BIO 221 Exam 2
1/412
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MCQs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
413 Terms
At the molecular level, how is a proton gradient generated by the quinone loop?
The quinone donates both H +and electrons, but FeS proteins only accept electrons.
Compared to mitochondrial ETS (electron transport systems), bacterial ETS _____.
use a much greater variety of terminal electron acceptors
In oxygenic photosynthesis, as practiced in bacteria _____.
there are two electron transport chains
Why are purple sulfur bacteria considered metabolically unique?
They must perform reverse electron transport to make NADH.
How are respiratory and photosynthetic electron transport chains similar?
Both use heme-containing electron carriers.
Purple sulfur bacteria (PSB) must use reverse electron transport, but green sulfur bacteria (GSB) do not. Why is there a difference?
GSB use a bacteriochlorophyll with enough energy to donate its electrons directly to ferredoxin.
Which of the following is true for all electron carriers?
They must be capable of being oxidized and reduced.
During oxygenic photosynthesis, the terminal electron acceptor for the electron transport chain involving photosystem II and plastoquinone is ______.
the reaction center of photosystem I
Which of the following is similar in all three photosynthetic mechanisms we discussed?
the way ATP is formed
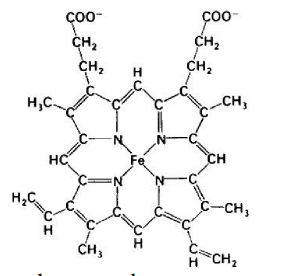
Which of the following statements correctly describes the molecule at right?
it carries only electrons, not H +
Which of the following is true of the mitochondrial electron transport system in eukaryotes, but NOT always true of bacterial electron transport systems?
cytochrome c oxidase is always the final electron transport complex
Some photosynthetic bacteria need to generate reducing power by reverse electron transport because ____.
their photosynthetic electron acceptor lacks the energy to donate electrons to NAD +
Why do most photosynthetic bacteria produce a complex containing antenna pigments?
it allows them to channel additional photons of light to the reaction center
During a reaction in the electron transport chain, an electron acceptor ______.
must be reduced by the electron donor
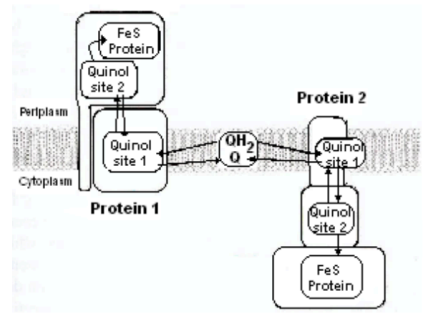
In an electron transport chain, proteins 1 and 2 (P1 and P2) are structured as shown in the diagram. Which of the following most accurately describes the roles of these proteins?
P1 contributes H + to the PMF, but P2 does not
Which of the following correctly describes the direct mechanism of chemiosmotic ATP synthesis?
Energy from a H +gradient turns a rotor to push ADP and ~P together.
The following electron transport chain . . .
is a type of respiration
The goal of reverse electron transport, as carried out by purple photosynthetic bacteria, is to _____.
make NADH
Why is it important that some electron carriers carry both electrons and protons, while others carry only electrons?
This is how the Q loop pumps protons across a membrane.
Which of the following statements most accurately compares how ATP is generated during cyclic versus non-cyclic photosynthesis (PS)?
ATP is produced by the same mechanism during cyclic PS as it is during non-cyclic PS.
When comparing green sulfur and purple sulfur bacteria _____.
purple sulfur bacteria have a lower energy photosystem than green sulfur bacteria do
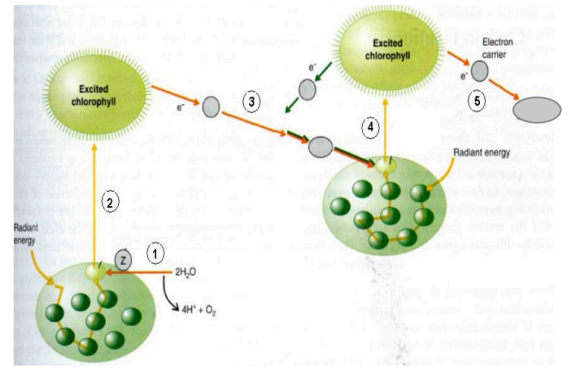
The outline of oxygenic photosynthesis is shown, with electron transfer steps marked 1 through 5. Which step is responsible for generation of reducing power?
electron transfer #5
The use of an organic electron acceptor without producing a PMF from the electron transfer is known as _____.
fermentation
How does electron transport lead to the formation of a proton gradient?
One member of the transport chain is reduced by both H +and electrons, but only the electrons are passed to the next member
What is meant by oxidative phosphorylation?
Production of ATP from the PMF using ATP Synthase
Why is non-cyclic photosynthesis also called "oxygenic" photosynthesis?
The electron donor for PSII is H2O.
Compare oxygenic photosynthetic (OPS) and respiratory (RES) electron transport chains
They both use quinones and cytochromes in a Q-loop to produce a PMF
The chemical DCCD binds irreversibly to the proton binding site of the FOF1 ATP Synthase. What is the most likely consequence if DCCD is added to a culture of a facultative anaerobe?
The flagellar rotation speed would briefly increase due to a larger PMF
How does oxidative phosphorylation make ATP?
It oxidizes electron carriers to make a PMF
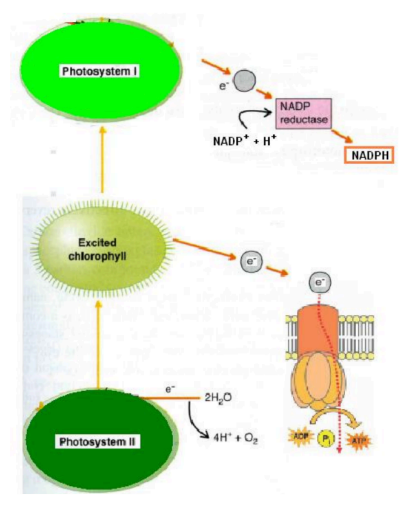
When asked to sketch the reaction scheme for green sulfur photosynthetic bacteria on an exam one year, a student presented the diagram at right. I tried to find something he got correct to give him some credit. What did he get correct?
The way NADPH is produced directly
A major difference between quinones and hemes in the electron transport chain is that ________.
quinones accept and donate both H +and electrons; hemes only electrons
Which of the following is NOT important in a bacterial electron transport chain when creating a PMF?
Having oxygen as the terminal electron acceptor
How could you best determine whether an unknown respiratory chain was from a bacterium or from a eukaryotic mitochondrion?
Whether a different magnitude of PMF can be produced under different conditions
Which of the following best describes how ATP is produced by oxidative phosphorylation?
The PMF turns a rotor which pushes ADP and phosphate together
What are the appropriate mechanisms by which excited electrons dissipate their energy and revert to the ground state among the provided options?
All of the following are correct
You notice a “rotten egg” smell coming from the black goo in the iron drain pipe in your kitchen. You could get rid of the smell by adding which of the following?
Sulfur oxidizing bacteria
Nitrifying bacteria cause a high biological oxygen demand (BOD) in a pond . . .
when NH4 + is present, since they metabolize it with O2 as the electron acceptor.
Rhizobium produces leghemoglobin . . .
to bind O2 in order to protect nitrogenase
Which of the following uses mainly fats and oils as carbon sources, producing acids and CO2 by fermentation?
Propionibacterium

If you see the following structure on a plant, you could conclude that . . .
The plant is producing food for a bacterium
This bacterium lives in packets of four cells, two of which have their DNA tightly surrounded by a protein ring that protects it against extreme levels of radiation.
Deinococcus
You live near a swamp, and notice the “rotten egg” smell of H2S. Having taken micro, you decide to bacterially remediate the odor. Which of the following bacterial types would NOT be able to do the job if added to the swamp?
Sulfate reducing bacteria
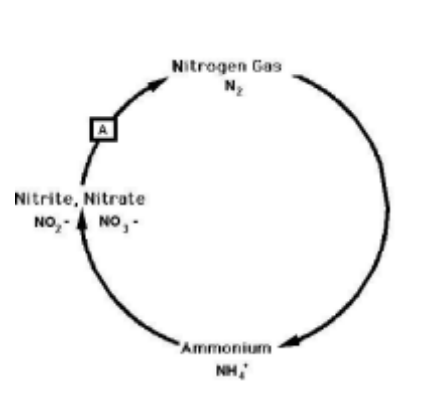
What bacteria carry out the reaction marked "A" in the nitrogen cycle?
Denitrifying bacteria
Because it has a large number of modular catabolic pathways that produce intermediates that feed into glycolysis, this bacterium can catabolize almost anything. It is often used to break down environmental pollutants in the process of bioremediation.
Pseudomonas
Agrobacterium tumifaciens is especially important to plant scientists. What is so special about it?
It can be used to insert foreign DNA into plant cells.
This bacterium produces CO2 and acids from growth on fats and oils, such as are present on your skin in hair follicles.
Propionibacterium
You're an engineer working on a bridge repair project. You notice that the buried iron bridge supports are coated in black, smelly ooze. What could you conclude is present in the soil?
Sulfate
The free-living nitrogen fixing bacterium Azotobacter has a much higher rate of cellular respiration than other bacteria. Why?
To protect the enzyme nitrogenase from oxygen
The bacterium Agrobacterium tumifaciens is very important in plant biology. Why?
It inserts a plasmid into plant cells, and can therefore be used in genetic engineering.
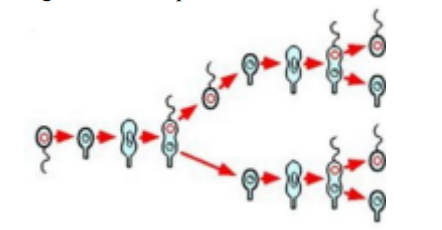
This bacterium has well defined stalked and flagellated poles, which interchange in alternate generations of its life cycle, as shown.
Caulobacter
Sulfate reducing bacteria . . .
produce sulfide, which forms a black precipitate on buried iron surfaces
Which of the following bacteria carry out fermentations important to the food industry in the production of dairy products and sauerkraut?
Lactic Acid Bacteria
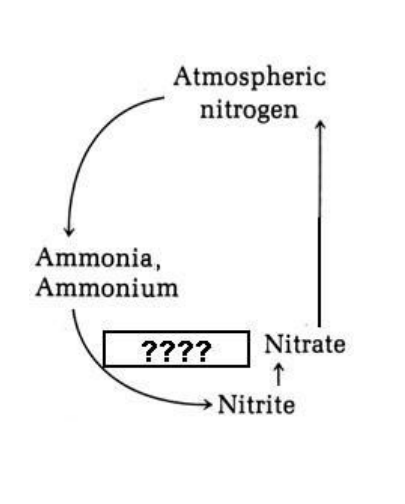
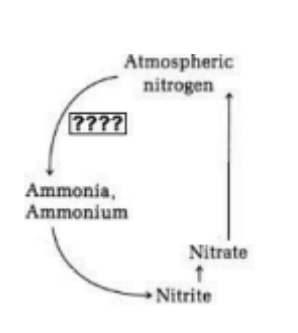
Which of the following would be the most appropriate term to put in the box marked "????" in the image at the right?
nitrification
What problem do all nitrogen fixing bacteria have in common?
They are aerobes, but nitrogenase is damaged by oxygen.
Sulfur oxidizing bacteria . . .
produce H2SO4 , and are therefore often acidophiles
In the diagram of the Nitrogen cycle at the right, which of the following bacteria could carry out the indicated step?
Azotobacter
Which of the following are famous for their ability to sense the presence of other bacteria, secrete slime trails and aggregate together by social gliding motility into large, complex, spore-producing structures called "fruiting bodies."
Myxobacterium
Some bacteria contain a large piece of circular DNA called the Ti plasmid. What is the purpose of this plasmid?
to make an infected plant produce nutrients for the bacterium
The bacterium Caulobacter crescentus is well known for its ability to . . .
distinguish one end of its cell (stalk) from the other (flagella)
Which of the following is an accurate comparison between sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfur oxidizing bacteria (SOB)?
SRB are generally undesirable; SOB can be used in biomining of sulfide ores.
Important industrial production of acetone, butanol and other organic solvents depends on . . .
Clostridial fermentation
To check the quality of an agricultural soil you sometimes pull up certain plants and look for pink lumpy structures on the roots. What do these structures indicate?
the soil is rich in a form of nitrogen that plants can use
Which of the following reactions is carried out by methanogenic Archaea?
CO2 is reduced to CH4 using electrons from H2
Which of the following is true about Sulfate Reducing Bacteria?
Their presence in anaerobic soil is indicated by a "rotten egg" odor.
Which of the following bacteria both carry out fermentation reactions that are used in the preparation of important food products?
Lactococcus and Propionibacterium

You notice that one part of a plant is covered with small pinkish spherical structures, as shown in the picture at right. What can you conclude?
The spherical structures contain the enzyme nitrogenase.
Purple nonsulfur bacteria can grow both aerobically and anaerobically, but they use different biochemical mechanisms to do so. How do these bacteria obtain reducing power when they are growing anaerobically?
by using a photosynthetic PMF to reverse a part of the electron transport chain
Which of the following are typically lithotrophs?
Nitrifying Bacteria
How does Clostridial ABE fermentation differ from the lactic acid fermentation performed by many other bacteria?
ABE fermentation can produce some additional ATP.
Deinococcus bacteria can be found uniquely in what environment?
Very high radiation levels
What bacteria would you expect to find in dense, pink or red clusters associated with plants?
Rhizobium
What is Agrobacterium noted for?
Natural insertion of DNA into plant cells
You are a soil scientist trying to bioremediate (use bacteria to clean up) an area of soil contaminated by a pesticide. Which of the following bacteria would be your best choice to do this, and why?
Pseudomonas, because it is adaptable to growth on many different carbon source
Myxobacteria are noted best for their . . .
ability to aggregate in response to quorum sensing
Which of the following has a unique cell cycle, in which only one of the two daughter cells is able to replicate directly?
Caulobacter
Instruments that are considered medically “critical” must be
sterilized
Place the following organisms in order from HARDEST to kill to EASIEST. (1) naked viruses (2) Pseudomonas cells (3) Bacillus endospores (4) Giardia cysts
HARDEST (3) > (4) > (1) > (2) EASIEST
Which of the following methods would be acceptable to sterilize a chicken thigh that is intended for long-term storage and eventual consumption (i.e. as part of a military ration)?
gamma ray irradiation
A mouthwash called “Hexodent” lists the following ingredients: 8% alcohol, 0.2% chlorhexidine, mint flavor. How does this mouthwash kill bacteria?
The chlorhexidine dissolves cell membranes
Using chlorox, it takes 20 minutes to decontaminate a water bottle with 10 4 Cryptosporidium cysts in it. The decimal reduction time for this procedure is 10 minutes. Using the same method, how long would it take to decontaminate the water bottle if it had 10 8 Cryptosporidium cysts?
60 minutes
What is the difference between high-level and low-level disinfectants?
High-level can kill Mycobacterium, low level often cannot
Rank the following treatments in terms of numbers of organisms that can survive the procedure: 1: autoclave 2: high temperature, short time (HTST) pasteurization 3: boiling 4: microwaving (not in water)
MOST SURVIVORS (4) > (2) > (3) > (1) LEAST SURVIVORS
Why are naked viruses more resistant to disinfection than enveloped viruses are?
Enveloped viruses require at least some water for the envelope to remain intact
How does UV light kill bacterial cells?
By mutating the DNA
Pasteurized milk . . .
can still have dozens of bacteria per ml
The decimal reduction time for disinfecting a Staphylococcus-contaminated steel countertop with 500 ppm chlorine bleach is 2 minutes. Which of the following would decrease the decimal reduction time?
using 5000 ppm chlorine bleach rather than 500 ppm
Iodine and its water-soluble derivative, betadine, are commonly used disinfectants. How do they kill cells?
Oxidize and denature proteins
Why is hydrogen peroxide (H2O2 ) considered high-level if used as a disinfectant, but only low level if used as an antiseptic?
Skin contains catalase, which can make H2O2 less effective.
Which of the following is the best method for sterilizing an implanted cardiac pacemaker?
Irradiate it with gamma (γ) rays
Which of the following medical instruments is NOT matched properly with an antimicrobial method that could be used to cleanse it?
Surgical sponge - Quaternary ammonium salt (QUAT)
Triclosan and Lysol both kill cells by damaging cell membranes. Bacterial resistance to Lysol is unknown, but triclosan resistance has become a major medical problem. Why the difference?
Triclosan acts against a single enzyme, mutations in which allow resistance.
HTST pasteurization reduces bacterial contamination of milk by 5 logs in 15 seconds. What is the decimal reduction time for this procedure?
3 seconds
A HEPA filter is used to filter the air in a hospital room. Filtered air is most likely to still contain . . .
Naked viruses
The most practical way to decontaminate a semi-critical medical device made of soft plastic is to . . .
soak it in 70% ethanol
Which of the following is the most likely to be decontaminated by exposure to ethylene oxide?
a pacemaker
You are cleaning a food preparation surface with a disinfectant. Which of the following is the hardest to kill, and why?
Naked viruses, because they have no sensitive external structures
Compared to a dry surface, an oily surface . . .
is likely to require a longer decimal reduction time for disinfection
Why can UV radiation be used to kill bacteria, but microwaves cannot?
microwaves do not have enough energy to damage DNA
____________ is a low-level antiseptic that damages bacterial membranes. It is often used in mouthwashes and skin care products.
chlorhexidine
___________ are high-level disinfectants when used in the food industry, but only work at intermediate level when used medically on human skin.
peroxides