Unit III" Translation
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What 2 gene expression types control the level of expression for the trp operon?
Global Control
When trp (level) are high … gene expression is repressed by trpR (a repressor that binds to an operator)
Attenuation
(fine-tuned control)
What parts of the dies the trp mRNA leader seq contain?
An attenuator region (ends prematurely)
Can be controlled through STEM loop location
2 trp codons
Draw STEM Loop when trp is high? Does transcription terminate or continue
What two locations can mRNA leader stem loops alternate from to manage attenuation for trp?
High Level of trp= stem loop between 2 & 3 domain
=TERMINATION of transcription
Low level of trp = STEM loop btwn 2 & 3
Ribosome gets stalled at trp codon
= TRANSCRIPTION CONTINUES
Describe function of guanine switch
Guanine in stem loop keeps ribosome off from transcription, remove the guanine in the stem loos transcription turns on
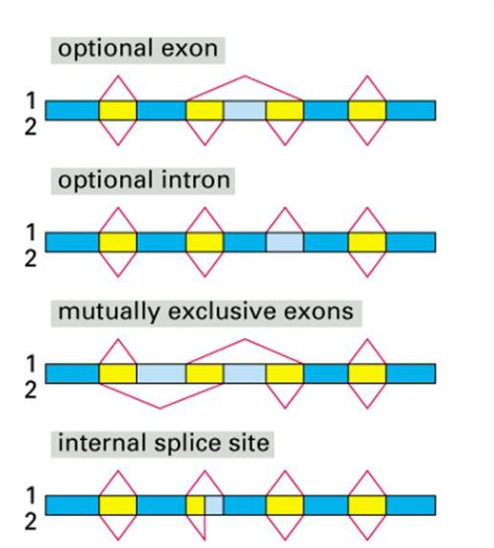
Describe the four mechanisms for alternative splicing
optional exon
an exon is spliced into the mRNA strand
optional intron
skipped on intron & kept in coding seq
mutually exclusive exons
exons get spliced together & placed in the coding strand
internal splice site
splicing within the intron is altered
Define Isoform
Different proteins translated using the same mRNA strand although have different splicing patterns
Evidence for isoform recognition
Isoforms of the same splicing patterns in dendrites repel from each other in self avoidance
isoforms of different splicing patterns in dendrites branches attract to each other
Mechanism of RNA Splicing
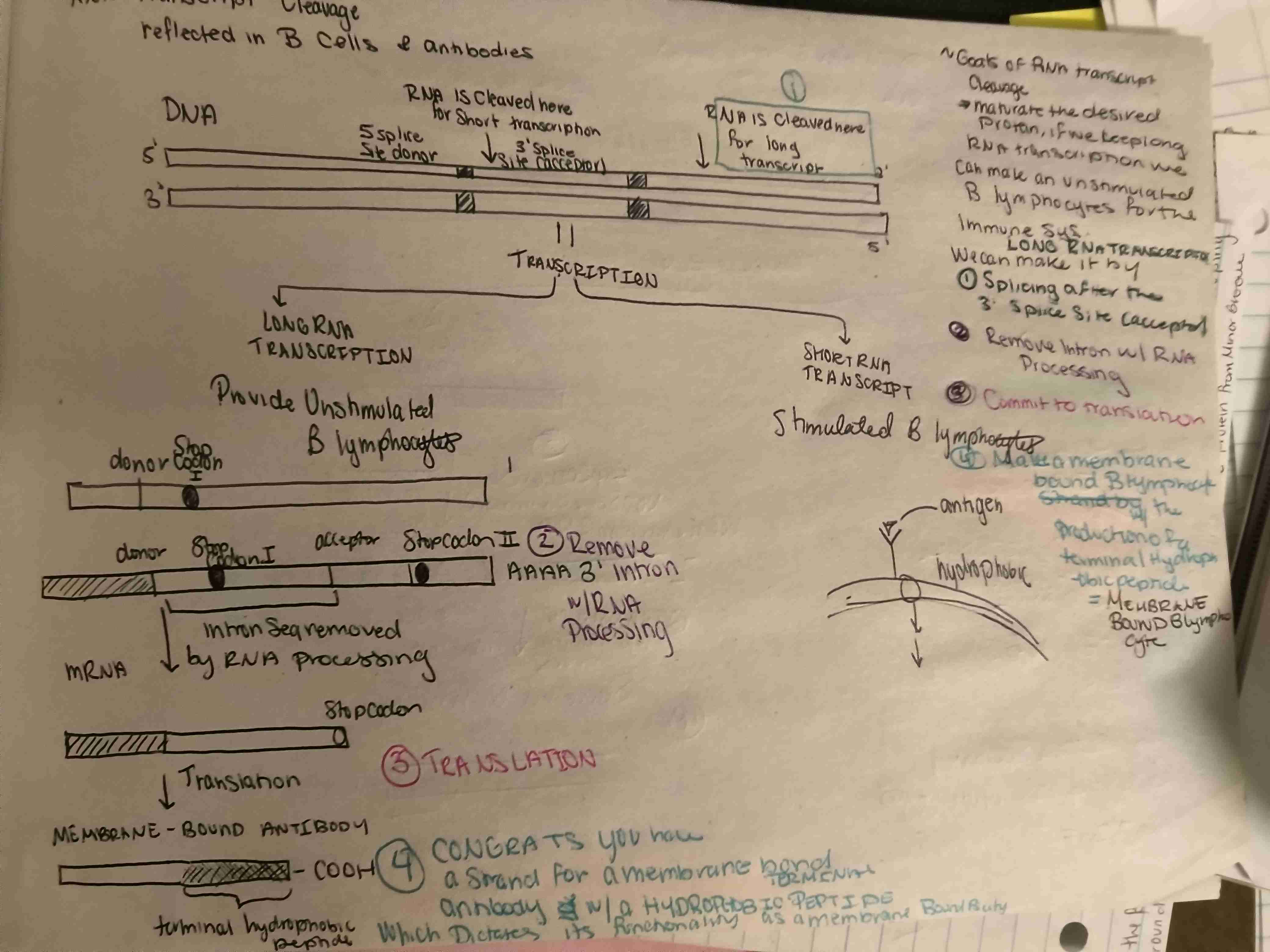
What are the steps to RNA transcription cleavage to produce a membrane bound lymphocyte is this long or short transcription?
Long transcription
Cleave mRNA sequence after 3’ splice acceptor site
Remove introns w/ RNA Processing
Commit to translation
Make membrane bound B lymphocyte w/ production of terminal hydrophobic peptide = MEMBRANE BOUND B LYMPHOCYTE
SHORT Transcription
Cleave before the 5’ for short transcript
DO NOT SPLICE the introns because the splice junction is mission
Translation w/o splicing intron
Congrats you secreted Protein Lymphocyte w/ high CstF
RNA Editing
What are the steps to produce a secreted antibody? Is this long of short transcription?
Membrane bound antibody is produced through a hydrophobic terminal protein & long transcription
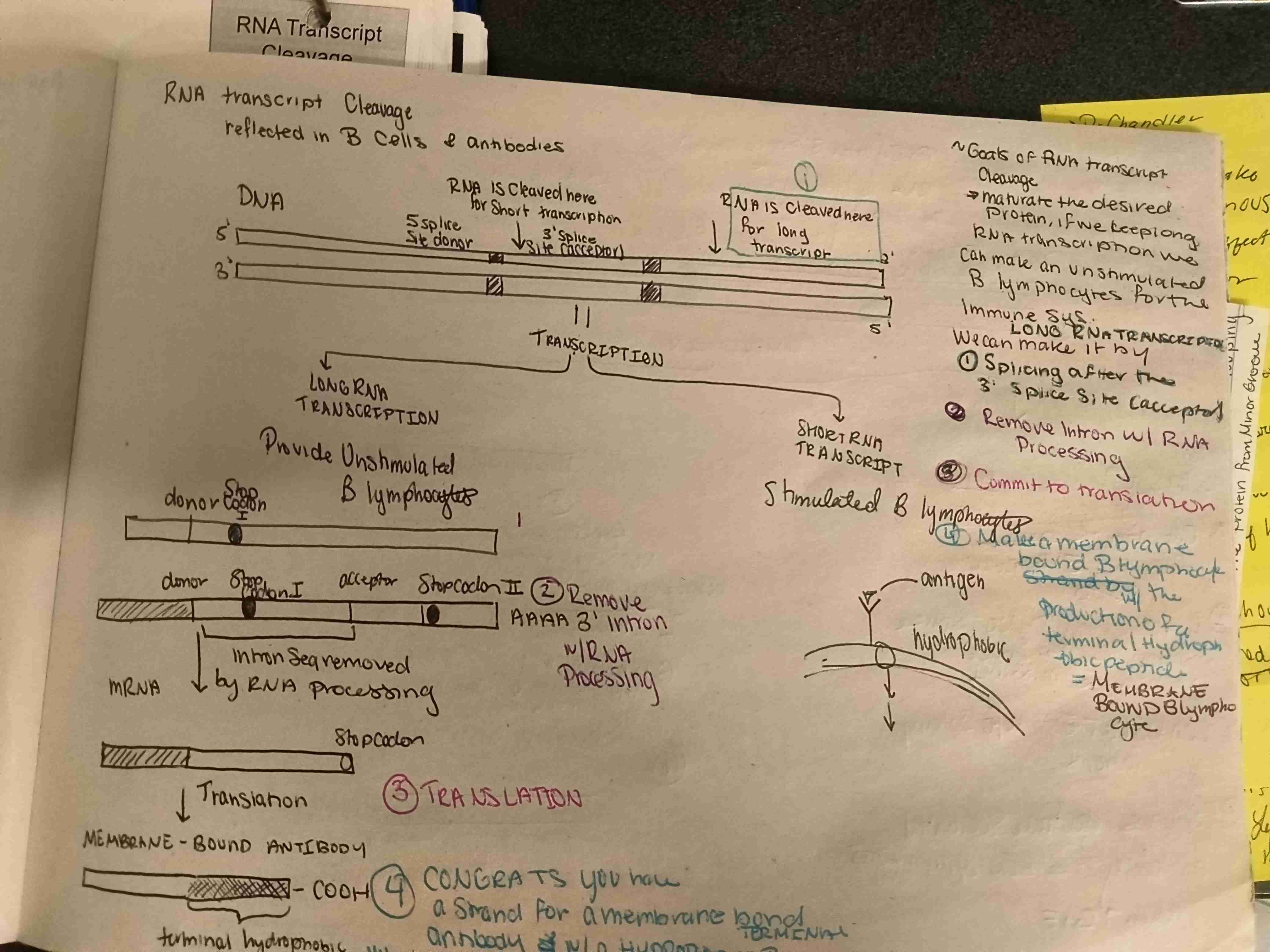
What are the steps to RNA transcription cleavage to produce a secreted antibody is this long or short transcription?
A secreted antibody is produced by a short RNA transcript
Steps in antibody secretion for CstF
Cut the RNA transcript after the 5’ end
Do not remove introns
Translate
You have secreted antibody with protein lymphocyte
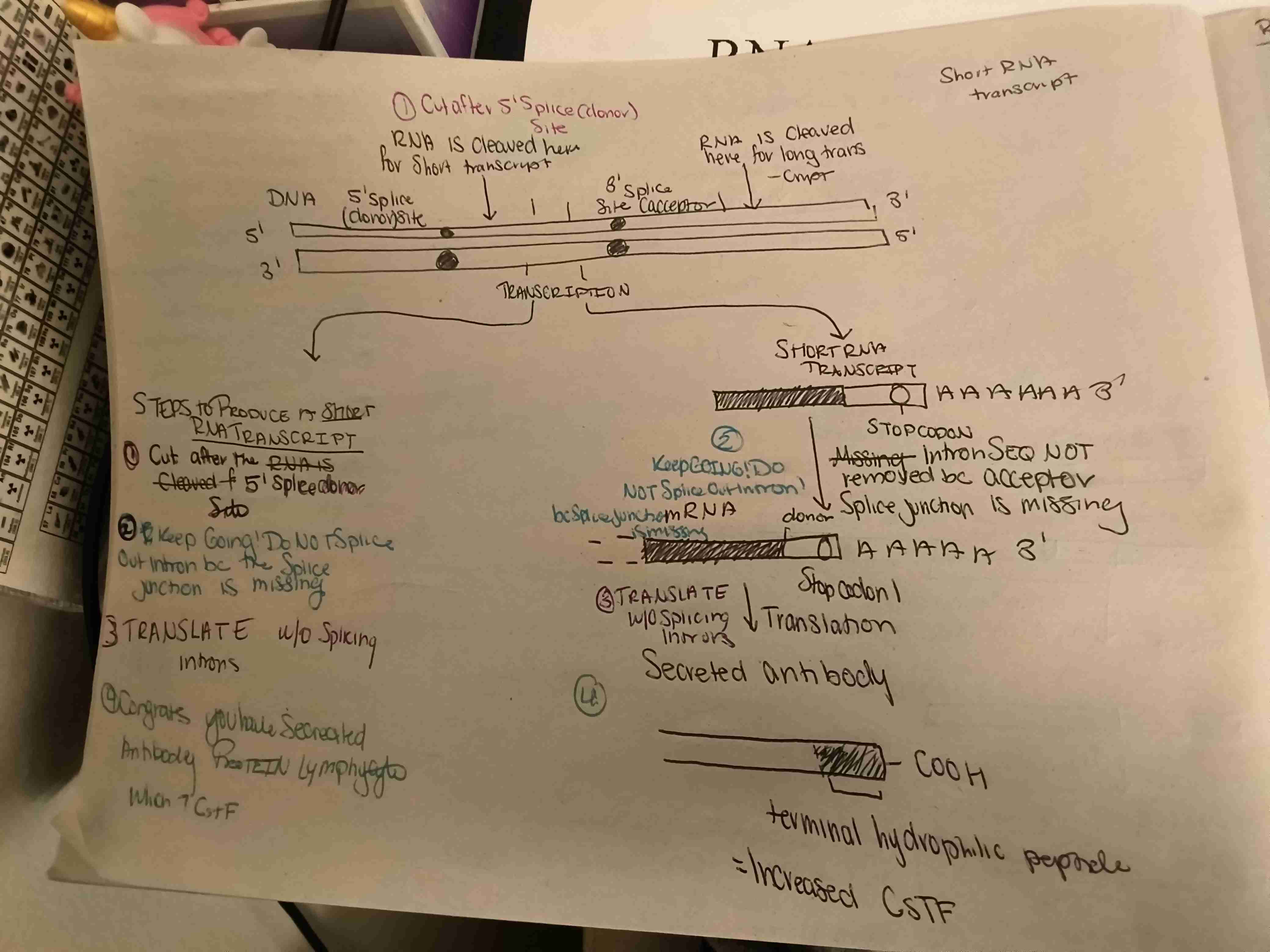
Describe how RNA edits itsself
Guide RNAs
Guide RNA 1 have nucleotides in guide RNA specifying missing U nucleotides
Guide RNA 2 (with its ‘disposible’ poly U tail) pairs with the mRNA transcript finalizing the fully edited mRNA transcription

Describe the pathway for A to I RNA Editing
First, we use A to I RNA Editing to edit a RNA strand with a wrong nucleotide
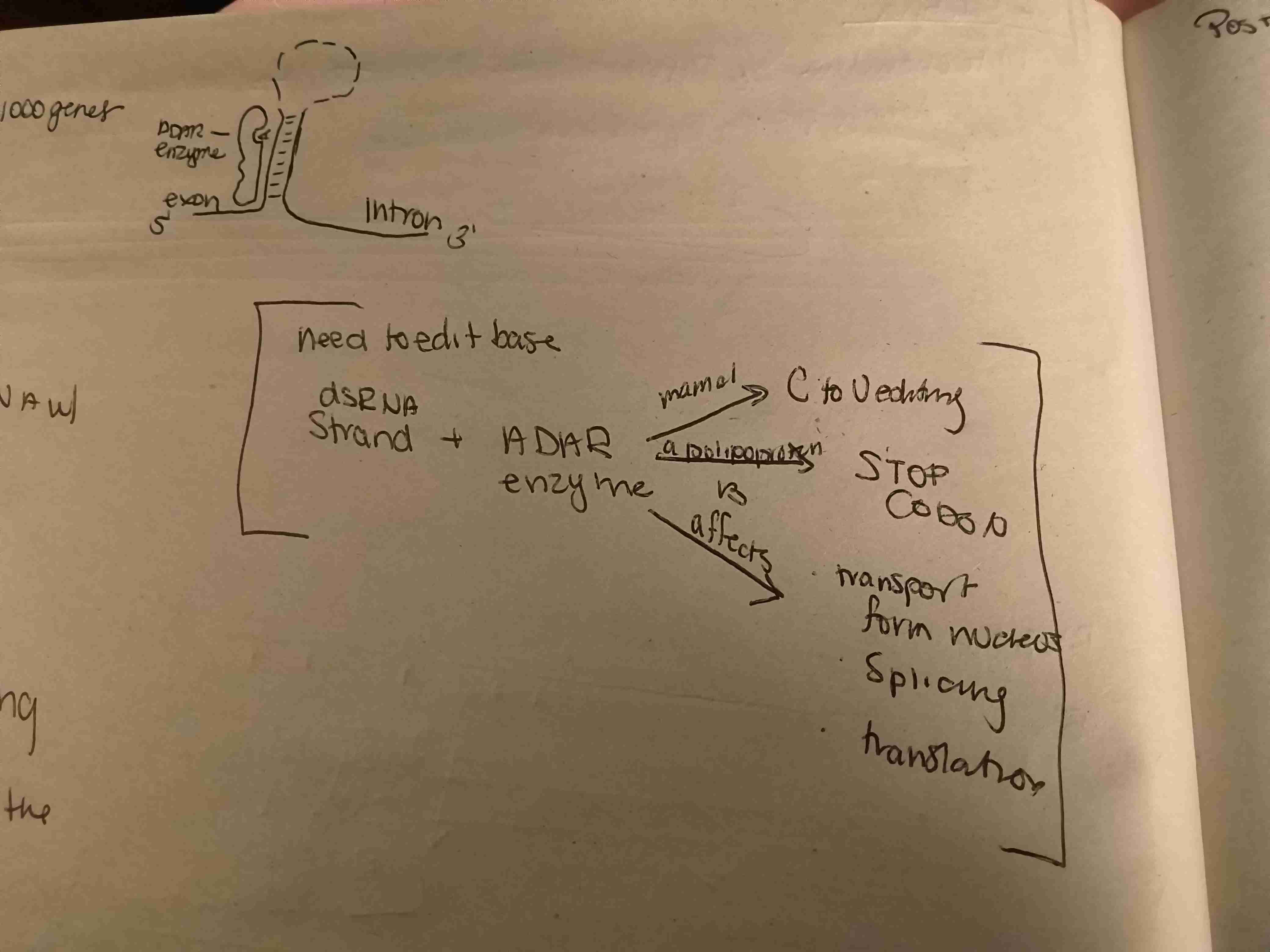
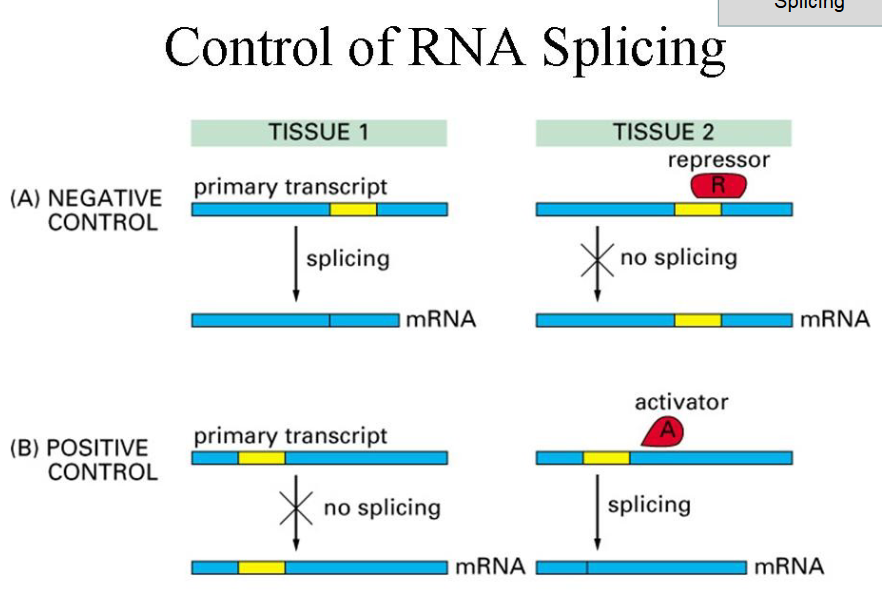
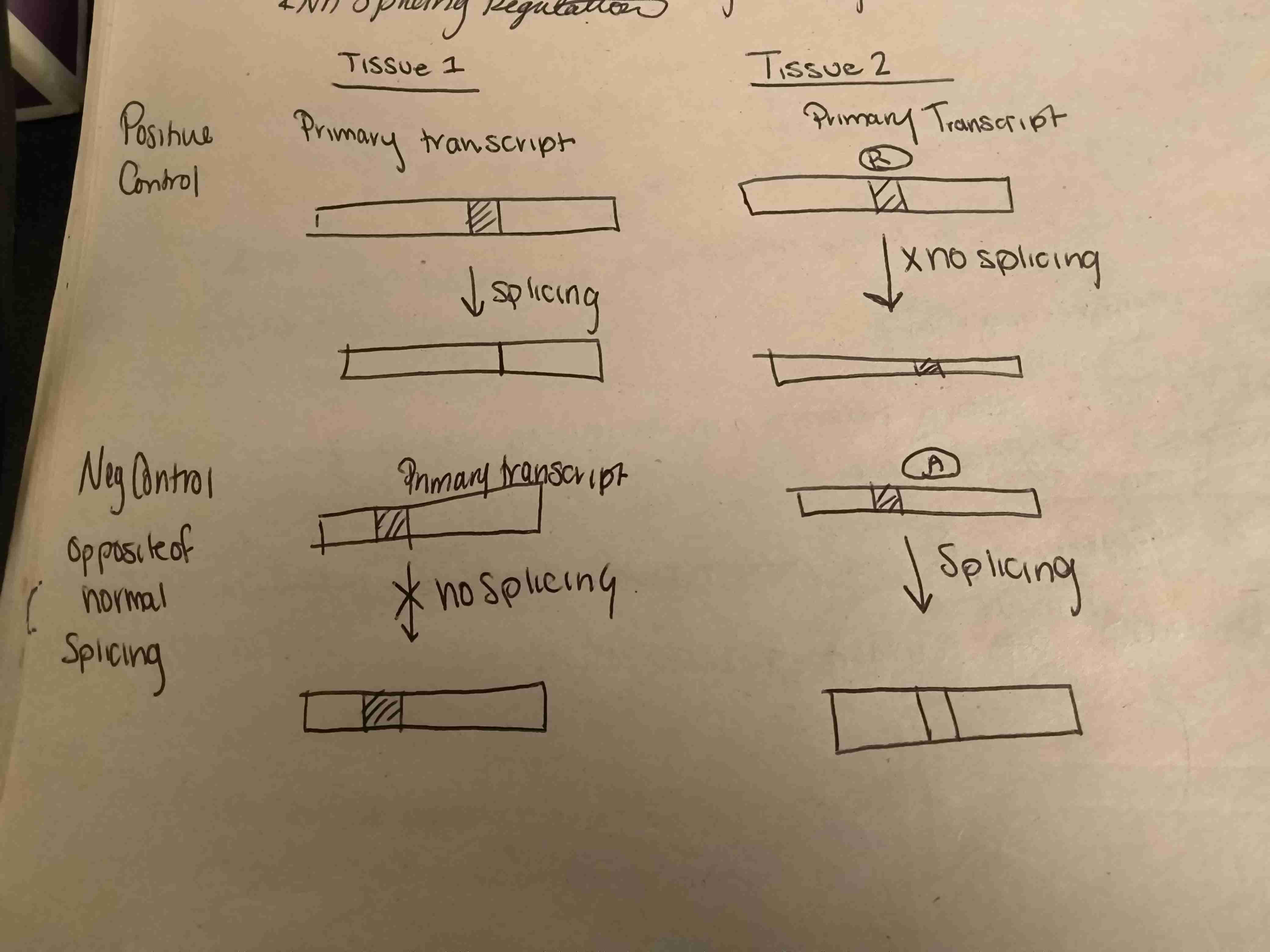
Pathways for post transcriptional controls
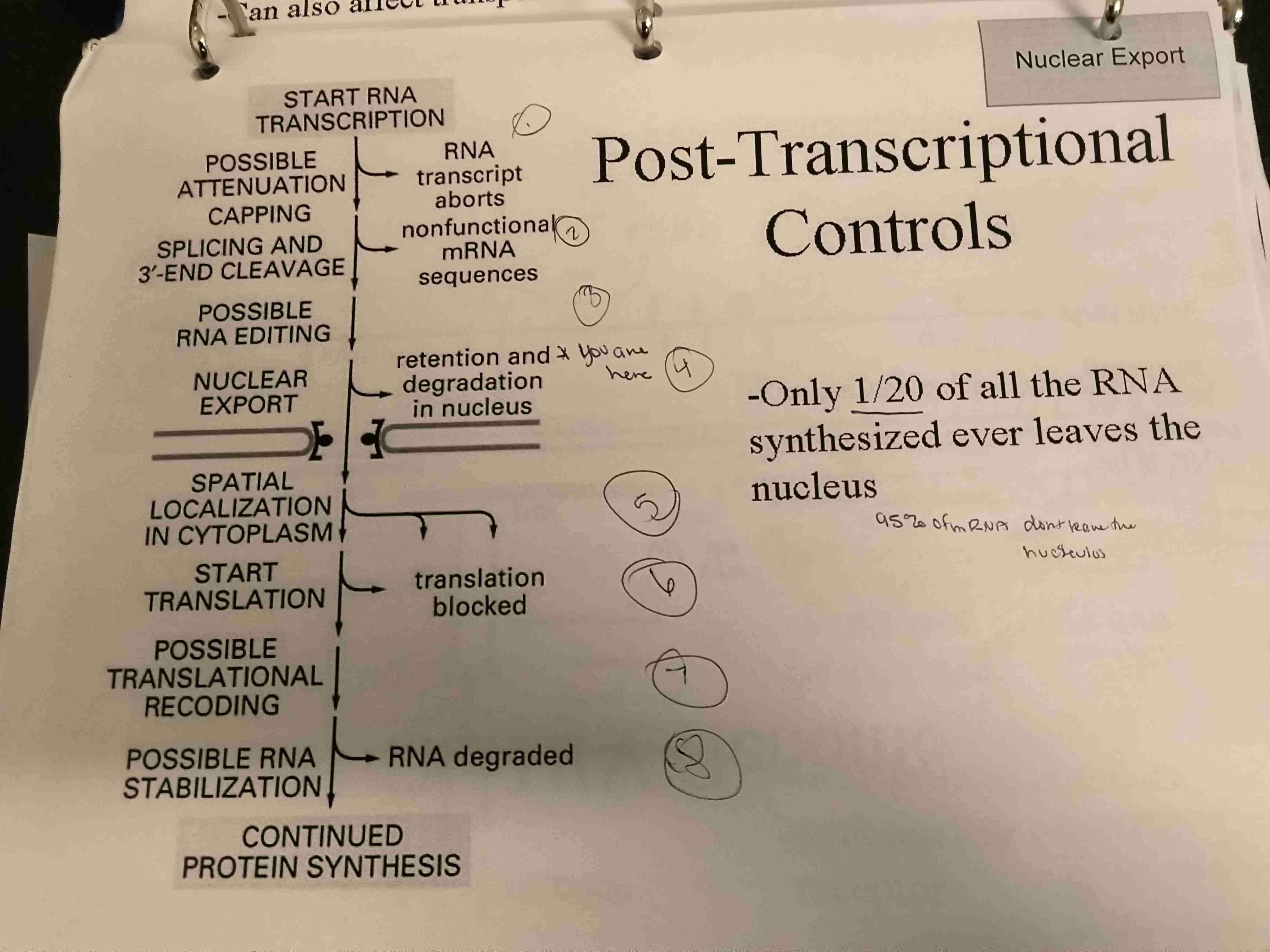
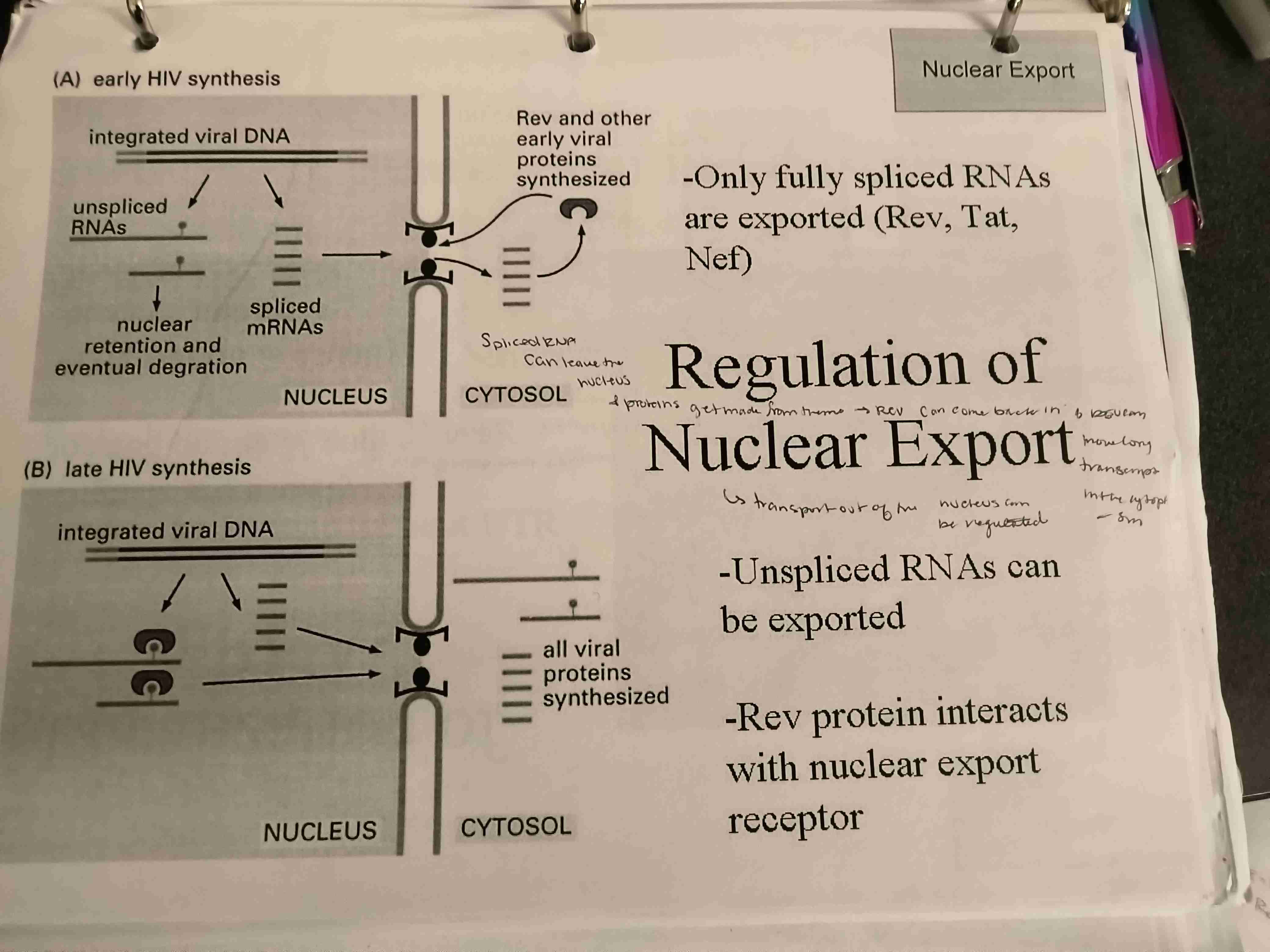
Describe pathways of regulation of nuclear export with both late and early HIV synthesis
Early HIV Synthesis
Rev & other early viral proteins synthesis
only fully spliced RNAs are exported with Rev, Tat & Nef
~ Rev protein interacts with nuclear export receptor
In late stage unspliced RNA can be exproted
Where is signalling typically located on in mRNA
3’ end
How does mRNA get localized?
Translation is usually blocked until it is localized properly;
RNAs bind to protiens at the 3’ end of RNA to so the RNA does not get in the way of synthesis
Ways for mRNA localization
Direct transport on cytoskeleton
Random diffusing and trapping
Generalized degradation in combination with local protection
Negative translational control example
Sequence-specific RNA-binding protein

What were the two major hypotheses for the number of codons coding for proteins and how was the answer determined?
The major hypotheses were that codons were coded with an odd number or an even number of codons
If there was an even number of codons then= resulting peptide would be homopolypeptide
If there was an odd number of codons then = repeating dipeptide
They found a poly(Serine-leucine) after translating a poly(U) to make polyphenylalanine
Translation of poly(UUC)
if the number of bases in codons was three or a multiple of three, a homopolypeptide
Polyphenylalanine, polyserine, polyleucine
Yielded poly(tyrosine-leucine-serine-isoleucine)
UAU