mutations
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Sources of mutation
Replication errors in dna and rna
Environmental: radiation, chemicals, infectious agents
Mutations that influence evolution
Germline/reproductive tissue on ovaries and testis with mutations get passed down to offspring not somatic
Point mutations/substitutions
One base change to another
Nonsynonomous: aa change so function change
Synonymous: (silent) same aa same function
Nonsense: premature stop codon
Transition: purines (a to g) prymadins (t to c)
Trans version: (a/g to t/c) purine to prymadin
Frameshift mutation
Insertion/deletion usually in three shifts entire codon reading
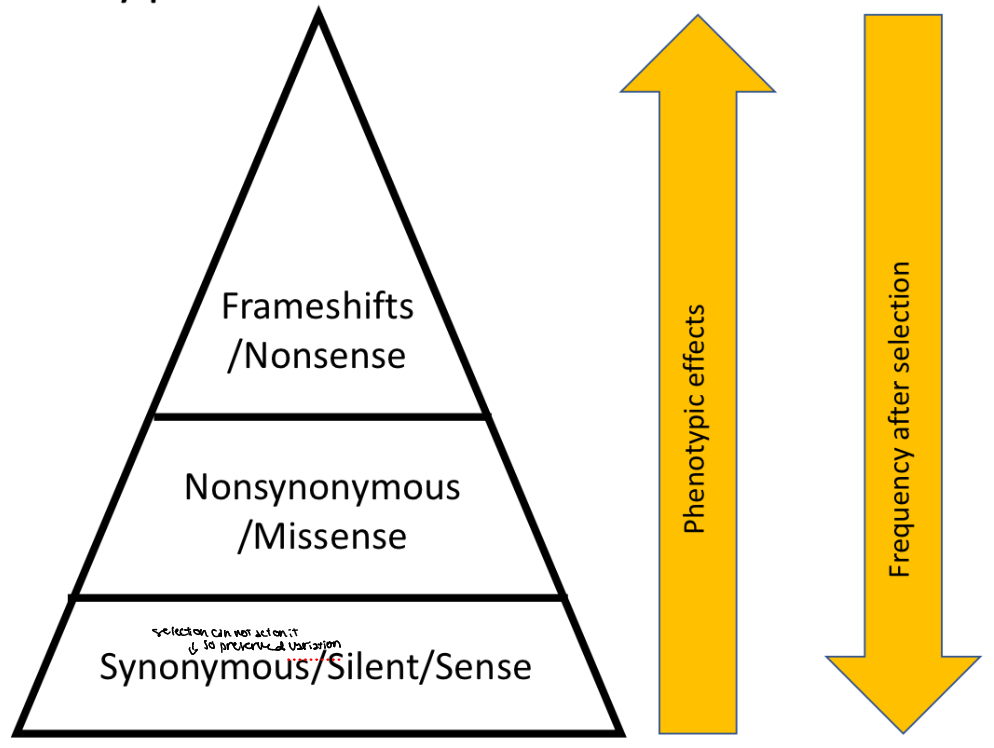
Substitution effects ranked
Phenotypic and frequency after selection
Sickle cell example
Amino acid change by substitution results in many phenotypic changes like blood cell shape, o2 binding altered and lifespan shortened
Mutations neutral by
Synonymous changes
Nonsynonymous changed aa to similar aa so protein has similar/same function
Effect of mutation depends on environment: wild type outperforms mutant in favorable conditions but under stress results in a more neutral effect
Could affect part of protein not important to function ex. Certain parts of spike proteins on COVID
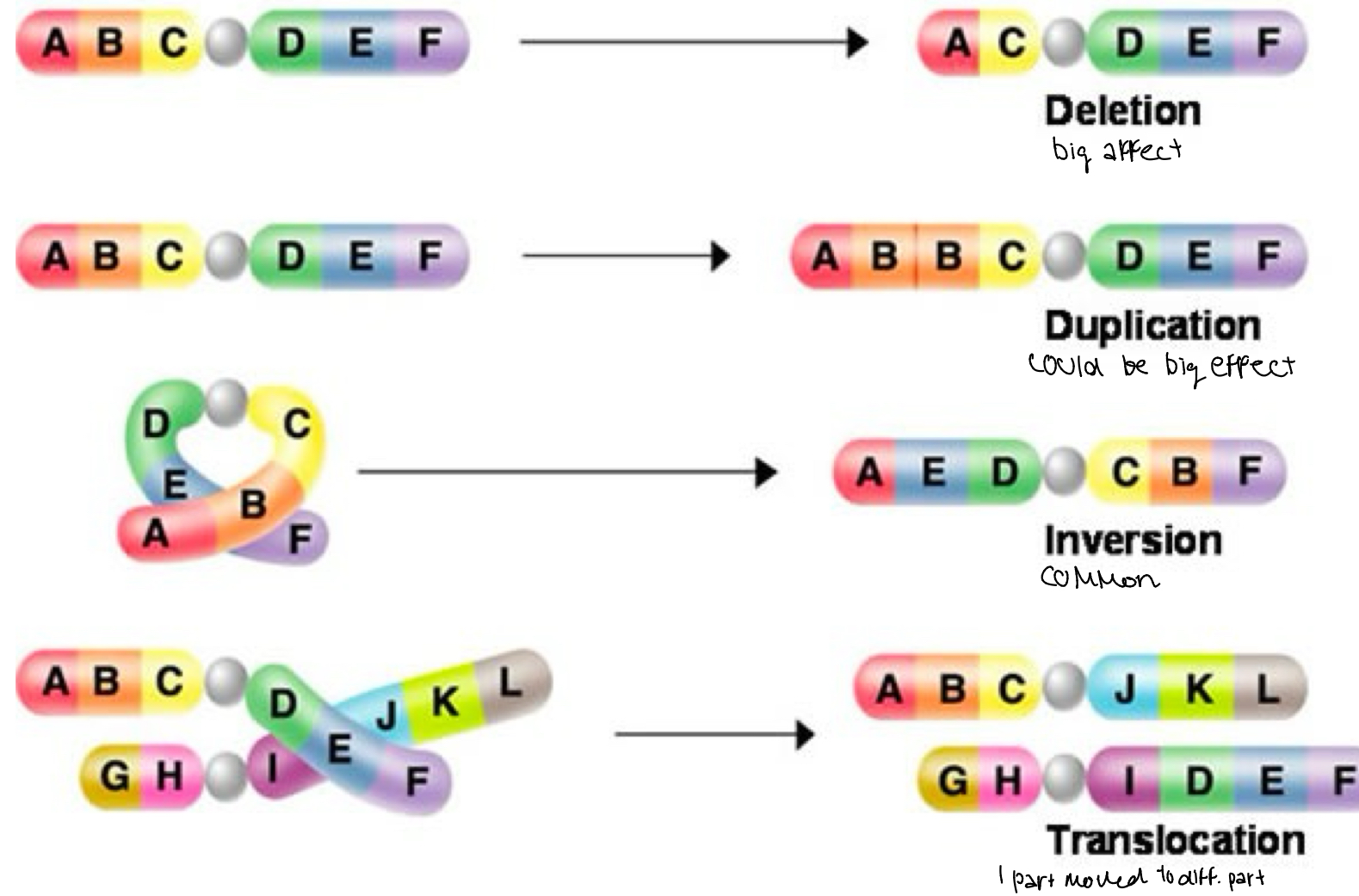
Chromosomal mutations
Deletion big affect
Duplication could be big effect
Inversion common
Translocation one part moved to different part
Genome duplication
Tetraplois and diploid have diploid and haploid gametes when reproduce results in triploid which dies off causing speciation between the two
Pleiotropy
Allele affects multiple traits
Mutations are usuallypleiotropic
Has genetic correlation, neutral mutation bc of trade off, epistasis
Mutations are
Generally bad or neutral
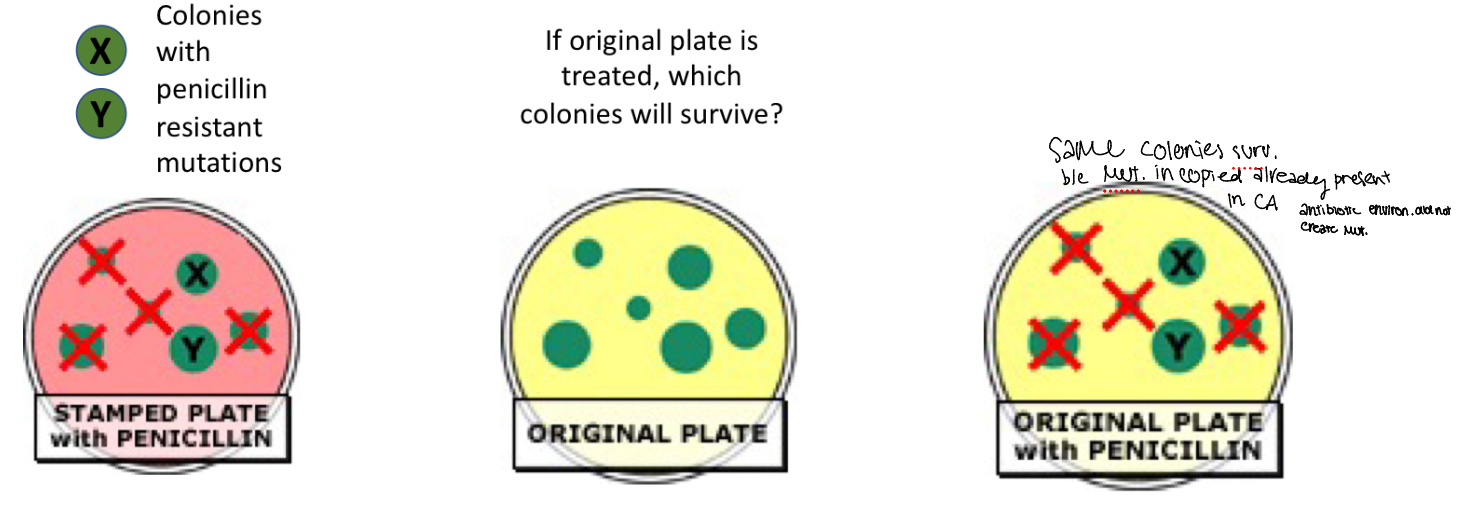
Lederberg experiment
penicillin resistance mutations occurred before the
addition of penicillin, not in response to it Because original colony had same results as copied colony