Lectures on Neurobiology, Muscle, Digestion, and Immunity
1/318
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
319 Terms
Presynaptic Cell
Signal comes from this cell
Synaptic cleft
Gap (~20nm) where chemicals cross

Postsynaptic cell
Starts action potential in this cell
Action Potential (AP)
Depolarizes membrane of the presynaptic neuron
Voltage gated Ca2+ channels
Open in response to AP in presynaptic neuron
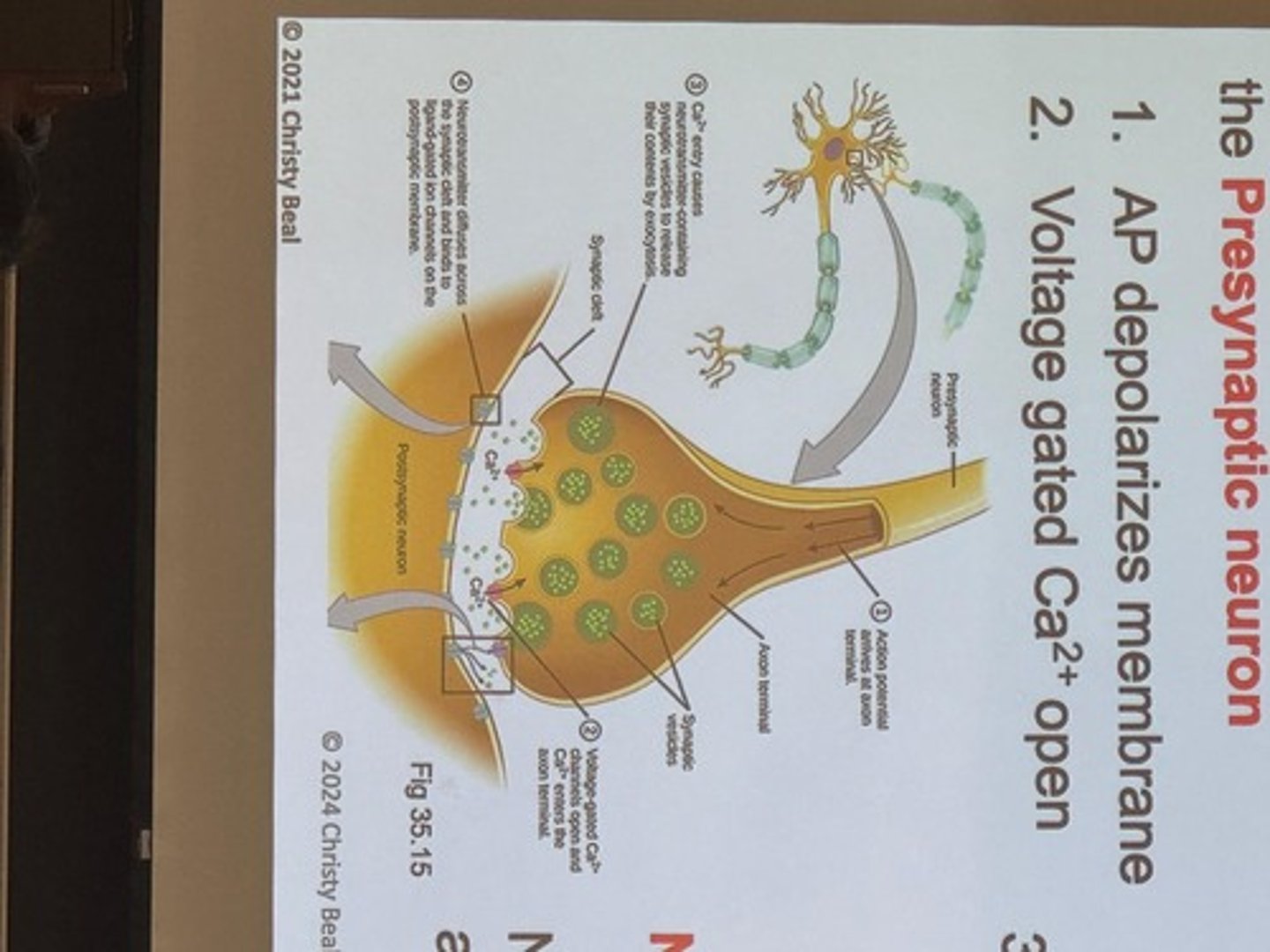
Neurotransmitter
Chemical that diffuses across the synaptic cleft
Ligand-gated ion channels
Channels that open when neurotransmitter binds to them
Postsynaptic potential
Generated when neurotransmitter binds to receptors
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP)
Depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP)
Hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic membrane
Axon hillock
Integrates EPSPs and IPSPs
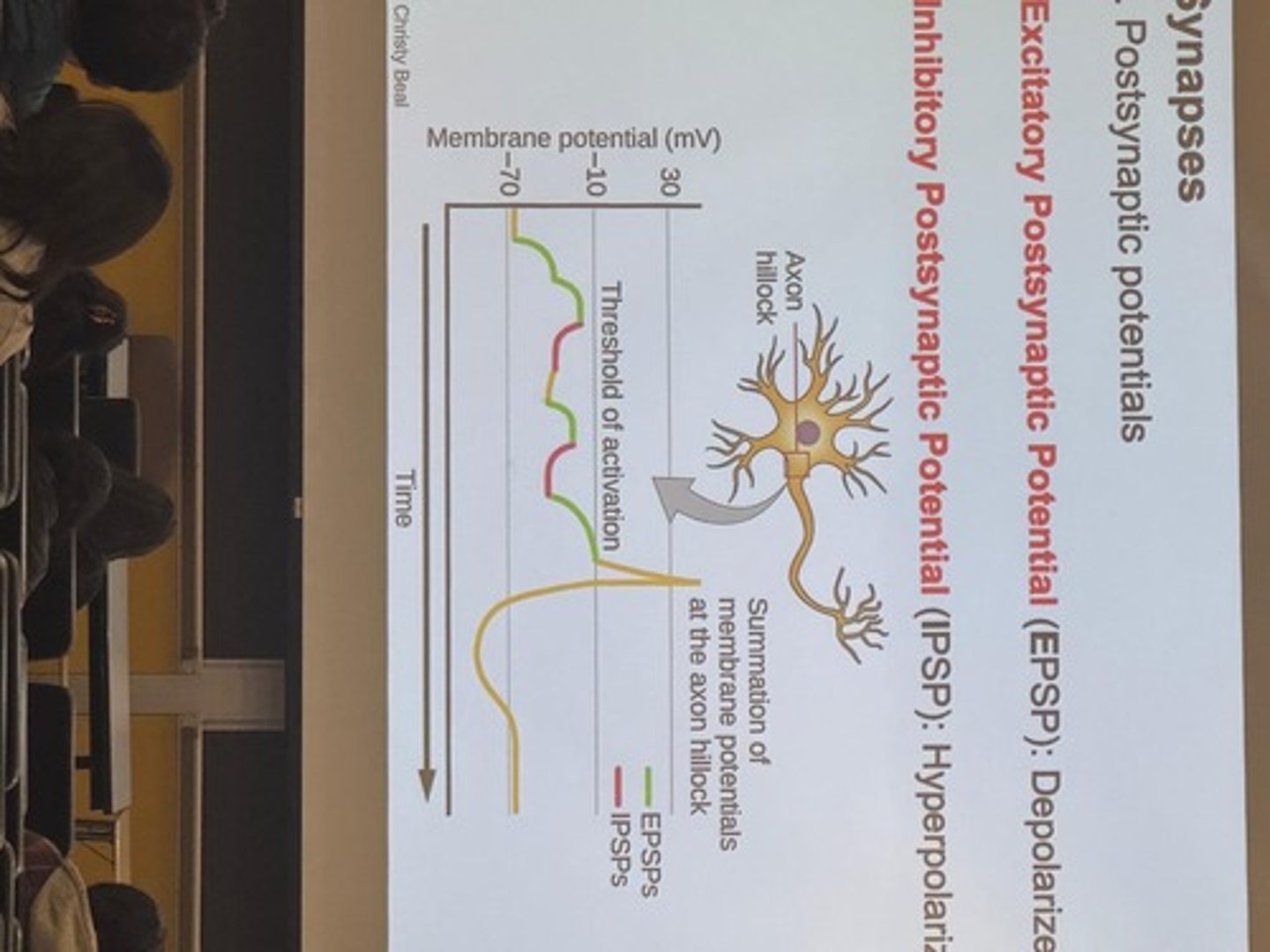
Threshold
If sum of EPSPs minus IPSPs is greater than this, an AP occurs
Long Term Memory
Permanent connections in the cerebral cortex
Short Term Memory
Held for a short time and accessed by temporary links in hippocampus
Neuronal Plasticity
Brain's ability to change and adapt after birth

Long-term Potentiation (LTP)
Strengthening of synaptic transmission over time

Conditions for LTP in presynaptic neuron
High frequency of AP's and depolarization from a second stimulus
AMPA receptors
One type of ligand-gated channel involved in LTP
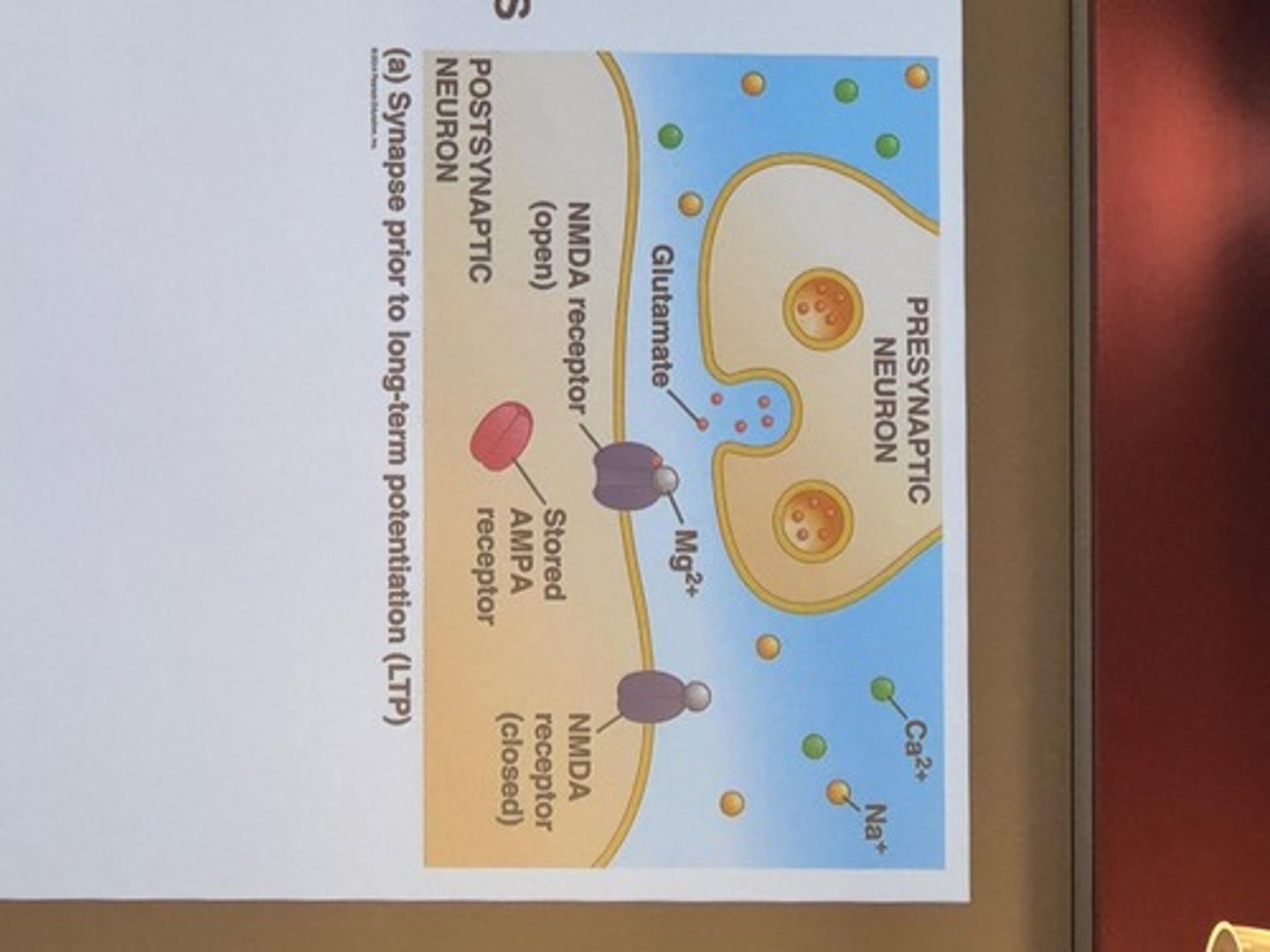
NMDA receptors
Another type of ligand-gated channel involved in LTP, blocked by Mg2+
Glutamate
Neurotransmitter that activates NMDA receptors
Sleep
Consolidates memories
NMDA
Releases Mg2+
Na+ & Ca2+
Some flow in
AMPA receptors
Upregulate
Sensory Reception
Detect Stimulus
Sense Organs
Organs that detect stimuli
Sensory Transduction
Converts stimulus to receptor potential
Receptor potential
Change in membrane potential
Sensory receptor
Depolarizes → AP triggered
Higher receptor potential
More frequent AP's
Perception
Brain processes information
Chemo receptors
Taste and smell
Mechano receptors
Touch, hearing
Photo receptors
Light, seeing
Hearing
Sense changes in external vibrations
Equilibrium
Balance controlled by sensing movement of fluid in ears
Mechanoreceptors
Used in both hearing and equilibrium
Sound
Waves of air or water pressure
Pinna
Collects sound waves
Auditory Canal
Channels waves to tympanic membranes
Tympanic Membrane
Thin membrane - vibrates → transmits to middle ear
Middle Ear
Air-filled cavity
Ossicles
3 small bones - Malleus → Incus → Stapes
Cochlea
Spiral tube, where sound is detected
Hair cells
Mechanoreceptors with cilia
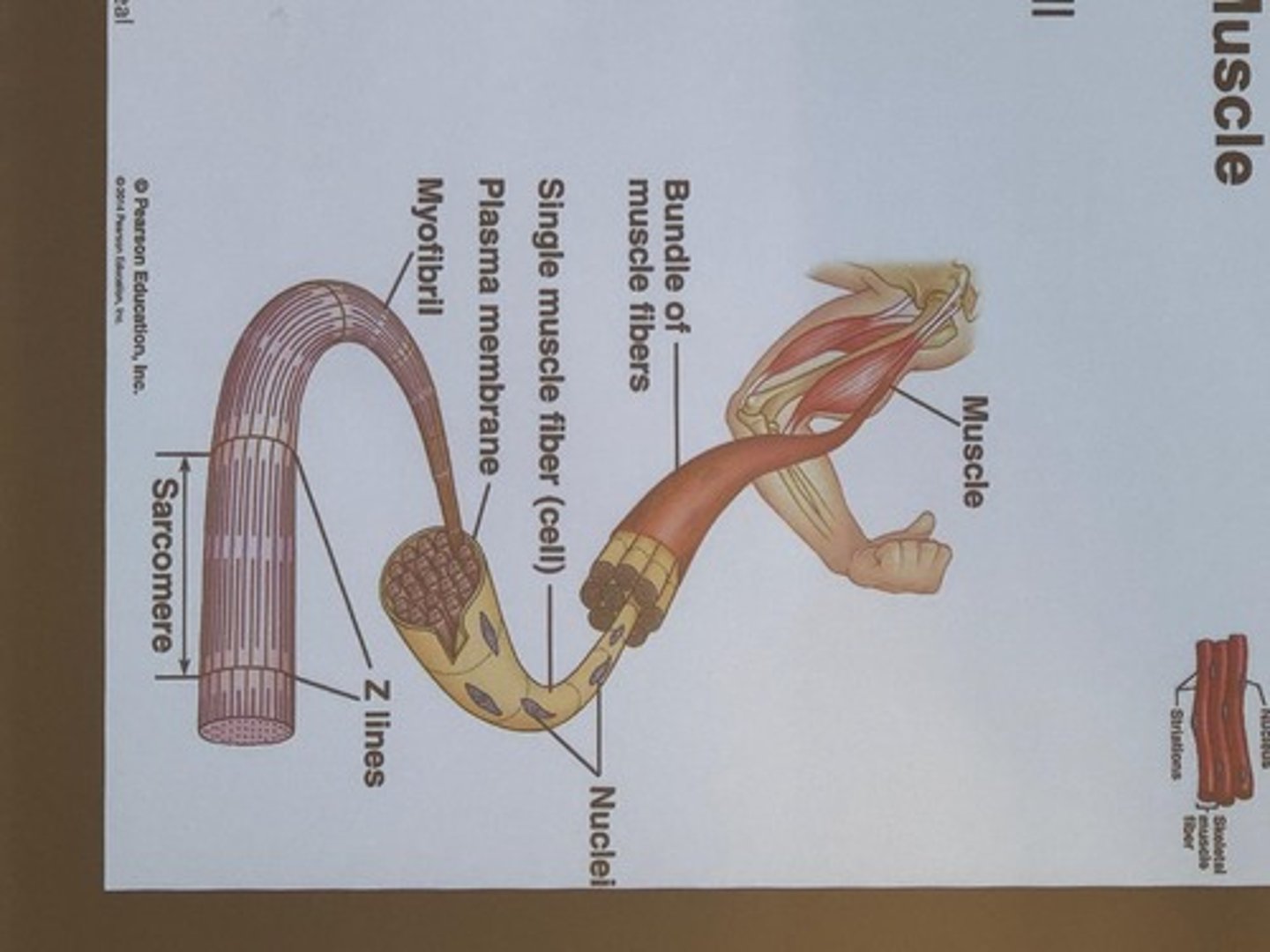
Skeletal Muscle
Movement
Muscle fiber
Muscle cell
Myofibrils
Bundles within muscle fibers
Sarcomere
Basic unit of contraction
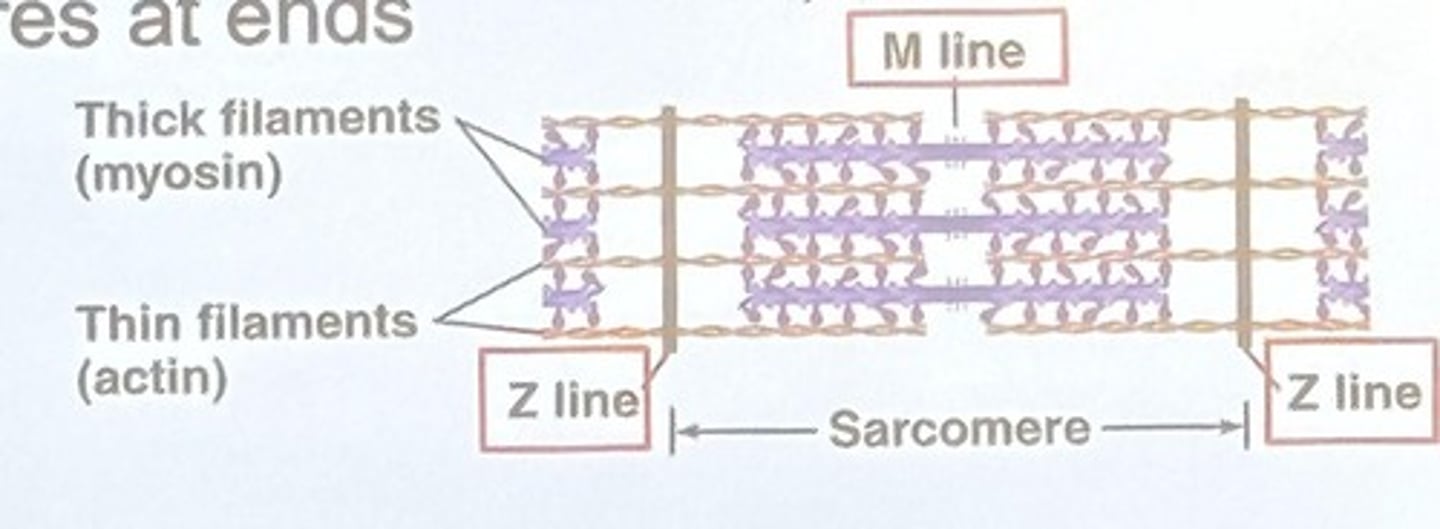
Thin filaments
Have 3 types of proteins including actin
Thick filaments
Made of 350 myosin molecules
Sliding Filament Model
Describes muscle contraction mechanism
Cross bridge
Formed when myosin binds to actin
Power Stroke
ADP + Pi released - myosin head bends & pulls thin filament to center of sarcomere
Myosin
A protein that binds to ATP and breaks cross-bridge.
ATP hydrolysis
The process where ATP is broken down, allowing the myosin head to return to a high-energy position.
Creatine phosphate
A molecule that transfers its phosphate to ADP, providing energy for muscle contraction.
Glycogen
A stored form of glucose in muscle fibers, consisting of hundreds of glucose units.
Rigor mortis
The stiffening of muscles after death due to no ATP production, preventing new bridges from forming.
Cardiac Muscle
Muscle found in the heart walls that must contract together and has high Na+ permeability.
Intercalated discs
Specialized junctions in cardiac muscle that permit ions to move between cells and allow action potentials to pass quickly.
Smooth Muscle
Muscle found in the digestive tract, bladder, and blood vessels, characterized by slow and sustained contractions.
Heterotrophy
The characteristic of all animals being heterotrophs, meaning they must consume food.
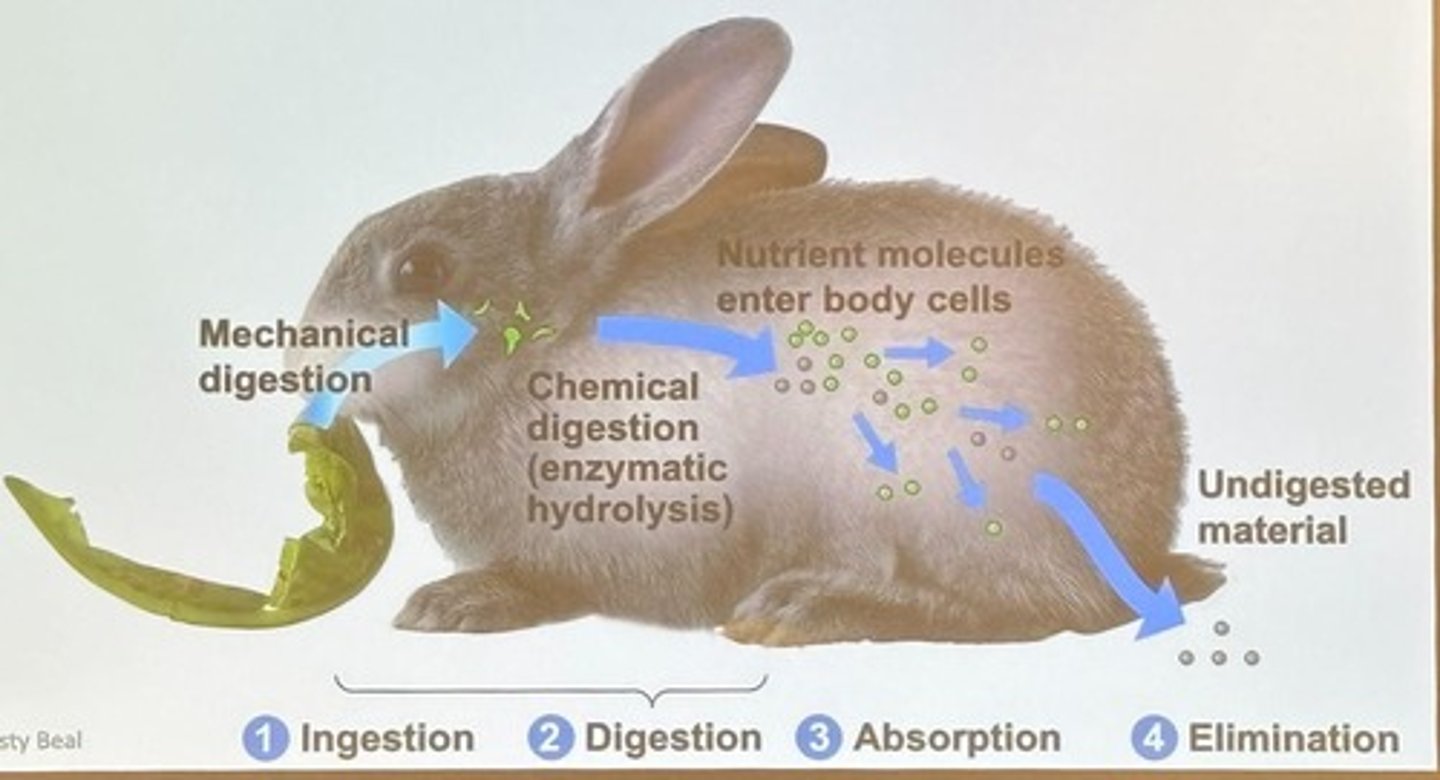
Ingestion
The first stage of food processing where food enters the body.
Digestion
The process of breaking down complex organics into smaller pieces, increasing surface area for enzymes.
Mechanical digestion
The physical process of breaking down food into smaller pieces.
Chemical digestion
The process where enzymes break down food through hydrolysis.
Absorption
The stage where cells take up molecules from digested food, often into the bloodstream.
Elimination
The final stage of food processing where undigested material passes out of the system.
Compartments
Structures that help avoid self-digestion by separating digestive processes.
Single Cell Digestion
Digestion occurs within food vacuoles and lysosomes.
Multicellular Digestion
Involves extracellular digestion in compartments.
Gastrovascular Cavity
A digestive cavity with one opening found in thin/tiny animals.
Alimentary Canal
A digestive system with two openings, allowing one-way food movement.
Accessory Glands
Include 3 pairs of salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gall bladder.
Peristalsis
Smooth muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
Sphincters
Ring-like muscular valves that control the passage of food.
Pre-indigestion
Digestive processes triggered by salivary secretion before ingestion.
Mechanical Digestion
Involves teeth chewing food in the oral cavity.
Bolus
A mass of chewed food formed by the tongue.
Epiglottis
Prevents food from entering the airway during swallowing.
Esophagus
Muscular tube connecting the pharynx to the stomach.
Stomach
An elastic organ that can hold about 2 liters and digests proteins.
Gastric Glands
Cells in the stomach lining that secrete mucus, HCl, and pepsinogen.
Pepsin
An enzyme that breaks down proteins into smaller polypeptides.
Chyme
The mixture of food and digestive juices in the stomach.
Small Intestines
About 6 meters long, with a high surface area for nutrient absorption.
Villi and Microvilli
Structures in the small intestine that increase surface area for absorption.
Pancreatic Juice
Contains bicarbonate and enzymes for digestion in the small intestine.
Bile
Produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder, aids in fat digestion.
Duodenum
The first section of the small intestine where most chemical digestion occurs.
Monosaccharides
The end product of carbohydrate digestion from polysaccharides and disaccharides.
Amino Acids
The end product of protein digestion from polypeptides.
Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA, only digested in the small intestine.
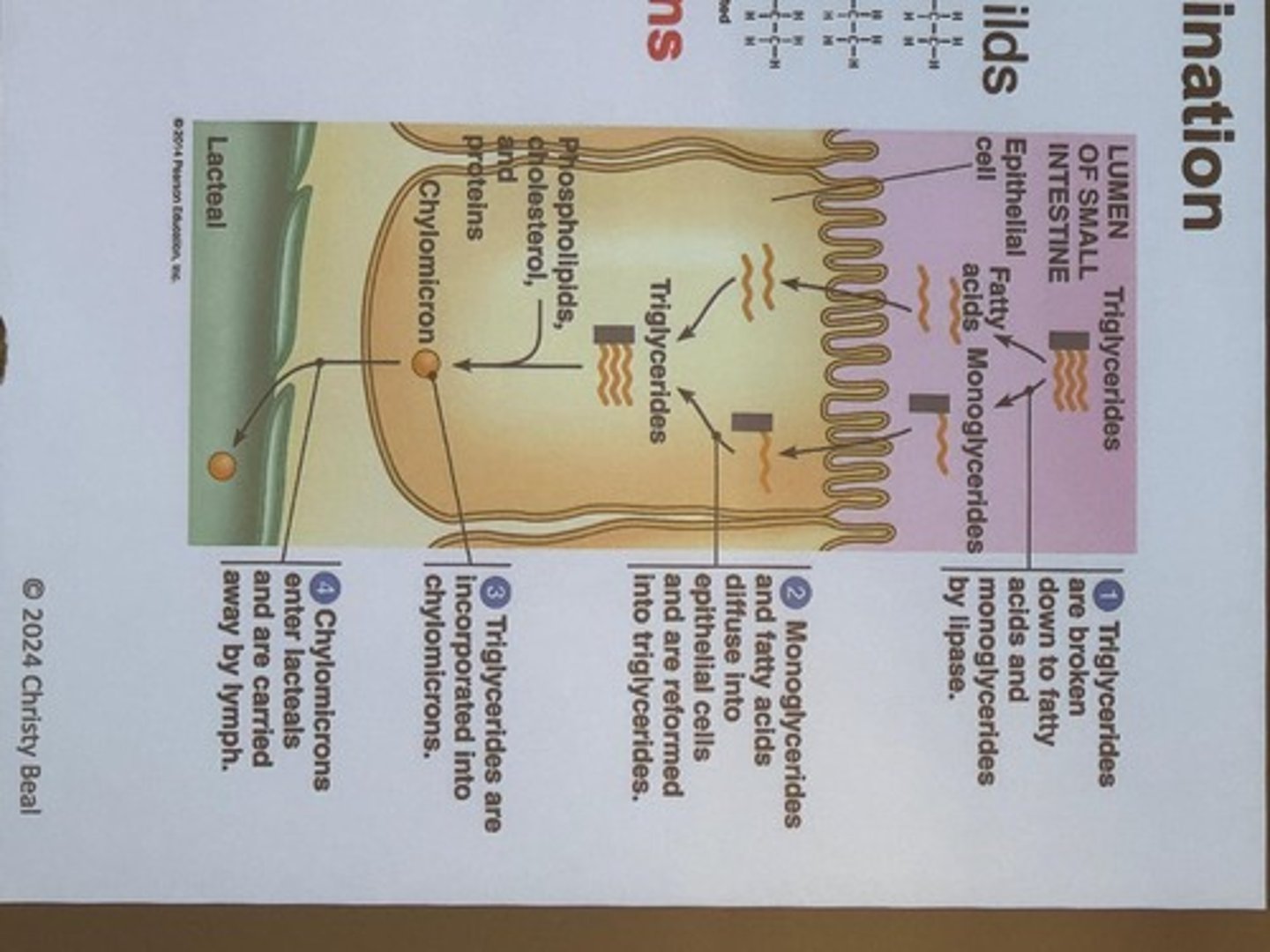
Lipids
Ingested as triacylglycerols; emulsified by bile salts for digestion.
Chylomicrons
Particles that transport triglycerides after absorption in the small intestine.
Large Intestines
Mainly absorbs water and has four divisions: ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid.
Hepatic Portal Vein
Carries nutrients absorbed by the intestine to the liver for processing.
Opportunistic Feeders
Animals that can feed on a variety of food sources.
Chemical Energy
Used for ATP