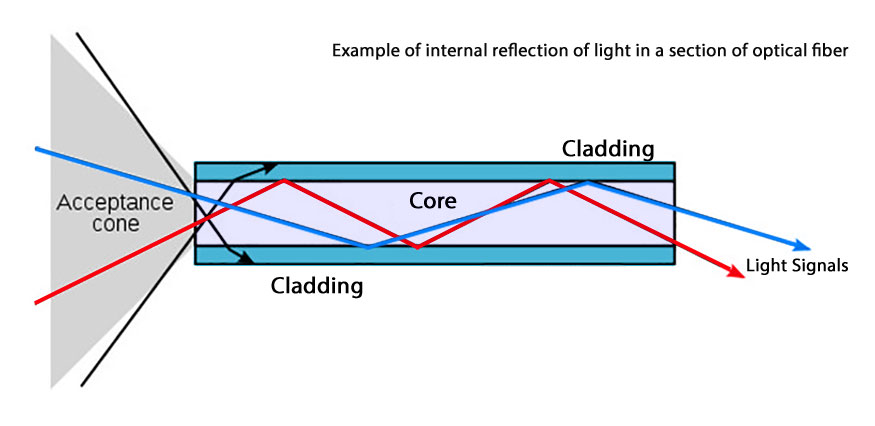
Refractive index between the cladding and core
The cladding has a lower refractive index than the core
What does the cladding do?
The cladding protects the core from damage while assisting total internal reflection
Why must the core be narrow?
To prevent multipath dispersion, where multiple light rays catch up with each other
An optical fibre consists of a core, cladding and an outer sheath. State the purpose of the outer sheath in an optical fibre
Prevents damage to the fibre
Explain why optical fibres used for communications need to have cladding
Keeps signal secure
Maintains quality
It keeps light rays in (due to internal reflection)