Comprehensive Guide to Amino Acids, Peptides, and Protein Structure
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Amino Acids
Building blocks of protein.
Proteins
Main agents of biological function.
Catalysis
The process by which enzymes accelerate chemical reactions.
Transport
The function of proteins that involves moving substances across cell membranes.
Structure
The role of proteins in providing support and shape to cells and tissues.
Motion
The function of proteins that enables movement in muscle tissue.
α-amino acids
The building blocks of proteins, characterized by having an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a unique R group.
Chirality in Amino Acids
All amino acids are chiral except glycine.
L amino acids
The form of amino acids that proteins only contain.
Classification of Amino Acids
Common amino acids can be classified into five groups based on their R substituents.
Nonpolar, aliphatic amino acids
A group of amino acids that includes 7 members.
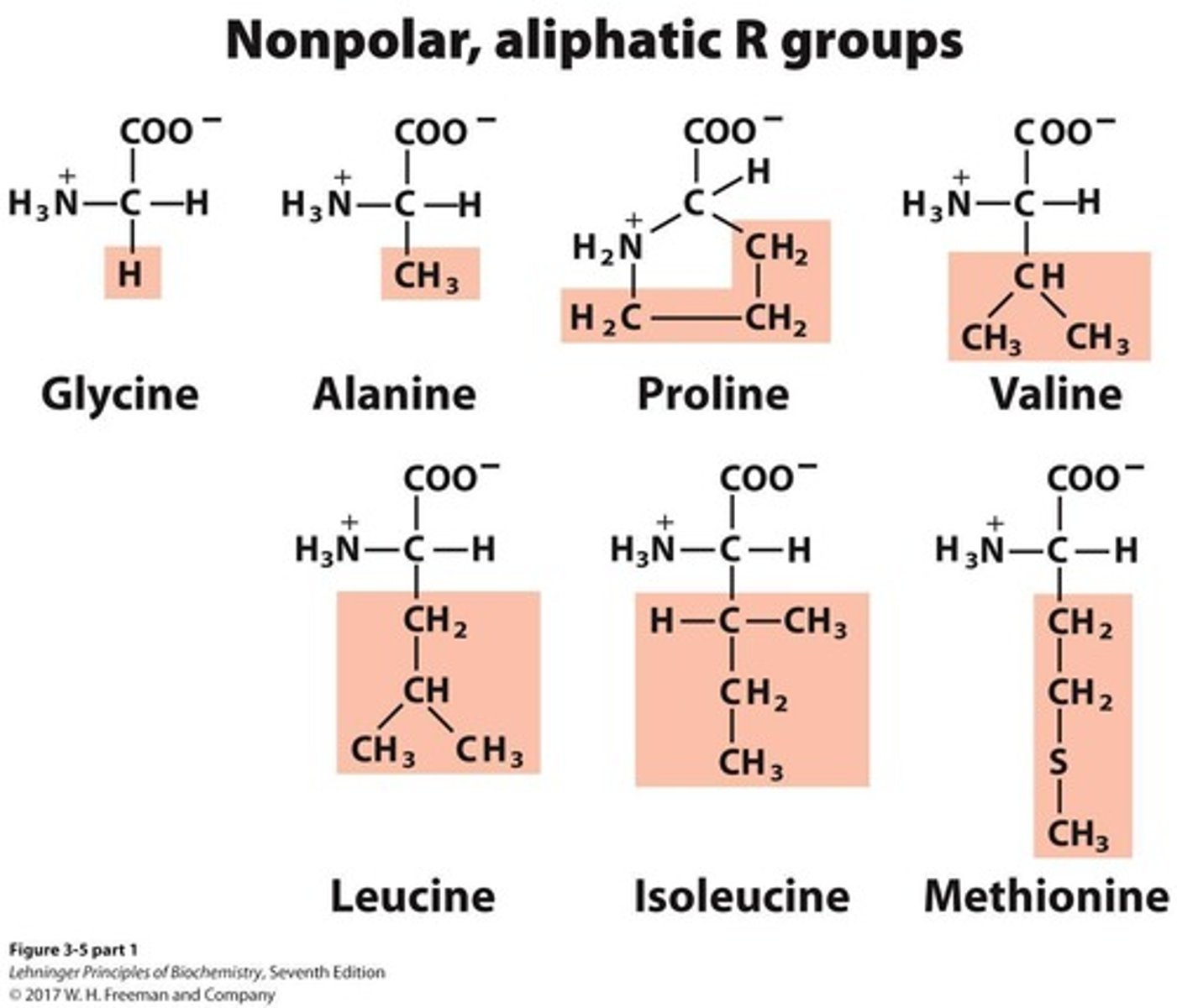
Aromatic amino acids
A group of amino acids that includes 3 members.
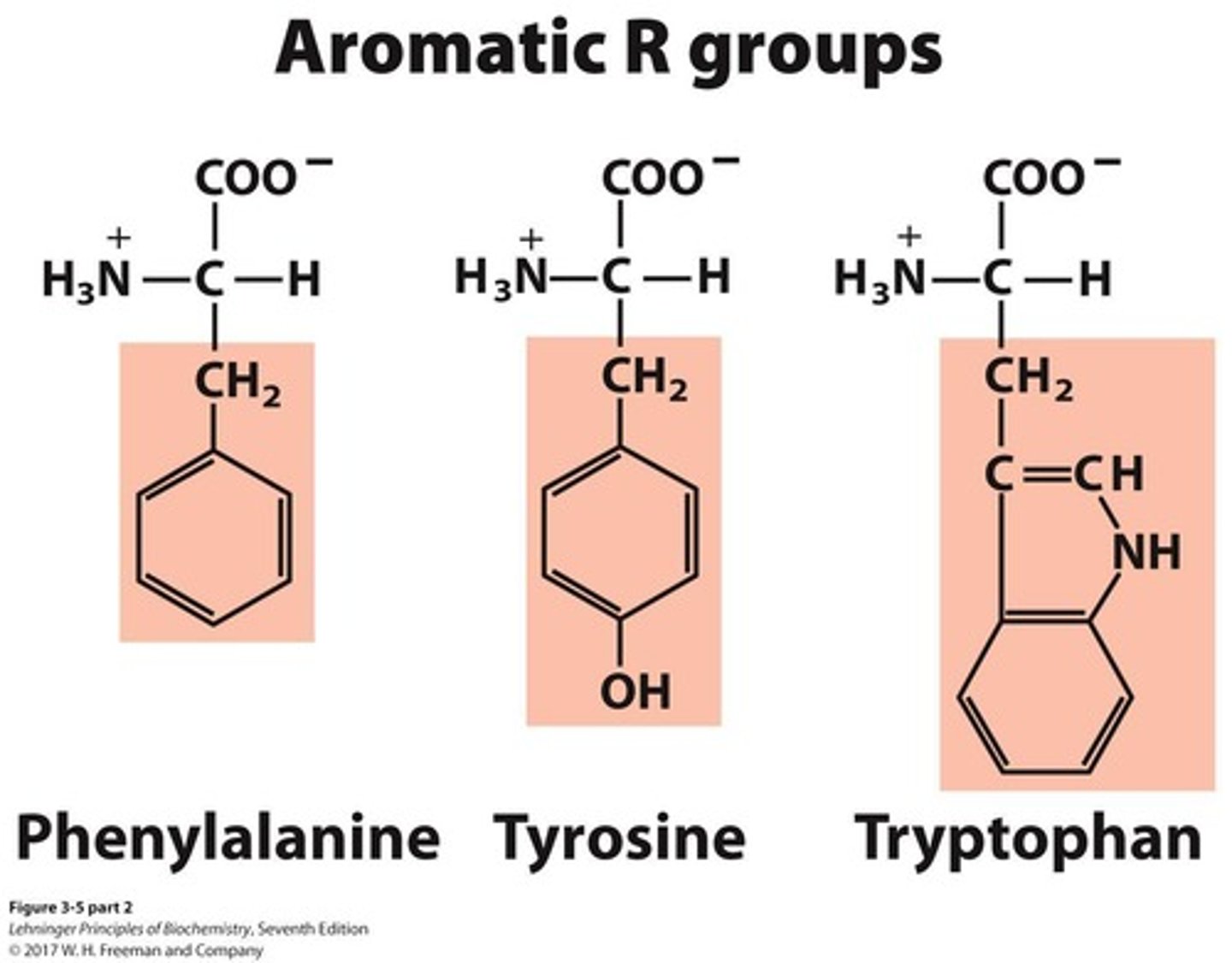
Polar, uncharged amino acids
A group of amino acids that includes 5 members.
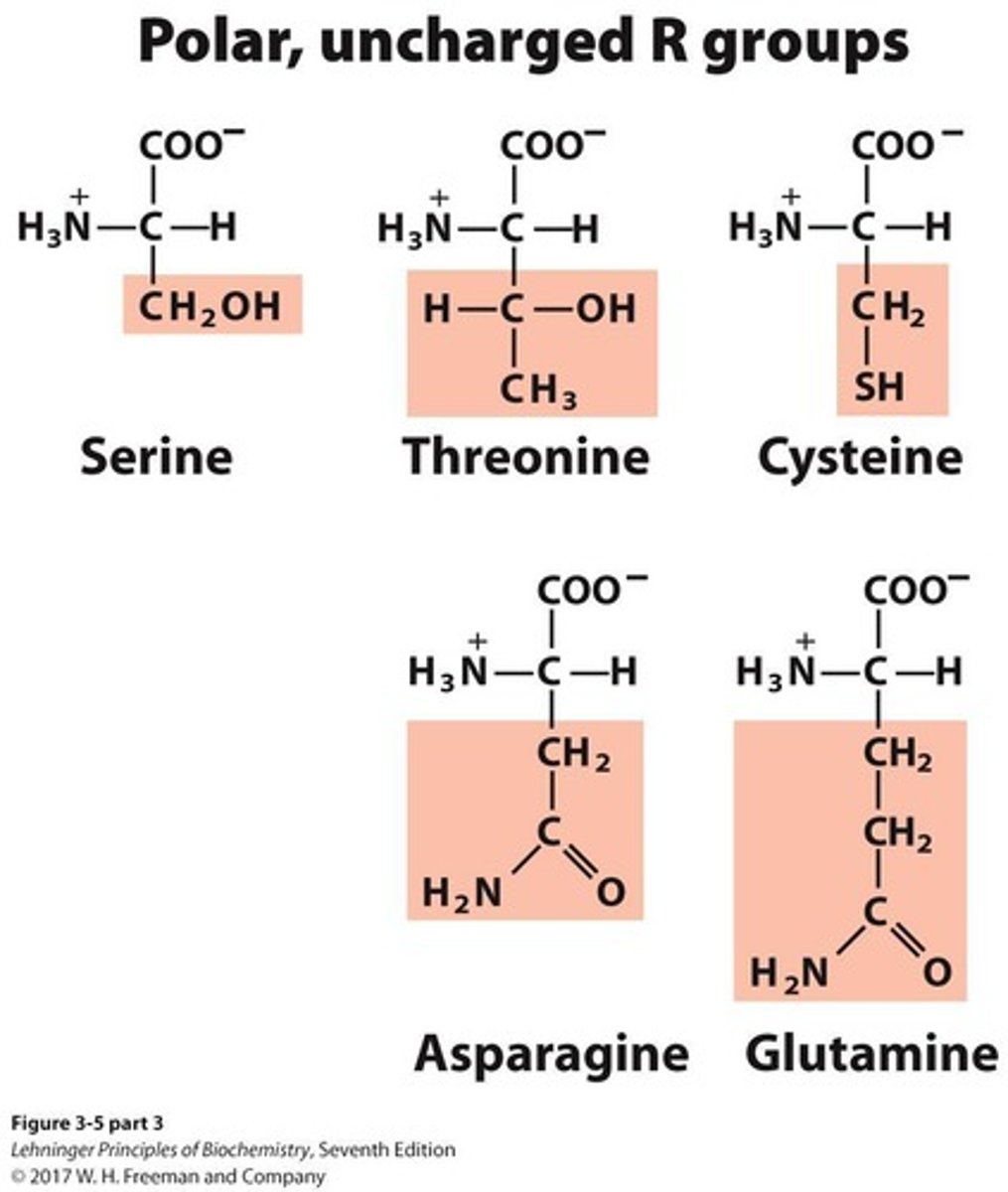
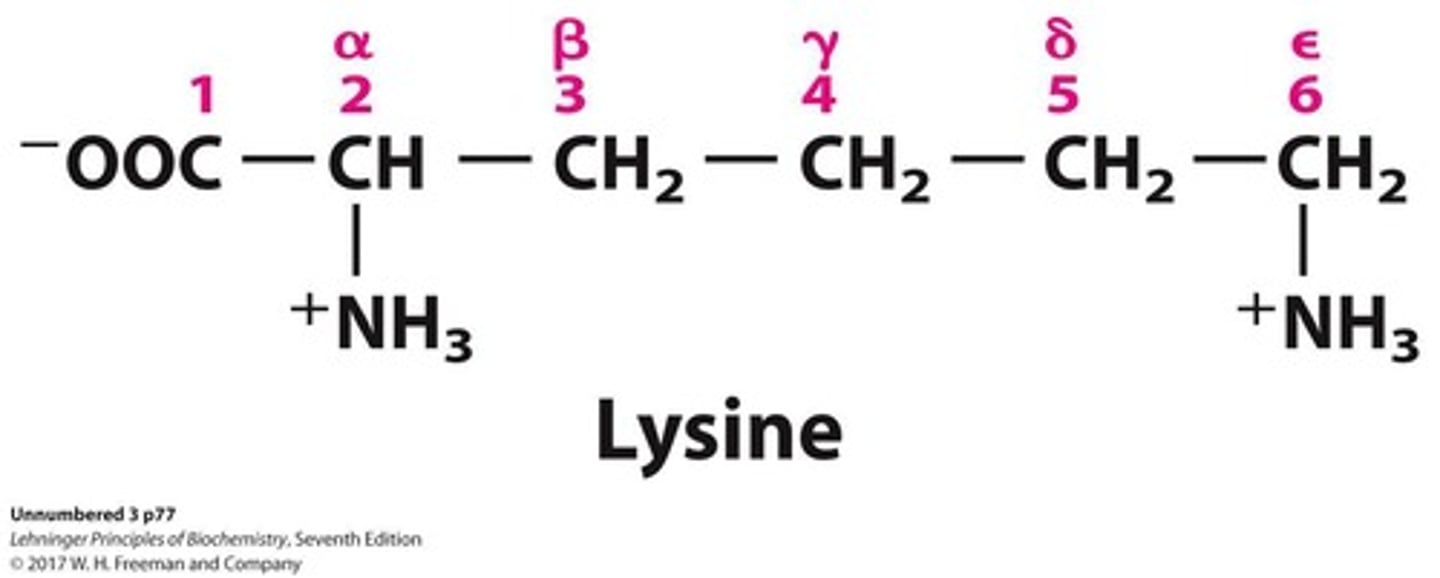
Positively charged amino acids
A group of amino acids that includes 3 members.
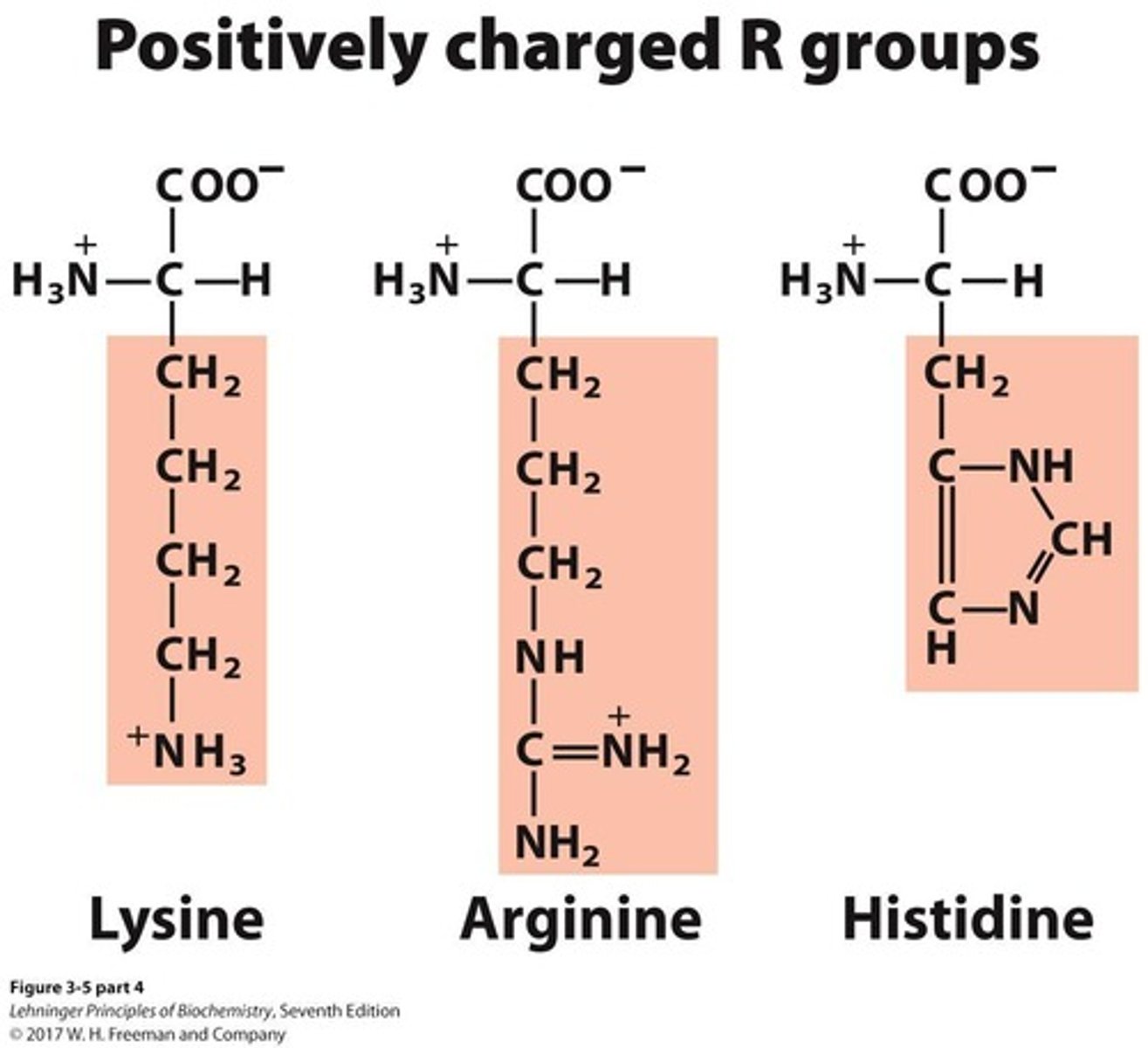
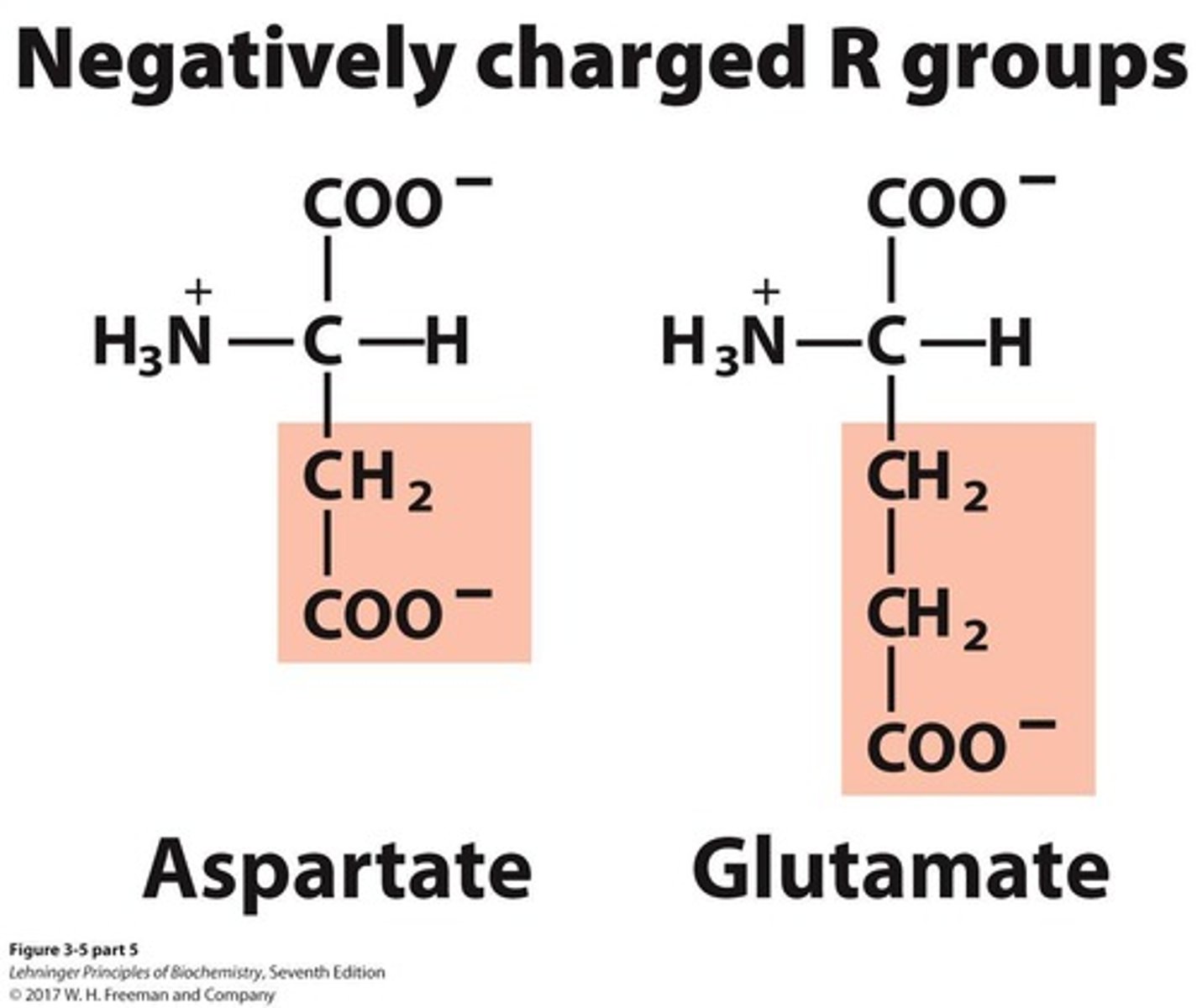
Negatively charged amino acids
A group of amino acids that includes 2 members.
UV light absorption by amino acids
Amino acid side chains absorb UV light at 270-280 nm.
Hydrogen bonds in amino acids
Amino acid side chains can form hydrogen bonds.
Disulfide bonds
Cysteine can form these types of bonds.
One Letter Code for Amino Acids
A system where each amino acid is represented by its first letter or a unique letter.
Cysteine
Amino acid represented by the letter C.
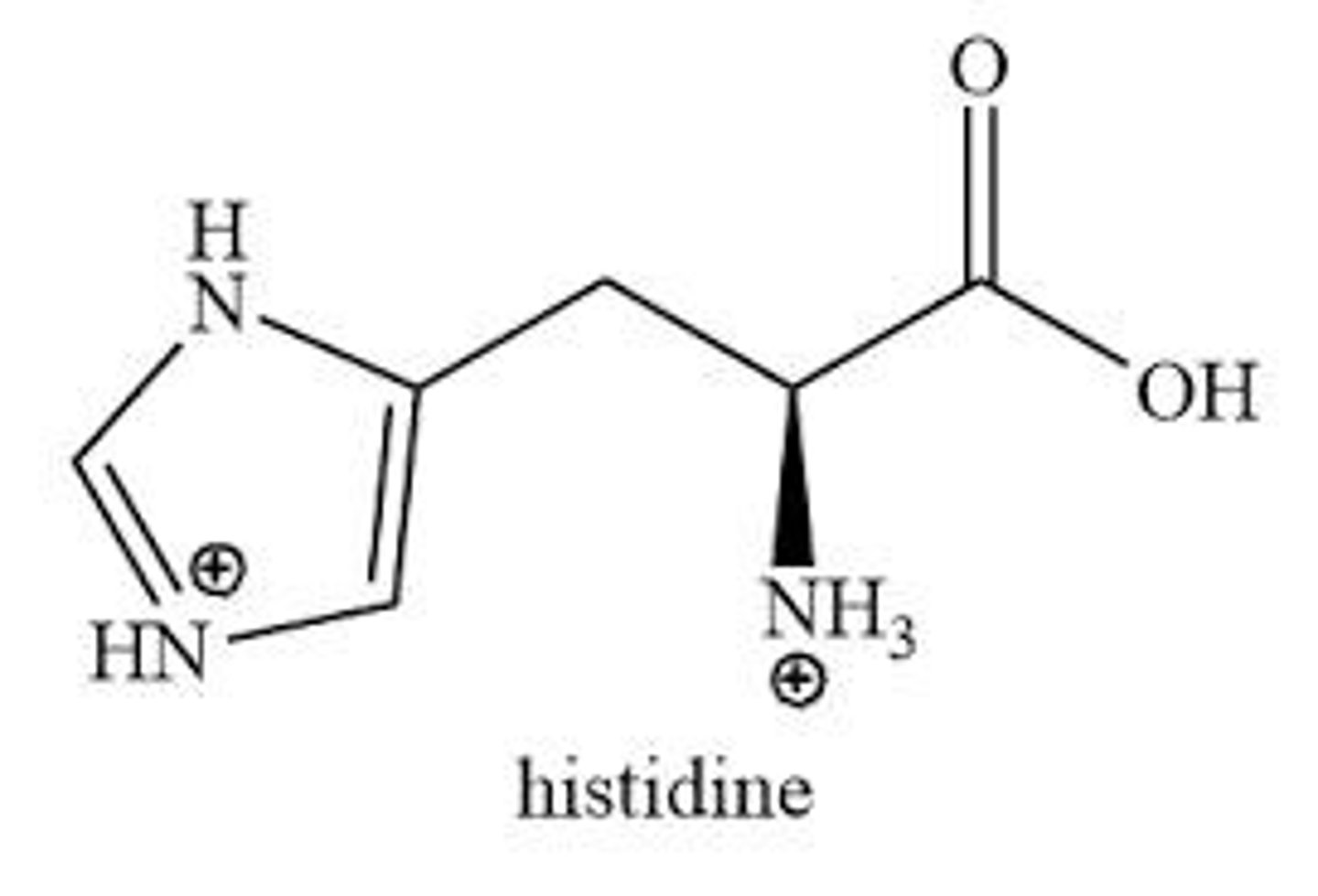
Histidine
Amino acid represented by the letter H.
Isoleucine
Amino acid represented by the letter I.
Methionine
Amino acid represented by the letter M.
Serine
Amino acid represented by the letter S.
Valine
Amino acid represented by the letter V.
Alanine
Amino acid represented by the letter A.
Glycine
Amino acid represented by the letter G.
Leucine
Amino acid represented by the letter L.
Proline
Amino acid represented by the letter P.
Threonine
Amino acid represented by the letter T.
Arginine
Amino acid represented by the letter R.
Phenylalanine
Amino acid represented by the letter F.
Tyrosine
Amino acid represented by the letter Y.
Tryptophan
Amino acid represented by the letter W.
Aspartate
Amino acid represented by the letter D.
Glutamate
Amino acid represented by the letter E.
Asparagine
Amino acid represented by the letter N.
Glutamine
Amino acid represented by the letter Q.
Lysine
Amino acid represented by the letter K.
Free energy (ΔG)
The values reflect the free energy (ΔG) of transfer of the amino acid side chain from a hydrophobic solvent to water.
Favorable transfer
This transfer is favorable (ΔG < 0; negative value in the index) for charged or polar amino acid side chains.
Unfavorable transfer
This transfer is unfavorable (ΔG > 0; positive value in the index) for amino acids with nonpolar or more hydrophobic side chains.
Hydropathy index
A scale combining hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of R groups.
Cysteine classification
Cysteine is generally classified as polar despite having a positive hydropathy index.
Sulfhydryl group
The ability of the sulfhydryl group to act as a weak acid and to form a weak hydrogen bond with oxygen or nitrogen.
Proline surface occurrence
As originally composed, the hydropathy index takes into account the frequency with which an amino acid residue appears on the surface of a protein.
pKa values
The values at which protons can be ionized from an amino acid, with each group having its own pKa.
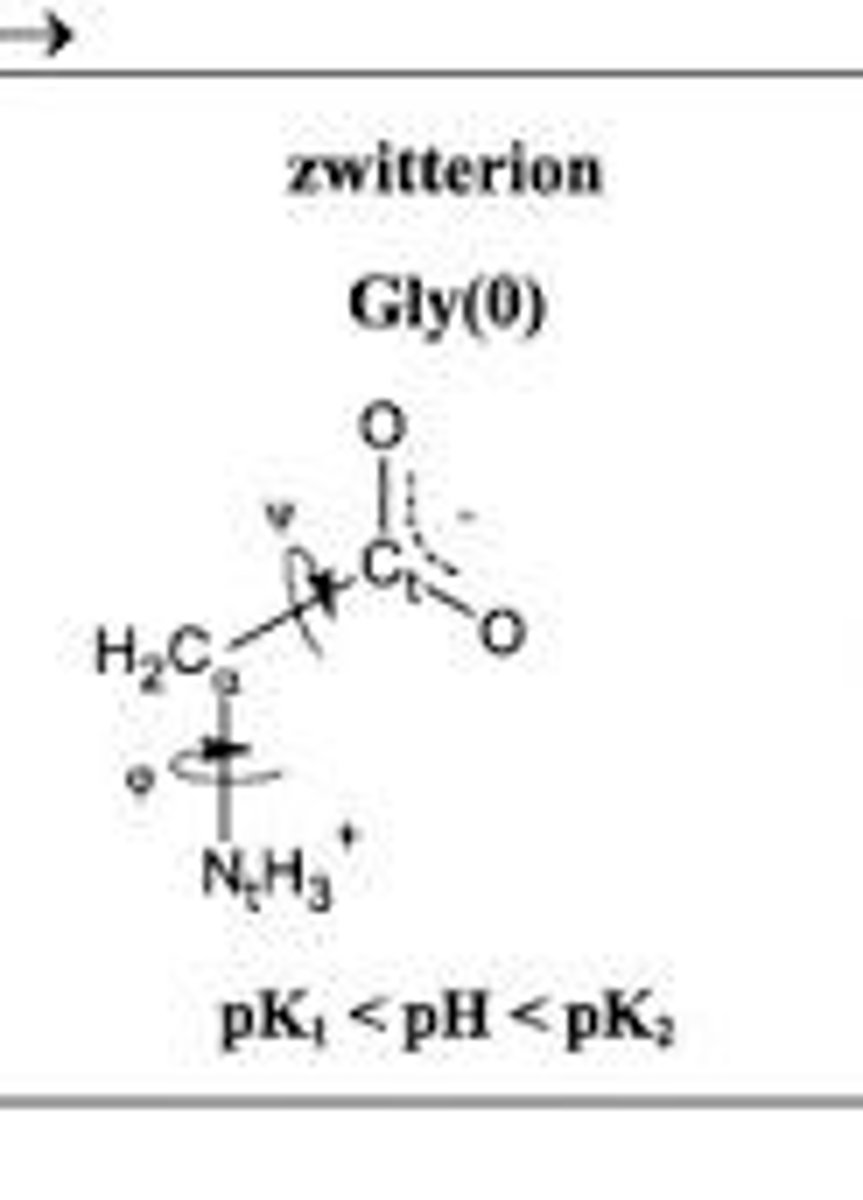
Zwitterion
A form of an amino acid that has both a positive and negative charge, existing between the pKa values of the amino and carboxyl groups.
Isoelectric Point (pI)
The specific pH at which an amino acid carries a net charge of zero, calculated as pI = (pK1 + pK2)/2.
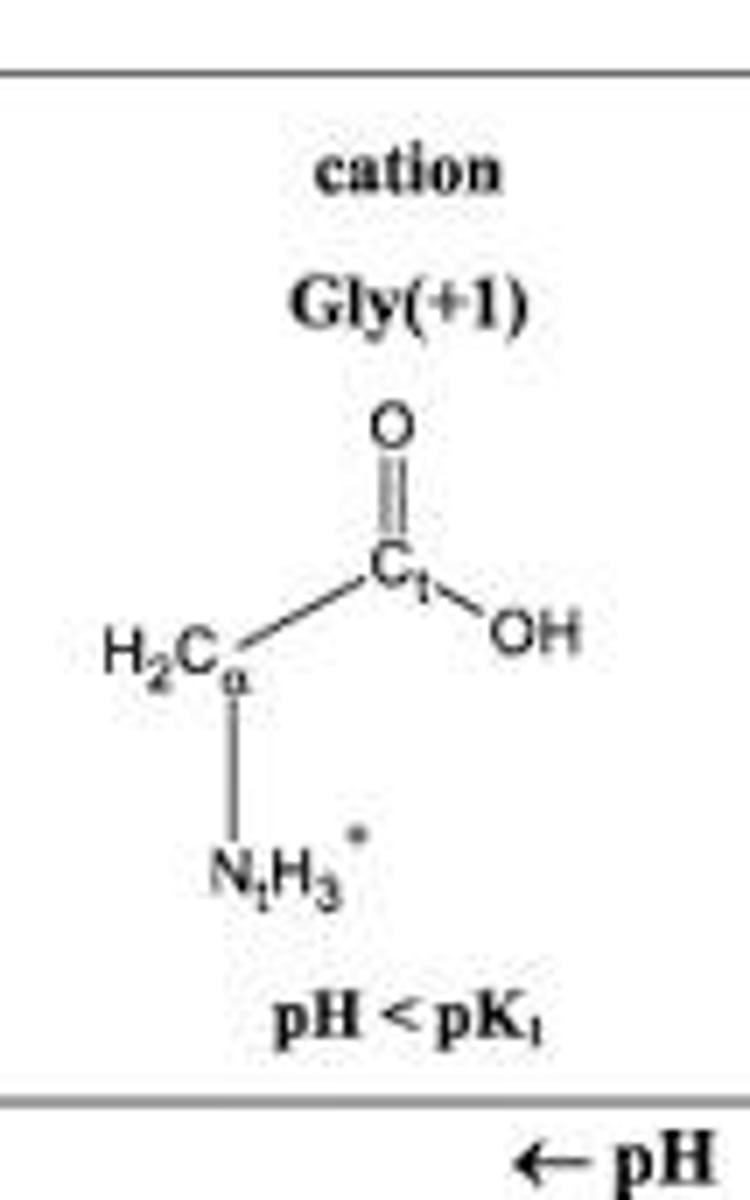
Cation
The positively charged form of an amino acid that exists at low pH.
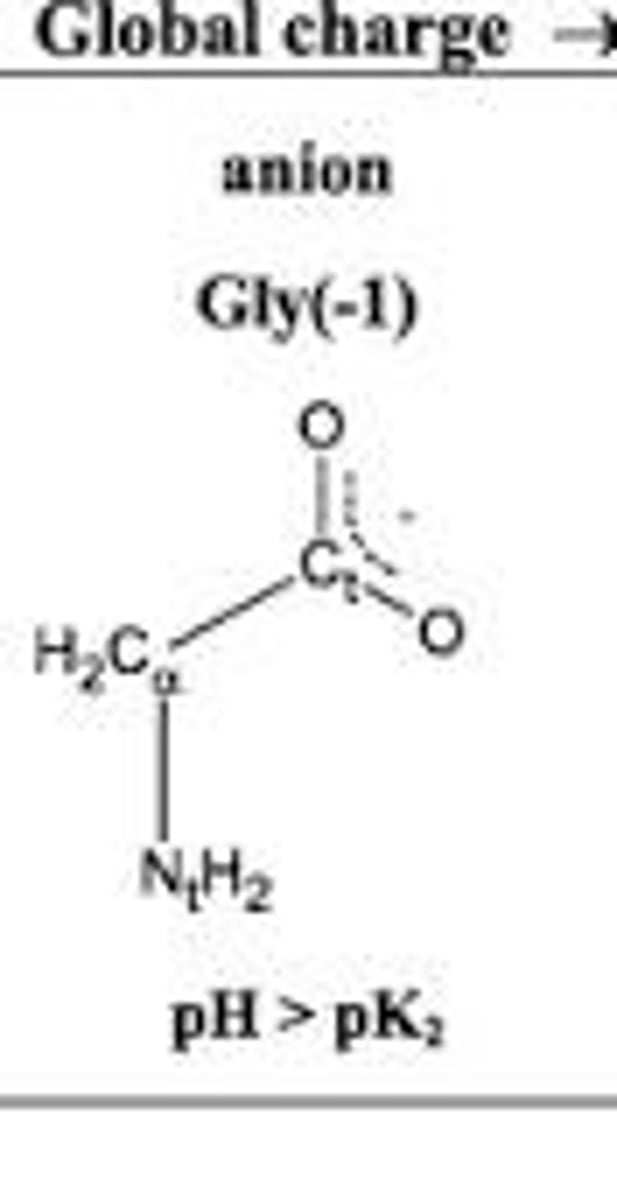
Anion
The negatively charged form of an amino acid that exists at high pH.
Buffer
A substance that prevents changes in pH, with amino acids acting as buffers in two pH ranges based on their pKa values.
Ionizable side chains
Side chains of amino acids that can influence the pI and can also be titrated.
Titration curves
Graphs that show how the pH of a solution changes as acid or base is added, becoming more complex with ionizable side chains.
pK1
The pKa value associated with the carboxylic acid group of an amino acid.
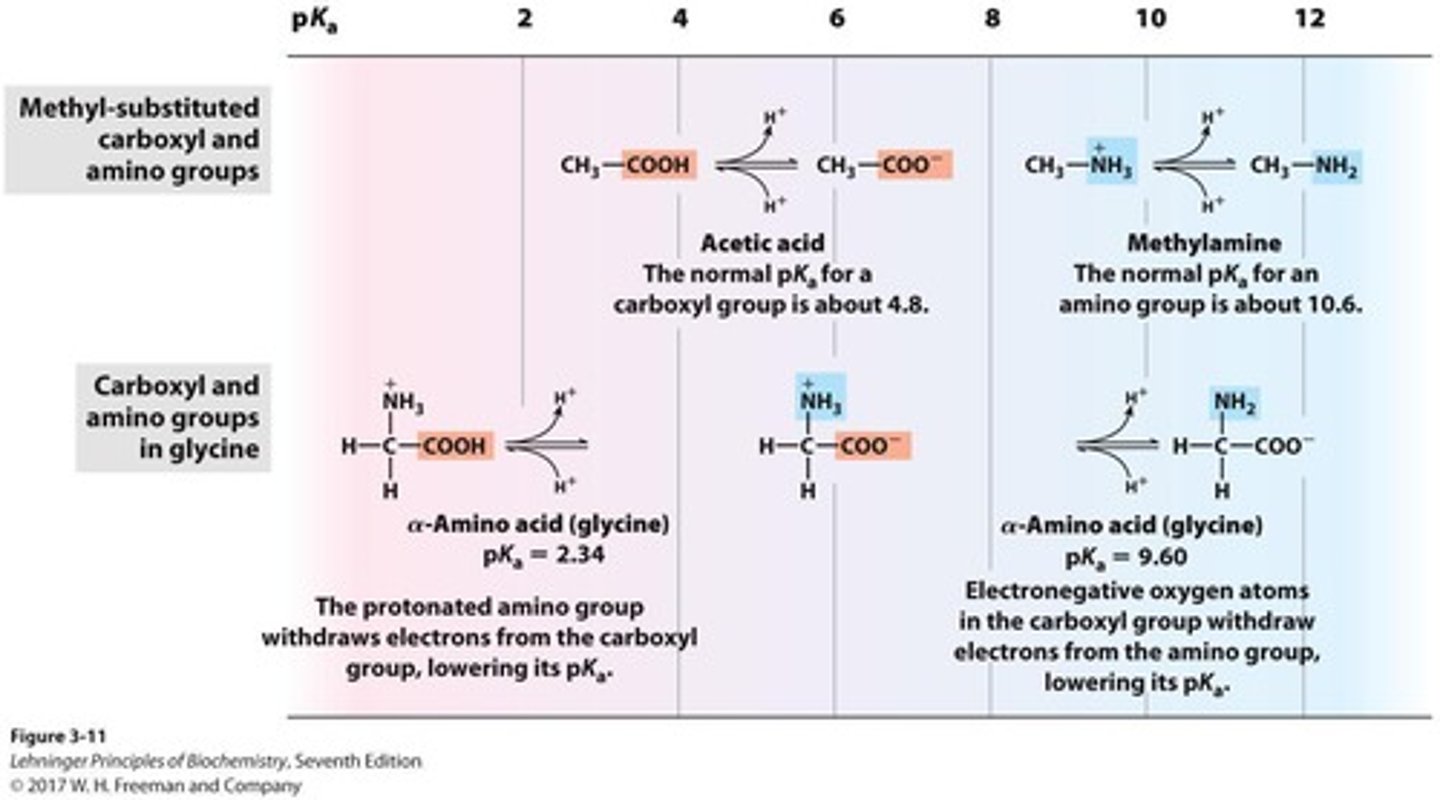
pK2
The pKa value associated with the amino group of an amino acid.
Chemical Environment
Factors that affect the pKa values of amino acids, making the α-carboxy group more acidic and the α-amino group slightly less basic.
Protonation
The process of adding a proton (H+) to a molecule, occurring at low pH for the carboxylic acid and at high pH for the amino group.
Hydrophilic
Referring to molecules that are attracted to water, often associated with charged or polar amino acid side chains.
Hydrophobic
Referring to molecules that repel water, often associated with nonpolar amino acid side chains.
Average occurrence
The frequency of an amino acid's presence in more than 1,150 proteins, providing insight into its biological significance.
pKa of α-carboxyl group
The pKa value of the α-carboxyl group, which is 2.34 for glycine.
pKa of α-amino group
The pKa value of the α-amino group, which is 9.6 for glycine.
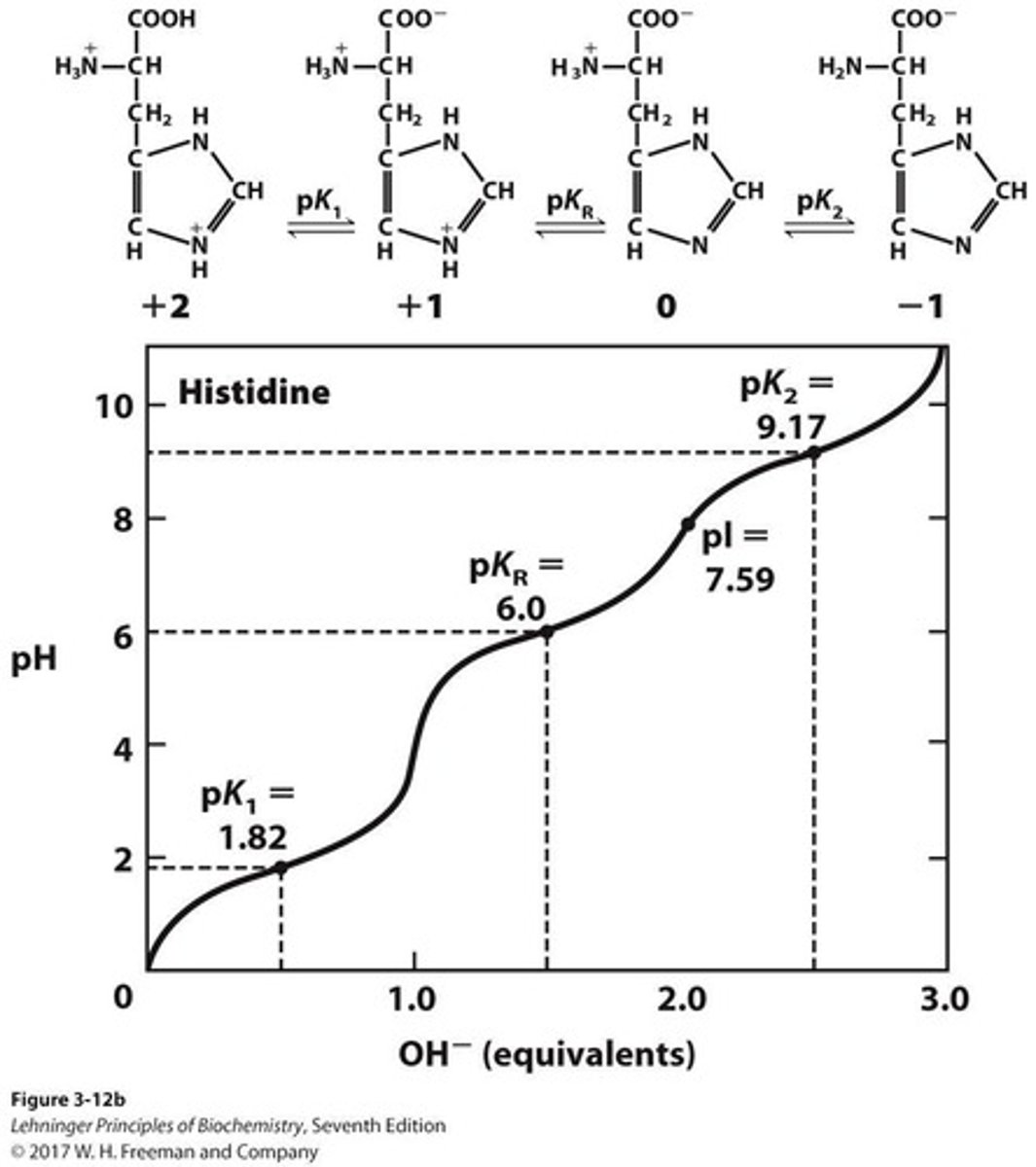
pI
Isoelectric point, calculated as (pKR + pK2)/2.
pI Calculation
To calculate the pI when the side chain is ionizable, identify the species with net zero charge, the pKa value defining acid strength (pKR), the pKa value defining base strength (pK2), and take the average of these two pKa values.
Peptides
Small condensation products of amino acids, typically with a molecular weight less than 10 kDa.
N-terminal
The amino terminus of a peptide where numbering and naming starts.
Insulin
A hormone involved in sugar metabolism.
Oxytocin
A hormone associated with childbirth.
Substance P
A neuropeptide that acts as a pain mediator.
Polymyxin B
An antibiotic effective against Gram-negative bacteria.
Bacitracin
An antibiotic effective against Gram-positive bacteria.
Amanitin
A toxin found in mushrooms.
Conotoxin
A toxin from cone snails.
Chlorotoxin
A toxin from scorpions.
Cofactors
Functional non-amino acid components that can be metal ions or organic molecules.
Coenzymes
Organic cofactors, such as NAD+ in lactate dehydrogenase.
Prosthetic groups
Covalently attached cofactors, such as heme in myoglobin.
Posttranslational modifications
Other modifications that proteins may undergo after translation.
Cytochrome c
A protein with a molecular weight of 12,400 and 104 polypeptide residues.
Ribonuclease A
A protein with a molecular weight of 13,700 and 124 polypeptide residues.
Lysozyme
A protein with a molecular weight of 14,300 and 129 polypeptide residues.
Myoglobin
A protein with a molecular weight of 16,700 and 153 polypeptide residues.
Chymotrypsin
A protein with a molecular weight of 25,700 and 245 polypeptide residues.
Hemoglobin
A protein with a molecular weight of 64,500 and 574 polypeptide residues.
Serum albumin
A protein with a molecular weight of 66,000 and 609 polypeptide residues.
Hexokinase
A protein with a molecular weight of 107,900 and 972 polypeptide residues.
Polypeptides
Chains of amino acids that can have differing sequences and arrangements, giving them unique chemical characteristics.
Chromatography
A technique used for the separation of proteins based on their physical and chemical properties.
Column Chromatography
A method that allows separation of a mixture of proteins over a solid phase using a liquid phase.
Ion Exchange Chromatography
A separation technique based on the charge of proteins.
Size Exclusion Chromatography
A separation method that separates proteins based on their size.
Affinity Chromatography
A technique that separates proteins based on their binding affinity for a specific ligand.
Specific Activity
The ratio of activity to total protein concentration, indicating the purity of the protein of interest.
Electrophoresis
A method for separating proteins based on their charge and size using an electric field.
SDS-PAGE
A type of electrophoresis that separates proteins by molecular weight using sodium dodecyl sulfate.
Isoelectric Focusing
A technique used to determine the isoelectric point (pI) of a protein.
2D Electrophoresis
A method that combines isoelectric focusing and SDS-PAGE for protein separation.
Lambert-Beer Law
A principle used in UV-visible spectrophotometry to relate absorbance to concentration.
Edman Degradation
A classical method for determining the amino acid sequence of a protein by successive rounds of modification and cleavage.