The Hindbrain / Rhombencephalon
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
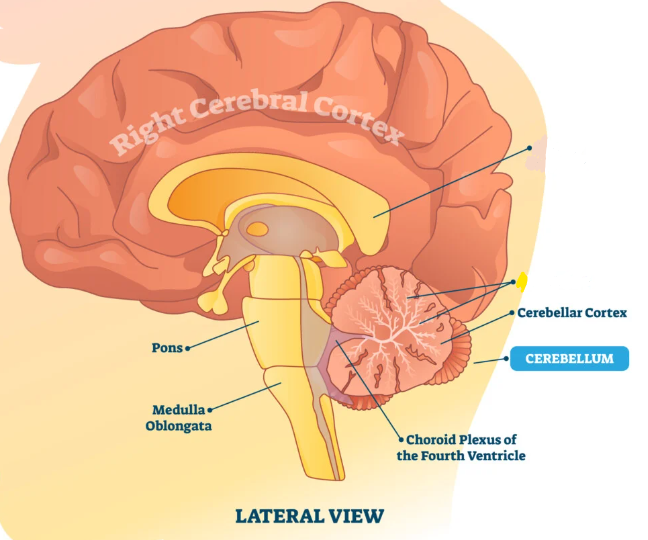
Cerebellum - Pons - Medulla
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
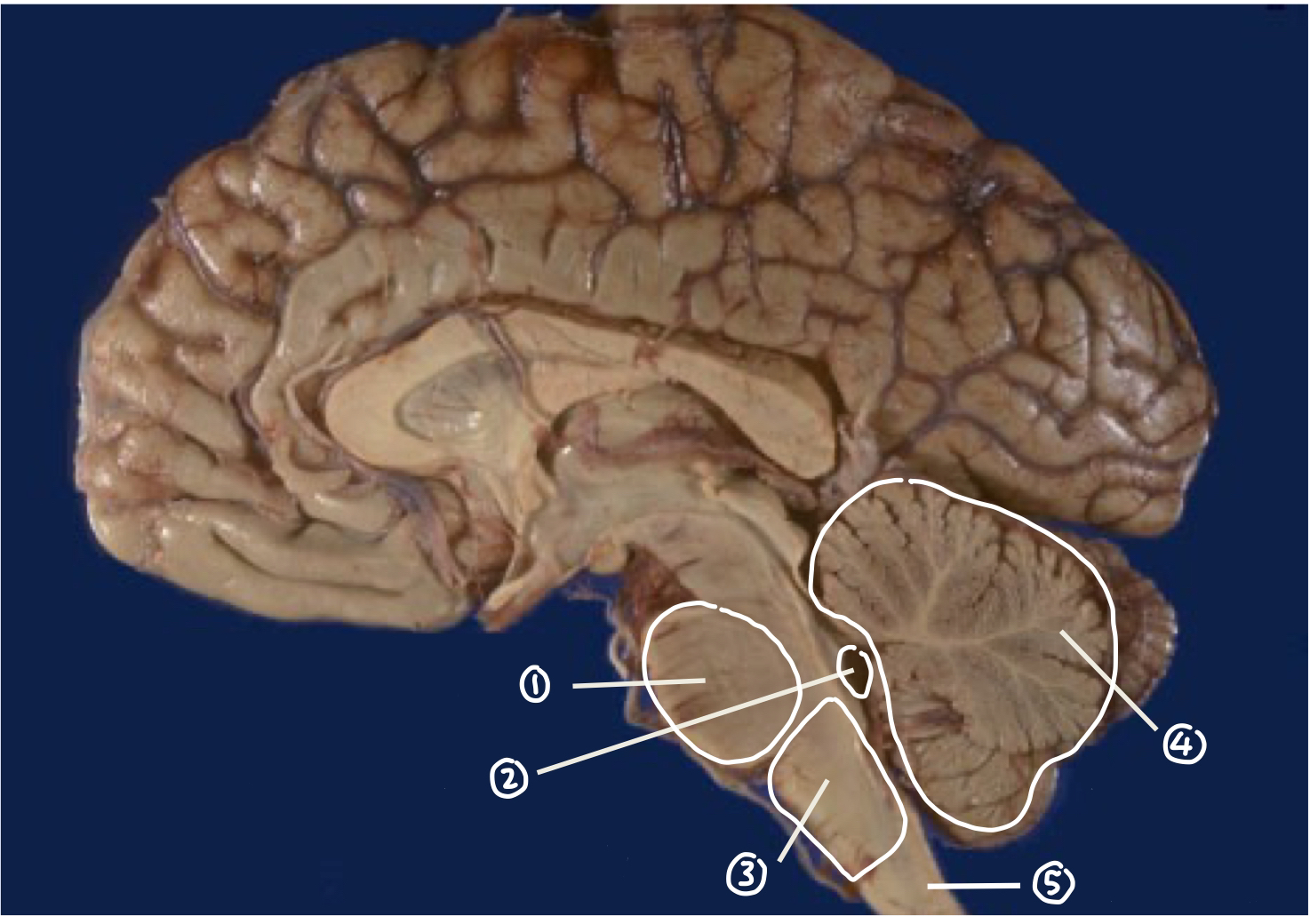
Major components of Hindbrain
Cerebellum
Medulla Oblongata
Pons
Fourth Ventricle - filled with CSF
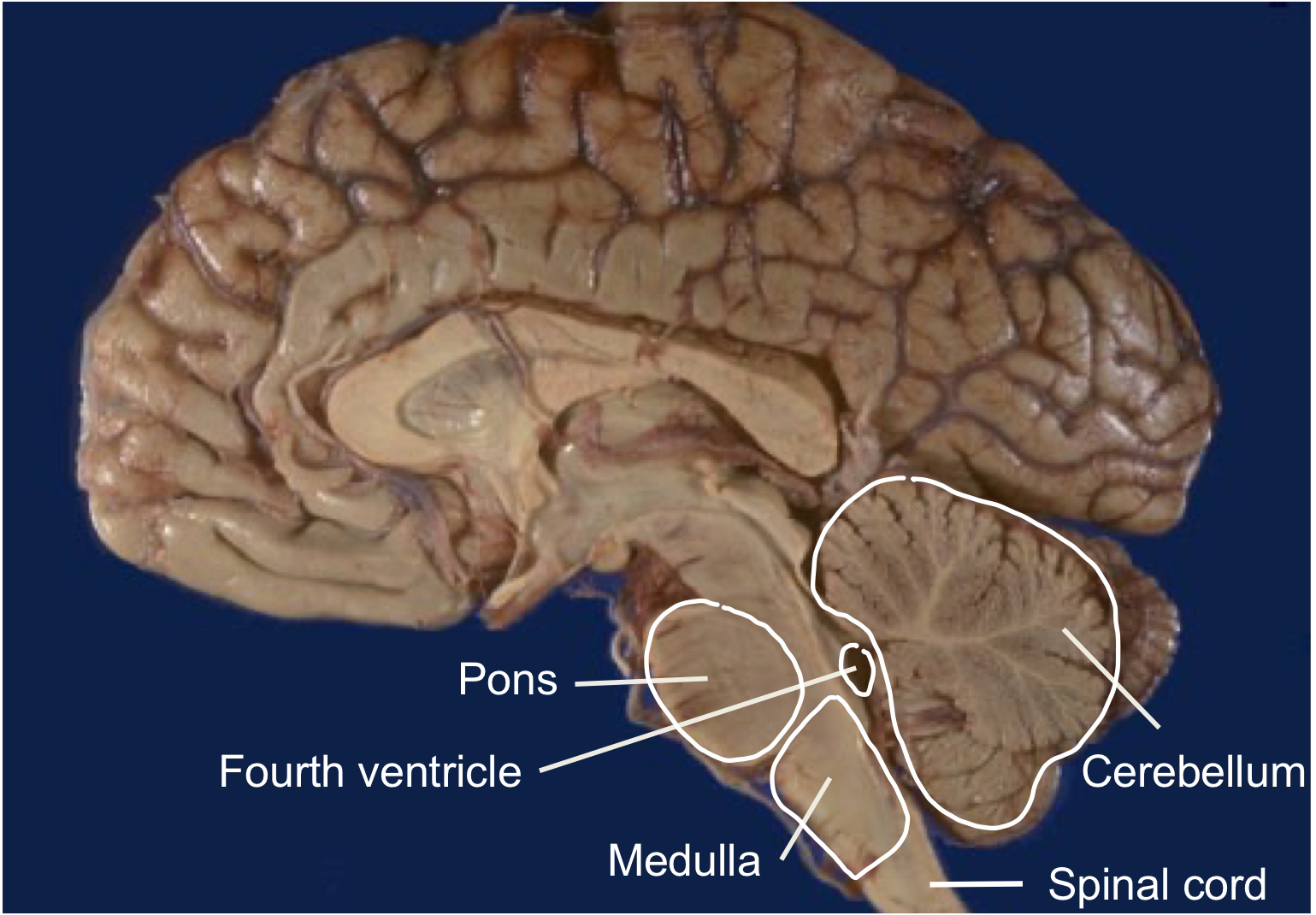
Medulla
Functions :
regulation of INVOLUNTARY processes
— generate breathing rhythm
— regulate heart rate frequency
— regulate blood pressure
— regulate gag reflex / vomiting
— regulate cough reflex
contains caudal (back) region of Reticular Formation
contains nuclei for Cranial Nerves
medulla receives sensory info —> sends to cerebellum —> processes info & help you coordinate movements
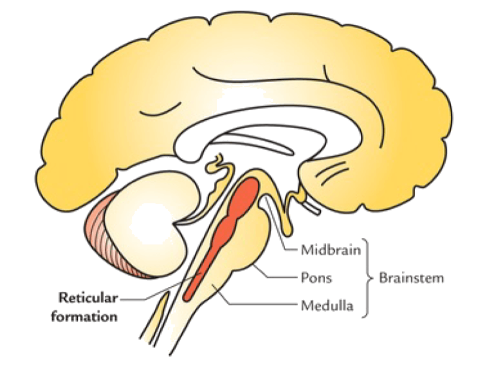
Reticular Formation
Functions :
regulate sleep / wake cycle / circadian cycle
coordinate heart rate
motor coordination
— stabilize posture during VOLUNTARY movement
LONGGG network of interconnected nuclei
go through medulla, pons, midbrain => brainstem
contains Raphe Nuclei
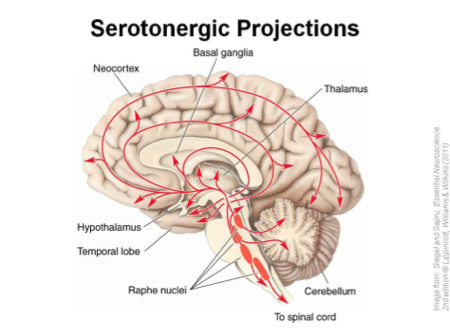
Raphe Nuclei
Function :
produce serotonin
— affect
→ regulate mood
→ emotions
→ perception of pain
→ response to stress
Cranial Nerves
nerves originated from the brain
Types of Cranial Nerves :
Afferent Nerves
— sends signals from sensory structures TOWARDS CNS
Efferent Nerves
— sends signals AWAY from CNS to target tissues (ex: muscles)
Mixed Nerves
— some afferent & some efferent
Pons
Functions :
regulate breathing
regulate sleep / wake cycles
contains Locus Coeruleus (LC)
contains nuclei for Cranial Nerves
contains part of Reticular Formation
Location where FIbre Tracts pass through & axons from both sides of brain cross
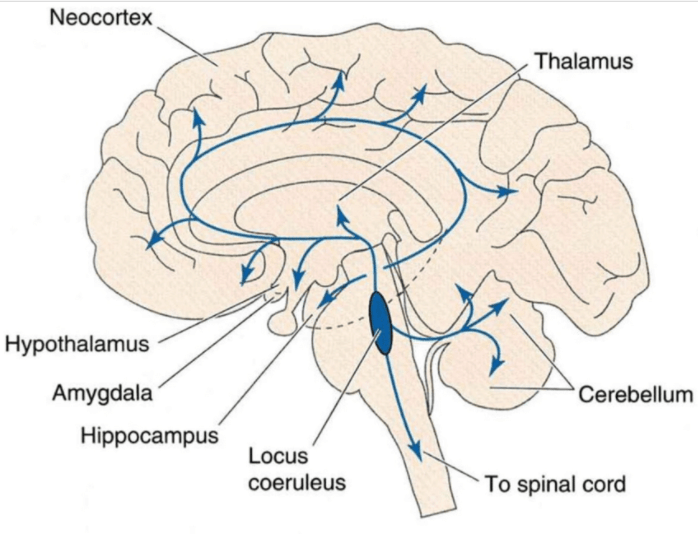
Locus Coeruleus
Nucleus that produces Norepinephrine (a neurotransmitter)
responsible for
mental awakeness / being aware
attention
memory
stress response
Cerebellum
Functions :
regulate motor movement, balance and coordination
procedural memories / long term memory to remember skills (ex: riding bike, playing piano) —> important for certain types of learning
shifting attention between auditory & visual stimuli
Extensively folded
an outer Cerebellar Cortex of grey matter
white matter in the surrounding